Published online May 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i13.2201
Revised: March 3, 2024
Accepted: April 1, 2024
Published online: May 6, 2024
Processing time: 104 Days and 19.1 Hours
The Correa sequence, initiated by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), commonly pro
To demonstrate the effectiveness of YWXY in patients with CAG and spleen-stomach deficiency syndrome (DSSS), by alleviating histological scores, im
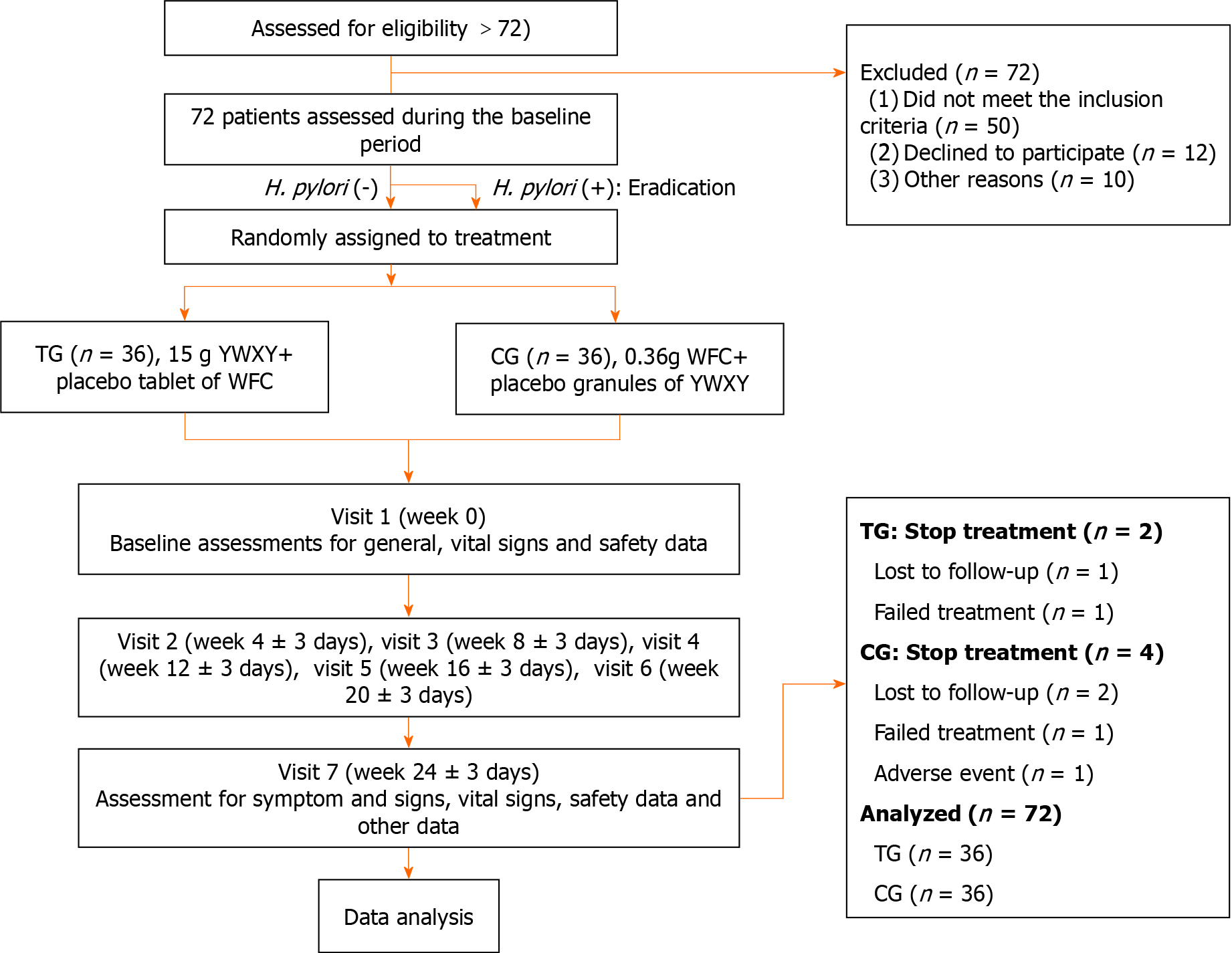
We designed a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. The study enrolled seventy-two H. pylori-negative patients (mean age, 52.3 years; 38 men) who were randomly allocated to either the treatment group or control group in a 1:1 ratio, and treated with 15 g YWXY or 0.36 g Weifuchun (WFC) tablet combined with the respective dummy for 24 wk. The pre-randomization phase resulted in the exclusion of 72 patients: 50 participants did not meet the inclusion criteria, 12 participants declined to participate, and 10 participants were excluded for various other reasons. Seven visits were conducted during the study, and histopathological examination with target endoscopic biopsy of narrow-band imaging was requested before the first and seventh visits. We also evaluated endoscopic performance scores, total symptom scores, serum pepsinogen and gastrin-17.
Six patients did not complete the trial procedures. Treatment with YWXY improved the Operative Link on Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia Assessment (OLGIM) stage, compared with WFC (P < 0.05). YWXY provided better relief from symptoms of DSSS and better improvement in serum gastric function, compared with WFC (P < 0.05).
YWXY compared with WFC significantly reduced the risk of mild or moderate atrophic disease, according to OLGIM stage, significantly relieved symptoms of DSSS, and improved serum gastric function.
Core Tip: Despite the successful eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), which has been shown to reduce the risk of gastric cancer (GC), patients with chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) still remain susceptible to disease progression leading to GC. Our findings suggest that treatment with Yiwei Xiaoyu granules for CAG patients without H. pylori improved the stage of Operative Link on Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia Assessment, provided better clinical symptoms relief and better improvement in serum gastric function levels compared to Weifuchun tablet. However, the total sample size of this study is limited and prolong follow-up hasn’t been carried out.
- Citation: Chen WQ, Fan QF, He YJ, Li F, Wu X, Li YP, Yang XJ. Yiwei Xiaoyu granules for treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis with deficiency syndrome of the spleen and stomach. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(13): 2201-2209
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i13/2201.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i13.2201
The global burden of stomach cancer remains substantial, with it being ranked fifth in terms of incidence and fourth in terms of mortality worldwide[1]. Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) is one of the most common stages in the progression to gastric cancer for the Correa sequence caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)[2]. The latest research has already demonstrated that the eradication of H. pylori can reduce the risk of gastric cancer, although it cannot completely eliminate the risk of neoplastic progression. This progression is associated with the extent of genetic alterations and epigenetic modifications present at the time of H. pylori eradication[3,4]. More therapeutic methods, but not only of H. pylori eradication, should be explored for CAG or gastric precancerous lesions.
Some traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) herbs that are effective for therapy of CAG have gradually gained global recognition, as for Moluodan’s recommendation in the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline update 2019[5,6]. However, because of the specific characteristics of TCM such as holistic theory and syndrome differentiation and treatment, the comprehensive comprehension and application of TCM for the treatment of CAG necessitates the conduction of rigorous clinical trials with high methodological quality and standardized animal experiments.
Our group has focused on the effects of TCM on CAG for > 20 years. Yiwei Xiaoyu granules (YWXY) are a commonly used composite preparation in Chinese clinics. YWXY have been shown to improve mucosal atrophy, intestinal metaplasia (IM) and dysplasia of CAG[7], and water reflux extraction technology and quality standards of YWXY have been optimized[8,9]. The mechanisms of inhibition of YWXY on spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia lesions, atrophy and IM have been explored[10-12]. The widely used high-definition endoscopy with chromoendoscopy has improved the diagnostic accuracy for atrophy, IM and dysplasia[5]. H. pylori eradication has been recognized as the basic treatment for CAG[13]; and the present study was designed as a double-blinded, randomized controlled trial in order to substantiate the therapeutic efficacy of YWXY.
The study design employed in this research was a single-center, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. We recruited patients with a previous endoscopic and histological diagnosis of CAG, with or without IM, from both outpatient and inpatient units of the Department of Gastroenterology at Chongqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, in accordance with the Consensus on Chronic Gastritis in China[14].
The diagnosis and treatment of CAG is based on the consensus reached by integrating TCM and Western medicine in 2017[15], the diagnosis of DSSS was as follows: Primary symptoms and tongue manifestations were indispensable, and more than two secondary symptoms were needed, at the same time, pulse condition must be referred to as indications to assist in DSSS diagnosis.
The study included patients exhibiting the following characteristics: Age 19-69 years; without H. pylori infection; and mild or moderate grade of atrophic border (C1–C3, O1) according to the Kimura–Takemoto classification[16]. Patients with TCM syndrome differentiation according to DSSS and with mild or moderate histological severity of atrophic changes were referred to the Operative Link on Gastritis Assessment (OLGA) and Updated Sydney System[17,18].
The following patients were excluded: Patients with severe dysplasia and atrophy; suspected stomach or other cancers; patients who underwent gastric surgery; combination of gastric or duodenal ulceration; patients with severe systemic disease (cardiovascular, hepatic, blood, kidney or lung disease); administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; pregnant or lactating women; or patients who refuses to undergo gastroscopic examination or give informed consent.
The criteria for withdrawal or dropout were as follows: Patients who no longer continued to use the study drugs or were receiving visits; patients who decided to withdraw on their own volition, after failing to be dissuaded by the investigator; or patients experiencing serious adverse events or complications.
Participants were randomized into the treatment group (TG) and control group (CG). Before the trial, YWXY and Weifuchun (WFC) tablets (Hangzhou Huqing Yutang Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., China; batch No. Z20040003) were prepared, along with placebo granules of YWXY and placebo tablets of WFC. YWXY and the two placebos were made by the Pharmaceutical Department of Chongqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The TG received 15 g/package of YWXY (four times a day) and placebo tablets of WFC (three times a day) for 24 wk. The CG received 0.36 g WFC and placebo YWXY with the same frequency and duration as the TG.
A random allocation sequence number of 72 patients was obtained by an independent researcher via SAS version 9.1.3 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, United States). Sequentially numbered opaque sealed envelopes were used to store randomized numbers associated with specific drugs based on group assignments. Each envelope was assigned a unique number. When recruiting eligible patients, a researcher independently and randomly selected one envelope from a pool without knowledge of its code's meaning. Experimental conditions "1" and "2" were represented by chosen envelopes, where "1" indicated TG and "2" represented CG. The TG and CG groups were allocated to consecutive patients in a 1:1 ratio through random assignment.
Researchers and patients were blinded to the grouping. Because of the difference in formation and dosage between YWXY and WFC, placebo granules and placebo tablets were made identical to the two drugs in terms of color, odor and packaging. Otherwise, the tablets of WFC (0.36 g) were packaged into a sealed plastic bag, with the exact appearance of YWXY. The Pharmaceutical Department marked the medicine packages with "1" or "2" codes, corresponding to YWXY + placebo or WFC + placebo respectively. Patients were instructed to take 92 tablets of YWXY and 84 tablets of placebo, or 92 tablets of placebo and 84 tablets of WFC every 4 wk. An independent researcher, who did not participate in case observations or efficacy assessments, was responsible for drug distribution, storage and return.
The recruitment was advertised at our hospital, targeting potential patients who had previously been diagnosed with a mild to moderate grade of CAG for the purpose of endoscopic and histological presentation. After signing informed consent, the patients were interviewed to collect demographic data, symptoms and signs, medical and treatment history, complications and drug combinations, as well as undergo physical examinations. In addition, vital signs and safety data were recorded.
All participants included were requested to perform endoscopy prior to treatment (visit 1) and 24 wk after treatment completion (visit 7), by experienced senior endoscopists using a high-resolution magnifying endoscope (GIF-290H; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). According to the Kyoto global consensus[19], the following endoscopic characteristics were evaluated: atrophic change, severity of atrophy (open/closed, O/C), IM and its location, hyperplasia, regular arran
Following the screening stage, targeted biopsy utilizing narrow-band imaging (NBI) was conducted in accordance with the updated Sydney System biopsy protocol[17]. Five biopsies of the suspicious places were confirmed in combination with NBI. The submucosa was injected with 0.2-0.3 mL of India ink solution (manufactured by the Pharmaceutical Department of Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Hangzhou, China) using an endoscopic needle (ENDO-FLEX GmbH, NET2522-C4, Germany). Five biopsies were obtained from the stomach: two from the antrum, one from the incisura, one along the lesser curvature of the gastric body, and one along the greater curvature of the gastric body. Each biopsy specimen was sufficiently large to reach the lamina propria. The final visit was 24 wk after the termination of treatment, when all participants were required to undergo another endoscopy with five biopsies at the edges of the marked areas.
The biopsy specimen was retrieved, immersed in a 10% formalin solution, and subsequently dispatched to the Pathology Department of Chongqing Hospital. The histological diagnosis of the lesion and assessment of resection margin involvement were conducted in accordance with the Consensus on Chronic Gastritis in China (Shanghai, 2017) and the updated Sydney System[17]. Two independent senior histopathologists were called in to examine the biopsies. When disagreements arose, they stopped and re-examined the relevant biopsy until agreement was reached.
Seven clinical visits were scheduled, consisting of baseline visit (visit 1), follow-up visit every 4 wk for the consecutive six treatment periods (visits 2–6), and follow-up at 24 wk after completing the treatment (visit 7). Each visit allowed a window of 3 d. For each treatment visit, the patient was required to return the plastic outer packaging and was inter
The main aim was to assess the effectiveness of YWXY in alleviating histological scores, response rates for pathological lesions, and rate of disappearance of atrophy or IM. The atrophy, chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, and IM were assessed using a four-tiered scale (0-3) based on the visual analog scale of the Houston-updated Sydney system. The secondary objectives were to evaluate the efficacy of YWXY in alleviating the total symptom score, the change in the score of the endoscopic findings, and the shift in the serum pepsinogen test between the two groups after treatment. The total symptom scores were evaluated with reference to the TCM symptom evaluation table of gastrointestinal diseases[21]. The 32 most common symptoms were assessed using a four-tiered scale (0, 3, 5, and 7), with the efficacy score calculated as the difference between the total number of syndrome points before and after treatment divided by the total number of syndrome points before treatment multiplied by 100%.
After enrollment and the day following completion of the intervention period, all participants underwent a comprehensive range of tests including electrocardiography, complete blood cell count, assessment of renal function (serum uric acid, serum creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen), evaluation of liver function (alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, and total bilirubin), and routine stool examination. Any details pertaining to adverse events such as occurrence time, severity, duration, measures taken for mitigation or resolution, and outcomes were meticulously recorded in a Clinical Research Form. Based on the severity of adverse events observed, the investigators made informed decisions regarding suspension or withdrawal of patients from the trial.
The study design, reporting, and informed consent procedures were conducted in accordance with the recommendations of the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice guidelines. The protocol received approval from the Ethics Review Board of Chongqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 2019-ky-24), and was registered on the Chinese clinical trial registry website (http://www.chictr.org.cn/index.aspx, ChiCTR1900026455).
The responsibility of data management was entrusted to an independent data safety and monitoring committee, comprising statisticians and gastroenterologists, who operated independently from the sponsor's and competing interests. Prior to commencing the trial, all investigators underwent a comprehensive 2-h training session to ensure their proficiency in overseeing the entire trial process. Patient data was securely stored in a password-protected Excel file.
The data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States), with a significance level set at P < 0.05. The baseline data between groups were compared using either Student's t-test or chi-square test. Efficacy primary outcomes were analyzed based on the intention-to-treat principle, utilizing both the intent-to-treat (ITT) and per-protocol (PP) populations. The missing data were managed using the last-observation-carried-forward approach. Continuous variables were presented as mean ± SD or median, with t-tests used for normally distributed variables and paired t-tests conducted to assess significant differences before and after treatment. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was employed to analyze non-normally distributed data.
Patients were recruited from December 1, 2019 to November 30, 2021. The follow-up period ended on July 31, 2022. The study enrolled a total of 72 patients. The CORSORT graph of patient recruitment and analysis is shown in Figure 1. Two patients were discharged for self-induced causes such as long travel and taken other drugs of the same type. In the CG, two patients were withdrawn for self-induced causes, two were lost to follow-up, and one had an adverse reaction of mild liver enzyme elevation. The clinical characteristics are presented in Table 1. There were no significant differences observed in terms of sex, age, Kimura-Takemoto staging, OLGA stage, and OLGIM stage between the two groups prior to treatment (P > 0.05). The symptom scores of DSSS were compared, and no significant differences were observed in the six typical symptoms between the two groups.
| Characteristics | TG | CG | P value |
| Age at enrollment (yr) | 0.38 | ||
| ≤ 45 | 6 | 11 | |
| 46–55 | 11 | 9 | |
| ≥ 55 | 19 | 16 | |
| Age, year (mean ± SD) | 54.61 ± 10.20 | 50.06 ± 11.27 | 0.08 |
| Sex | 0.64 | ||
| Female | 18 | 16 | |
| Male | 18 | 20 | |
| Kimura–Takemoto classification | 0.80 | ||
| C1 | 4 | 4 | |
| C2 | 18 | 19 | |
| C3 | 13 | 13 | |
| O1 | 1 | 0 | |
| OLGA stage | 0.39 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| I | 14 | 20 | |
| II | 14 | 8 | |
| III | 6 | 5 | |
| IV | 2 | 3 | |
| OLGIM stage | 0.63 | ||
| 0 | 13 | 17 | |
| I | 15 | 13 | |
| II | 7 | 6 | |
| III | 1 | 0 | |
| IV | 0 | 0 | |
| Symptom scores of DSSS (mean ± SD) | |||
| Abdominal bloating | 3.58 ± 0.30 | 3.42 ± 0.36 | 0.72 |
| Epigastric pain | 2.5 ± 0.39 | 2.81 ± 0.34 | 0.55 |
| Loose stools | 2.42 ± 0.34 | 1.83 ± 0.34 | 0.23 |
| Fatigue | 2.14 ± 0.33 | 2.36 ± 0.38 | 0.66 |
| Feel weakness of limps | 2.36 ± 0.34 | 3.75 ± 0.30 | 0.39 |
| Stomach cold | 3.25 ± 0.35 | 3.33 ± 0.34 | 0.86 |
| Total symptomatic scores | 61.5 ± 3.55 | 57.67 ± 3.98 | 0.47 |
After 6 months of treatment, we examined by gastroscopy whether there was any change in atrophy between the two groups. Extent of atrophy according to Kimura–Takemoto classification showed no change (Table 2). Two patients showed regression in the TG compared with five in the CG, using ITT and PP statistical analysis, and there was no significant difference between the TG and CG.
| TG (n = 36) | CG (n = 36) | P value | |||||
| Regression | No change | Progression | Regression | No change | Progression | ||
| Kimura–Takemoto classification | 2 | 32 | 2 | 5 | 30 | 1 | 0.43 |
| OLGA stage | 29 | 5 | 2 | 26 | 7 | 2 | 0.79 |
| OLGIM stage | 16 | 18 | 2 | 6 | 27 | 3 | 0.04 |
OLGA classification improved in most patients in both groups (P > 0.05). OLGIM stage showed regression in 16 patients in the TG, but only six in the CG. Patients with YWXY had better results for OLGIM stage improvement than those with WFC (P < 0.05).
Among the six specific symptoms of DSSS, patients in the TG had better relief than those in the CG for epigastric pain, limb weakness and stomach chill afraid of cold. The efficacy scores for patients in the TG were better than those in the CG (P < 0.05) (Table 3). We evaluated the effect of YWXY and WFC on serum gastric function in patients with CAG, and we published this part[22]. Exclusively in a Chinese journal, the results showed that YWXY significantly improved the serum gastric function level in patients with CAG.
| TG | CG | P value | |
| Symptom scores of DSSS (mean ± SD) | |||
| Abdominal bloating | 1.83 ± 0.25 | 2.47 ± 0.30 | 0.11 |
| Epigastric pain | 1.56 ± 0.27 | 2.33 ± 0.26 | 0.04 |
| Loose stools | 1.17 ± 0.25 | 1.81 ± 0.31 | 0.11 |
| Fatigue | 1.17 ± 0.25 | 1.86 ± 0.32 | 0.09 |
| Limb weakness | 1.25 ± 0.25 | 2.22 ± 0.28 | 0.01 |
| Stomach chill afraid of cold | 1.58 ± 0.25 | 2.39 ± 0.27 | 0.03 |
| Symptomatic relief (n) | 0.11 | ||
| Cure | 0 | 0 | |
| Obvious effect | 5 | 2 | |
| Effective | 26 | 22 | |
| Ineffective | 5 | 12 |
In China, approximately 24.5% of the population is estimated to be diagnosed with CAG according to a nationwide multicenter cross-sectional study[23]. However, faced with such a large number of patients with CAG, there were only limited therapeutic strategies with anti-H. pylori treatment and endoscopic monitoring worldwide[5,24]. The risk of gastric cancer, however, only decreases by less than 50% after undergoing H. pylori eradication therapy[25].
YWXY have been widely used to treat CAG in China for > 20 years, which are a compound preparation formulated by Professor Yan-Ping Li of our team. According to the principles of TCM, the spleen governs the processes of transformation and transportation, as well as the elevation of pure substances; whereas, the stomach is responsible for receiving and maturing ingested food and fluids. In other words, the spleen regulates upward movements while the stomach controls downward movements. If there is a deficiency in the spleen and stomach, it can lead to impaired digestion and manifest as symptoms such as abdominal distention or pain, diarrhea, or appetite disorders. YWXY is a Chinese formula, whose primary therapeutic effect is to benefit the spleen and stomach, and the secondary therapeutic effect is to remotivate Qi or invigorate circulation of the blood. That is why YWXY had a better effect on the relief of characteristic symptoms of DSSS (P < 0.05).
The effects of the two drugs were evaluated in this study using both invasive and noninvasive serological tests. The elimination of H. pylori was a notable aspect of our study, aimed at mitigating its persistent impact on the gastric mucosa. Eradication of H. pylori or H. pylori negativity was required before enrollment because H. pylori infection could have influenced the gastric mucosa and its histology, as well as associated dyspeptic symptoms[19]. Another feature is a consistent team of skilled endoscopists and a standardized biopsy protocol, particularly with endoscopists, histopathologists, investigators and patients blinded to the evaluation. Also, the primary outcome was assessed by combination of serum pepsinogen levels and OLGA/OLGIM stage[26,27].
The OLGIM system is derived from the OLGA system, both of which are utilized for the classification and grading of atrophy and IM severity and distribution. In particular, as some evidence has shown[28], guided biopsies by virtual chromoendoscopy can upgrade OLGA and OLGIM stages, and can be used in combination with target biopsies, as in this study. IM is claimed to be the most reliable marker of risk for gastric cancer[29]. Our results show that YWXY improved the OLGIM stage more than WFC (P < 0.05), which is consistent with our previous animal experiments.
We selected WFC as the positive control medication due to its well-established status as a Chinese herbal preparation, comprising Panax ginseng (HS: 131 g), Citrus aurantium (ZQ: 250 g), and Isodon amethystoides (XCC: 2500 g) as documented in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, 2020 edition. The inclusion of WFC in this pharmacopoeia highlights its efficacy in tonifying spleen Qi, promoting blood circulation, and facilitating detoxification. Moreover, WFC has been extensively utilized for numerous years in China for the treatment of GPL[30].
There were some limitations to our study. First, the 24-wk study period was difficult for many patients to endure, so the dropout rate was high throughout the study. Second, although eradication of H. pylori was a prerequisite for enrollment, the enduring impact of H. pylori on the gastric mucosa cannot be disregarded. For instance, research has demonstrated that even one year after H. pylori eradication, gastric microbes continue to contribute to the progression of gastric carcinogenesis[31], since H. pylori was negative in the included patients, we did not analyze the length of time between H. pylori eradication and inclusion. Twenty-four weeks of treatment was not sufficient and future follow-up at 2 and 5 years after treatment should be carried out. Finally, the sample size may have limited the results.
Our randomized study suggests that YWXYs, compared with WFC, significantly reduce the risk of mild or moderate atrophic disease, according to OLGA/OLGIM stage, clearly relieves symptoms of DSSS, and improves serum gastric function levels.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kirkik D, Turkey S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhao S
| 1. | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209-249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75126] [Cited by in RCA: 64628] [Article Influence: 16157.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (176)] |
| 2. | Correa P, Houghton J. Carcinogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:659-672. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 467] [Cited by in RCA: 505] [Article Influence: 28.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Rugge M, Meggio A, Pravadelli C, Barbareschi M, Fassan M, Gentilini M, Zorzi M, Pretis G, Graham DY, Genta RM. Gastritis staging in the endoscopic follow-up for the secondary prevention of gastric cancer: a 5-year prospective study of 1755 patients. Gut. 2019;68:11-17. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 134] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 20.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Choi IJ, Kook MC, Kim YI, Cho SJ, Lee JY, Kim CG, Park B, Nam BH. Helicobacter pylori Therapy for the Prevention of Metachronous Gastric Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1085-1095. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 397] [Cited by in RCA: 495] [Article Influence: 70.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Pimentel-Nunes P, Libânio D, Marcos-Pinto R, Areia M, Leja M, Esposito G, Garrido M, Kikuste I, Megraud F, Matysiak-Budnik T, Annibale B, Dumonceau JM, Barros R, Fléjou JF, Carneiro F, van Hooft JE, Kuipers EJ, Dinis-Ribeiro M. Management of epithelial precancerous conditions and lesions in the stomach (MAPS II): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE), European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group (EHMSG), European Society of Pathology (ESP), and Sociedade Portuguesa de Endoscopia Digestiva (SPED) guideline update 2019. Endoscopy. 2019;51:365-388. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 712] [Cited by in RCA: 672] [Article Influence: 112.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Liu S, Su ZQ, Liu XY, Fan QY, Gao J, Ma XJ, Wang T. Literature Study on Current Status of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Based on PubMed and Web of Science Databases. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi. 2021;27:149-158. |
| 7. | Wu LJ, Xie HM, Tian FL, Li YP, Zhang CY. 30 cases of chronic atrophic gastritis treatment with Yiwei Xiaoyu granules. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xiaohua Zazhi. 2007;15:57-58. |
| 8. | Liu X, Xu C, Leng J, Guo XH, Tian FL. Optimization of the water extraction process of Yiwei Xiaoyu Granules by orthogonal test. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi. 2018;33:1605-1607. |
| 9. | Liu X, Xu C, Wu WH, Guo XH, Sun Q, Tian FL. Study on Quality Standard of Yiwei Xiaoyu Granules. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xinxi Zazhi. 2018;25:77-80. |
| 10. | Chen WQ, Tian FL, Zhang JW, Yang XJ, Li YP. Preventive and inhibitive effects of Yiwei Xiaoyu granules on the development and progression of spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia lesions. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2021;13:1741-1754. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Tian FL, Li YP, Yang XJ, Liu Y, Chen WQ. Improvement effect of Yiwei Xiaoyu granules on gastric mucosa intestinal metaplasia of rats. Chongqing Yixue. 2018;47:6. |
| 12. | Yang XJ, Tian FL, Liu Y, Li YP. Effects of yiwei xiaoyu granules on intestinal metaplasia of gastric mucosa and the related inflammatory mediators in the rats. Shijie Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2019;14:5. |
| 13. | Mera RM, Bravo LE, Camargo MC, Bravo JC, Delgado AG, Romero-Gallo J, Yepez MC, Realpe JL, Schneider BG, Morgan DR, Peek RM Jr, Correa P, Wilson KT, Piazuelo MB. Dynamics of Helicobacter pylori infection as a determinant of progression of gastric precancerous lesions: 16-year follow-up of an eradication trial. Gut. 2018;67:1239-1246. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 119] [Cited by in RCA: 134] [Article Influence: 19.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 14. | Fang JY, Du YQ, Liu WZ, Ren JL, Li YQ, Chen XY, Lv NH, Chen YX, Lv B; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese consensus on chronic gastritis (2017, Shanghai). J Dig Dis. 2018;19:182-203. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 7.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Li JX, Chen J, Lv B, Wang YG; Chinese Association of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine digestive diseases professional committee. Consensus of chronic atrophic gastritis on integrated TCM and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment (in 2017). Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xiaohua Zazhi. 2018;26:121-131. |
| 16. | Kimura K, Takemoto T. An Endoscopic Recognition of the Atrophic Border and its Significance in Chronic Gastritis. Endoscopy. 1969;1:87-97. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 612] [Cited by in RCA: 742] [Article Influence: 43.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (3)] |
| 17. | Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P. Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996;20:1161-1181. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3221] [Cited by in RCA: 3553] [Article Influence: 122.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (3)] |
| 18. | Rugge M, Meggio A, Pennelli G, Piscioli F, Giacomelli L, De Pretis G, Graham DY. Gastritis staging in clinical practice: the OLGA staging system. Gut. 2007;56:631-636. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 290] [Cited by in RCA: 349] [Article Influence: 19.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Sugano K, Tack J, Kuipers EJ, Graham DY, El-Omar EM, Miura S, Haruma K, Asaka M, Uemura N, Malfertheiner P; faculty members of Kyoto Global Consensus Conference. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut. 2015;64:1353-1367. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1322] [Cited by in RCA: 1183] [Article Influence: 118.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Wang P, Tang XD, Liu BY, Zi MJ. [Development of a patient-reported outcome instrument for chronic gastrointestinal diseases: item selection]. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012;10:1092-1098. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Digestive Diseases Professional Committee of Chinese Association of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine. Evaluation table of TCM symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases (2010, Suzhou). Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xiaohua Zazhi. 2011;19:66-68. |
| 22. | Chen WQ, Fan QF, Li F, He YJ, Wu X, Tang ZR, Luo Y, Li YP, Yang XJ. The effect of Yiwei Xiaoyu Granules on serum gastric function in chronic atrophic gastritis. Xiandai Yiyao Weisheng. 2023;39:21-25. |
| 23. | Cai Q, Zhu C, Yuan Y, Feng Q, Feng Y, Hao Y, Li J, Zhang K, Ye G, Ye L, Lv N, Zhang S, Liu C, Li M, Liu Q, Li R, Pan J, Yang X, Zhu X, Li Y, Lao B, Ling A, Chen H, Li X, Xu P, Zhou J, Liu B, Du Z, Du Y, Li Z; Gastrointestinal Early Cancer Prevention & Treatment Alliance of China (GECA). Development and validation of a prediction rule for estimating gastric cancer risk in the Chinese high-risk population: a nationwide multicentre study. Gut. 2019;68:1576-1587. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 149] [Article Influence: 24.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine; Chinese Medical Doctor Association; National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Cardiology; Cardiovascular Disease Working Group; Encephalopathy Disease Working Group; China Center for Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine, Chen KJ. Chinese Expert Consensus on Clinical Application of Oral Ginkgo biloba Preparations (2020). Chin J Integr Med. 2021;27:163-169. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Lee YC, Chiang TH, Chou CK, Tu YK, Liao WC, Wu MS, Graham DY. Association Between Helicobacter pylori Eradication and Gastric Cancer Incidence: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1113-1124.e5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 737] [Cited by in RCA: 674] [Article Influence: 74.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Ogutmen Koc D, Bektas S. Serum pepsinogen levels and OLGA/OLGIM staging in the assessment of atrophic gastritis types. Postgrad Med J. 2022;98:441-445. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Unc OD. [Obituary. Dr. Nicole Botezatu (18.09.1942-19.02.2014)]. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2014;109:280-281. [PubMed] |
| 28. | Bornschein J, Rugge M. Bright future for endoscopy: the new frontier of gastric cancer secondary prevention. Gut. 2020;69:1723-1724. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Dinis-Ribeiro M, Kuipers EJ. How to Manage a Patient With Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: An International Perspective. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1534-1537. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Jin Y, Tian T, Ma Y, Xu H, Du Y. Simultaneous determination of ginsenoside Rb1, naringin, ginsenoside Rb2 and oridonin in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Weifuchun tablet. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015;1000:112-119. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Sung JJY, Coker OO, Chu E, Szeto CH, Luk STY, Lau HCH, Yu J. Gastric microbes associated with gastric inflammation, atrophy and intestinal metaplasia 1 year after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gut. 2020;69:1572-1580. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 88] [Cited by in RCA: 170] [Article Influence: 34.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |