Published online Dec 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i36.8589
Peer-review started: October 26, 2023
First decision: November 22, 2023
Revised: November 24, 2023
Accepted: December 7, 2023
Article in press: December 7, 2023
Published online: December 26, 2023
Processing time: 57 Days and 0.6 Hours
Coronary artery spasm (CAS) is a rare but critical condition during surgery. Clinical manifestations can vary from only subtle electrocardiography change to sudden death. In this case report, we present the case of a patient with myasthenia gravis (MG) who developed refractory CAS-related cardiogenic shock during thymoma surgery.
A 61-year-old man had a history of cigarette smoking and coronary artery disease with a bare metal stent placed. Three months ago, he suffered from coronary spasms, with three vessels involved, after surgery for cervical spine injury. He started having progressive dysphagia 4 wk prior and was diagnosed with MG via serologic tests, and computed tomography declared a thymoma in the anterior mediastinum. After the symptoms of MG subsided, he was referred for thy
Our case highlights the importance of being prepared for clinical situations such as the one described here and suggests the necessity of developing an appropriate anesthesia plan that includes proactive analgesia and preemptive coronary vaso
Core Tip: In previous literature reviews, it has been noted that a correlation exists between myasthenia gravis (MG) and cardiac complications, such as coronary artery spasm (CAS), which frequently manifests as chest pain in affected patients. Nevertheless, when MG coincides with thymoma, surgical intervention is often necessary. The diagnosis of CAS while the patient is under general anesthesia poses a considerable challenge. Our case report aims to underscore scenarios of this nature and suggests an optimal anesthesia strategy in such cases.
- Citation: Hsu CW, Chang CC, Lin CS. Intraoperative cardiogenic shock induced by refractory coronary artery spasm in a patient with myasthenia gravis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(36): 8589-8594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i36/8589.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i36.8589
Coronary artery spasm (CAS) was recently recognized as a cause of myocardial infarction with nonobstructive coronary arteries[1]. The transient cessation of the coronary blood supply causes clinical manifestations that mimic ischemic heart disease. Perioperative CAS can be challenging for anesthesiologists, especially when patients are sedated or under general anesthesia. We present a case of myasthenia gravis (MG) that developed coronary spasm-related cardiogenic shock during thymoma surgery.
A 61-year-old man was diagnosed with MG and thymoma. He was scheduled for median sternotomy to undergo resection of the thymoma.
The patient started having progressive dysphagia 4 wk prior, and the associated symptoms included diplopia, ptosis, general weakness, and easy choking. He denied chest pain, bloody sputum, and fever. Serologic tests were positive for antibodies against the acetylcholine receptor (serum level: 88.3 nmol/L). Computed tomography revealed a 5.4 cm enhanced lobular mass in the anterior mediastinum, which was declared to be a thymoma. He was diagnosed with MG, and intravenous immunoglobulin was administered at a dose of 600 mg/kg once-daily for 5 consecutive days. The symptoms of MG subsided after 20 d, and he was referred for surgical intervention. Preoperative echocardiography revealed preserved systolic function and normal wall motion without major valvular dysfunction. Thus, a medium sternotomy for anterior mediastinum tumor resection was arranged.
In the operating theater, general anesthesia was induced with lidocaine 60 mg, thiamylal sodium 300 mg, fentanyl 50 μg, and rocuronium 40 mg. A 37-Fr double lumen endotracheal tube was intubated, and then an arterial line and a central venous catheter were placed smoothly. The operation was uneventful until the closing of the sternal wound. Electrocardiography showed sudden onset ST elevation, followed by ventricular tachycardia and severe hypotension. Cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation was initiated immediately with electrical defibrillation (200 J), and the surgeon started to perform direct cardiac massage. However, ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation and hypotension persisted. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) was performed 40 min after the initiation of cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation.
The patient had a history of cigarette smoking and coronary artery disease with a bare metal stent placed 11 years prior. In January 2021, he suffered from a cervical spine injury with disc fracture at C5–6 and central cord syndrome from a traffic accident. He underwent cervical discectomy and interbody fusion with a cervical cage. After transfer to the intensive care unit, chest pain was mentioned. Then, sudden onset bradycardia following ventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest occurred. Coronary angiography showed spasms in three vessels without obvious atherosclerotic lesions. He was transferred to a normal ward 10 d later and then discharged after rehabilitation was completed.
The patient denied any family history of MG.
After ECMO insertion, the patient’s arterial blood pressure was approximately 90/50 mmHg. The heart rate was around 70 beats per minute and respiratory rate was set at 12 breaths per minute. Capnography showed a low end tidal CO2 level (under 20 mmHg).
Arterial blood gas data showed acidosis (PH = 7.304) with elevated PaCO2 (70.4 mmHg) and HCO3- (35.3 mEq/L). Serum lactate level also increased (8.5 mmol/L). Serum creatine kinase (CK) and CK muscle and brain isoenzyme levels were in normal range but troponin-T level was elevated (0.039 ng/mL).
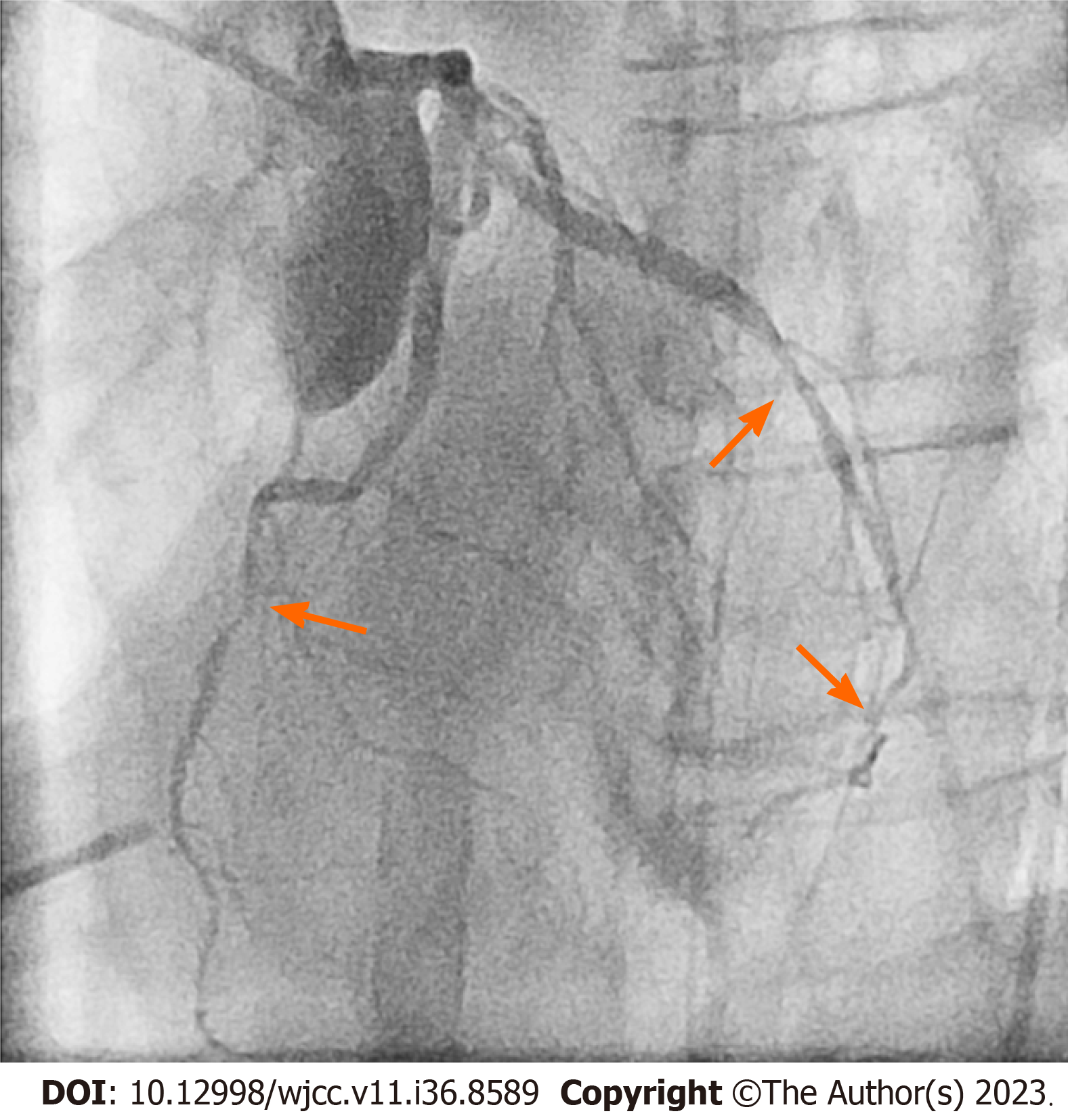
Electrocardiography indicated a return to sinus rhythm with ST elevation within 10 min. Subsequent transesophageal echocardiography exhibited global hypokinesia. Further assessment through angiography unveiled diffuse CAS with three vessels involved (Figure 1).
Cardiogenic shock due to diffuse CAS with three vessels involved.
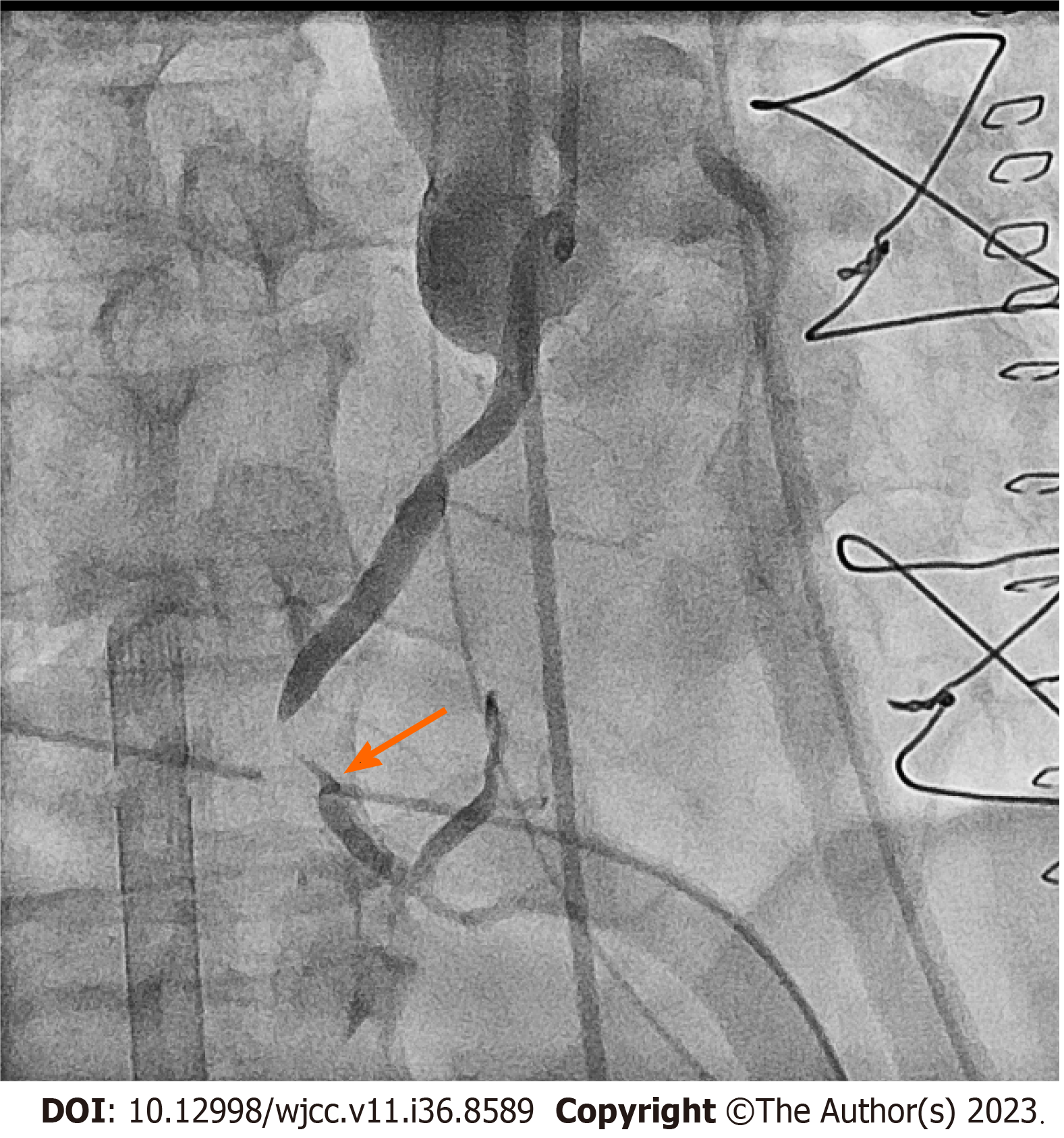
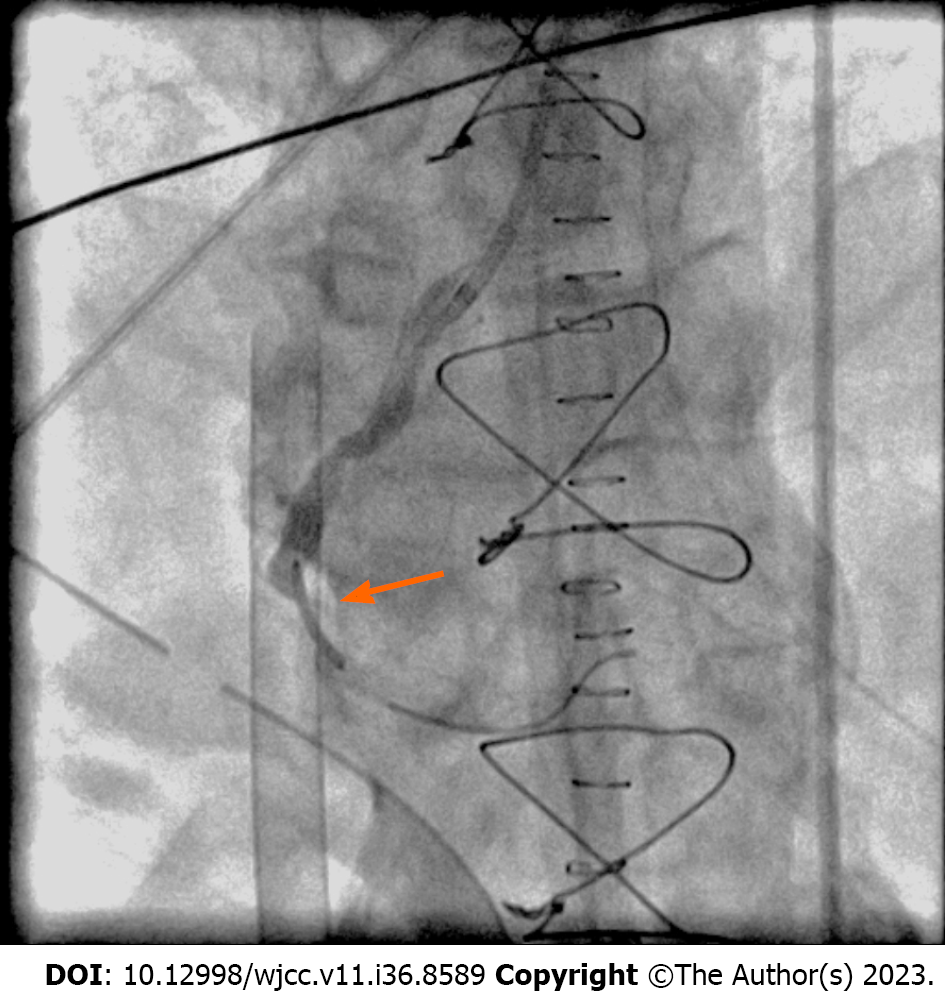
A total of 1600 mg intracoronary isosorbide dinitrate and 360 mg adenosine were administered. After transient relief, refractory spasm was noted at the right coronary artery (Figure 2); thus, a bare metal stent was placed (Figure 3). An intra-arterial balloon pump was placed due to poor contraction of the left ventricle, and then the patient was transferred to the intensive care unit.
The patient regained consciousness on the following day. A week later, echocardiography revealed improved left ventricular systolic function; thus, the intra-arterial balloon pump and ECMO were removed. He was then transferred to a ward for a rehabilitation program and discharged. However, he had pneumonia and progressed into sepsis 5 mo later and expired due to multiorgan failure.
CAS is a rare condition, and its diverse manifestations can sometimes be critical, especially perioperatively. Some risk factors for CAS have been identified, such as age, sex, smoking, and physical and mental stress, and the usage of sympathomimetic and parasympathomimetic agents can be precipitating factors. The pathophysiology of CAS can be multifactorial, including endothelial dysfunction, autonomic nervous system disorder, and oxidative stress. One study reviewed 115 cases with perioperative CAS, and most cases of CAS occurred during abdominal or thoracic surgery. The authors considered inadequate depth of general anesthesia, use of vasopressors, and vagus nerve stimulation as possible contributing factors. Most patients had normal preoperative electrocardiograms. However, almost every patient (97%) presented ST segment changes when CAS occurred, and approximately 20% were associated with ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest[2].
MG is an autoimmune neuromuscular disease, and antibodies to acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junctions cause muscle weakness. Usually, antibodies bind only to the skeletal system. However, in patients with MG combined with thymoma, specific striational antibodies bind to heart muscle, which may be related to the myocarditis and myositis that occur in MG patients[3]. Several case reports have presented the occurrence of CAS in patients with MG after cholinesterase inhibitor or intravenous immunoglobulin treatment[4]. Acetylcholine, as a parasympathetic neurotransmitter of the endothelium, is usually related to coronary dilation; however, it can induce vasospasm through vascular smooth muscle constriction when the endothelium is damaged[5,6]. While the precise mechanism is not fully understood, MG and its treatments can influence myocardial and coronary function through different pathways, causing patients to be at risk of cardiovascular events.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of intraoperative coronary spasm in a patient with MG who underwent thymectomy. Our case had several risk factors for CAS, including cigarette smoking and atherosclerotic coronary artery disease. He also suffered from coronary spasm after traumatic cervical spine injury. He was diagnosed with MG and administered anticholinergic and intravenous immunoglobulin treatments. Thus, we cannot simply attribute the cause to a single factor. In our case, high-quality cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation and successful ECMO cannulation were crucial, and the patient recovered without complications. A previous study announced that prophylactic coronary vasodilators may bring benefits that reduce the risk of CAS[7]. To avoid noxious stimuli, an adequate anesthesia depth is necessary. The epidural catheter technique is widely used in thymectomy as an effective analgesia method. However, it can also induce coronary spasm, so the risks and benefits need to be determined[2,8]. We suggest that sugammadex should be used for the reversal of neuromuscular function if postoperative extubation is indicated. In summary, the potential risk of cardiovascular events should be taken into consideration for patients with MG undergoing surgery.
In past literature reviews, an association between MG and CAS has been reported. Patients with these conditions often present with chest pain. However, when MG is combined with thymoma, surgical intervention is frequently required. Diagnosing CAS under general anesthesia can be very challenging. Our case report presented a particularly devastating CAS that necessitated the use of ECMO and an intra-aortic balloon pump. We identified severe heart failure using transesophageal echocardiography and promptly closed the surgical incision to transfer the patient to the catheterization room for further treatment. Reflecting on this case, we propose an appropriate anesthesia plan, including proactive pain management, prophylactic coronary vasodilators, and always keeping the possibility of such complications as a differential diagnosis. Further research is needed to explore this complex relationship in the future.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Corresponding Author's Membership in Professional Societies: Taiwan Society of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia, 0022.
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: Taiwan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Liu YC, China S-Editor: Lin C L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Lin C
| 1. | Pasupathy S, Tavella R, Beltrame JF. Myocardial Infarction With Nonobstructive Coronary Arteries (MINOCA): The Past, Present, and Future Management. Circulation. 2017;135:1490-1493. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 100] [Cited by in RCA: 125] [Article Influence: 17.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Koshiba K, Hoka S. Clinical characteristics of perioperative coronary spasm: reviews of 115 case reports in Japan. J Anesth. 2001;15:93-99. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Suzuki S, Utsugisawa K, Yoshikawa H, Motomura M, Matsubara S, Yokoyama K, Nagane Y, Maruta T, Satoh T, Sato H, Kuwana M, Suzuki N. Autoimmune targets of heart and skeletal muscles in myasthenia gravis. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:1334-1338. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 126] [Cited by in RCA: 144] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Yanagihashi M, Okamoto R, Morioka H, Sawada M, Matsumoto S, Ikeda T, Kano O. Coronary spastic angina after the administration of intravenous immunoglobulin in myasthenia gravis: a case report. BMC Neurol. 2020;20:319. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Sato K, Kaikita K, Nakayama N, Horio E, Yoshimura H, Ono T, Ohba K, Tsujita K, Kojima S, Tayama S, Hokimoto S, Matsui K, Sugiyama S, Yamabe H, Ogawa H. Coronary vasomotor response to intracoronary acetylcholine injection, clinical features, and long-term prognosis in 873 consecutive patients with coronary spasm: analysis of a single-center study over 20 years. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e000227. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 119] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Ishii M, Kaikita K, Sato K, Tanaka T, Sugamura K, Sakamoto K, Izumiya Y, Yamamoto E, Tsujita K, Yamamuro M, Kojima S, Soejima H, Hokimoto S, Matsui K, Ogawa H. Acetylcholine-Provoked Coronary Spasm at Site of Significant Organic Stenosis Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients With Coronary Vasospastic Angina. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66:1105-1115. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Kurabayashi M, Okishige K, Asano M, Suzuki H, Shimura T, Iwai S, Kato N, Ihara K, Aoyagi H, Isobe M. Cardiopulmonary arrest caused by coronary spasm after coronary vasodilator withdrawal during the peri-operative period of gastrectomy. Intern Med. 2013;52:81-84. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Easley RB, Rosen RE, Lindeman KS. Coronary artery spasm during initiation of epidural anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2003;99:1015-1017. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |