Published online Aug 6, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i22.99221
Revised: October 22, 2024
Accepted: April 18, 2025
Published online: August 6, 2025
Processing time: 300 Days and 23.2 Hours
In recent years, the number of studies on spondylolisthesis has been increasing, and there are many publications on this disorder. To our knowledge, there is no bibliometric analysis of spondylolisthesis to date.
To investigate emerging directions in Spondylolisthesis research and systematically evaluate the academic literature with the highest citation impact within this field.
All data were collected from the Web of Science Core Collection database. Years of publications, countries, journals, institutions and total number of citations were extracted and analyzed by VOSviewer software. In addition, we analyzed the top 100 most-cited articles on spondylolisthesis.
A total of 1831 articles related to spondylolisthesis were identified. The frequency of publications on spon
In recent years, academic investigations on spondylolisthesis have exhibited significant growth. As the inaugural bibliometric evaluation in this domain, our research establishes a methodological framework for synthesizing the historical progression and current advancements of spondylolisthesis studies.
Core Tip: We aim to identify the future trends in spondylolisthesis - related research and to analyze the most highly cited scientific publications on spondylolisthesis. This study provides a unique insight into the development of spondylolisthesis research and serves as a useful guide for clinicians and researchers.
- Citation: Xu JN, Li Y, Zhao TX, Wu WY, Yang XW, Zhang HW, Chen Q, Xia C, Zhang J. Mapping the field of spondylolisthesis: A bibliometric analysis. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(22): 99221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i22/99221.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i22.99221
Spondylolisthesis is an acquired anterior displacement of one vertebra relative to the adjacent vertebra associated with degenerative changes, but not with disruption or defect of the vertebral ring. Lumbar spondylolisthesis is a common cause of low back pain, affecting approximately 11.5% of the United States population[1]. It is divided into 6 major categories, including isthmic, traumatic, degenerative, pathologic, developmental abnormalities and postoperative; among these, the most commonly reported is degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis[2]. Anteroposterior and lateral plain films, as well as lateral flexion-extension plain films, are the standard for the initial diagnosis of spondylolisthesis[3-7]. The assessment of lumbar segmental instability relies primarily on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT)[8-10]. The Meyerding classification system measure the degree of slippage and classifies spon
Contemporary scholarly investigations into Spondylolisthesis have proliferated across multiple dimensions, spanning mechanistic explorations of disease origins, progression pathways, therapeutic stratification frameworks, and inter
The inaugural domain-specific bibliometric profiling of spondylolisthesis was conducted, employing co-citation networks and temporal trend analysis to quantify research maturity (H-index = 47) and forecast innovation pathways. Concurrently, a citation-weighted inventory of seminal works (n = 100) was generated through systematic evaluation of publications over eight decades (1932-2017).
All data were from the Web of Science Core Collection database. The search was conducted on September 26, 2022. Initially, we searched the PubMed MeSH database for spondylolisthesis and found its entry terms. Finally, the search strategy was as follows: Title = (spondylolisthesis OR Spondylolistheses OR Spondylisthesis OR Spondylistheses OR Olisthesis OR Olistheses) AND Document type (article OR review) AND Language = English AND Time span = 1900 to 2022.
The research data were processed and interpreted through the integrated application of VOSviewer (version 1.6.19) in conjunction with Microsoft Excel 2021. As the primary data source, Web of Science provides access to a comprehensive multi-disciplinary database encompassing scholarly journals, conference proceedings, and other academic resources. For bibliometric network analysis, VOSviewer was employed as a Java-based application specifically designed for con
Data extraction was performed by two independent reviewers (Xu JN and Li Y) using a piloted and standardized data extraction form. Disagreements were resolved by consensus or a third investigator (Zhang J) was consulted. The research synthesized a comprehensive analytical matrix to facilitate bibliometric evaluation. Key metadata including contributing authors, periodical sources, affiliated institutions, geographic distributions, and citation frequencies were systematically compiled for subsequent quantitative examination.
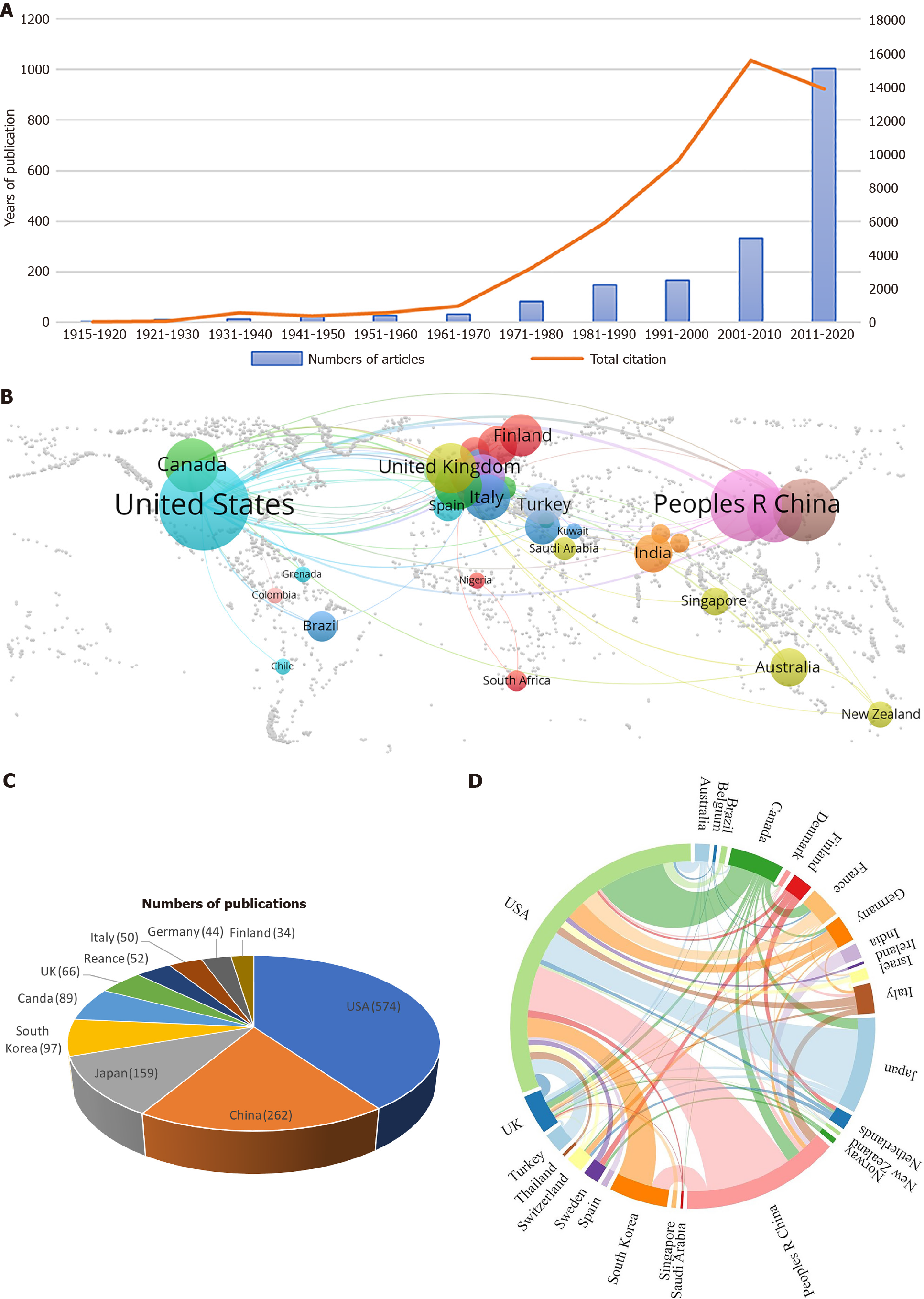
The bibliometric analysis revealed a cumulative scholarly output of 1831 publications, encompassing contributions from 6379 researchers across 1645 institutions spanning 55 geographically diverse nations. These works appeared in 271 academic periodicals, with publication volumes demonstrating a marked surge in scientific productivity, particularly post-2010 as shown in Figure 1A.
The geographical distribution of scholarly output is presented in Figure 1B, revealing significant national disparities in research productivity. As demonstrated in Figure 1C, the United States emerges as the predominant contributor with 574 publications, accounting for nearly half of the total output. This is followed by China (262 articles), Japan (159), and South Korea (97) in descending order. The substantial lead maintained by the United States in both academic influence (H-index = 78) and quantitative output aligns with its established scientific infrastructure, as illustrated in Figure 1D. This dominance correlates strongly with the nation's substantial demographic base (332 million population) and global leadership in biomedical research investment.
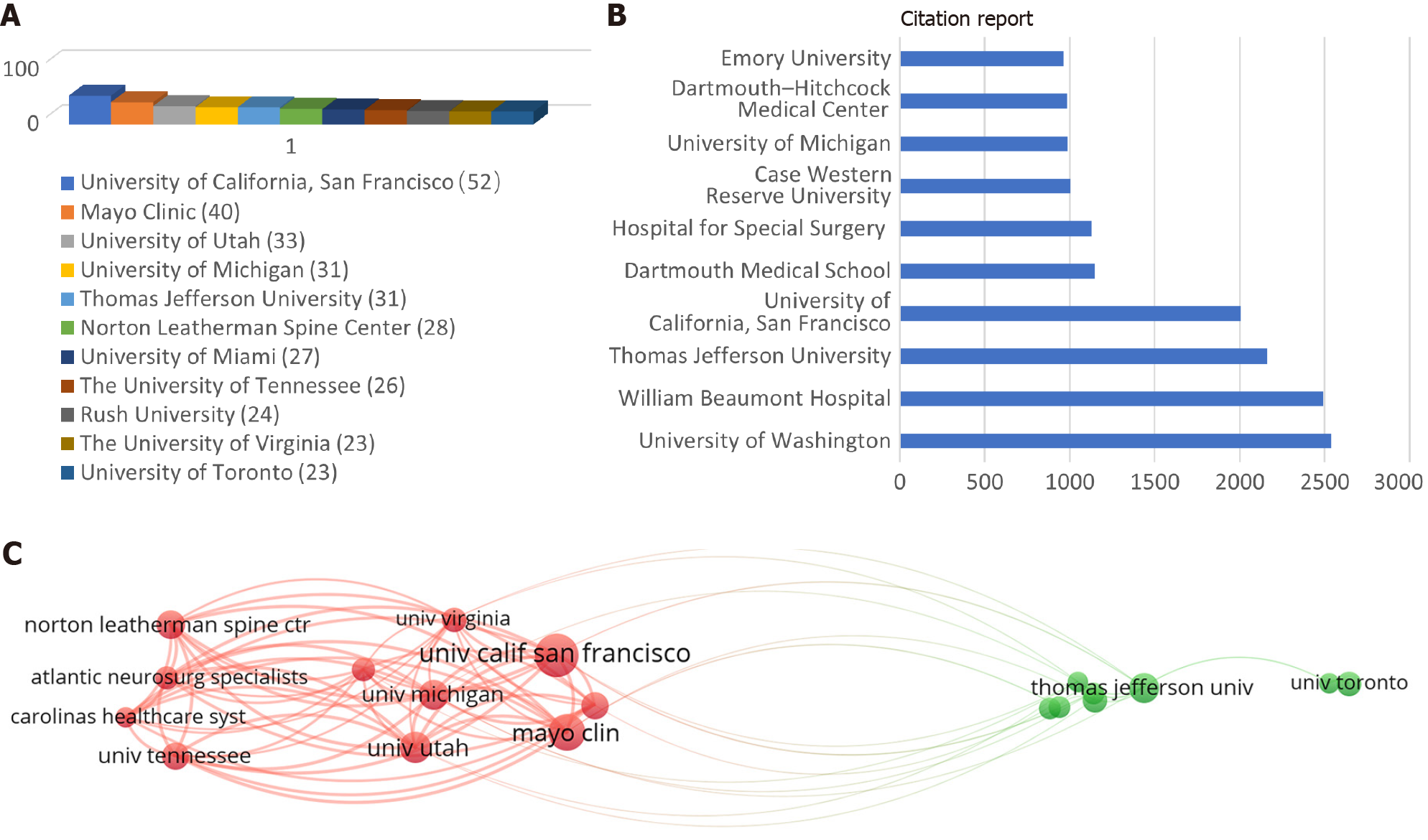
A total of 1645 institutions were represented in the published papers. The top 11 institutions were the University of California, San Francisco (United States; n = 52), Mayo Clinic (United States; n = 40), University of Utah (United States; n = 33), University of Michigan (United States; n = 31), Thomas Jefferson University (United States; n = 31), Norton Leatherman Spine Center (United States; n = 28), University of Miami (United States; n = 27), The University of Tennessee (United States; n = 26), Rush University (United States; n = 24), The University of Virginia (United States; n = 23), and University of Toronto (Canda; n = 23; Figure 2A). The University of Washington publication was cited for most times (2537 citations), followed by William Beaumont Hospital (2489 citations) and Thomas Jefferson University (2159 citations; Figure 2B).
In terms of collaborative relationships between institutions examined in our network visualization analysis, the University of California, San Francisco had the highest total link strength (n = 455), followed by Mayo Clinic (n = 377), University of Utah (n = 367) and University of Michigan (n = 358). In this analysis, the thickness of the line reflects the frequency of co-authorship collaboration among the institutions (Figure 2C).
The 1831 publications were published in 271 journals. The top 10 journals published 48% of all publications (Table 1). The top 3 journals were: Spine, European Spine Journal and Journal of Neurosurgery-spine. Spine had the highest number of citations. The journals had more than 32 of the publications on spondylolisthesis, and the mean impact factor was 3.229.
| Rank | Source | Publications | Citations | Mean citations | Impact factor |
| 1 | Spine | 291 | 14443 | 49.63 | 3.241 |
| 2 | European Spine Journal | 146 | 3572 | 24.47 | 2.721 |
| 3 | Journal of Neurosurgery-spine | 86 | 2364 | 27.49 | 3.467 |
| 4 | World Neurosurgery | 70 | 676 | 9.66 | 2.210 |
| 5 | Spine Journal | 63 | 1338 | 21.24 | 4.297 |
| 6 | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 58 | 5184 | 89.38 | 6.558 |
| 7 | Clinical Spine Surgery | 48 | 281 | 5.85 | 1.723 |
| 8 | Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques | 45 | 1175 | 26.11 | 2.202 |
| 9 | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume | 36 | 1579 | 43.86 | 3.309 |
| 10 | BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders | 35 | 581 | 16.60 | 2.562 |
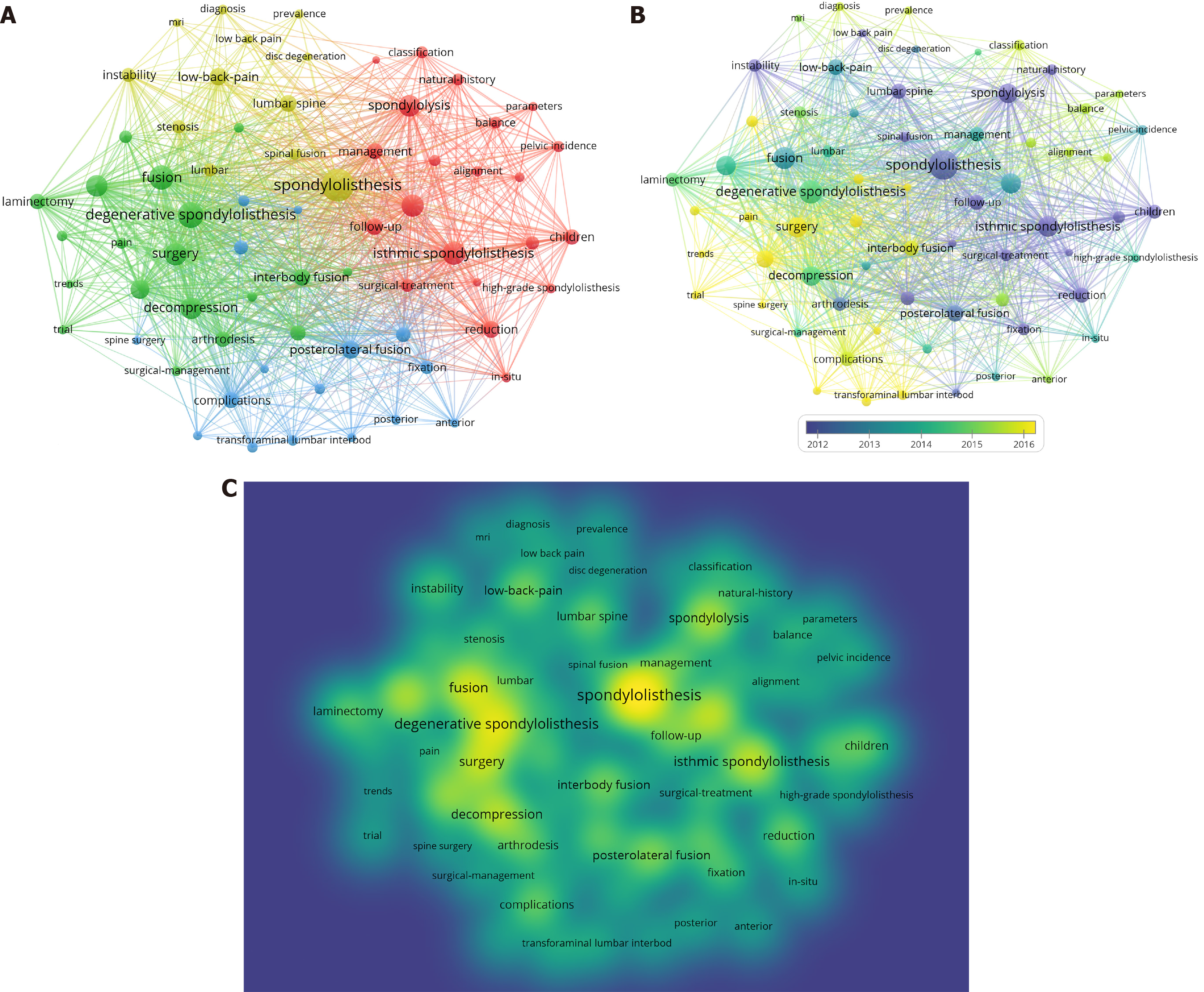
The co-occurrence network analysis presented in Figure 3 delineates the conceptual landscape of high-frequency terminology in spondylolisthesis literature. Applying a minimum occurrence threshold of 35 publications yielded 68 lexically significant terms, which predominantly clustered around four major thematic domains: clinical presentation, diagnostic classification systems, therapeutic management approaches, and long-term clinical outcomes.
Temporal evolution analysis (Figure 3B) demonstrates significant chronological variations in keyword prominence, as evidenced by progressive color gradations corresponding to publication years. Cross-temporal examination in Figure 3C reveals persistent academic focus on core terminology including "spondylolisthesis", "degenerative spondylolisthesis", "spinal fusion", and "decompressive surgery", demonstrating semantic stability across research periods.
Historical trajectory analysis identifies formative research clusters (1965-2000) emphasizing fundamental concepts: anatomical localization ("lumbar spine"), biomechanical considerations ("spinal instability"), pediatric manifestations ("juvenile spondylolisthesis"), and operative interventions ("open surgical procedures"). Contemporary investigations (2015-2023) demonstrate shifting priorities toward advanced surgical techniques ("transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion"), outcome optimization ("postoperative complications"), and predictive modeling ("risk stratification"), reflecting paradigm shifts in evidence-based practice.
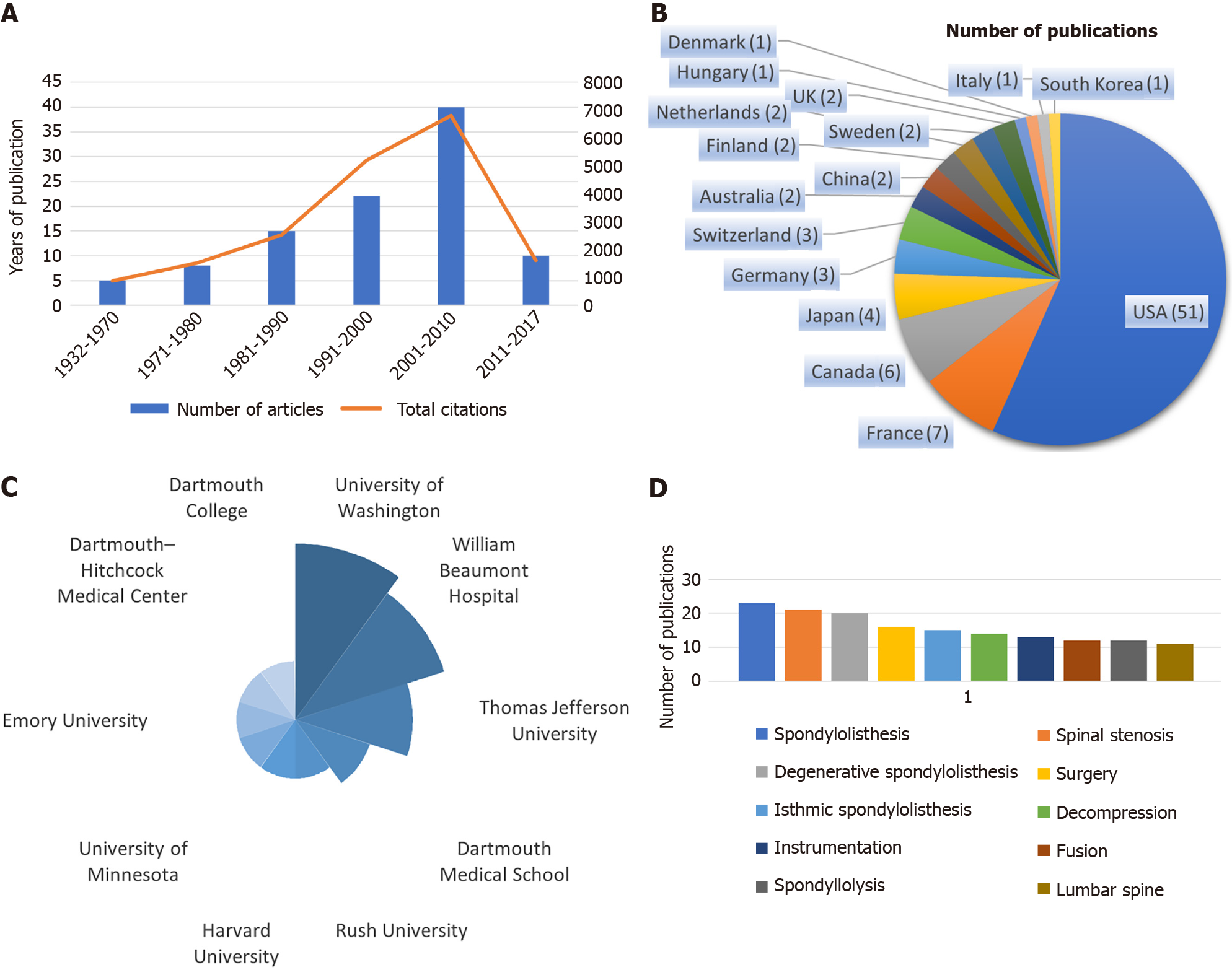
The bibliometric analysis of spondylolisthesis research revealed a longitudinal publication span of 85 years (1932–2017) among the 100 most-cited articles (Table 2). Peak academic productivity occurred during the 2001–2010, accounting for 40% of the total amount (Figure 4A). Geospatial mapping of research contributions identified 16 distinct geopolitical entities, with four nations demonstrating dual dominance in both quantitative output and collaborative influence: the United States (51% of total publications, centrality = 0.72), France (7%, 0.31), Canada (6%, 0.28), and Japan (4%, 0.25) (Figure 4B). Network topology analysis further highlighted institutional leadership, with the University of Washington producing 9% of high-impact studies (mean citation count = 327 ± 42), surpassing second-ranked William Beaumont Hospital (8%, 298 ± 38) in both output volume and citation metrics (Figure 4C). Overall, the 100 most cited publications were published in 18 journals. Spine was the most popular journal with 49 articles and a total of 7606 citations. This was followed by Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume with 14 articles and 3579 citations. European Spine Journal contributed 9 articles with 1078 citations. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume published 5 articles with 693 citations (Table 3).
| Rank | Ref. | Title | Journal | Citations | Citations/year |
| 1 | Tosteson et al[27], 2008 | Surgical Treatment of Spinal Stenosis with and Without Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Cost-Effectiveness After 2 Years | Annals of Internal Medicine | 189 | 12.60 |
| 2 | Morscher et al[28], 1984 | Surgical-Treatment of Spondylolisthesis by Bone-Grafting and Direct Stabilization of Spondylolysis by Means of a Hook Screw | Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery | 124 | 3.18 |
| 3 | Capener[29], 1932 | Spondylolisthesis | British Journal of Surgery | 149 | 1.64 |
| 4 | Wiltse et al[30], 1976 | Classification of Spondylolisis and Spondylolisthesis | Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research | 208 | 4.43 |
| 5 | Farfan et al[31], 1976 | Mechanical Etiology of Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis | Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research | 172 | 3.66 |
| 6 | Marty et al[32], 2002 | The Sagittal Anatomy of The Sacrum Among Young Adults, Infants, and Spondylolisthesis Patients | European Spine Journal | 202 | 9.62 |
| 7 | Jacobs et al[33], 2006 | Fusion for Low-Grade Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: A Systematic Review of The Literature | European Spine Journal | 129 | 7.59 |
| 8 | Kalichman and Hunter[34], 2008 | Diagnosis and Conservative Management of Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis | European Spine Journal | 114 | 7.60 |
| 9 | Yan et al[35], 2008 | Comparative Study of Pilf and Tlif Treatment in Adult Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | European Spine Journal | 133 | 8.87 |
| 10 | Verhoof et al[36], 2008 | High Failure Rate of The Interspinous Distraction Device (X-Stop) for The Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Caused by Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | European Spine Journal | 116 | 7.73 |
| 11 | Wang et al[37], 2010 | Comparison of One-Level Minimally Invasive and Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Degenerative and Isthmic Spondylolisthesis Grades 1 and 2 | European Spine Journal | 203 | 15.62 |
| 12 | Schuller et al[38], 2011 | Sagittal Spinopelvic Alignment and Body Mass Index in Patients with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | European Spine Journal | 112 | 9.33 |
| 13 | Lamartina et al[39], 2012 | Criteria to Restore the Sagittal Balance in Deformity and Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | European Spine Journal | 117 | 10.64 |
| 14 | Sato et al[40], 2017 | Radiographic Evaluation of Indirect Decompression of Mini-Open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Degenerated Lumbar Spondylolisthesis | European Spine Journal | 151 | 25.17 |
| 15 | Gill et al[41], 1955 | Surgical Treatment of Spondylolisthesis Without Spine Fusion - Excision of The Loose Lamina with Decompression of The Nerve Roots | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 168 | 2.47 |
| 16 | Wiltse[42], 1962 | The Etiology of Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 186 | 3.05 |
| 17 | Turner and Bianco[43], 1971 | Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis in Children and Teen-Agers | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 116 | 2.23 |
| 18 | Wiltse et al[44], 1975 | Fatigue Fracture - Basic Lesion in Isthmic Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 326 | 6.79 |
| 19 | Rosenberg[45], 1975 | Degenerative Spondylolisthesis - Predisposing Factors | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 201 | 4.19 |
| 20 | Boxall et al[46], 1979 | Management of Severe Spondylolisthesis in Children and Adolescents | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 279 | 6.34 |
| 21 | Wiltse and Winter[47], 1983 | Terminology and Measurement of Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 234 | 5.85 |
| 22 | Fredrickson et al[48], 1984 | The Natural-History of Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 547 | 14.03 |
| 23 | Levine and Edwards[49], 1985 | The Management of Traumatic Spondylolisthesis of The Axis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 329 | 8.66 |
| 24 | Harris and Weinstein[50], 1987 | Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients with Grade-Ill and Grade-Iv Spondylolisthesis - Treatment With and Without Posterior Fusion | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 122 | 3.39 |
| 25 | Hensinger[51], 1989 | Current Concepts Review - Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis in Children and Adolescents | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 130 | 3.82 |
| 26 | Herkowitz and Kurz[25], 1991 | Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis with Spinal Stenosis - A Prospective-Study Comparing Decompression with Decompression and Intertransverse Process Arthrodesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 670 | 20.94 |
| 27 | Hu et al[52], 2008 | Spondylolisthesis and Spondylolysis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 96 | 6.40 |
| 28 | Weinstein et al[53], 2009 | Surgical Compared with Nonoperative Treatment for Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Four-Year Results in The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (Sport) Randomized and Observational Cohorts | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 402 | 28.71 |
| 29 | Macnab[54], 1950 | Spondylolisthesis With an Intact Neural Arch - The So-Called Pseudo-Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume | 130 | 1.78 |
| 30 | Newman and Stone[55], 1963 | The Etiology of Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume | 244 | 4.07 |
| 31 | Fitzgerald and Newman[7], 1976 | Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume | 108 | 2.30 |
| 32 | Wynne-Davies and Scott[56], 1979 | Inheritance and Spondylolisthesis - Radiographic Family Survey | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume | 112 | 2.55 |
| 33 | Francis et al[57], 1981 | Traumatic Spondylolisthesis of The Axis | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume | 129 | 3.07 |
| 34 | Ghogawala et al[58], 2004 | Prospective Outcomes Evaluation after Decompression with Or Without Instrumented Fusion for Lumbar Stenosis and Degenerative Grade I Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Neurosurgery-Spine | 119 | 6.26 |
| 35 | Anderson et al[59], 2006 | Treatment of Neurogenic Claudication by Interspinous Decompression: Application of The X Stop Device in Patients with Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Neurosurgery-Spine | 135 | 7.94 |
| 36 | Min et al[60], 2007 | Comparison of Anterior- and Posterior-Approach Instrumented Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Neurosurgery-Spine | 111 | 6.94 |
| 37 | Parker et al[61], 2011 | Utility of Minimum Clinically Important Difference in Assessing Pain, Disability, and Health State after Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Neurosurgery-Spine | 201 | 16.75 |
| 38 | Saraste[62], 1987 | Long-Term Clinical and Radiological Follow-Up of Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics | 103 | 2.86 |
| 39 | Lenke et al[63], 1992 | Results of Insitu Fusion for Isthmic Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Spinal Disorders | 230 | 7.42 |
| 40 | Bridwell et al[64], 1993 | The Role of Fusion and Instrumentation in The Treatment of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis with Spinal Stenosis | Journal of Spinal Disorders | 421 | 14.03 |
| 41 | Deguchi et al[65], 1998 | Posterolateral Fusion for Isthmic Spondylolisthesis in Adults: Analysis of Fusion Rate and Clinical Results | Journal of Spinal Disorders | 120 | 4.80 |
| 42 | Ishihara et al[66], 2001 | Minimum 10-Year Follow-Up Study of Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Isthmic Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Spinal Disorders | 129 | 5.86 |
| 43 | Rajnics et al[67], 2002 | The Association of Sagittal Spinal and Pelvic Parameters in Asymptomatic Persons and Patients with Isthmic Spondylolisthesis | Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques | 118 | 5.62 |
| 44 | Barrey et al[68], 2007 | Spinopelvic Alignment of Patients with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Neurosurgery | 142 | 8.88 |
| 45 | Park and Foley[69], 2008 | Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Reduction of Spondylolisthesis: Technique and Outcomes After a Minimum of 2 Years' Follow-Up | Neurosurgical Focus | 134 | 8.93 |
| 46 | Weinstein et al[70], 2007 | Surgical Versus Nonsurgical Treatment for Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | New England Journal of Medicine | 572 | 35.75 |
| 47 | Ghogawala et al[71], 2016 | Laminectomy Plus Fusion Versus Laminectomy Alone for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis | New England Journal of Medicine | 409 | 58.43 |
| 48 | Collier et al[72], 1985 | Painful Spondylolysis or Spondylolisthesis Studied by Radiography and Single-Photon Emission Computed-Tomography | Radiology | 127 | 3.34 |
| 49 | Steiner and Micheli[73], 1985 | Treatment of Symptomatic Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis with The Modified Boston Brace | Spine | 125 | 3.29 |
| 50 | Lombardi et al[74], 1985 | Treatment of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 117 | 3.08 |
| 51 | Feffer et al[75], 1985 | Degenerative Spondylolisthesis - to Fuse or Not to Fuse | Spine | 94 | 2.47 |
| 52 | Herron and Trippi[76], 1989 | L4-5 Degenerative Spondylolisthesis - The Results of Treatment by Decompressive Laminectomy Without Fusion | Spine | 108 | 3.18 |
| 53 | Hanley and Levy[77], 1989 | Surgical-Treatment of Isthmic Lumbosacral Spondylolisthesis - Analysis of Variables Influencing Results | Spine | 91 | 2.68 |
| 54 | Matsunaga et al[78], 1990 | Natural-History of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis - Pathogenesis and Natural Course of The Slippage | Spine | 149 | 4.52 |
| 55 | Seitsalo et al[79], 1991 | Progression of Spondylolisthesis in Children and Adolescents - A Long-Term Follow-Up Of 272 Patients | Spine | 120 | 3.75 |
| 56 | Grobler et al[80], 1993 | Etiology of Spondylolisthesis - Assessment of The Role Played by Lumbar Facet Joint Morphology | Spine | 188 | 6.27 |
| 57 | McGuire and Amundson[81], 1993 | The Use of Primary Internal-Fixation in Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 126 | 4.20 |
| 58 | Poussa et al[82], 1993 | Surgical-Treatment of Severe Isthmic Spondylolisthesis in Adolescents - Reduction or Fusion in Stu | Spine | 115 | 3.83 |
| 59 | Boos et al[83], 1993 | Treatment of Severe Spondylolisthesis by Reduction and Pedicular Fixation - A 4-6-Year Follow-Up-Study | Spine | 98 | 3.27 |
| 60 | Mardjetko et al[84], 1994 | Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis - A Meta Analysis of Literature 1970-1993 | Spine | 258 | 8.90 |
| 61 | Wood et al[85], 1994 | Radiographic Evaluation of Instability in Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 103 | 3.55 |
| 62 | Herkowitz[86], 1995 | Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 117 | 4.18 |
| 63 | O'Sullivan et al[24], 1997 | Evaluation of Specific Stabilizing Exercise in The Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain with Radiologic Diagnosis of Spondylolysis or Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 686 | 26.38 |
| 64 | Fischgrund et al[26], 1997 | 1997 Volvo Award Winner in Clinical Studies - Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis with Spinal Stenosis: A Prospective, Randomized Study Comparing Decompressive Laminectomy and Arthrodesis with And Without Spinal Instrumentation | Spine | 643 | 24.73 |
| 65 | Suk et al[87], 1997 | Adding Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion to Pedicle Screw Fixation and Posterolateral Fusion after Decompression in Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 280 | 10.77 |
| 66 | Molinari et al[88], 1999 | Complications in The Surgical Treatment of Pediatric High-Grade, Isthmic Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis - A Comparison of Three Surgical Approaches | Spine | 148 | 6.17 |
| 67 | Booth et al[89], 1999 | Minimum 5-Year Results of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Treated with Decompression and Instrumented Posterior Fusion | Spine | 136 | 5.67 |
| 68 | Lonstein[90], 1999 | Spondylolisthesis in Children - Cause, Natural History, and Management | Spine | 98 | 4.08 |
| 69 | Möller and Hedlund[91], 2000 | Surgery Versus Conservative Management in Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis - A Prospective Randomized Study: Part 1 | Spine | 198 | 8.61 |
| 70 | Miyakoshi et al[92], 2000 | Outcome of One-Level Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Spondylolisthesis and Postoperative Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Adjacent to The Fusion | Spine | 165 | 7.17 |
| 71 | Möller and Hedlund[93], 2000 | Instrumented and Noninstrumented Posterolateral Fusion in Adult Spondylolisthesis - A Prospective Randomized Study: Part 2 | Spine | 144 | 6.26 |
| 72 | Kuntz et al[94], 2000 | Cost-Effectiveness of Fusion with and Without Instrumentation for Patients with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis and Spinal Stenosis | Spine | 131 | 5.70 |
| 73 | Hanson et al[95], 2002 | Correlation of Pelvic Incidence with Low- and High-Grade Isthmic Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 177 | 8.43 |
| 74 | Kawakami et al[96], 2002 | Lumbar Sagittal Balance Influences the Clinical Outcome After Decompression and Posterolateral Spinal Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 138 | 6.57 |
| 75 | Madan and Boeree[97], 2002 | Outcome of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Versus Posterolateral Fusion for Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 156 | 7.43 |
| 76 | Beutler et al[98], 2003 | The Natural History of Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis - 45-Year Follow-Up Evaluation | Spine | 236 | 11.80 |
| 77 | Jackson et al[99], 2003 | Pelvic Lordosis and Alignment in Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 108 | 5.40 |
| 78 | Kornblum et al[100], 2004 | Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis with Spinal Stenosis - A Prospective Long-Term Study Comparing Fusion and Pseudarthrosis | Spine | 317 | 16.68 |
| 79 | Labelle et al[101], 2004 | Spondylolisthesis, Pelvic Incidence, and Spinopelvic Balance - A Correlation Study | Spine | 276 | 14.53 |
| 80 | Vaccaro et al[102], 2004 | A Pilot Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Op-1 Putty (Rhbmp-7) as A Replacement for Iliac Crest Autograft in Posterolateral Lumbar Arthrodesis for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 131 | 6.89 |
| 81 | Labelle et al[103], 2005 | The Importance of Spino-Pelvic Balance in L5-S1 Developmental Spondylolisthesis - A Review of Pertinent Radiologic Measurements | Spine | 189 | 10.50 |
| 82 | Sengupta and Herkowitz[104], 2005 | Degenerative Spondylolisthesis - Review of Current Trends and Controversies | Spine | 177 | 9.83 |
| 83 | McAfee et al[105], 2005 | The Indications for Interbody Fusion Cages in The Treatment of Spondylolisthesis - Analysis of 120 Cases | Spine | 98 | 5.44 |
| 84 | Schnake et al[106], 2006 | Dynamic Stabilization in Addition to Decompression for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 189 | 11.12 |
| 85 | Roussouly et al[107], 2006 | Sagittal Alignment of The Spine and Pelvis in The Presence of L5-S1 Isthmic Lysis and Low-Grade Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 156 | 9.18 |
| 86 | Cummins et al[108], 2006 | Descriptive Epidemiology and Prior Healthcare Utilization of Patients in The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial'S (Sport) Three Observational Cohorts - Disc Herniation, Spinal Stenosis, and Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 101 | 5.94 |
| 87 | Lauber et al[109], 2006 | Clinical and Radiologic 2 - 4-Year Results of Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Degenerative and Isthmic Spondylolisthesis Grades 1 and 2 | Spine | 113 | 6.65 |
| 88 | Martin et al[110], 2007 | The Surgical Management of Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis - A Systematic Review | Spine | 172 | 10.75 |
| 89 | Jacobsen et al[111], 2007 | Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: An Epidemiological Perspective - The Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study | Spine | 181 | 11.31 |
| 90 | Chaput et al[112], 2007 | The Significance of Increased Fluid Signal on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Lumbar Facets in Relationship to Degenerative Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 99 | 6.19 |
| 91 | Schaeren et al[113], 2008 | Minimum Four-Year Follow-Up of Spinal Stenosis with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Treated with Decompression and Dynamic Stabilization | Spine | 157 | 10.47 |
| 92 | Kalichman et al[1], 2009 | Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis Prevalence and Association with Low Back Pain in The Adult Community-Based Population | Spine | 227 | 16.21 |
| 93 | Kalanithi et al[114], 2009 | National Complication Rates and Disposition after Posterior Lumbar Fusion for Acquired Spondylolisthesis | Spine | 135 | 9.64 |
| 94 | Abdu et al[115], 2009 | Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Does Fusion Method Influence Outcome? Four-Year Results of The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial | Spine | 123 | 8.79 |
| 95 | Tsutsumimoto et al[116], 2009 | Mini-Open Versus Conventional Open Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for The Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Comparison of Paraspinal Muscle Damage and Slip Reduction | Spine | 108 | 7.71 |
| 96 | Tosteson et al[117], 2011 | Comparative Effectiveness Evidence from The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial Surgical Versus Nonoperative Care for Spinal Stenosis, Degenerative Spondylolisthesis, and Intervertebral Disc Herniation | Spine | 159 | 13.25 |
| 97 | Rihn et al[118], 2012 | Does Obesity Affect Outcomes of Treatment for Lumbar Stenosis and Degenerative Spondylolisthesis? Analysis of The Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (Sport) | Spine | 105 | 9.55 |
| 98 | Matz et al[18], 2016 | Guideline Summary Review: An Evidence-Based Clinical Guideline for The Diagnosis and Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis | Spine Journal | 105 | 15.00 |
| 99 | Parker et al[119], 2012 | Cost-Effectiveness of Minimally Invasive Versus Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Associated Low-Back and Leg Pain Over Two Years | World Neurosurgery | 101 | 9.18 |
| 100 | Parker et al[120], 2014 | Minimally Invasive Versus Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Utility Analysis | World Neurosurgery | 146 | 16.22 |
| Rank | Journal | Article | Total citation | Mean citation | Impact factor |
| 1 | Spine | 49 | 7606 | 86.2 | 3.241 |
| 2 | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume | 14 | 3579 | 70.1 | 6.558 |
| 3 | European Spine Journal | 9 | 1078 | 55.5 | 2.721 |
| 4 | Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-British Volume | 5 | 693 | 46.6 | 3.309 |
The most common research focus was classification (35 articles), followed by clinical treatment (26 articles) and clinical manifestation (21 articles; Figure 4D).
Spondylolisthesis is the anterior, lateral or posterior slippage of one vertebral body over another. Vertebral anterior displacement is caused by a defect in the joint space, usually caused by L5-S1 joint lysis, and eventually spondylolisthesis of the isthmus occurs. As the most common type of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis, X-ray, CT and MRI have irreplaceable roles in its diagnosis. The investigative domains of spondylolisthesis have undergone a paradigmatic expansion, now systematically encompassing pathomechanistic explorations, phenotypic characterization, longitudinal disease progression patterns, and evidence-based therapeutic algorithms. This pioneering bibliometric investigation implements scientometric mapping techniques to decode the scientific evolution of the field, employing a multi-metric analytic framework to chronologically profile research trajectories while identifying seminal works that have shaped contemporary clinical paradigms.
In the field of spondylolisthesis research, the United States demonstrates unparalleled academic productivity and scholarly influence, maintaining global leadership in both research output quantity and citation impact. Analysis of institutional performance revealed that the University of California, San Francisco was the most active contributor with 52 published studies, while the University of Washington achieved exceptional recognition through accumulated citations reaching 2537, representing the highest citation metrics among participating institutions. Spine, European Spine Journal and Journal of Neurosurgery-spine are the top 3 productive journals on spondylolisthesis, indicating that there will be more high-quality publications on this topic published on these journals.
Bibliometric analysis revealed distinct thematic clusters in spondylolisthesis research, centering around core terminology including "spondylolisthesis", "isthmic spondylolisthesis", "degenerative spondylolisthesis", and "fusion" with scholarly focus undergoing temporal evolution. The temporal analysis demonstrated a paradigm shift from historical emphasis on "posterolateral fusion" techniques to contemporary preference for "interbody fusion" methodologies, reflecting evolving surgical approaches in this domain.
The most cited publication on spondylolisthesis was "Evaluation of specific stabilizing exercise in the treatment of chronic low back pain with radiologic diagnosis of spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis" by O'Sullivan et al[24] in 1997. They evaluated the efficacy of specific training of muscles surrounding the spine by performing a randomized, controlled trial, test-retest design, with a 3-month, 6-month, and 30-month postal questionnaire follow-up. They found that the specific exercise group showed a statistically significant reduction in pain intensity and functional disability levels.
"Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis with Spinal Stenosis - A Prospective-Study Comparing Decompression with Decompression and Intertransverse Process Arthrodesis" published by Herkowitz and Kurz[25] in 1991 was the second d most-cited article. They conducted a prospective clinical and imaging study of 50 patients with spinal stenosis associated with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis to determine whether concurrent intertransverse arthroplasty provided better outcomes than laminar decompression alone. They found that in the patients who had a concomitant arthrodesis, the results were significantly better with respect to relief of pain in the back and lower limbs.
"1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies - Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: A prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation" by Fischgrund et al[26] in 1997 was the third most-cited article. They analyzed the influence of transpedicular instruments on the operative treatment of patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis. Studies have found that in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis, the use of pedicle screws may result in higher fusion rates, but clinical results have shown no improvement in back and lower extremity pain.
This investigation conducted a bibliometric analysis of spondylolisthesis research using data sourced exclusively from the Web of Science Core Collection database. While employing systematic methodological approaches, three principal constraints warrant acknowledgment: (1) The inherent database limitations resulted in the unavoidable exclusion of seminal works not indexed within the Web of Science platform; (2) Linguistic constraints imposed by English-only inclusion criteria may have omitted impactful contributions published in other academic lingua francas; and (3) The dataset's temporal cutoff of September 2022 creates a dynamic parameter gap, though subsequent citation patterns are anticipated to maintain established trajectory profiles. These methodological boundaries notwithstanding, the study's core findings retain validity within defined parameters.
This scientometric investigation revealed a progressive growth in scholarly outputs addressing spondylolisthesis management during the last decade. Analysis of geographical contributions indicates that the United States maintains dominance in spinal pathology research productivity. Three principal periodicals emerged as leading knowledge dissemination platforms: Spine, European Spine Journal, and Journal of Neurosurgery Spine, collectively accounting for 18.7% of total publications. Contemporary research trajectories demonstrate intensified focus on intervertebral body fusion techniques and associated instrumentation innovations. Furthermore, our citation network analysis identifies seminal works within the century club (≥ 100 citations) that continue to shape current clinical paradigms, offering foundational guidance for subsequent investigators in this evolving orthopedic domain.
| 1. | Kalichman L, Kim DH, Li L, Guermazi A, Berkin V, Hunter DJ. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: prevalence and association with low back pain in the adult community-based population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34:199-205. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 303] [Cited by in RCA: 272] [Article Influence: 17.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Margetis K, Gillis CC. Spondylolisthesis. 2025 Mar 28. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2025. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Cabraja M, Mohamed E, Koeppen D, Kroppenstedt S. The analysis of segmental mobility with different lumbar radiographs in symptomatic patients with a spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2012;21:256-261. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Luk KD, Ruan DK, Lu DS, Fei ZQ. Fresh frozen intervertebral disc allografting in a bipedal animal model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28:864-9; discussion 870. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Wáng YXJ, Deng M, Griffith JF, Kwok AWL, Leung JC, Ahuja AT, Kwok T, Leung PC. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Progression and De Novo Spondylolisthesis in Elderly Chinese Men and Women: A Year-4 Follow-up Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41:1096-1103. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Kanayama M, Hashimoto T, Shigenobu K, Oha F, Ishida T, Yamane S. Intraoperative biomechanical assessment of lumbar spinal instability: validation of radiographic parameters indicating anterior column support in lumbar spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28:2368-2372. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Fitzgerald JA, Newman PH. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976;58:184-192. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 93] [Cited by in RCA: 89] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Kreiner DS, Baisden J, Mazanec DJ, Patel RD, Bess RS, Burton D, Chutkan NB, Cohen BA, Crawford CH 3rd, Ghiselli G, Hanna AS, Hwang SW, Kilincer C, Myers ME, Park P, Rosolowski KA, Sharma AK, Taleghani CK, Trammell TR, Vo AN, Williams KD. Guideline summary review: an evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2016;16:1478-1485. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Alqarni AM, Schneiders AG, Cook CE, Hendrick PA. Clinical tests to diagnose lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: A systematic review. Phys Ther Sport. 2015;16:268-275. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Kuhns BD, Kouk S, Buchanan C, Lubelski D, Alvin MD, Benzel EC, Mroz TE, Tozzi J. Sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of mobile and nonmobile L4-L5 degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2015;15:1956-1962. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Koslosky E, Gendelberg D. Classification in Brief: The Meyerding Classification System of Spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478:1125-1130. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 21.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Bydon M, Alvi MA, Goyal A. Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: Definition, Natural History, Conservative Management, and Surgical Treatment. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019;30:299-304. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 127] [Article Influence: 21.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Gajdosik RL, Albert CR, Mitman JJ. Influence of hamstring length on the standing position and flexion range of motion of the pelvic angle, lumbar angle, and thoracic angle. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1994;20:213-219. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Hey HW, Lau ET, Lim JL, Choong DA, Tan CS, Liu GK, Wong HK. Slump sitting X-ray of the lumbar spine is superior to the conventional flexion view in assessing lumbar spine instability. Spine J. 2017;17:360-368. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Tarpada SP, Cho W, Chen F, Amorosa LF. Utility of Supine Lateral Radiographs for Assessment of Lumbar Segmental Instability in Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43:1275-1280. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Bouras T, Korovessis P. Management of spondylolysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis in fine athletes. A comprehensive review. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25 Suppl 1:S167-S175. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Baker JF, Errico TJ, Kim Y, Razi A. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: contemporary review of the role of interbody fusion. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27:169-180. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Matz PG, Meagher RJ, Lamer T, Tontz WL Jr, Annaswamy TM, Cassidy RC, Cho CH, Dougherty P, Easa JE, Enix DE, Gunnoe BA, Jallo J, Julien TD, Maserati MB, Nucci RC, O'Toole JE, Rosolowski K, Sembrano JN, Villavicencio AT, Witt JP. Guideline summary review: An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2016;16:439-448. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 215] [Cited by in RCA: 174] [Article Influence: 19.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Schöller K, Alimi M, Cong GT, Christos P, Härtl R. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Associated With Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Secondary Fusion Rates Following Open vs Minimally Invasive Decompression. Neurosurgery. 2017;80:355-367. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Koreckij TD, Fischgrund JS. Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28:236-241. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Ding X, Yang Z. Knowledge mapping of platform research: a visual analysis using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Electron Commer Res. 2022;22:787-809. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 22. | Thelwall M. Bibliometrics to webometrics. J Inf Sci. 2008;34:605-621. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 167] [Cited by in RCA: 171] [Article Influence: 10.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Merigó JM, Yang JB. A bibliometric analysis of operations research and management science. Omega. 2017;73:37-48. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 24. | O'Sullivan PB, Phyty GD, Twomey LT, Allison GT. Evaluation of specific stabilizing exercise in the treatment of chronic low back pain with radiologic diagnosis of spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22:2959-2967. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 755] [Cited by in RCA: 638] [Article Influence: 22.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73:802-808. [PubMed] |
| 26. | Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM, Kurz LT. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22:2807-2812. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 690] [Cited by in RCA: 596] [Article Influence: 21.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Tosteson AN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Skinner JS, Herkowitz H, Albert T, Boden SD, Bridwell K, Longley M, Andersson GB, Blood EA, Grove MR, Weinstein JN; SPORT Investigators. Surgical treatment of spinal stenosis with and without degenerative spondylolisthesis: cost-effectiveness after 2 years. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:845-853. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 202] [Cited by in RCA: 184] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Morscher E, Gerber B, Fasel J. Surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis by bone grafting and direct stabilization of spondylolysis by means of a hook screw. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (1978). 1984;103:175-178. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 122] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Capener N. Spondylolisthesis. Br J Surg. 1932;19:374-386. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 160] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Wiltse LL, Newman PH, Macnab I. Classification of spondylolisis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;23-29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Farfan HF, Osteria V, Lamy C. The mechanical etiology of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;40-55. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Marty C, Boisaubert B, Descamps H, Montigny JP, Hecquet J, Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G. The sagittal anatomy of the sacrum among young adults, infants, and spondylolisthesis patients. Eur Spine J. 2002;11:119-125. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 216] [Cited by in RCA: 191] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Jacobs WC, Vreeling A, De Kleuver M. Fusion for low-grade adult isthmic spondylolisthesis: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2006;15:391-402. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 130] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Kalichman L, Hunter DJ. Diagnosis and conservative management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:327-335. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 136] [Cited by in RCA: 132] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Yan DL, Pei FX, Li J, Soo CL. Comparative study of PILF and TLIF treatment in adult degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:1311-1316. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 135] [Cited by in RCA: 124] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 36. | Verhoof OJ, Bron JL, Wapstra FH, van Royen BJ. High failure rate of the interspinous distraction device (X-Stop) for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis caused by degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:188-192. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 122] [Cited by in RCA: 99] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang ZF, Li CQ, Zheng WJ, Liu J. Comparison of one-level minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Eur Spine J. 2010;19:1780-1784. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 188] [Cited by in RCA: 194] [Article Influence: 12.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Schuller S, Charles YP, Steib JP. Sagittal spinopelvic alignment and body mass index in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2011;20:713-719. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 94] [Cited by in RCA: 124] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Lamartina C, Berjano P, Petruzzi M, Sinigaglia A, Casero G, Cecchinato R, Damilano M, Bassani R. Criteria to restore the sagittal balance in deformity and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2012;21 Suppl 1:S27-S31. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 100] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Sato J, Ohtori S, Orita S, Yamauchi K, Eguchi Y, Ochiai N, Kuniyoshi K, Aoki Y, Nakamura J, Miyagi M, Suzuki M, Kubota G, Inage K, Sainoh T, Fujimoto K, Shiga Y, Abe K, Kanamoto H, Inoue G, Takahashi K. Radiographic evaluation of indirect decompression of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerated lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2017;26:671-678. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 171] [Article Influence: 17.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Gill GG, Manning JG, White HL. Surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis without spine fusion; excision of the loose lamina with decompression of the nerve roots. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1955;37-A:493-520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Wiltse LL. The etiology of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962;44-A:539-560. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 167] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Turner RH, Bianco AJ Jr. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and teen-agers. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53:1298-1306. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Wiltse LL, Widell EH Jr, Jackson DW. Fatigue fracture: the basic lesion is inthmic spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57:17-22. [PubMed] |
| 45. | Rosenberg NJ. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. Predisposing factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57:467-474. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 205] [Cited by in RCA: 180] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Boxall D, Bradford DS, Winter RB, Moe JH. Management of severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:479-495. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 47. | Wiltse LL, Winter RB. Terminology and measurement of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983;65:768-772. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 259] [Cited by in RCA: 192] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Fredrickson BE, Baker D, McHolick WJ, Yuan HA, Lubicky JP. The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66:699-707. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 49. | Levine AM, Edwards CC. The management of traumatic spondylolisthesis of the axis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67:217-226. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 334] [Cited by in RCA: 273] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Harris IE, Weinstein SL. Long-term follow-up of patients with grade-III and IV spondylolisthesis. Treatment with and without posterior fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69:960-969. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 151] [Cited by in RCA: 113] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Hensinger RN. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989;71:1098-1107. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 52. | Hu SS, Tribus CB, Diab M, Ghanayem AJ. Spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:656-671. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 53. | Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Zhao W, Blood EA, Tosteson AN, Birkmeyer N, Herkowitz H, Longley M, Lenke L, Emery S, Hu SS. Surgical compared with nonoperative treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. four-year results in the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) randomized and observational cohorts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:1295-1304. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 448] [Cited by in RCA: 455] [Article Influence: 28.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 54. | Macnab I. Spondylolisthesis with an intact neural arch; the so-called pseudo-spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1950;32-B:325-333. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 55. | Newman PH, Stone KH. The etiology of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Jt Surg. 1963;45-B:39-59. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 208] [Cited by in RCA: 165] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Wynne-Davies R, Scott JH. Inheritance and spondylolisthesis: a radiographic family survey. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979;61-B:301-305. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 140] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Francis WR, Fielding JW, Hawkins RJ, Pepin J, Hensinger R. Traumatic spondylolisthesis of the axis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981;63-B:313-318. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 139] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Ghogawala Z, Benzel EC, Amin-Hanjani S, Barker FG 2nd, Harrington JF, Magge SN, Strugar J, Coumans JV, Borges LF. Prospective outcomes evaluation after decompression with or without instrumented fusion for lumbar stenosis and degenerative Grade I spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2004;1:267-272. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 122] [Cited by in RCA: 127] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Anderson PA, Tribus CB, Kitchel SH. Treatment of neurogenic claudication by interspinous decompression: application of the X STOP device in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4:463-471. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 156] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Min JH, Jang JS, Lee SH. Comparison of anterior- and posterior-approach instrumented lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;7:21-26. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 119] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Parker SL, Adogwa O, Paul AR, Anderson WN, Aaronson O, Cheng JS, McGirt MJ. Utility of minimum clinically important difference in assessing pain, disability, and health state after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14:598-604. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 203] [Cited by in RCA: 291] [Article Influence: 20.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 62. | Saraste H. Long-term clinical and radiological follow-up of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1987;7:631-638. [PubMed] |
| 63. | Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, Betz RR, Baldus C, Schoenecker PL. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5:433-442. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 263] [Cited by in RCA: 242] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA, O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Baldus C. The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord. 1993;6:461-472. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 430] [Cited by in RCA: 395] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Deguchi M, Rapoff AJ, Zdeblick TA. Posterolateral fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults: analysis of fusion rate and clinical results. J Spinal Disord. 1998;11:459-464. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 129] [Cited by in RCA: 107] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Ishihara H, Osada R, Kanamori M, Kawaguchi Y, Ohmori K, Kimura T, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Minimum 10-year follow-up study of anterior lumbar interbody fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 2001;14:91-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 149] [Cited by in RCA: 125] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 67. | Rajnics P, Templier A, Skalli W, Lavaste F, Illés T. The association of sagittal spinal and pelvic parameters in asymptomatic persons and patients with isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2002;15:24-30. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Barrey C, Jund J, Perrin G, Roussouly P. Spinopelvic alignment of patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery. 2007;61:981-986. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 117] [Cited by in RCA: 132] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Park P, Foley KT. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with reduction of spondylolisthesis: technique and outcomes after a minimum of 2 years' follow-up. Neurosurg Focus. 2008;25:E16. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 148] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Hanscom B, Tosteson AN, Blood EA, Birkmeyer NJ, Hilibrand AS, Herkowitz H, Cammisa FP, Albert TJ, Emery SE, Lenke LG, Abdu WA, Longley M, Errico TJ, Hu SS. Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2257-2270. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 747] [Cited by in RCA: 648] [Article Influence: 36.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Ghogawala Z, Dziura J, Butler WE, Dai F, Terrin N, Magge SN, Coumans JV, Harrington JF, Amin-Hanjani S, Schwartz JS, Sonntag VK, Barker FG 2nd, Benzel EC. Laminectomy plus Fusion versus Laminectomy Alone for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1424-1434. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 461] [Cited by in RCA: 585] [Article Influence: 65.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Collier BD, Johnson RP, Carrera GF, Meyer GA, Schwab JP, Flatley TJ, Isitman AT, Hellman RS, Zielonka JS, Knobel J. Painful spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis studied by radiography and single-photon emission computed tomography. Radiology. 1985;154:207-211. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 130] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 73. | Steiner ME, Micheli LJ. Treatment of symptomatic spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis with the modified Boston brace. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10:937-943. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 154] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Lombardi JS, Wiltse LL, Reynolds J, Widell EH, Spencer C 3rd. Treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10:821-827. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Feffer HL, Wiesel SW, Cuckler JM, Rothman RH. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. To fuse or not to fuse. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10:287-289. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 76. | Herron LD, Trippi AC. L4-5 degenerative spondylolisthesis. The results of treatment by decompressive laminectomy without fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14:534-538. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 122] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Hanley EN Jr, Levy JA. Surgical treatment of isthmic lumbosacral spondylolisthesis. Analysis of variables influencing results. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14:48-50. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 109] [Cited by in RCA: 89] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 78. | Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Morizono Y, Masuda A, Demirtas AM. Natural history of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Pathogenesis and natural course of the slippage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15:1204-1210. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 173] [Cited by in RCA: 157] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | Seitsalo S, Osterman K, Hyvãrinen H, Tallroth K, Schlenzka D, Poussa M. Progression of spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. A long-term follow-up of 272 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16:417-421. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 160] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 80. | Grobler LJ, Robertson PA, Novotny JE, Pope MH. Etiology of spondylolisthesis. Assessment of the role played by lumbar facet joint morphology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18:80-91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 227] [Cited by in RCA: 187] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | McGuire RA, Amundson GM. The use of primary internal fixation in spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18:1662-1672. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 128] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 82. | Poussa M, Schlenzka D, Seitsalo S, Ylikoski M, Hurri H, Osterman K. Surgical treatment of severe isthmic spondylolisthesis in adolescents. Reduction or fusion in situ. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18:894-901. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 112] [Cited by in RCA: 95] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 83. | Boos N, Marchesi D, Zuber K, Aebi M. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by reduction and pedicular fixation. A 4-6-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18:1655-1661. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 113] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 84. | Mardjetko SM, Connolly PJ, Shott S. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. A meta-analysis of literature 1970-1993. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19:2256S-2265S. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 286] [Cited by in RCA: 224] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 85. | Wood KB, Popp CA, Transfeldt EE, Geissele AE. Radiographic evaluation of instability in spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19:1697-1703. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 109] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 86. | Herkowitz HN. Spine update. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20:1084-1090. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 113] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 87. | Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, Lee JH, Cho KJ, Kim HG. Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22:210-9; discussion 219. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 222] [Cited by in RCA: 209] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 88. | Molinari RW, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Ungacta FF, Riew KD. Complications in the surgical treatment of pediatric high-grade, isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis. A comparison of three surgical approaches. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24:1701-1711. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 164] [Cited by in RCA: 147] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 89. | Booth KC, Bridwell KH, Eisenberg BA, Baldus CR, Lenke LG. Minimum 5-year results of degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and instrumented posterior fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24:1721-1727. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 144] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 90. | Lonstein JE. Spondylolisthesis in children. Cause, natural history, and management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24:2640-2648. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 127] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 91. | Möller H, Hedlund R. Surgery versus conservative management in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis--a prospective randomized study: part 1. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:1711-1715. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 223] [Cited by in RCA: 194] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 92. | Miyakoshi N, Abe E, Shimada Y, Okuyama K, Suzuki T, Sato K. Outcome of one-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis and postoperative intervertebral disc degeneration adjacent to the fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:1837-1842. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 142] [Cited by in RCA: 134] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 93. | Möller H, Hedlund R. Instrumented and noninstrumented posterolateral fusion in adult spondylolisthesis--a prospective randomized study: part 2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:1716-1721. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 160] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 94. | Kuntz KM, Snider RK, Weinstein JN, Pope MH, Katz JN. Cost-effectiveness of fusion with and without instrumentation for patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:1132-1139. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 135] [Cited by in RCA: 118] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 95. | Hanson DS, Bridwell KH, Rhee JM, Lenke LG. Correlation of pelvic incidence with low- and high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27:2026-2029. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 178] [Cited by in RCA: 177] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 96. | Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Ando M, Yamada H, Hashizume H, Yoshida M. Lumbar sagittal balance influences the clinical outcome after decompression and posterolateral spinal fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27:59-64. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 134] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 97. | Madan S, Boeree NR. Outcome of posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion for spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27:1536-1542. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 137] [Cited by in RCA: 125] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 98. | Beutler WJ, Fredrickson BE, Murtland A, Sweeney CA, Grant WD, Baker D. The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: 45-year follow-up evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28:1027-1035. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 176] [Cited by in RCA: 195] [Article Influence: 8.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 99. | Jackson RP, Phipps T, Hales C, Surber J. Pelvic lordosis and alignment in spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28:151-160. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 110] [Cited by in RCA: 102] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 100. | Kornblum MB, Fischgrund JS, Herkowitz HN, Abraham DA, Berkower DL, Ditkoff JS. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29:726-733. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 340] [Cited by in RCA: 305] [Article Influence: 14.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 101. | Labelle H, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Transfeldt E, O'Brien M, Chopin D, Hresko T, Dimnet J. Spondylolisthesis, pelvic incidence, and spinopelvic balance: a correlation study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29:2049-2054. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 281] [Cited by in RCA: 281] [Article Influence: 13.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 102. | Vaccaro AR, Patel T, Fischgrund J, Anderson DG, Truumees E, Herkowitz HN, Phillips F, Hilibrand A, Albert TJ, Wetzel T, McCulloch JA. A pilot study evaluating the safety and efficacy of OP-1 Putty (rhBMP-7) as a replacement for iliac crest autograft in posterolateral lumbar arthrodesis for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29:1885-1892. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 145] [Cited by in RCA: 107] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 103. | Labelle H, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J, O'Brien M. The importance of spino-pelvic balance in L5-s1 developmental spondylolisthesis: a review of pertinent radiologic measurements. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30:S27-S34. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 191] [Cited by in RCA: 180] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 104. | Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: review of current trends and controversies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30:S71-S81. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 162] [Cited by in RCA: 172] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 105. | McAfee PC, DeVine JG, Chaput CD, Prybis BG, Fedder IL, Cunningham BW, Farrell DJ, Hess SJ, Vigna FE. The indications for interbody fusion cages in the treatment of spondylolisthesis: analysis of 120 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30:S60-S65. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 106. | Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B. Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31:442-449. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 171] [Cited by in RCA: 150] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 107. | Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, Labelle H, Weidenbaum M. Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis in the presence of L5-s1 isthmic lysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31:2484-2490. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 157] [Cited by in RCA: 154] [Article Influence: 8.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 108. | Cummins J, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Hanscom B, Abdu WA, Birkmeyer NJ, Herkowitz H, Weinstein J. Descriptive epidemiology and prior healthcare utilization of patients in the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial's (SPORT) three observational cohorts: disc herniation, spinal stenosis, and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31:806-814. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 112] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 109. | Lauber S, Schulte TL, Liljenqvist U, Halm H, Hackenberg L. Clinical and radiologic 2-4-year results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31:1693-1698. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 110. | Martin CR, Gruszczynski AT, Braunsfurth HA, Fallatah SM, O'Neil J, Wai EK. The surgical management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32:1791-1798. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 180] [Cited by in RCA: 167] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 111. | Jacobsen S, Sonne-Holm S, Rovsing H, Monrad H, Gebuhr P. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: an epidemiological perspective: the Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32:120-125. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 181] [Cited by in RCA: 204] [Article Influence: 11.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 112. | Chaput C, Padon D, Rush J, Lenehan E, Rahm M. The significance of increased fluid signal on magnetic resonance imaging in lumbar facets in relationship to degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32:1883-1887. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 115] [Cited by in RCA: 119] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 113. | Schaeren S, Broger I, Jeanneret B. Minimum four-year follow-up of spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and dynamic stabilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33:E636-E642. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 114. | Kalanithi PS, Patil CG, Boakye M. National complication rates and disposition after posterior lumbar fusion for acquired spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34:1963-1969. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 137] [Cited by in RCA: 141] [Article Influence: 8.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 115. | Abdu WA, Lurie JD, Spratt KF, Tosteson AN, Zhao W, Tosteson TD, Herkowitz H, Longely M, Boden SD, Emery S, Weinstein JN. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: does fusion method influence outcome? Four-year results of the spine patient outcomes research trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34:2351-2360. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 125] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 116. | Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M, Ohta H, Misawa H. Mini-open versus conventional open posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison of paraspinal muscle damage and slip reduction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34:1923-1928. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 110] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 117. | Tosteson AN, Tosteson TD, Lurie JD, Abdu W, Herkowitz H, Andersson G, Albert T, Bridwell K, Zhao W, Grove MR, Weinstein MC, Weinstein JN. Comparative effectiveness evidence from the spine patient outcomes research trial: surgical versus nonoperative care for spinal stenosis, degenerative spondylolisthesis, and intervertebral disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36:2061-2068. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 149] [Cited by in RCA: 155] [Article Influence: 11.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 118. | Rihn JA, Radcliff K, Hilibrand AS, Anderson DT, Zhao W, Lurie J, Vaccaro AR, Freedman MK, Albert TJ, Weinstein JN. Does obesity affect outcomes of treatment for lumbar stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis? Analysis of the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37:1933-1946. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 124] [Article Influence: 9.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 119. | Parker SL, Adogwa O, Bydon A, Cheng J, McGirt MJ. Cost-effectiveness of minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis associated low-back and leg pain over two years. World Neurosurg. 2012;78:178-184. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 120. | Parker SL, Mendenhall SK, Shau DN, Zuckerman SL, Godil SS, Cheng JS, McGirt MJ. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparative effectiveness and cost-utility analysis. World Neurosurg. 2014;82:230-238. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 140] [Cited by in RCA: 177] [Article Influence: 14.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |