Published online Jan 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i2.354
Peer-review started: September 19, 2023
First decision: November 22, 2023
Revised: December 6, 2023
Accepted: December 25, 2023
Article in press: December 25, 2023
Published online: January 16, 2024
Processing time: 113 Days and 14.3 Hours
There are few cases of pulmonary granulomatous changes secondary to primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). No case of granulomatous lung disease secondary to PBC misdiagnosed as lung cancer had been reported.
A middle-aged woman presented with lung nodules and was misdiagnosed with lung cancer by positron emission tomography/computed tomography. She underwent left lobectomy, and the pathology of the nodules showed granulomatous inflammation, which was then treated with antibiotics. However, a new nodule appeared. Further investigation with lung biopsy and liver serology led to the diagnosis of PBC, and chest computed tomography indicated significant reduction in the pulmonary nodule by treatment with methylprednisolone and ursodeoxycholic acid.
Diagnosis of pulmonary nodules requires integrating various clinical data to avoid unnecessary pulmonary lobectomy.
Core Tip: Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) can present as granulomatous lung disease when the lungs are involved. A patient with pulmonary granulomatous disease secondary to PBC was misdiagnosed with lung cancer by positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT), leading to unnecessary lobectomy. The symptoms and imaging of pulmonary granulomatous disease secondary to PBC are nonspecific. It also appears as high fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on PET/CT scan. Diagnosis should not rely solely on PET/CT findings but should consider clinical data, lung aspiration biopsy, and immune-related disease indexes to avoid unnecessary physical and financial burden.
- Citation: Feng SL, Li JY, Dong CL. Primary biliary cholangitis presenting with granulomatous lung disease misdiagnosed as lung cancer: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(2): 354-360
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i2/354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i2.354
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC, formerly called primary biliary cirrhosis) is an immune-mediated and progressive intrahepatic cholestatic liver ailment of unknown etiology[1]. A variety of respiratory manifestations, including pulmonary granulomas, occur when the pulmonary system is affected[2]. Granulomatous lung diseases (GLDs) are heterogeneous, with multiple etiologies and nonspecific clinical and imaging manifestations. Differential diagnosis is challenging, and sometimes it is easy to misdiagnose granulomatous pulmonary disease as lung cancer. Therefore, positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) offers more assistance in diagnosis. PET provides detailed information regarding the metabolism and function of a pulmonary nodule, whereas CT accurately identifies the location of the pulmonary nodule. Simultaneously, pathophysiological changes and the morphological structure of a pulmonary nodule are visualized by PET/CT, resulting in complementary functional and anatomical image information, which is of value in defining the nature of lung occupancy. However, there is an inaccuracy in identifying specific benign pulmonary nodules owing to the limitations of their functional diagnostic characteristics[3]. Comprehensive analysis of clinical data and well-timed tissue biopsies can reduce misdiagnoses.
In this case, we report a patient with pulmonary granulomas secondary to PBC misdiagnosed as lung cancer by PET/CT who was effectively treated with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). We also reviewed the literature regarding pulmonary granulomas and pulmonary changes secondary to PBC. These documents help to explain the changes in pulmonary granuloma associated with PBC, which provides instructions and assistance to clinicians for diagnosis and treatment. Awareness of this identification can avoid disease progression and unnecessary physical injury.
A middle-aged woman presented to our outpatient clinic with a complaint of intermittent cough, a small amount of white foamy sputum with activity-related breathlessness for 5 mo, and the discovery of a new pulmonary nodule in the right lower lobe on chest CT 5 mo after pulmonary lobectomy.
Her symptoms started 5 mo before presentation, with intermittent cough and a small amount of white foamy sputum with activity-related breathlessness.
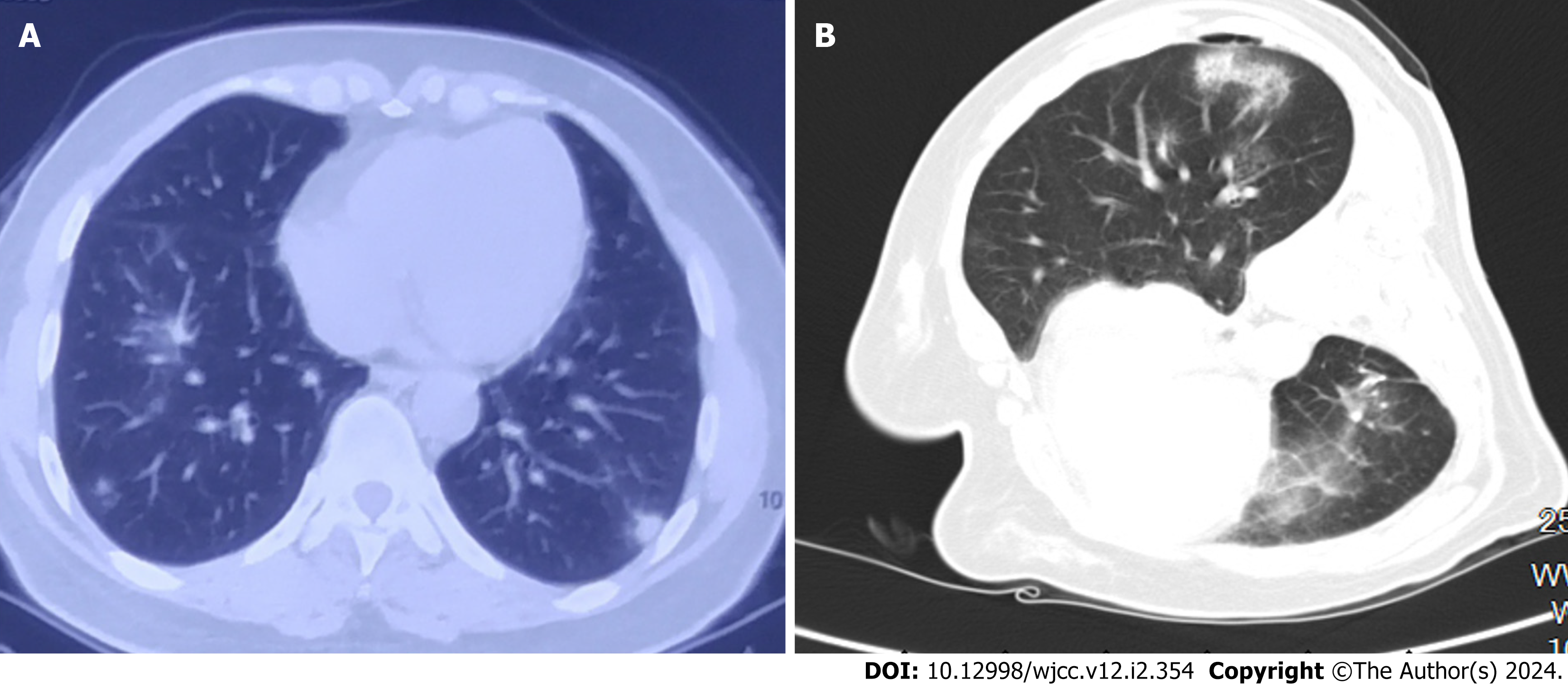
During a medical examination, two high-density pulmonary nodules were accidentally found by chest CT in the posterior basal segment of the left lower lobe in a middle-aged woman (Figure 1A). The pulmonary nodules displayed lobar and burr signs on chest CT and strong 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) ingestion (SUVmax = 2.5, 4.5) on PET/CT, which led to misdiagnosis of lung cancer. Left lower lobectomy was offered to the patient in the hospital because of growing concern about the possibility of lung cancer, although the tumor marker levels were within the normal range. Both operative frozen section and postoperative pathological examination revealed pulmonary granuloma nodules and active epithelial cell proliferation. Morphologically, the diagnosis could not be determined, and a further clinical investigation was recommended to guide the diagnosis and treatment. However, the patient neglected the recommendation because of the absence of significant symptoms.
The patient denied any family history of malignant tumors.
Physical examination was as follows: Body temperature, 36.5 °C; heart rate, 84 beats per min; respiratory rate, 16 breaths per min; and blood pressure, 126/81 mmHg. The skin and mucous membranes were free of yellow staining, rash, bleeding spots, liver palms, and spider nevus. The thorax was symmetrical, and the rib space was not widening or narrowed. Chest breathing was normal; respiratory movement was symmetrical; speech fibrillation was symmetrical bilaterally; both lungs were clear on percussion; voice conduction was normal; breath sounds in the left lower lung were diminished, and no obvious dry or wet rales were heard. There was no pleural friction sound.
Laboratory tests indicated an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (40 mm/h) and IgG (25.8 g/L) levels. Both alkaline phosphatase (322 U/L; normal, < 135 U/L) and -glutamyl transpeptidase (435 U/L; normal, < 45 U/L) exhibited marked elevation, while the tumor markers and tests of renal and thyroid function were normal. The outcome of T-SPOT [interferon (IFN)-γ release assay based on detecting IFN-γ secreted by T cells stimulated by specific Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens] was negative. Screening of the antinuclear antibody (ANA) profiles revealed moderate positivity (++) for anti-52-kDa antibodies and weak positivity for Sjögren’s syndrome A antigen (SS-A) antibodies, and indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) determined ANA titers to be 1:320. The serum tested for perinuclear anti-neutrophil cyto
Chest CT revealed a pulmonary nodule in the right lower lobe (Figure 1B).
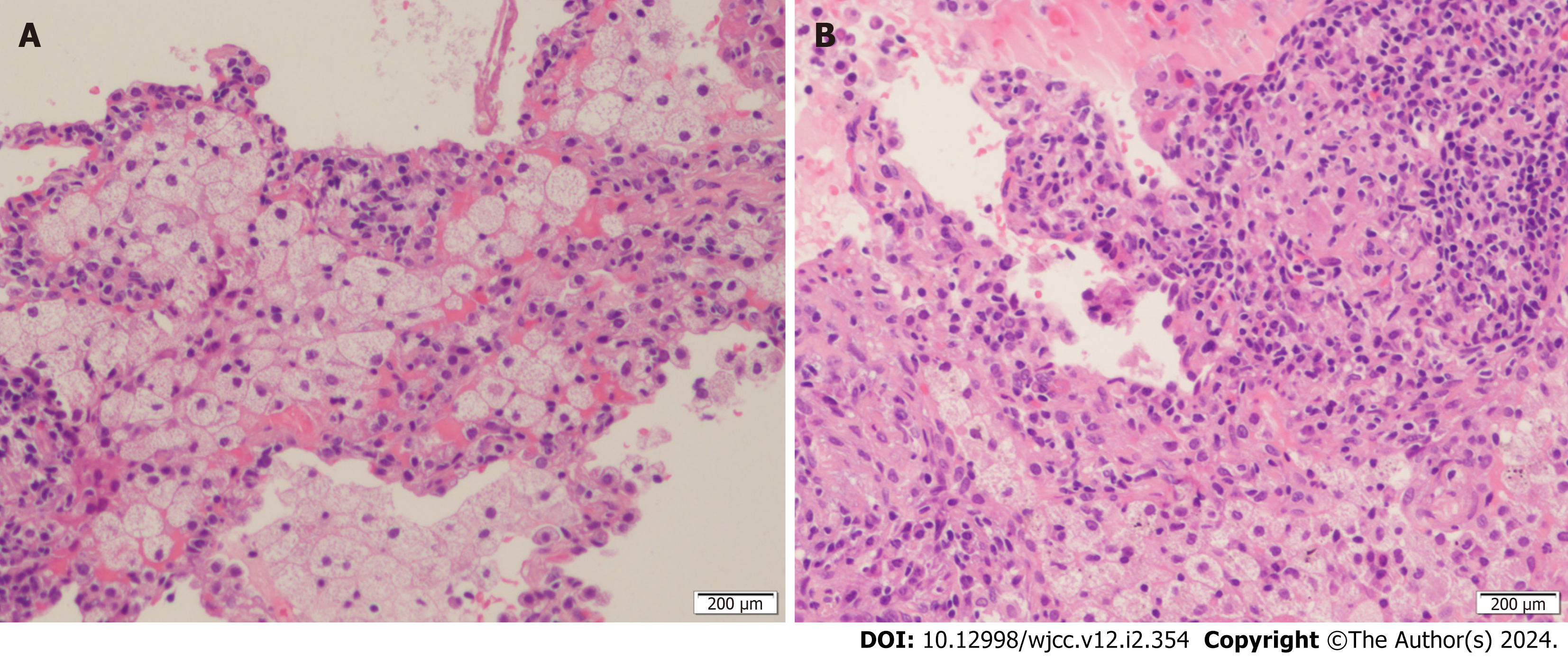
The patient showed poor outcomes after anti-infective therapy with piperacillin sodium and sulbactam sodium. CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of the pulmonary nodule was performed to clarify the diagnosis. The biopsy of a pulmonary nodule in the lower lobe of the right lung revealed granuloma formation (Figure 2A), fibrous hyperplasia in the pulmonary interstitium, and infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells and histiocytes (Figure 2B). Based on these clinical findings, tumors and infectious diseases were excluded. To exclude autoimmune liver disease, the patient was tested for autoantibodies against autoimmune liver diseases. The test revealed positivity (+++) for antibodies against GP210 and SP100 and weak positivity for autoantibodies to soluble liver antigens, while the antimitochondrial antibody (AMA) was negative. An invasive liver biopsy was advised for the patient for further definitive diagnosis. Unfortunately, the patient refused.
According to the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), PBC was diagnosed considering the biochemical evidence of cholestasis and the presence of sp100 and gp210.
The patient was started on UDCA and methylprednisolone.
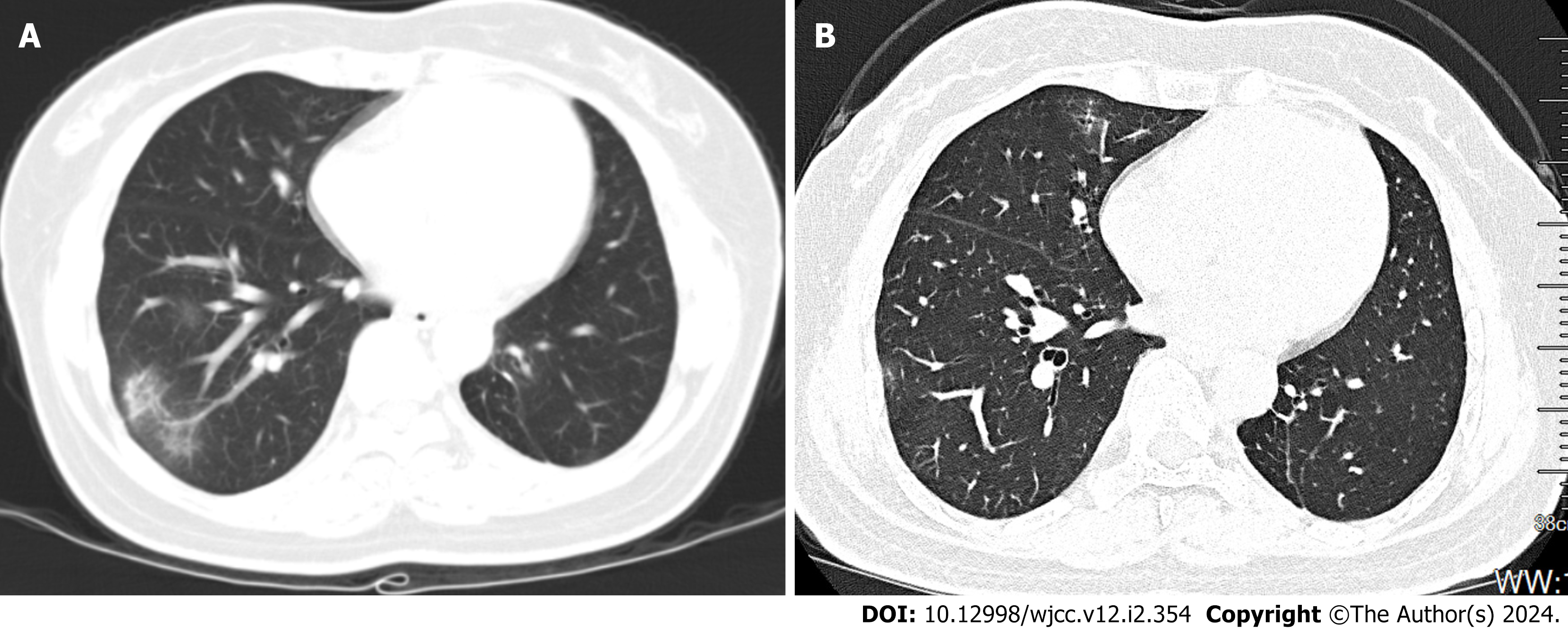
Approximately 20 d later, the patient showed significant improvement in her symptoms and liver function tests. The patient’s pulmonary nodule condition improved significantly, as evaluated by chest CT (Figure 3A). The patient continued to take UDCA and methylprednisolone for > 6 mo and was found to have a significant reduction in pulmonary nodular shadow by high-resolution thoracic CT (Figure 3B).
PBC is an immune-mediated, progressive intrahepatic cholestatic liver disease of unknown etiology that leads to cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and liver failure[4]. PBC is predominant in middle-aged women and presents as fatigue and itching, or is asymptomatic[5]. The pathogenesis of PBC needs to be clarified. Current data show that it is an autoimmune disease involving genetic susceptibility and environmental factors[6]. Antibodies are essential for diag
Extrahepatic autoimmune diseases can be found in 70%–85% of PBC patients. PBC is an autoimmune liver disease reported most frequently in pulmonary diseases. However, the incidence of PBC-related lung diseases is unknown[10]. Various pulmonary manifestations may occur in patients with PBC, including subclinical alveolitis, GLD, airway disease, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary hemorrhage, and pleural effusion[11]. Few studies have reported the histopathological features of the lungs. Frechen et al[12] reported a case of pulmonary necrotizing granulomatosis in a patient with PBC. Lee et al[13] analyzed 16 patients with PBC who underwent lung biopsy and found that 13 had pathological manifestations of non-necrotizing granulomas and lymphocyte infiltration, which parallel histopathology in our case. This indicates that pulmonary disease secondary to PBC should be considered regarding the differential diagnosis of GLD.
In our case, the patient was found to have a pulmonary nodule on incidental physical examination. The initial chest CT findings revealed a lung nodule showing lobulated, burred, and irregular margins, features reminiscent of a lung malignancy. Furthermore, the nodule was found to show high FDG uptake on PET/CT. 18F-FDG-PET/CT is now widely used in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant diseases. FDG-PET can measure the uptake of the glucose analog FDG to assess glucose metabolism. Tumor FDG uptake is based on tumor hyperglycolysis, but FDG is not a specific tracer, as high FDG uptake also occurs in inflammatory or infectious pathologies[14]. Therefore, clinicians should not hastily rely on PET/CT results for pulmonary nodules of unknown etiology.
GLDs represent a group of heterogeneous diseases with a myriad of etiologies, classified into infectious (fungus and tuberculosis) and noninfectious lung diseases (allergic pneumonia, sarcoidosis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)[15]. The lack of specificity in clinical manifestations and chest CT findings makes definitive diagnosis difficult. The high rate of false positives makes it difficult to distinguish between GLDs and malignancy using FDG-PET/CT. Pulmonary granulomatous disease secondary to PBC is frequently observed in middle-aged women and is characterized by symptoms such as dyspnea, dry cough, and systemic symptoms. Chest X-rays or CT scans can show pulmonary nodules, interstitial changes, or lung infiltrates, which may resemble those of lung cancer or other GLDs, potentially resulting in misdiagnosis. The patient in this case was discovered to have a pulmonary nodule with initial chest CT findings showing lobulated, burred, and irregular margins and high FDG uptake on PET/CT, mistakenly suggestive of lung malignancy. Therefore, specific symptoms and typical extrapulmonary manifestations are indicative. For example, GLD combined with keratitis, conjunctivitis, scleritis, oral ulcer gingivitis, and proteinuria often indicate GPA, while EGPA is often associated with multiple mononeuropathy[16-18]. In our case, the presence of positive antibodies for autoimmune liver disease, along with significantly elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase and -glutamyl transpeptidase, substantially supports the diagnosis of PBC.
A pulmonary biopsy is needed for atypical clinical presentations or to exclude pulmonary malignancy. The characteristics of lung granulomas differ depending on the cause, making pathological features crucial for diagnosis. It mainly includes granuloma distribution, necrosis, pathogens, and other concomitant features[19]. Angiocentric distribution is usually linked with granulomatous vasculitis, and lymphatic distribution is mainly found in nodular disease. The pre
In summary, GLDs are insidious diseases with multiple etiologies and nonspecific manifestations in clinical symptoms and imaging findings. PBC should be considered in the differential diagnosis of GLD. Reliance solely on PET/CT for indeterminate pulmonary nodules is discouraged, and a comprehensive evaluation including clinical, pathological and immunological markers is essential. Identifying and categorizing autoimmune conditions is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of GLD. Heightened awareness and caution regarding autoimmune-related GLDs can prevent unwarranted surgical procedures and decrease instances of misdiagnosis.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Gurakar A, United States S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: Kerr C P-Editor: Xu ZH
| 1. | Lleo A, Leung PSC, Hirschfield GM, Gershwin EM. The Pathogenesis of Primary Biliary Cholangitis: A Comprehensive Review. Semin Liver Dis. 2020;40:34-48. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 85] [Article Influence: 17.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Floreani A, Cazzagon N. PBC and related extrahepatic diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2018;34-35:49-54. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Anan N, Zainon R, Tamal M. Correction: A review on advances in 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics standardisation and application in lung disease management. Insights Imaging. 2022;13:32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Lleo A, Wang GQ, Gershwin ME, Hirschfield GM. Primary biliary cholangitis. Lancet. 2020;396:1915-1926. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 163] [Cited by in RCA: 155] [Article Influence: 31.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Cheung AC, Lammers WJ, Murillo Perez CF, van Buuren HR, Gulamhusein A, Trivedi PJ, Lazaridis KN, Ponsioen CY, Floreani A, Hirschfield GM, Corpechot C, Mayo MJ, Invernizzi P, Battezzati PM, Parés A, Nevens F, Thorburn D, Mason AL, Carbone M, Kowdley KV, Bruns T, Dalekos GN, Gatselis NK, Verhelst X, Lindor KD, Lleo A, Poupon R, Janssen HLA, Hansen BE; Global PBC Study Group. Effects of Age and Sex of Response to Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Transplant-free Survival in Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17:2076-2084.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Gershwin ME, Selmi C, Worman HJ, Gold EB, Watnik M, Utts J, Lindor KD, Kaplan MM, Vierling JM; USA PBC Epidemiology Group. Risk factors and comorbidities in primary biliary cirrhosis: a controlled interview-based study of 1032 patients. Hepatology. 2005;42:1194-1202. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 504] [Cited by in RCA: 438] [Article Influence: 21.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Hu SL, Zhao FR, Hu Q, Chen WX. Meta-analysis assessment of GP210 and SP100 for the diagnosis of primary biliary cirrhosis. PLoS One. 2014;9:e101916. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Levy C, Bowlus CL. Role of Antinuclear Antibodies in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:1604-1606. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Lindor KD, Bowlus CL, Boyer J, Levy C, Mayo M. Primary Biliary Cholangitis: 2018 Practice Guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2019;69:394-419. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 164] [Cited by in RCA: 416] [Article Influence: 69.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Wallace JG Jr, Tong MJ, Ueki BH, Quismorio FP. Pulmonary involvement in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987;9:431-435. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Akulkina LA, Brovko MY, Sholomova VI, Rozina TP, Yanakayeva AS, Frantsuzevich LY, Lebedeva MV, Fomin VV. Variety of lung involvement in autoimmune liver diseases. Ter Arkh. 2018;90:107-112. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Frechen D, Cornelissen C, Schreiner K, Jäkel J, Krüger S. [Pulmonary necrotizing sarcoid granulomatosis in a patient with primary biliary cirrhosis]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2010;135:1733-1736. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Lee HE, Churg A, Ryu JH, Bilawich AM, Larsen BT, Tazelaar HD, Yi ES. Histopathologic findings in lung biopsies from patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Hum Pathol. 2018;82:177-186. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Groheux D, Quere G, Blanc E, Lemarignier C, Vercellino L, de Margerie-Mellon C, Merlet P, Querellou S. FDG PET-CT for solitary pulmonary nodule and lung cancer: Literature review. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2016;97:1003-1017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Stellmacher F, Perner S. [Overview: granulomatous diseases of the lung]. Pathologe. 2021;42:64-70. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Chopra A, Avadhani V, Tiwari A, Riemer EC, Sica G, Judson MA. Granulomatous lung disease: clinical aspects. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020;14:1045-1063. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Casal A, Díaz-Garel J, Pereiro T, Toubes ME, Ricoy J, Valdés L. Pulmonary vasculitis. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:5560-5575. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Batra K, Chamarthy M, Chate RC, Jordan K, Kay FU. Pulmonary vasculitis: diagnosis and endovascular therapy. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2018;8:297-315. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | El-Zammar OA, Katzenstein AL. Pathological diagnosis of granulomatous lung disease: a review. Histopathology. 2007;50:289-310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Respiratory Pathology Committee of Chinese Association of Chest Physician and Expert Group on Consensus Preparation. [Recommendation on the principle and procedure of pathological diagnosis of pulmonary granulomatous diseases]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2021;50:719-727. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Samsonova MV, Chernyaev AL. [Histological differential diagnosis of granulomatous lung diseases (part I)]. Arkh Patol. 2019;81:65-70. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 22. | Ohshimo S, Guzman J, Costabel U, Bonella F. Differential diagnosis of granulomatous lung disease: clues and pitfalls: Number 4 in the Series "Pathology for the clinician" Edited by Peter Dorfmüller and Alberto Cavazza. Eur Respir Rev. 2017;26. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |