Published online Mar 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1320
Peer-review started: November 1, 2023
First decision: December 31, 2023
Revised: January 8, 2024
Accepted: February 5, 2024
Article in press: February 5, 2024
Published online: March 6, 2024
Processing time: 120 Days and 16 Hours
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is a common osteoarticular deformity in pediatric orthopedics. A patient with bilateral DDH was diagnosed and treated using our improved technique "(powerful overturning acetabuloplasty)" com
A 4-year-old girl who was diagnosed with bilateral DDH could not stand normally, and sought surgical treatment to solve the problem of double hip extension and standing. As this child had high dislocation of the hip joint and the acetabular index was high, we changed the traditional acetabuloplasty to "powerful turnover acetabuloplasty" combined with femoral rotation shortening osteotomy. During the short-term postoperative follow-up (1, 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15 months), the child had no discomfort in her lower limbs. After the braces and internal fixation plates were removed, formal rehabilitation training was actively carried out.
Our "powerful overturning acetabuloplasty" combined with femoral rotational shortening osteotomy is feasible in the treatment of DDH in children. This technology may be widely used in the clinic.
Core Tip: Developmental dysplasia of the hip is a common disease in children, which may be related to genetic, environmental, and mechanical factors. Because of the particularities of this case, a special surgical method was adopted. On the basis of traditional surgery, we made slight improvements to obtain a better curative effect.
- Citation: Yu XX, Chen JY, Zhan HS, Liu MD, Li YF, Jia YY. Treatment of bilateral developmental dysplasia of the hip joint with an improved technique: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(7): 1320-1325
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i7/1320.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1320
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is a congenital acetabular dysplasia, which is related to genetic, environmental, and mechanical factors[1]. The acetabular morphology of patients diagnosed with DDH is mainly characterized by a shallow and flat acetabular fossa, head-side deviation of the rotation center of the hip joint, massive proliferation of osteophytes, and dysplasia of the anterior and posterior walls of the acetabulum[2]. Satisfactory results can be obtained by conservative treatment in the early stage of the disease[3]. However, due to the delay in diagnosis and treatment, some children miss the best treatment opportunity and often require surgery[4].
On the basis of traditional acetabular capping, we improved this method using "powerful overturning acetabuloplasty", and combined this technique with a femoral rotation shortening osteotomy to treat a 4-year-old child. The function of both lower limbs recovered well after surgery, and no complications were observed during follow-up.
A four-year-old girl attended hospital because her bilateral hip joints could not be straightened for 4 years.
The patient's family reported that the child had been moving similar to a frog, and could not stand or walk. After being diagnosed with DDH, no treatment was given prior to the current surgery.
The patient had no other diseases except DDH.
The mother of the child had DDH. Other family members were healthy.
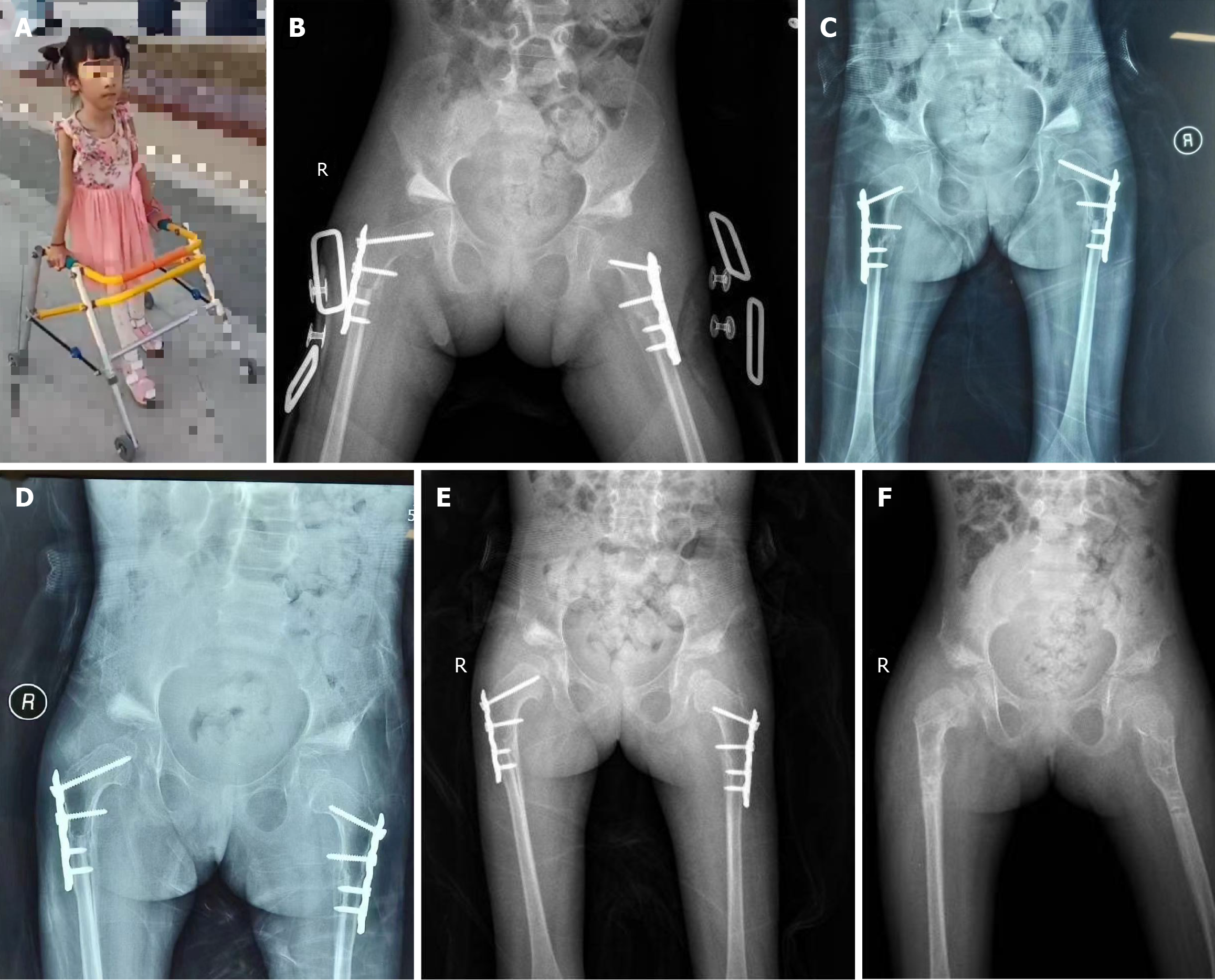
The child moved by squatting (Figure 1A). When the child laid flat, her lower limbs could not be straightened, and her knees were bent by approximately 20. Both lower limbs were of equal length. Bone eminence was seen on both hips, abduction of both lower limbs was limited, and Aills sign was not obvious. There was no obvious tenderness or tapping pain in her hips.
Routine blood tests, biochemical examinations, and routine urine and stool tests were all within the normal ranges.
Bilateral acetabular development was shallow, and bilateral femoral heads were dislocated outward and upward (acetabular index: left side: 50.81°; right side: 46.03°) (Figure 1B). The epiphysis of the bilateral femur and femoral head were well developed. Crowe classification was type IV (bilateral). On the right side, the femoral head displacement distance/pelvic height ratio was 21.9% (> 20%) and the femoral head displacement distance/femoral head height ratio was 143% (> 100%). On the left side, the femoral head displacement distance/pelvic height ratio was 22.1% (> 20%) and the femoral head displacement distance/femoral head height ratio was 166% (> 100%) (Figure 1C).
The child was diagnosed with bilateral DDH.
A Smith-Peterson incision was performed, the sartorius muscle, tensor fascia lata muscle, and rectus femoris were completely released, and the straight head, inverted head, gluteus medius muscle, and gluteus minimus of the rectus femoris, as well as the iliopsoas muscle which pressed on the front side of the primary acetabulum entrance, were cut. An incision in the hip joint capsule and thorough removal of the filling tissue in the acetabulum were performed. The proximal femur was exposed, the anteversion angle was measured with two Kirschner wires, and an osteotomy under the femur trochanter was carried out. Moderate internal rotation of the distal osteotomy segment horizontal with the patella on this side was performed, and the osteotomy ends were well butted. The broken end of the osteotomy was fixed using a four-hole steel plate, and then the Kirschner wire pulled out. Traction, abduction, and internal rotation of the affected hip were conducted, the hip joint was reset, and the anteversion angle was adjusted to approximately 10 degrees. At about 1 cm from the upper edge of the true acetabulum, a downward arc osteotomy was performed with an arc osteotome in the direction of the acetabulum top. During the osteotomy, it should be noted that the osteotome should not penetrate through the ilium inner plate and acetabular cartilage. The length of the bone flap determined the length of the osteotomy according to the size of the acetabulum, and the bone flap was turned down at an appropriate angle. According to the preoperative acetabular index, it is generally turned down 30°-40°. A triangular bone block was implanted in the osteotomy gap, and was then firmly hammered in place. The iliac bone, allograft bone support, and bone flap were fixed to the upper edge of the acetabulum using the wedging force of the implanted bone block. After the operation, the patient was fitted with a double hip abduction brace. Six weeks after the operation, the patient was instructed to exercise the hip joint in bed, and was able to get out of bed approximately 3 months after the operation, and the internal fixation plate was removed 8 months after the operation.
Our improved "powerful overturning acetabuloplasty" strengthened the coverage of the acetabulum on the femoral head. For overturning roof-building, the drilling position should not be too low, and it should be 1-1.5 cm away from the true acetabular margin and linear in side view, and should be gradually deepened along the true acetabular roof to strengthen the contact area of allogenic bone pieces. Instead of adding a piece of flat bone or a piece of broken bone into the gap, a piece of triangular bone of an appropriate length and about 30 degrees can be placed vertically, and tightly inserted. This technique is called "powerful overturning acetabuloplasty" (Figure 2).
After removing the brace and osteotomy healing, the patient could walk normally with the help of a walker (Figure 3A). One year later, the internal fixation steel plate was removed. During the follow-up period, no abnormalities were observed, such as asymmetric length of the lower limbs, pain, and limping (Figure 3B-F).
The tissues around the hip joint of DDH patients are abnormal during development, including the acetabulum, femur, soft tissue, blood vessels, and nerves[5]. Due to the lack of effective stimulation of the femoral head, the acetabular fossa is small and shallow, and the anterior and posterior walls of the acetabulum are underdeveloped. In the case of severe dislocation, the false acetabulum is located above the real acetabulum, which results in difficulties in identification of the acetabulum. The upward movement of the rotation center of the hip joint, dysplasia of the anterior and posterior walls of the acetabulum, proliferation of osteophytes, and the appearance of a false acetabulum make it more difficult for the surgeon to restore the position of the femoral head and acetabulum[6].
The early stage of the disease can be treated with braces, such as the Tubingen splint and Pavlik sling, with satisfactory treatment outcomes[7]. In the later stage, it is necessary to reconstruct the hip joint by surgery. The purpose of DDH open reduction is to restore the concentric structure of the acetabulum and femoral head. If severe malposition requires osteotomy, such as Salter osteotomy[8], Pemberton osteotomy[9], Chiari osteotomy[10], acetabuloplasty[11], etc., combined femoral osteotomy is often needed. The purpose of combined surgery is to reduce the pressure between the femoral head and acetabulum, restore the anteversion angle of the femoral neck and neck shaft angle, balance the tension of soft tissue, and correct the force line of the lower limbs[12].
The 4-year-old child in this report had DDH from birth, but her condition worsened as she was not seen by a doctor. When she attended our hospital, we evaluated the imaging and clinical characteristics, and finally chose treatment by the "powerful turnover acetabuloplasty". As this patient had high dislocation of the hip joint and a high acetabular index, we adopted acetabular topping combined with femoral rotational shortening osteotomy. If the acetabular index is to be reduced, it is necessary to use a bone chisel above the outer edge of the acetabulum, and then turn down the original acetabulum, which is the traditional acetabular ceiling surgery, described by Gill[13], Dickson[14], Wiberg[15], and so on.
In the traditional acetabular ceiling operation, the original acetabulum is turned down after the corresponding bone is chiseled, and a flat half-layer iliac bone plate is added to the upper space (such as in the Gill operation and Dickson operation) or the broken bone pieces are filled (such as in the Wiberg operation). If the roof is built according to this method, not only is the acetabular turnover angle insufficient, but also the supporting force of flat bone fragments or broken bones is weak, which cannot achieve or maintain the goal of fully reducing the pulp and socket index, and is prone to growth obstacles and other risks[16].
"Powerful overturning acetabuloplasty" still has the advantages of traditional capping, and has good tolerance and coverage for the femoral head after reduction. Its flip angle is more random and can be adapted for a wider range of ages. Compared with other pelvic osteotomies, it is less invasive and results in less bleeding. After surgery, there is no need to use Kirschner wires or screws for internal fixation, and other metal implants are unnecessary, thus avoiding increased economic burden on patients' families due to needle withdrawal. After the improved operation, the stress is transferred to the iliac bone through the vertical bone block instead of stress on the top alone.
However, during the process of acetabulum turnover and shaping, it is easy to damage the blood supply around the femoral head, which can increase the risk of avascular necrosis and dislocation of the femoral head[17,18]. During this operation, peripheral muscles and nerves can also be damaged[19]. Postoperative brace fixation is required, and contracture around the hip joint can occur. If this is not corrected in time, movement of the hip joint may be limited[20]. Although iliac osteotomy is avoided by using an allogenic triangular bone block, problems such as roof breaking and allogenic bone block absorption easily occur due to the improper quality and placement of the bone block, which requires the surgeon to have excellent skills and patients to undergo long-term follow-up.
It is feasible to treat pediatric DDH by simultaneous open reduction and "powerful overturning acetabuloplasty" combined with femoral rotational shortening osteotomy without complications. As the child in this report experienced only short-term follow-up, more cases and long-term follow-up are required to provide sufficient evidence on this improved technique.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Saracco M, Italy S-Editor: Qu XL L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Zheng XM
| 1. | Wu H, Wang Y, Tong L, Yan H, Sun Z. The Global Research Trends and Hotspots on Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study. Front Surg. 2021;8:671403. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Zhang S, Doudoulakis KJ, Khurwal A, Sarraf KM. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2020;81:1-8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Ali M, Malviya A. Complications and outcome after periacetabular osteotomy - influence of surgical approach. Hip Int. 2020;30:4-15. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Irie T, Takahashi D, Asano T, Arai R, Konno T, Onodera T, Kondo E, Iwasaki N. Comparison of femoral head translation following eccentric rotational acetabular osteotomy and rotational acetabular osteotomy. Hip Int. 2017;27:49-54. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Tippabhatla A, Torres-Izquierdo B, Cummings JL, Rosenfeld S, Johnson M, Goldstein R, Georgopoulos G, Stephenson L, Hosseinzadeh P. Fate of acetabular dysplasia after closed and open reduction of hips in children with developmental hip dislocation. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2023;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Bakarman K, Alsiddiky AM, Zamzam M, Alzain KO, Alhuzaimi FS, Rafiq Z. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH): Etiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Cureus. 2023;15:e43207. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Nair A, Yatsonsky D, Liu J. Comparison of outcomes of different Graf grades of developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants treated with Tubingen splint versus Pavlik harness - A systematic review. J Orthop. 2024;49:68-74. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Balioğlu MB, Öner A, Aykut ÜS, Kaygusuz MA. Mid term results of Pemberton pericapsular osteotomy. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49:418-424. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Wada A, Fujii T, Takamura K, Yanagida H, Taketa M, Nakamura T. Pemberton osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip in older children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003;23:508-513. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Hosny GA, Fabry G. Chiari osteotomy in children and young adults. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2001;10:37-42. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Trevor D, Johns DL, Fixsen JA. Acetabuloplasty in the treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975;57:167-174. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Greber EM, Pelt CE, Gililland JM, Anderson MB, Erickson JA, Peters CL. Challenges in Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Setting of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32:S38-S44. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 100] [Cited by in RCA: 144] [Article Influence: 18.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | GILL AB. The end results of early treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip, with an inquiry into the factors that determine the results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1948;30A:442-453. [PubMed] |
| 14. | Dickson FD. The shelf operation in the treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg. 1935;17:43-47. |
| 15. | Wiberg G. Shelf operation in congenital dysplasia of the acetabulum and in subluxation and dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953;35-A:65-80. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Weber M, Wirtz D, Jaeschke C, Niethard FU. [Growth disorders of the acetabular roof after acetabuloplasty in congenital hip dysplasia]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1998;136:525-533. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Ellsworth BK, Lee JY, Sankar WN. Femoral Head Remodeling After Surgical Reduction of Developmental Hip Dislocations. J Pediatr Orthop. 2024;44:e211-e217. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Xiang D, Liu X, Xia Z. Letter to: risk factors for dislocation following total hip arthroplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2024;48:309-310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | AlGhufaily AA, Alshunaifi AI, AlHarbi JS. Femoral Nerve Palsy Post Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) via a Posterolateral Approach. Cureus. 2023;15:e50771. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Li Y, Liu H, Guo Y, Chen S, Canavese F, Liu Y, Li J, Xu H, Xia H; Chinese Multicenter Pediatric Orthopaedic Study Group (CMPOS). Factors influencing outcomes of pelvic osteotomy for residual acetabular dysplasia following closed reduction in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2023;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |