Published online Mar 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i8.1406
Peer-review started: November 27, 2023
First decision: January 15, 2024
Revised: January 23, 2024
Accepted: February 27, 2024
Article in press: February 27, 2024
Published online: March 16, 2024
Processing time: 105 Days and 14.9 Hours
Ischemic stroke (IS) is a widely recognized disease characterized by high preva
To explore the impact of comprehensive nursing care on the quality of life and swallowing function in individuals diagnosed with IS.
This study comprised 172 patients with IS admitted to our hospital between February 2018 to March 2021. The participants were divided into two groups, namely the control group (n = 80) receiving routine care and the research group (n = 92) receiving comprehensive care. Various assessment scales, including the standard swallowing function assessment scale (SSA), National Institutes of Health Stroke scale (NIHSS), European stroke scale (ESS), self-rating anxiety scale (SAS), self-rating depression scale (SDS), Barthel index (BI), and the motor func
After the nursing intervention, the research group exhibited significantly improved SSA and NIHSS scores com
Comprehensive nursing effectively improved swallowing function, quality of life, and patient satisfaction, high
Core Tip: In this study, the effect of a comprehensive nursing model on ischemic stroke (IS) patients and their swallowing function were analyzed. This model could provide more choices for nursing plans for patients suffering from IS.
- Citation: Hu HF, Sang YF, Xiao YQ. Effect of comprehensive nursing on the quality of life and swallowing function in individuals diagnosed with ischemic stroke. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(8): 1406-1415
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i8/1406.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i8.1406
Ischemic stroke (IS) is a widely recognized disease characterized by high prevalence, mortality, morbidity, disability, and recurrence rates. It ranks prominently in terms of mortality, constituting 60%-80% of stroke cases[1]. In 2019, there were 12.22 million new cases of stroke globally, with 7.63 million being classified as IS, 3.41 million as intracerebral he
Despite clinical treatment, patients with stroke often experience lingering sequelae such as speech disorders, impaired limb movement, and sensory disorders. Swallowing dysfunction, attributed to true or pseudobulbar palsy, is a prevalent complication of IS, significantly affecting patient quality of life[4].
Current clinical nursing measures predominantly focus on treatment cooperation and monitoring the patient’s reco
Comprehensive nursing intervention represents a relatively comprehensive nursing model grounded in patient-centered care, encompassing diverse aspects of patient well-being, including both physiological and psychological di
This study aimed to analyze the efficacy of the comprehensive nursing model in patients with IS by evaluating its influence on their swallowing function. The findings hold the potential to broaden the spectrum of available nursing plans for individuals with IS.
A total of 172 patients with IS who were treated at Hengyang Maternal and Child Health Hospital between February 2020 and March 2023 were selected for this study. Among them, 100 were males and 72 were females, with an average age of 63.71 ± 4.25 years. The duration of illness ranged from 10-28 d. Eighty patients, receiving care under the conventional nursing model, constituted the control group, while the research group comprised 92 patients who received comprehensive nursing based on the care provided in the control group. The inclusion criteria encompassed patients meeting the diagnostic criteria for IS and aged between 55 years and 75 years. The exclusion criteria involved patients lacking self-care ability, those with malignant tumors, severe liver and kidney dysfunction, and severe coagulation dysfunction, and those unwilling to cooperate with the study. Ethical approval was received by the Ethics Committee of the Hengyang Maternal and Child Health Hospital, adhering to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for this study was obtained through signed informed consent forms from patients and their families.
All patients received conventional treatment for IS. Patients in the control group underwent conventional nursing care, employing specific methods as outlined below: (1) Provision of routine psychological intervention and health education for patients and their families to alleviate anxiety; (2) Close monitoring of the patient’s blood pressure, consciousness, limb function, muscle strength, dietary habits, urine and stool output, electrolyte levels, complete blood count, and coa
Patients in the research group underwent treatment with a comprehensive nursing model based on the control group, involving specific measures detailed as follows: (1) Psychological care. First, a positive nurse-patient relationship was established, gaining the trust of patients to comprehend their condition and understand individual characteristics, living conditions, and social background. Subsequently, targeted psychological counselling and comfort were provided to address individual situations, fostering confidence in overcoming the disease and ensuring close collaboration with nursing guidance. Active communication, care, and respect were maintained, encouraging patients to express their feelings. Their thoughts were attentively listened to, avoiding any words or actions that might provoke distress, and endeavored to fulfil their normal needs. Patients exhibiting positive treatment effects were encouraged to share their experiences to promote optimism and alleviate depression and fear; (2) Early health education intervention. Patients received explanations about the primary causes, progression, and outcomes of stroke. Additionally, details about the treatment plan, functions, adverse reactions, and precautions associated with the prescribed medications were provided. The importance of patient cooperation, the necessity of rehabilitation training, and its impact on future life were also communicated during this early health education intervention; (3) Directed patients to engage in early physical exercise rehabilitation training, incorporating ipsilateral stimulation. All nursing tasks, including assistance with washing, eating, and measuring vital signs, were executed on the ipsilateral side. This involved communication, handholding, and guiding the patient’s head towards the affected side, while avoiding intravenous infusion in the affected limb. Emphasis was placed on good limb placement and regular position changes every 2-3 h, particularly focusing on the affected side. Special activities, such as supine position maintenance, bed exercise training, and limited grasping movements were advised to a limited extent. Grasping actions involved fixing the affected wrist joint in an extended position and instructing patients to make fists simultaneously. Wrist extension exercises were performed by maintaining the wrist in an extended position, discouraging sagging. Joint finger extension exercises used four fingers to hold the affected hand’s thenar, abducting the thumb, and supinating the forearm to stretch spastic spasm fingers automatically. Other exercises included supination exercises, finger-to-finger exercises, bridge exercises, passive joint exercises, and sit-up training. Sit-up training encouraged patients to transition from a side-lying position to a sitting position using the healthy leg to push the affected one, achieving a 90° flexion in the hip joint, with the affected hand placed on an adjustable desk instead of hanging to the side; and (4) Swallowing function training primarily comprised basic exercises such as empty swallowing. Muscle training for the lips, soft palate, tongue, and larynx involved activities such as abdominal breathing, combined with stimuli such as cold objects, puffing, and finger sucking. Additionally, feeding function training and pronunciation practice, starting from syllables such as “ah” to small words and progressing to short sentences, were implemented. This training aimed to coordinate exhalation and vocal cord vibration, combined with verbal guidance and other training. Throughout the process, careful attention was given to ensure that the patients experienced no fatigue or pain, and progress was gradual. After 4 wk of nursing, both groups underwent evaluations based on the indicators.
The standard swallowing function assessment scale[10] was used to assess the improvement in patient swallowing function. The neurological deficit of patients before and after nursing was evaluated using the National Institutes of Health Stroke scale (NIHSS)[11], with a total score of 42 (higher scores indicating more severe neurological deficits). Clinical outcomes were assessed using the European stroke scale (ESS)[12], with a full score of 80 points (higher scores indicated better physical condition). Patient anxiety and depression were gauged using the self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and self-rating depression scale (SDS), respectively[13]. Activities of daily living were scored using the Barthel index[14], with a total score of 100 points (scores categorized as ≥ 60, self-care; 41-60, required considerable assistance; < 40, needed extensive care; < 20, complete dependence). The motor function assessment scale by Janet H. Carr and Roberta B. Shepherd was used for motor function assessment, with a total score of 54 points (higher scores indicated better motor function)[15]. The occurrence of adverse reactions, including reflux, aspiration, fever, and pulmonary infection, was compared between the two groups during the nursing period. The generic quality of life inventory-74[16] was used to evaluate the life quality of patients before and after the intervention across four scoring dimensions, namely physical, social, psychological, and role, with a full score of 100 points per dimension (higher scores indicating better quality of life). Patients’ rehabilitation compliance was assessed using a self-made questionnaire, with a full score of 100 points. Scores below 60 were considered “non-compliance,” scores of 60-79 were considered “partial compliance,” and scores ≥ 80 were considered “complete compliance.” The rehabilitation compliance rate was calculated as the sum of the complete compliance and partial compliance rates. Nursing satisfaction was evaluated using the “nursing satisfaction ques
In this study, statistical analysis of the collected data was conducted using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 26.0 software package. GraphPad 6 software was employed for the creation of necessary figures. The independent sample t-test was used for between-group comparisons, while the paired t-test was used for before-and-after nursing comparisons. The χ2 test was used for data counting. Measurement data were presented as the mean ± SD, and statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
The two groups were comparable, showing no significant differences in sex, age, body mass index, and disease type (P > 0.05; Table 1).
| Factors | Research group, n = 92 | Control group, n = 80 | χ2 value | P value |
| Sex | 0.023 | 0.880 | ||
| Male | 53 (57.61) | 47 (58.75) | ||
| Female | 39 (42.39) | 33 (41.25) | ||
| Age (yr) | 0.032 | 0.857 | ||
| ≥ 63 | 61 (66.30) | 52 (65.00) | ||
| < 63 | 31 (33.70) | 28 (35.00) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.001 | 0.977 | ||
| ≥ 23 | 55 (59.78) | 48 (60.00) | ||
| < 23 | 37 (40.22) | 32 (40.00) | ||
| Underlying disease | 0.028 | 0.956 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 25 (23.21) | 22 (20.37) | ||
| Hypertension | 31 (25.00) | 26 (27.78) | ||
| Hyperlipidemia | 36 (28.58) | 32 (27.78) | ||
| Smoking | 0.001 | 0.983 | ||
| ≥ 400 | 47 (51.09) | 41 (51.25) | ||
| < 400 | 45 (48.91) | 39 (48.75) | ||
| Education level | 0.069 | 0.793 | ||
| Middle school not completed | 57 (61.96) | 48 (60.00) | ||
| Middle school completed | 35 (38.04) | 32 (40.00) | ||
| Nutrition status | 0.011 | 0.915 | ||
| Good | 41 (44.57) | 35 (43.75) | ||
| Fair | 51 (55.43) | 45 (56.25) |
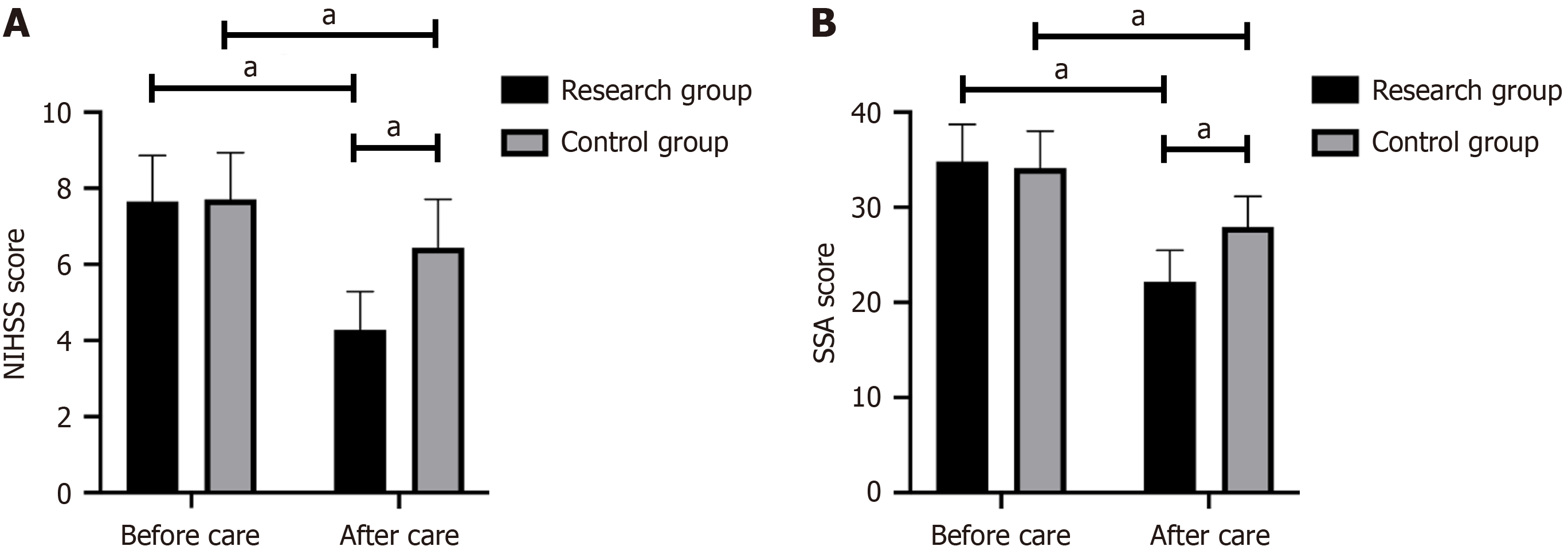
There was no significant difference observed in the NIHSS score and swallowing function between the two groups before nursing (P > 0.05). However, the NIHSS score and swallowing function score significantly improved in both groups after nursing, with the research group demonstrating a more obvious improvement (P < 0.05; Figure 1).
Minor differences were observed in ESS scores between the two groups before nursing (P > 0.05). After nursing, both groups exhibited a significant improvement in ESS scores (P < 0.05), with the research group achieving a higher score (P < 0.05; Table 2).
| Factor | Research group, n = 92 | Control group, n = 80 | t value | P value |
| Before nursing | 61.28 ± 5.82 | 61.32 ± 5.72 | 0.045 | 0.963 |
| After nursing | 78.19 ± 6.11 | 69.33 ± 5.92 | 9.624 | < 0.001 |
| t value | 9.22 | 8.75 | ||
| P value | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
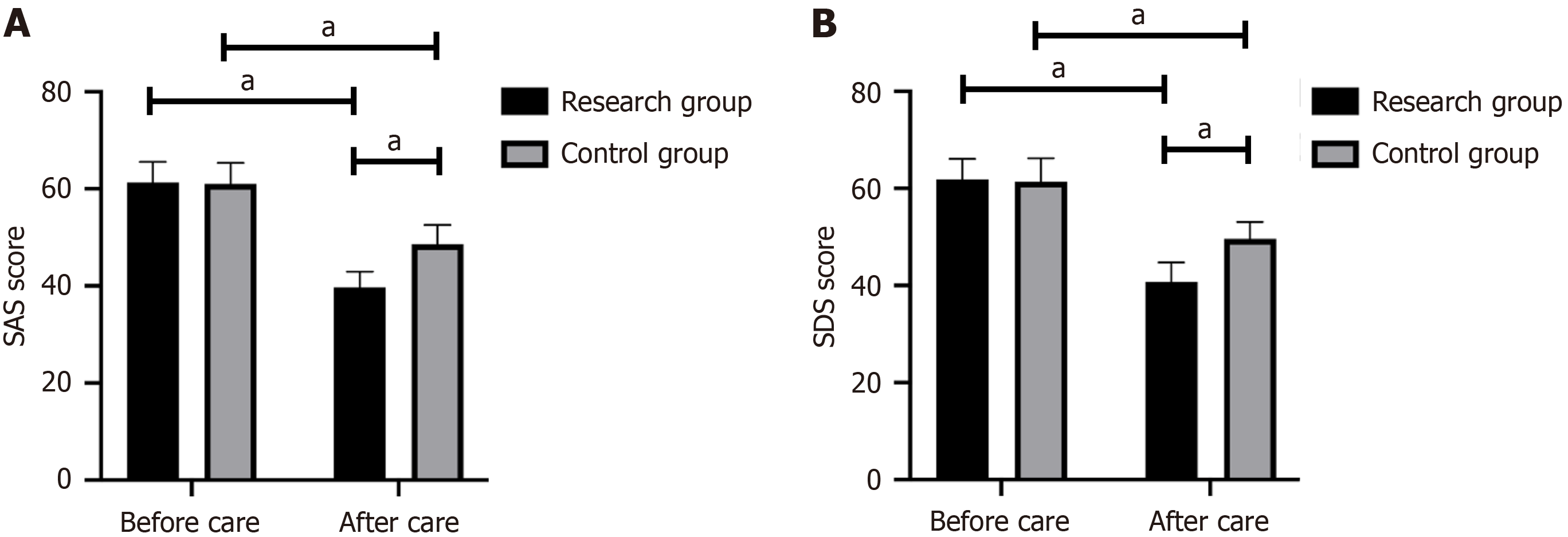
The SAS and SDS scores did not exhibit a significant difference between the two patient groups before nursing (P > 0.05). However, after nursing, the research group demonstrated significantly lower SAS and SDS scores compared to the control group (P < 0.05; Figure 2).
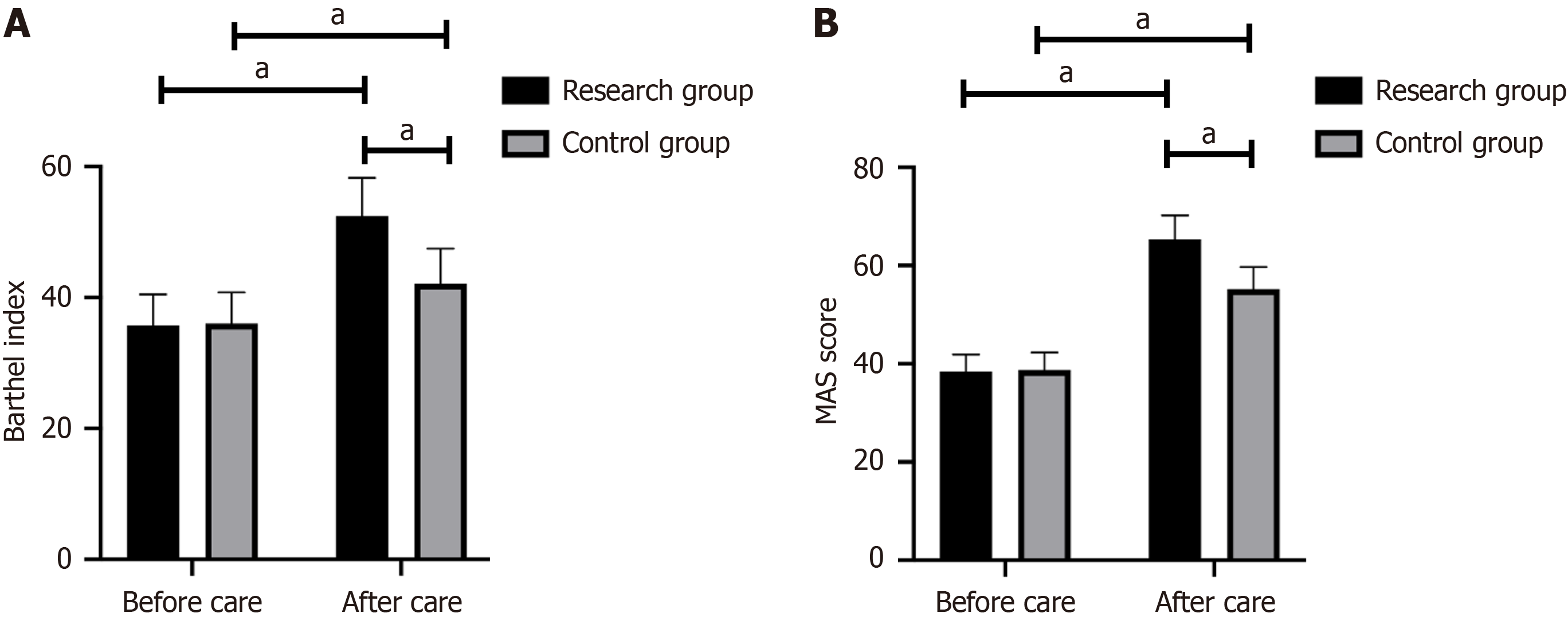
No significant difference was observed in daily living ability and motor function between the two groups before nursing
In the research group, 1 patient experienced reflux, 2 patients had a fever, and 1 patient had a pulmonary infection, resulting in an adverse reaction incidence of 4.35%. In contrast, the control group exhibited higher numbers, with 3 cases of reflux, 3 cases of aspiration, 4 cases of fever, and 3 cases of pulmonary infection, yielding an adverse reaction incidence of 16.25%. This indicated that patients in the research group were less likely to experience adverse reactions (P < 0.05; Table 3).
| Adverse reaction | Research group, n = 92 | Control group, n = 80 | χ2 value | P value |
| Reflux | 1 (1.09) | 3 (3.75) | ||
| Aspiration | 0 | 3 (3.75) | ||
| Fever | 2 (2.17) | 4 (5.00) | ||
| Lung infection | 1 (1.09) | 3 (3.75) | ||
| Adverse reaction rate | 4 (4.35) | 13 (16.25) | 6.806 | 0.009 |
Following nursing, the scores for role function, physical function, psychological function, and social function in the research group were 72.32 ± 2.54, 71.27 ± 2.64, 73.42 ± 2.65, and 72.55 ± 2.43, respectively. In contrast, the control group’s corresponding scores were 62.78 ± 2.42, 62.54 ± 2.33, 63.12 ± 2.98, and 61.73 ± 2.14. The research group exhibited a more obvious advantage in all indexes related to quality of life (P < 0.05; Table 4).
| Item | Research group, n = 92 | Control group, n = 80 | t value | P value |
| Role function | 72.32 ± 2.54 | 62.78 ± 2.42 | 19.01 | < 0.001 |
| Physical function | 71.27 ± 2.64 | 62.54 ± 2.33 | 17.26 | < 0.001 |
| Psychological function | 73.42 ± 2.65 | 63.12 ± 2.98 | 20.85 | < 0.001 |
| Social function | 72.55 ± 2.43 | 61.73 ± 2.14 | 24.74 | < 0.001 |
In the research group, there were 68 patients classified as completely compliant, 22 patients as partially compliant, and 2 patients as non-compliant, resulting in a rehabilitation compliance rate of 97.83%. Conversely, in the control group, the numbers were 32 patients, 30 patients, and 18 patients, respectively, leading to a rehabilitation compliance rate of 77.50%. The rehabilitation compliance rate in the research group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05; Table 5).
| Rehabilitation compliance | Research group, n = 92 | Control group, n = 80 | χ2 value | P value |
| Complete compliance | 68 (73.91) | 32 (40.00) | ||
| Partial compliance | 22 (23.91) | 30 (37.50) | ||
| Non-compliance | 2 (2.18) | 18 (22.50) | ||
| Rehabilitation compliance rate | 90 (97.83) | 62 (77.50) | 17.20 | < 0.001 |
In the research group, 72 patients expressed being very satisfied, 19 patients were satisfied, and 1 patient was dissatisfied with nursing care, resulting in a nursing satisfaction rate of 98.91%. In comparison, the numbers in the control group were 43 patients, 20 patients, and 17 patients, respectively, yielding a nursing satisfaction rate of 78.75%. Patients in the research group provided significantly more positive feedback than those in the control group (P < 0.05; Table 6).
| Nursing satisfaction | Research group, n = 92 | Control group, n = 80 | χ2 value | P value |
| Very satisfied | 72 (78.26) | 43 (53.75) | ||
| Satisfied | 19 (20.65) | 20 (25.00) | ||
| Dissatisfied | 1 (1.09) | 17 (21.25) | ||
| Nursing satisfaction rate | 53 (98.91) | 63 (78.75) | 18.57 | < 0.001 |
This study investigated the effect of comprehensive nursing care on the quality of life and swallowing function in patients with IS. The findings revealed that comprehensive nursing significantly enhanced the swallowing function, quality of life, and nursing satisfaction of patients. These results hold clinical significance and provide valuable insights for practical application.
Acute IS is characterized by a sudden onset and a heightened risk of disability, particularly in the elderly population. The current demographic shift towards an aging society in our country accentuates the severity of this issue, making acute IS a leading cause of mortality and disability among residents[17,18]. IS encompasses stroke resulting from ischemia and hypoxia as well as acute cerebral infarction caused by hemorrhage, carrying a substantial fatality rate and unfa
Frequently, patients face challenges in self-care related to dietary intake, compounded by a lack of comprehensive understanding among family members who might inadvertently employ incorrect feeding methods, leading to in
In this study, the comprehensive care model was employed for patients with IS. It was observed that in comparison to those receiving conventional care patients in the research group exhibited more significant recovery in both swallowing function and neurological deficit function. Within the framework of the comprehensive care model, targeted rehabilitation training guidance was individually tailored based on each patient’s dysfunction, facilitating enhanced recovery of their swallowing function[22]. Additionally, research[23] has indicated that improvements in swallowing function could help restore neurological function and improve the quality of life in patients with stroke.
Further comparisons were made between the ESS scores, daily living activities, and motor function of the patients in the two groups. The results revealed that although both groups demonstrated improvement in these functions after nursing, patients in the research group experienced more pronounced recovery. This suggests that the application of our comprehensive care model is more effective in improving clinical outcomes, daily living abilities, and motor function.
Beyond the inherent challenges posed by the disease itself, factors such as functional disability, diseased location, educational background, economic status, and living conditions can exacerbate patients’ negative emotions[24]. The comprehensive nursing model implemented a series of measures to address these negative emotions, including targeted psychological counselling and comfort tailored to individual circumstances. This approach aimed to help patients build confidence in overcoming their disease and foster close cooperation with nursing guidance. Notably, the observed improvements in the SAS and SDS scores for patients in the research group were more significant than those in the control group. Consistent with previous findings[25], our study suggest that the application of comprehensive care models in clinical settings effectively mitigates negative emotions in patients.
This study also underscored that after nursing interventions, the research group exhibited a significantly lower in
Additionally, a comparative analysis was conducted on rehabilitation compliance and nursing satisfaction between the two groups. The findings indicated significantly higher levels of rehabilitation compliance and nursing satisfaction among patients in the research group. This implies that the implementation of a comprehensive nursing model could improve nursing compliance in patients with IS through a series of psychological interventions, rehabilitation guidance, and symptomatic care. Consequently, this approach effectively contributes to the improvement of psychological and social functions, alleviation of stroke symptoms, enhancement of quality of life, and ultimately, elevated patient care satisfaction.
This study had several limitations. First, the small sample size introduced a potential element of chance into our findings, emphasizing the need for future multicenter and large-sample studies. Second, the absence of comparisons with other nursing models makes it somewhat premature to definitively conclude whether the comprehensive nursing model is the most suitable approach for patients with IS. Future research will incorporate a broader range of nursing models for a more comprehensive comparison. Additionally, considering the differences in pathophysiology, prognosis, and clinical features between patients with lacunar and non-lacunar infarcts, such as variations in age, hypertension, and length of hospital stay[26], it is imperative to investigate the effect of comprehensive nursing on the quality of life and swallowing function in patients with lacunar vs non-lacunar infarcts.
In conclusion, the implementation of comprehensive nursing for patients with IS was effective in enhancing swallowing function, alleviating negative emotions, facilitating patient recovery, and improving the overall quality of life. These positive outcomes underscore the potential for clinical application and merit widespread promotion. Future research endeavors should include multicenter and large-sample studies to comprehensively investigate the effect of various nursing models on patients with IS. Additionally, it is essential to explore the specific effects of comprehensive nursing on the quality of life and swallowing function in individuals with lacunar and non-lacunar infarcts.
Ischemic stroke (IS) is a widely recognized disease characterized by high prevalence, mortality, morbidity, disability, and recurrence rates. It ranks prominently in terms of mortality, constituting 60%-80% of stroke cases.
Although comprehensive nursing interventions have been shown to be effective in multiple aspects, there is still a significant gap in the research on their improvement of swallowing function in patients with IS.
This study aimed to analyze the efficacy of the comprehensive nursing model in patients with IS, evaluating its influence on their swallowing function. The findings hold the potential to broaden the spectrum of available nursing plans for individuals with IS.
The National Institutes of Health Stroke scale (NIHSS), European stroke scale (ESS), self-rating anxiety scale (SAS), self-rating depression scale (SDS), Barthel index (BI), and the motor func
After nursing intervention, the standard swallowing function assessment scale and NIHSS scores of the study group were significantly improved compared with those of the control group, and the SAS and SDS scores of the two groups were significantly lower than those before treatment. The ESS, BI and MAS scores of the study group were better than those of the control group, and the incidence of adverse reactions was lower than that of the control group. The quality of life, rehabilitation compliance, and nursing satisfaction of the study group were higher than those of the control group, and the differences were statistically significant.
Comprehensive nursing effectively improved the swallowing function of IS patients, relieved IS patients’ negative emotions, promoted the recovery of IS patients, and improved the life quality of IS patients.
Future studies will incorporate a wider range of care models for a more comprehensive comparison.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Nursing
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Arboix A, Spain S-Editor: Zhang H L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Xu ZH
| 1. | Henderson SJ, Weitz JI, Kim PY. Fibrinolysis: strategies to enhance the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16:1932-1940. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20:795-820. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4299] [Cited by in RCA: 3596] [Article Influence: 899.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Paul S, Candelario-Jalil E. Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp Neurol. 2021;335:113518. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 451] [Article Influence: 90.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Suda S, Nito C, Yokobori S, Sakamoto Y, Nakajima M, Sowa K, Obinata H, Sasaki K, Savitz SI, Kimura K. Recent Advances in Cell-Based Therapies for Ischemic Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Su XT, Wang L, Ma SM, Cao Y, Yang NN, Lin LL, Fisher M, Yang JW, Liu CZ. Mechanisms of Acupuncture in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Treating Ischemic Stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:7875396. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 20.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Nishida A, Ando S, Yamasaki S, Koike S, Ichihashi K, Miyakoshi Y, Maekawa S, Nakamura T, Natsubori T, Ichikawa E, Ishigami H, Sato K, Matsunaga A, Smith J, French P, Harima H, Kishi Y, Fujita I, Kasai K, Okazaki Y. A randomized controlled trial of comprehensive early intervention care in patients with first-episode psychosis in Japan: 1.5-year outcomes from the J-CAP study. J Psychiatr Res. 2018;102:136-141. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Elgezawi M, Hassan K, Alagl A, Al-Thobity AM, Al-Mutairi B, Al-Houtan T, Sadaf S. Complexity of comprehensive care treatments in undergraduate dental programs: The benefits of observing and assisting experienced faculty members. Saudi Dent J. 2017;29:161-166. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Goldberg DG, Gimm G, Burla SR, Nichols LM. Care Experiences of Patients with Multiple Chronic Conditions in a Payer-Based Patient-Centered Medical Home. Popul Health Manag. 2020;23:305-312. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Shyu YI, Liang J, Tseng MY, Li HJ, Wu CC, Cheng HS, Yang CT, Chou SW, Chen CY. Comprehensive care improves health outcomes among elderly Taiwanese patients with hip fracture. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013;68:188-197. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Huang JJ, Cao Z, Zhang LL, Zhang LX. Study on the therapeutic effect of comprehensive rehabilitation training on patients with swallowing dysfunction after stroke. Zhongguo Weisheng Tongji Za Zhi. 2021;38:563-565, 571. |
| 11. | Aoki J, Suzuki K, Kanamaru T, Kutsuna A, Katano T, Takayama Y, Nishi Y, Takeshi Y, Nakagami T, Numao S, Abe A, Suda S, Nishiyama Y, Kimura K. Association between initial NIHSS score and recanalization rate after endovascular thrombectomy. J Neurol Sci. 2019;403:127-132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Shroff G. Comparison of Nutech Functional Score with European Stroke Scale for Patients with Cerebrovascular Accident Treated with Human Embryonic Stem Cells: NFS for CVA Patients Treated with hESCs. J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2017;9:35-43. [PubMed] |
| 13. | Han J, Nian H, Zheng ZY, Zhao MM, Xu D, Wang C. Effects of health education intervention on negative emotion and quality of life of patients with laryngeal cancer after postoperative radiotherapy. Cancer Radiother. 2018;22:1-8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Liu F, Tsang RC, Zhou J, Zhou M, Zha F, Long J, Wang Y. Relationship of Barthel Index and its Short Form with the Modified Rankin Scale in acute stroke patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29:105033. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 10.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Madhoun HY, Tan B, Feng Y, Zhou Y, Zhou C, Yu L. Task-based mirror therapy enhances the upper limb motor function in subacute stroke patients: a randomized control trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;56:265-271. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Wang Z, Qu H, Zhong J, Han Y, Wan C, Wang H, Yang H, Lu S, Diao K, Zhang N, Ma H. Restoration of psychosocial functioning in remitted major depressive disorder patients: A 1-year longitudinal study. Compr Psychiatry. 2020;102:152204. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Tucker N, Stoffel JM, Hayes L, Jones GM. Blood Pressure Management Following Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Primary Literature. Crit Care Nurs Q. 2020;43:109-121. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Kuo YW, Huang YC, Lee M, Lee TH, Lee JD. Risk stratification model for post-stroke pneumonia in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19:513-520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Amatangelo MP. Cryptogenic Stroke: Anatomy of the Stroke Work-Up. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2020;32:37-50. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Leite KKA, Sassi FC, Medeiros GC, Comerlatti LR, Andrade CRF. Clinical swallowing prognostic indicators in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2019;77:501-508. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Amatangelo MP, Thomas SB. Priority Nursing Interventions Caring for the Stroke Patient. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2020;32:67-84. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Molnar T, Csecsei P. Prevention of Non-Cardiogenic Ischemic Stroke: Towards Personalized Stroke Care. In: Dehkharghani S. Stroke [Internet]. Brisbane (AU): Exon Publications; 2021 Jun 18. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Kusumaningsih W, Lestari NI, Harris S, Tamin S, Werdhani RA. The effectivity of pharyngeal strengthening exercise, hyolaryngeal complex range of motion exercise, and swallowing practice in swallowing function of ischemic stroke patients with neurogenic dysphagia. J Exerc Rehabil. 2019;15:769-774. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Lin RC, Chiang SL, Heitkemper MM, Weng SM, Lin CF, Yang FC, Lin CH. Effectiveness of Early Rehabilitation Combined With Virtual Reality Training on Muscle Strength, Mood State, and Functional Status in Patients With Acute Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2020;17:158-167. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Liu S, Zhou L, An L. Implementation of comprehensive rehabilitation therapy in postoperative care of patients with cholangiocarcinoma and its impact on patients' quality of life. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17:2703-2707. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Arboix A, Massons J, García-Eroles L, Targa C, Comes E, Parra O, Oliveres M. Nineteen-year trends in risk factors, clinical characteristics and prognosis in lacunar infarcts. Neuroepidemiology. 2010;35:231-236. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |