Published online Nov 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8022
Peer-review started: July 9, 2023
First decision: August 30, 2023
Revised: October 10, 2023
Accepted: October 30, 2023
Article in press: October 30, 2023
Published online: November 26, 2023
Processing time: 138 Days and 2.4 Hours
Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-like Nodules (MPMNs) are rare benign pul
A 70-year-old women was admitted to our institution with feeling sour in her back and occasional cough for more than 2 mo. Computerized electronic scanning scan and 3D reconstruction images in our institution showed there were multiple ground-glass nodules in both of her two lungs. The biggest one was in the apicoposterior segment of left upper lobe, about 2.5 mm × 9 mm in size. We performed thoracoscopic resection of the left upper lung apicoposterior segment of the patient, and the final pathological report was minimally invasive adenocarcinoma. Re-examination of high resolution computed tomography 21 mo after surgery showed multiple ground-glass nodules in both lungs, and a new ground-glass nodule was found in the superior segment of the right lower lobe. We took pathological biopsy of the right upper lung and right lower lung nodules for the patient under thoracoscopy. The histomorphology of the right lower lobe nodule showed multiple lesions in the lung tissue, and the small foci in the alveolar septum were distributed in mild form of the aggregation of short spindle cells. The immunohistochemistry showed that the lesion was epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) (+), somatostatin receptor 2a (SSTR2a) (+), S-100
The imaging manifestations of MPMNs are atypical, histomorphology and immunohistochemistry can assist in its diagnosis. This article reviews the relevant literature of MPMNs immunohistochemistry and shows that MPMNs are positive for EMA, SSTR2a, and progesterone receptor.
Core Tip: Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-like Nodules (MPMNs) are rare benign pulmonary nodules, which have a higher detection rate in lung tissues of patients with lung malignant diseases. The diagnosis of MPMN is difficult and often results in unnecessary or inappropriate treatment. Therefore, it is particularly important to correctly identify and diagnose the disease. This article reports a 70-year-old female patient with pulmonary adenocarcinoma combined with MPMNs and reviews of the relevant literature in order to better identify and diagnose MPMN.
- Citation: Ruan X, Wu LS, Fan ZY, Liu Q, Yan J, Li XQ. Pathological diagnosis and immunohistochemical analysis of minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(33): 8022-8029
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i33/8022.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i33.8022
Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules (MPMNs) are rare benign pulmonary nodule, which is often found accidentally in pathological specimens after surgical resection or autopsy due to other lung diseases[1,2]. Studies have shown that MPMNs are common in women, especially elderly women[3]. MPMNs are often manifested as single or multiple small lung lesions, which can be distributed anywhere in the lungs, and are often found in combination with other lung diseases[4,5]. Unlike benign lung diseases, MPMNs are more likely to be detected in lung malignant tumors, and the detection rate in pulmonary adenocarcinoma is higher than other lung diseases[6]. Because the lesions of MPMNs are very small and have no characteristic imaging features, it is difficult to diagnose, or because the imaging appearance is very similar to the misdiagnosis of malignant nodules, unnecessary or inappropriate treatment may be caused[7,8]. Therefore, it is particularly important to correctly identify and diagnose this disease. In this article, we reported a case of lung microinvasive adenocarcinoma with MPMNs, and reviewed the clinical manifestations, imaging features, pathological diagnosis and immunohistochemistry of MPMNs to help better identify and diagnose MPMNs.
Experiencing consistent back pain and an intermittent cough for over two months.
A 70-year-old female patient was admitted to our institution with feeling sour in her back and occasional cough for more than 2 mo. No other special clinical symptoms and signs were complained. Before admission, a computed tomography (CT) scan of her chest revealed multiple pulmonary nodules in both left and right upper lungs. No special treatment was given.
A history of hypertension, regular oral antihypertensive medication treatment, and well-controlled blood pressure.
Nothing special.
Nothing special.
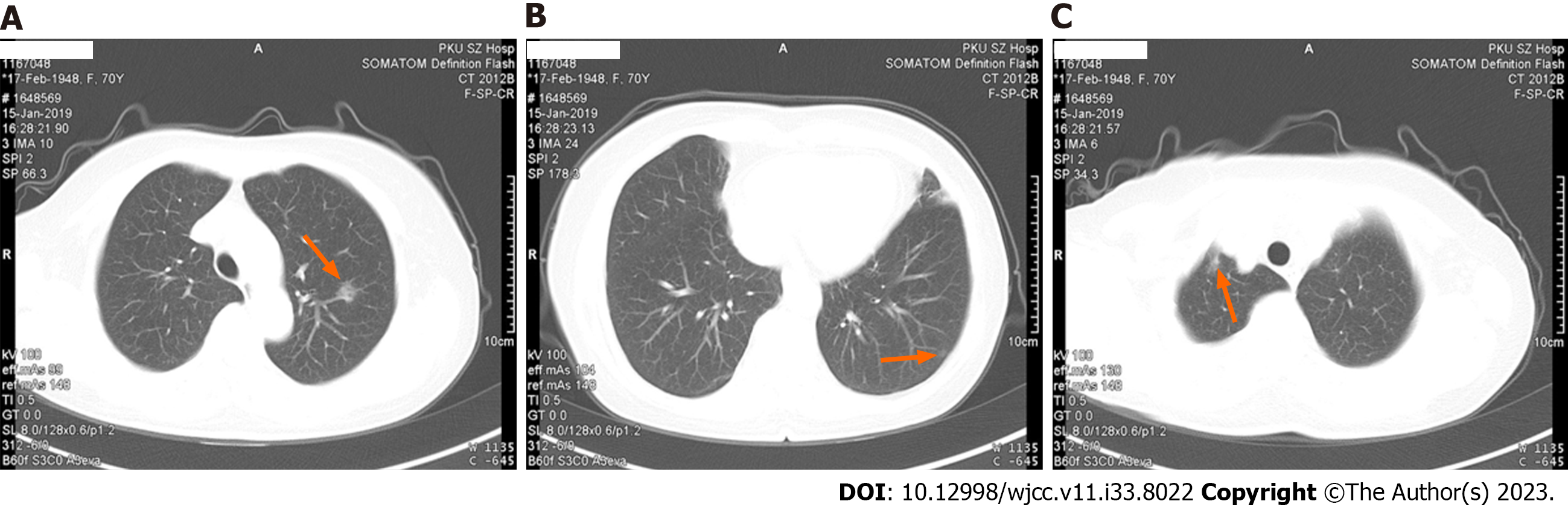
CT scanning scan and 3D reconstruction images showed that there were a ground-glass nodule with rough edges (about 2.5 mm × 9 mm in size) in the apicoposterior segment of left upper lobe, a ground-glass nodule with clear edges (about 6 mm × 4 mm in size) in the lateral basal segment of left lower lobe and ground-glass density shadows were seen in the apex of right lungs, with blurred edges, and the range was approximately 9 mm × 6 mm (Figure 1).
We performed thoracoscopic resection of the left upper lung apicoposterior segment of the patient. During the operation, the rapid freezing pathology suggested that the carcinoma in situ was accompanied by multifocal microinfiltration. Thus, we performed preventive dissection of the mediastinum and hilar lymph nodes for pathological examination. Postoperative pathological report was Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma, no metastatic in each group of lymph nodes.
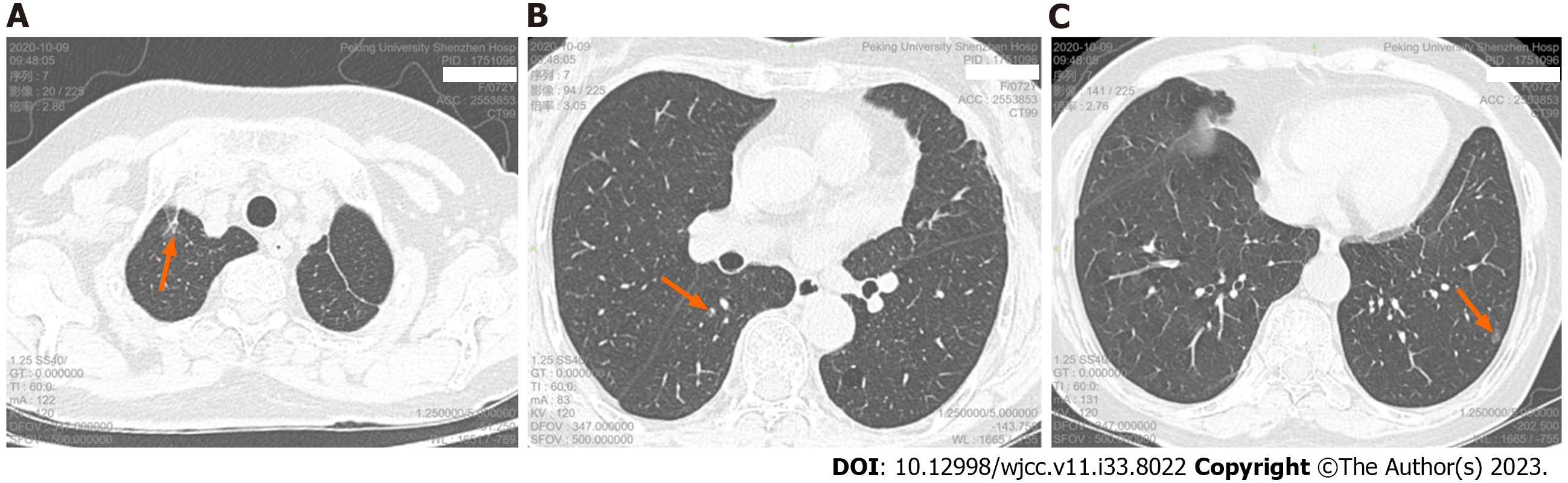
Re-examination of chest CT scan and high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) 21 mo after surgery showed: postoperative changes in the left upper lung, a pure ground-glass nodule in the apical segment of the right upper lobe (about 13.2 mm × 5.6 mm in size), a mixed ground glass in the superior segment of the right lower lobe Nodules (about 4.3 mm × 2.9 mm in size), a pure ground-glass nodule in the lateral basal segment of the left lower lobe (about 7.2 mm × 5.3 mm in size) (Figure 2), and there are other ground-glass nodules about 2-4 mm in diameter in the lower lobe of both lungs. We took pathological biopsy of the right upper lung and right lower lung lesions for the patient under thoracoscopy.
The histological findings of the right upper lobe nodule showed that cancer cells grew in a monolayer, with large nuclei, rich cytoplasm, mitotic figures were not easy to see, focal septal widening, interstitial fiber and fibroblast proliferation, dense proliferation or clustered proliferation of tumor cells, nucleoli was visible.
The immunohistochemistry experimental protocol for this project comprises the following key steps: Sample fixation, dehydration, paraffin embedding, sectioning, antibody staining, and result analysis. Firstly, tissue samples are subjected to fixation, followed by dehydration and paraffin embedding to prepare paraffin sections. Subsequently, specific antibodies such as CK7, thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1), and EMA are used for staining, followed by microscopic observation and image recording. Finally, result analysis and pathological diagnosis are conducted based on the staining outcomes. Immunohistochemistry experiments are a crucial step in the study, utilized to identify immune markers, thereby supporting accurate disease diagnosis and classification.
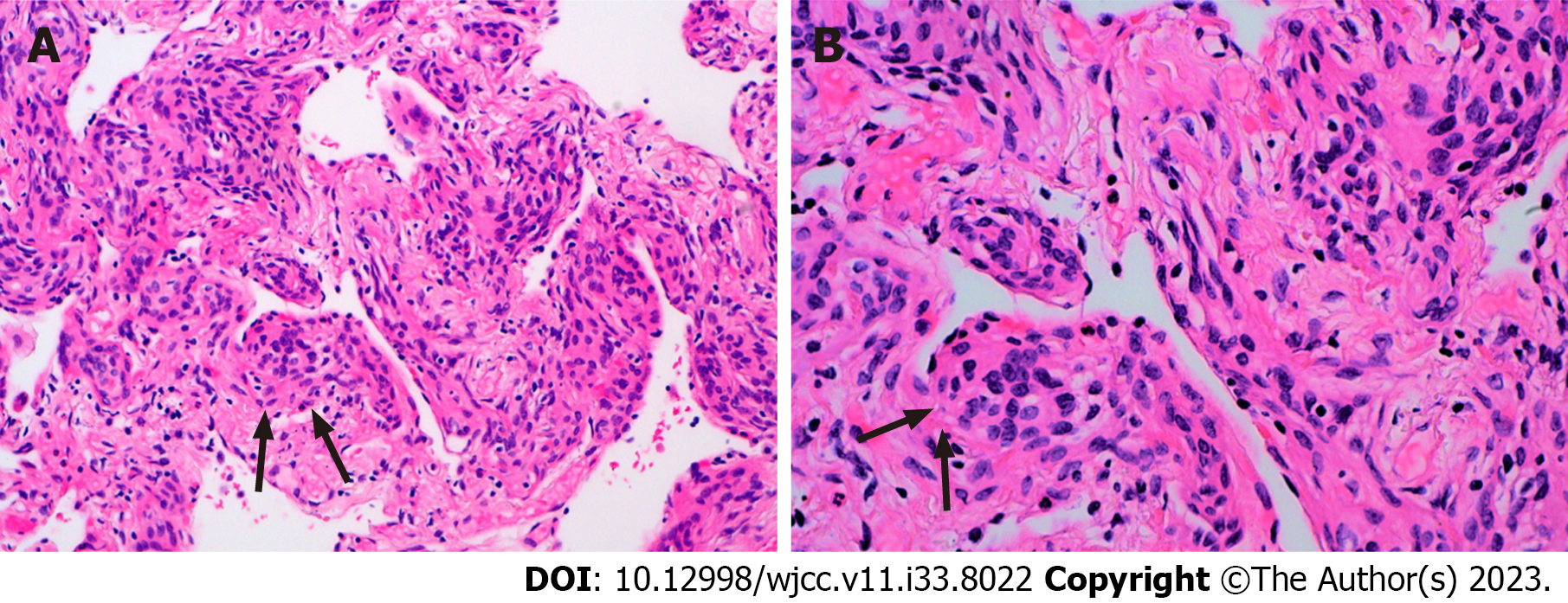
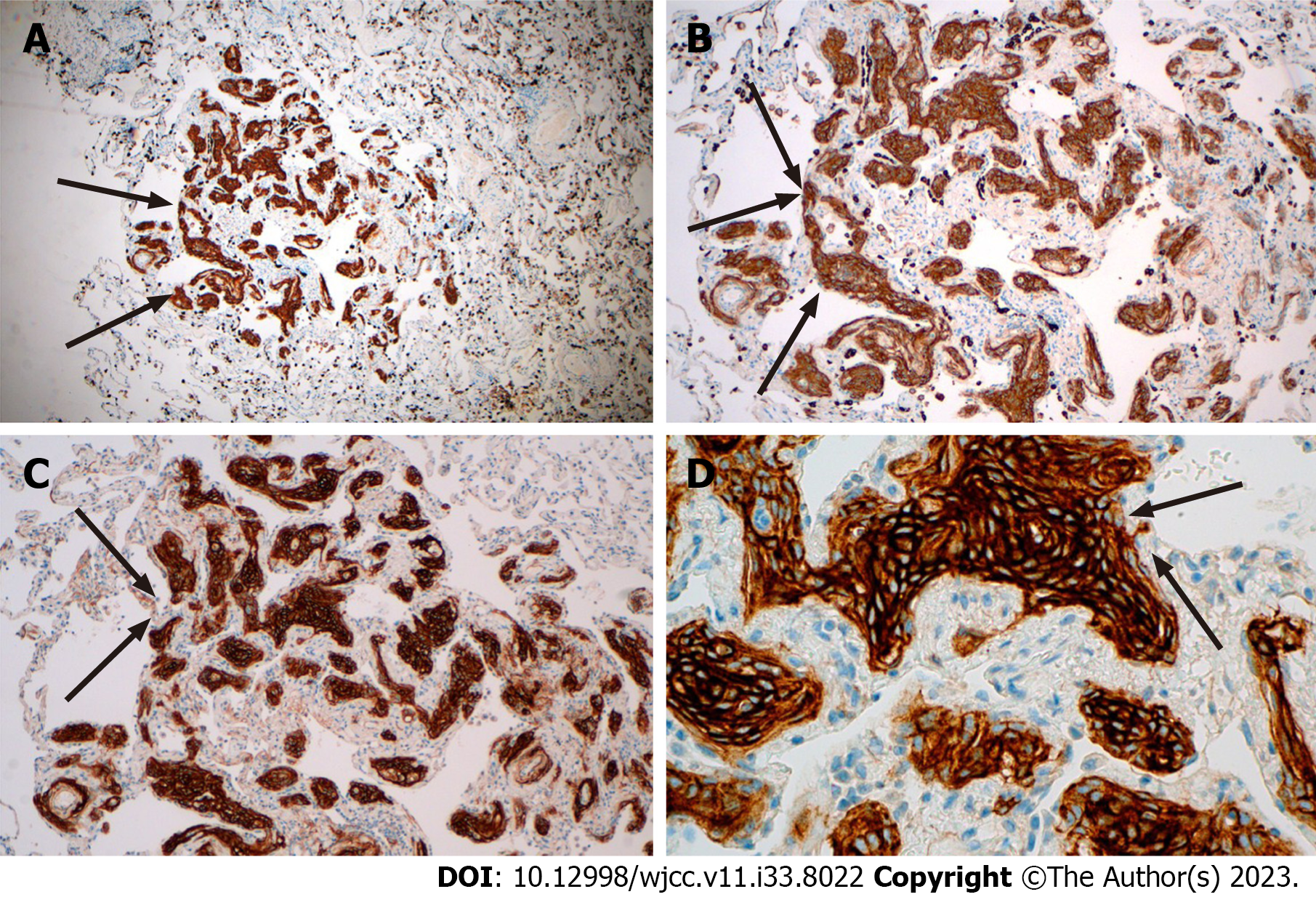
The pathological manifestation of the right lower lobe nodule was no obvious nodule was visible to the naked eye. Histomorphology showed multiple lesions in the lung tissue, with diameter of 0.5-1.8 mm, and the small foci in the alveolar septum were distributed in mild form of the aggregation of short spindle cells (Figure 3). And the Immunohistochemistry showed that the lesion was positive for Epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) and somatostatin receptor 2a (Figure 4), and negative for S-100, Chromogranin A (CgA), Synaptophysin (Syn), Cytokeratin (CK) and HMB-45.
The pathological diagnosis was Micro-invasive Adenocarcinoma with Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-like Nodules.
We recommend that patients continue to receive treatment after surgery and to do regular follow-up observations.
The patient recovered after operation, and no recurrence was found after 3 mo.
MPMNs, fist describe by Korn et al[9] in 1960, who considered they might be kinds of endocrine tumor called Minute Pulmonary Chemodectoma based on its cytologic characteristics, arrangement of cells and special relationship to vessels, have been considered to be benign lung lesions. Therefore, Gaffey et al[10] renamed it as "Minute Pulmonary Meningo
The immunohistochemistry markers selected for this project include CK7, TTF-1, and EMA, which play crucial roles in pathological diagnosis. CK7 is a cytokeratin commonly expressed in epithelial cells, particularly in tissues like the lung, stomach, and biliary tract, making it highly useful for determining the epithelial origin of tumor cells. TTF-1 is a nuclear transcription factor, highly expressed in normal lung tissue, and frequently found in lung adenocarcinomas, aiding in distinguishing lung cancer from other malignancies. EMA is a membrane-bound antigen specific to epithelial cells, providing valuable assistance in confirming epithelial lesions. The selection of these immunohistochemistry markers is based on their specific expression in lung and epithelial cells, aiding in the identification and classification of MPMNs. Immunohistochemistry experiments rely on the specificity of these markers, assisting in determining pathological types, guiding treatment strategy selection, and providing critical insights into disease progression and prognosis. Therefore, immunohistochemistry plays an indispensable role in MPMN pathological diagnosis, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and precision in clinical management.
The diagnosis of MPMNs needs to be confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Table 1 shows the literature review of MPMNs immunohistochemistry[20]. We can see that almost all MPMNs immunohistochemically showed positive responses to Vimentin, EMA, SSTR-2a, and CD56, and more than half of MPMNs were positive to PR; while negative for S-100, CK, Actin, HMB- 45. Syn and Cga. For NSE, the study[21] found that almost all MPMNs were weakly positive for NSE, but they believed that this behavior was non-specific because normal alveolar epithelium was also weakly positive for the antigen. The source of MPMNs is still unclear. They may come from reactive rather than neoplastic origin. At present, most studies believe that there are similarities between pulmonary meningeal epithelioid nodules and meningiomas in their histological, ultrastructural and immunohistochemical characteristics[22]. According to the research of Higuchi et al[23], both MPMNs and meningioma of the central nervous system may be related to the ectopic or deletion of neurofibromatosis type-2 gene, indicating that they may have a common genetic changes. However, a genotypic comparison between MPMNs and meningiomas showed that MPMNs lacked the molecular changes associated with loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 22 in meningioma cells. Imaging examination of the heads of most patients with MPMNs did not find signs of meningioma in some studies, indicating that it is not a metastasis of meningioma. At present, most studies believe that it is very similar to meningeal epithelial cells or meningioma cells. Multiple studies have shown that almost all MPMNs are positive for Vimentin and EMA phenotypes, which are very similar to meningeal epithelial cells or meningioma cells. Almost all MPMNs were positive for progesterone receptors and they believed that this once again proved the similarity between MPMNs and meningeal epithelial cells or meningioma cells, because progesterone receptors are in normal meningeal epithelial cells and the expression in meningiomas has been well confirmed, and it is believed that there might be lung meningeal epithelioid cells in normal lung tissues, while progesterone probably played an important role in controlling their growth. In addition, the retrospective analysis of the immunophenotypes of MPMNs including SSTR-2a, and found that all MPMNs lesions expressed constant expression of SSTR-2a, which once again proved MPMNs immunohistochemical characteristics similar to meningeal epithelial cells.
| Ref. | Number of nodules/lesions evaluated | Immunophenotype | |||||||||||
| EMA | VIM | PR | CD56 | SSTR2a | CK | Syn | Actin | S100 | HMB-45 | NSE | CgA | ||
| Bernabeu et al[13], 2013 | 1 | 1/0a | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 | – | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | – | 0/1 | – | 0/1 |
| Lee et al[18], 2013 | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 | – | 0/1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Tao et al[4], 2019 | 39 | 29/10 | – | 11/28 | – | 39/0 | 0/39 | 0/39 | – | 0/39 | – | – | 0/39 |
| Niho et al[6], 1999 | 29 | 22/0b | 29/0 | 9/9 | – | – | 0/29 | 2/27 | – | 10/11 | 0/28 | 25/4 | 1/28 |
| Pelosi et al[21], 2002 | 9 | 9/0 | 9/0 | 9/0 | – | – | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/6 | – | – |
| Peng et al[8], 2019 | 8 | 7/0 | 8/0 | 6/0 | – | – | 0/2 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Agozzino et al[19], 2006 | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 0/1 | – | – | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | – | 0/1 | 0/1 |
| Kfour et al[20], 2012 | 2 | 2/0 | 2/0 | 2/0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Torikata et al[5], 1990 | 24 | 0/18 | 24/0 | – | – | – | 0/17 | – | 0/21 | 0/16 | – | 0/17 | – |
| Gaffey et al[10], 1988 | 14 | 12/2 | 10/2 | – | – | – | 0/14 | – | 0/7 | 0/14 | – | 0/14 | – |
| Harada et al[7], 2019 | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Total | 129 | 85/30 | 86/2 | 40/38 | 3/0 | 39/0 | 0/110 | 2/74 | 0/36 | 10/87 | 0/35 | 25/36 | 1/68 |
In terms of treatment, MPMNs are benign lesions and can be treated conservatively, with long-term follow-up without further intervention. The study of Lin et al[24] found that patients with MPMNs surgically removed can get a good prognosis, but they believe that compared with the trauma of surgery, long-term follow-up observation may benefit more. However, MPMNs often appear along with other lung diseases. Therefore, it is particularly important to detect and identify their accompanying diseases in time and carry out corresponding clinical interventions. In general, the clinical manifestations of MPMNs are not typical. Image characteristics show single or multiple ground-glass nodules in the lungs with a diameter of no more than 10mm. Pathological biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosis. Immunohistochemically showes positive for Vimentin, EMA, SSTR-2a, CD56, PR, but negative for S-100, CK, Actin, HMB-45, Syn, and Cga. Its source is currently unclear, but most studies currently believe that it is similar to meningeal epithelial cells or meningioma cells. MPMNs are benign lesions and can be treated conservatively, but they often appear along with other lung diseases. Therefore, timely detection and identification of MPMNs and their accompanying diseases, and corresponding clinical interventions are also particularly important.
Through a comprehensive pathological diagnosis and immunohistochemical analysis of one case of MPMNs, we delved into the characteristics of this rare condition. The results demonstrated a certain diversity in immunohistochemical markers for MPMNs, with CK7, TTF-1, and EMA playing crucial roles in pathological diagnosis. Literature review further supported our findings. In conclusion, the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of MPMNs remain challenging and require the integration of various clinical and immunohistochemical information to ensure accurate diagnosis and selection of treatment strategies. This study provides valuable insights and references for the clinical management of MPMNs.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Pathology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Alkhatib AJ, Jordan S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Asakawa A, Horio H, Hishima T, Yamamichi T, Okui M, Harada M. Clinicopathologic features of minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2017;25:509-512. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Mizutani E, Tsuta K, Maeshima AM, Asamura H, Matsuno Y. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: clinicopathologic analysis of 121 patients. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:678-682. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Arafah MA, Raddaoui E, Alsheikh A, Hajjar WM, Alyousef F. Mimicry of sugar tumor and minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule to metastatic lung deposits in a patient with rectal adenocarcinoma. Ann Saudi Med. 2013;33:400-403. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Tao L, Chen Y, Huang Q, Yong J, Yan S, Huang Y. Constant expression of somatostatin receptor 2a in minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules. J Clin Pathol. 2019;72:525-528. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Torikata C, Mukai M. So-called minute chemodectoma of the lung. An electron microscopic and immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1990;417:113-118. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Niho S, Yokose T, Nishiwaki Y, Mukai K. Immunohistochemical and clonal analysis of minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules. Hum Pathol. 1999;30:425-429. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Harada M, Aono Y, Yasui H, Uto T, Sato J, Imokawa S, Suzuki S, Tanioka F, Suda T. Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-like Nodules Showing Multiple Ring-shaped Opacities. Intern Med. 2019;58:3149-3152. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Peng XX, Yan LX, Liu C, Wang SY, Li WF, Gao X, Wei XW, Zhou Q. Benign disease prone to be misdiagnosed as malignant pulmonary nodules: Minute meningothelioid nodules. Thorac Cancer. 2019;10:1182-1187. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | KORN D, BENSCH K, LIEBOW AA, CASTLEMAN B. Multiple minute pulmonary tumors resembling chemodectomas. Am J Pathol. 1960;37:641-672. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Gaffey MJ, Mills SE, Askin FB. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules. A clinicopathologic study of so-called minute pulmonary chemodectoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988;12:167-175. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kuhn C 3rd, Askin FB. The fine structure of so-called minute pulmonary chemodectomas. Hum Pathol. 1975;6:681-691. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Churg AM, Warnock ML. So-called "minute pulmonary chemodectoma": a tumor not related to paragangliomas. Cancer. 1976;37:1759-1769. [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 13. | Bernabeu Mora R, Sánchez Nieto JM, Hu C, Alcaraz Mateos E, Giménez Bascuñana A, Rodríguez Rodríguez M. Diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis diagnosed by transbronchial lung biopsy. Respiration. 2013;86:145-148. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Alkurashi AK, Almodallal Y, Albitar HAH, Cheville JC, Iyer VN. Diffuse Pulmonary Meningotheliomatosis: A Rare Lung Disease Presenting with Diffuse Ground-Glass Opacities and Cavitation. Am J Case Rep. 2020;21:e926172. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Kuroki M, Nakata H, Masuda T, Hashiguchi N, Tamura S, Nabeshima K, Matsuzaki Y, Onitsuka T. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: high-resolution computed tomography and pathologic correlations. J Thorac Imaging. 2002;17:227-229. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Sellami D, Gotway MB, Hanks DK, Webb WR. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: thin-section CT appearance. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2001;25:311-313. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Kraushaar G, Ajlan AM, English JC, Müller NL. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: a case of incidentally detected diffuse cystic micronodules on thin-section computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010;34:780-782. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Lee SK, Kim GJ, Kim YJ, Leem AY, Hwang ED, Kim SK, Chang J, Kang YA, Kim SY. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules simulating hematogenous lung metastasis: a case report. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2013;75:67-70. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Agozzino M, Inzani F, Cavallero A, Arbustini E, Meloni F, Oggionni T, Dore R, D'Armini A, Viganò M. Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules in the transbronchial biopsy of a lung transplant recipient. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2006;25:148-150. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Kfoury H, Arafah MA, Arafah MM, Alnassar S, Hajjar W. Mimicry of Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-like Nodules to Metastatic Deposits in a Patient with Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Korean J Pathol. 2012;46:87-91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Pelosi G, Maffini F, Decarli N, Viale G. Progesterone receptor immunoreactivity in minute meningothelioid nodules of the lung. Virchows Arch. 2002;440:543-546. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Ionescu DN, Sasatomi E, Aldeeb D, Omalu BI, Finkelstein SD, Swalsky PA, Yousem SA. Pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: a genotypic comparison with meningiomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:207-214. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Higuchi M, Watanabe M, Inoue T, Yamaura T, Suzuki T, Saito M, Niitsuma K, Endo K, Oshibe I, Soeta N, Saito T, Hojo H, Munakata M, Suzuki H. Brief report on similar mutational changes in neurofibromatosis type 2 gene in minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodule and meningioma of the central nervous system. Oncotarget. 2018;9:36012-36016. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Lin D, Yu Y, Wang H, Fang Y, Yin J, Shen Y, Tan L. Radiological manifestations, histological features and surgical outcomes of pulmonary meningothelial proliferation: a case series and rethinking. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020;9:1159-1168. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |