Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7424
Peer-review started: July 10, 2023
First decision: August 30, 2023
Revised: September 14, 2023
Accepted: October 8, 2023
Article in press: October 8, 2023
Published online: October 26, 2023
Processing time: 107 Days and 6.5 Hours
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is characterized by pain as well as sensory, motor, and sudomotor disorders. Generally, it is classified into two types CRPS-I and CRPS-II. There is no single diagnostic test or treatment approach for CRPS, and a multidisciplinary approach is gaining attention to improve patients’ symptoms and their quality of life.
A 35-year-old woman with an unremarkable medical history sought treatment for CRPS at a hospital of Korean medicine. During her first visit, she was wheelchair-bound due to severe pain in her left lower extremity. She had edema and discoloration of the left foot. She was treated with a combination of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) approaches, including acupuncture, moxibustion, pharmacopuncture, and herbal decoction, for approximately 20 sessions. The foot and ankle outcome score (FAOS) and visual analog scale (VAS) score for pain were eva
Combined TCM treatment may be a reasonable and safe option for alleviating symptoms and improving function in patients with CRPS.
Core Tip: A 35-year-old female patient presented with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) characterized by pain, swelling, and discoloration of the left lower extremity, along with difficulty in ambulation. She was treated with combined traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), comprising acupuncture, moxibustion, pharmacopuncture, and herbal medications along with conventional medicine. This treatment strategy achieved sustained, long-term improvements in the patient’s signs and symptoms. TCM is a promising and safe treatment option for patients with CRPS.
- Citation: Shin WC, Kim H, Chung WS. Traditional Chinese medicine for foot pain in a patient with complex regional pain syndrome: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(30): 7424-7431
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i30/7424.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7424
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is characterized by regional pain that is not confined to the boundaries of nerves or dermatomes. CRPS is usually characterized by hyperalgesia, allodynia, and hyperesthesia. It has several major symptoms, including sensory abnormalities, autonomic changes, trophic changes, and motor symptoms[1,2]. Generally, CRPS is categorized into two types: CRPS-I and CRPS-II. In cases of CRPS-I, there is no confirmed nerve injury, whereas CRPS-II is associated with nerve damage[3]. Although CRPS may be caused by dysfunction of the central and peripheral nervous systems due to factors such as inflammation, imbalance in the autonomic system, or autoimmune diseases, its exact pathogenesis is still poorly understood. Owing to its poorly understood pathogenesis, there are no specific diagnostic tests for CRPS; therefore, in clinical practice, it is diagnosed based on the patient’s symptoms and clinical findings. Furthermore, although CRPS is a chronic condition associated with multiple painful symptoms and long-term disability, optimal treatment options are yet to be established. Although several explanations exist, one reason for the difficulty in treating CRPS is that no single pathophysiology can explain the disease process. Despite these difficulties, several treatment strategies have been suggested to alleviate the symptoms of CRPS, including medications, physical and occupational therapies, surgical procedures, and neuromodulation. However, few studies have shown the efficacy of these treatment strategies, and evidence is lacking owing to the paucity of high-quality clinical studies on this condition[4-6].
Recently, a multidisciplinary approach for the management of CRPS has been strongly recommended to improve not only pain but also the quality of life of these patients. Consequently, complementary medicine is gaining attention for the treatment of CRPS. Systematic reviews on the use of acupuncture for the management of CRPS have shown promising effects; however, higher-quality studies are needed to further verify its therapeutic effects[7-9]. Herein, we present the case of a patient diagnosed with CRPS who was treated with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). This article provides a detailed description of the patients’ symptoms, treatment procedures and outcomes.
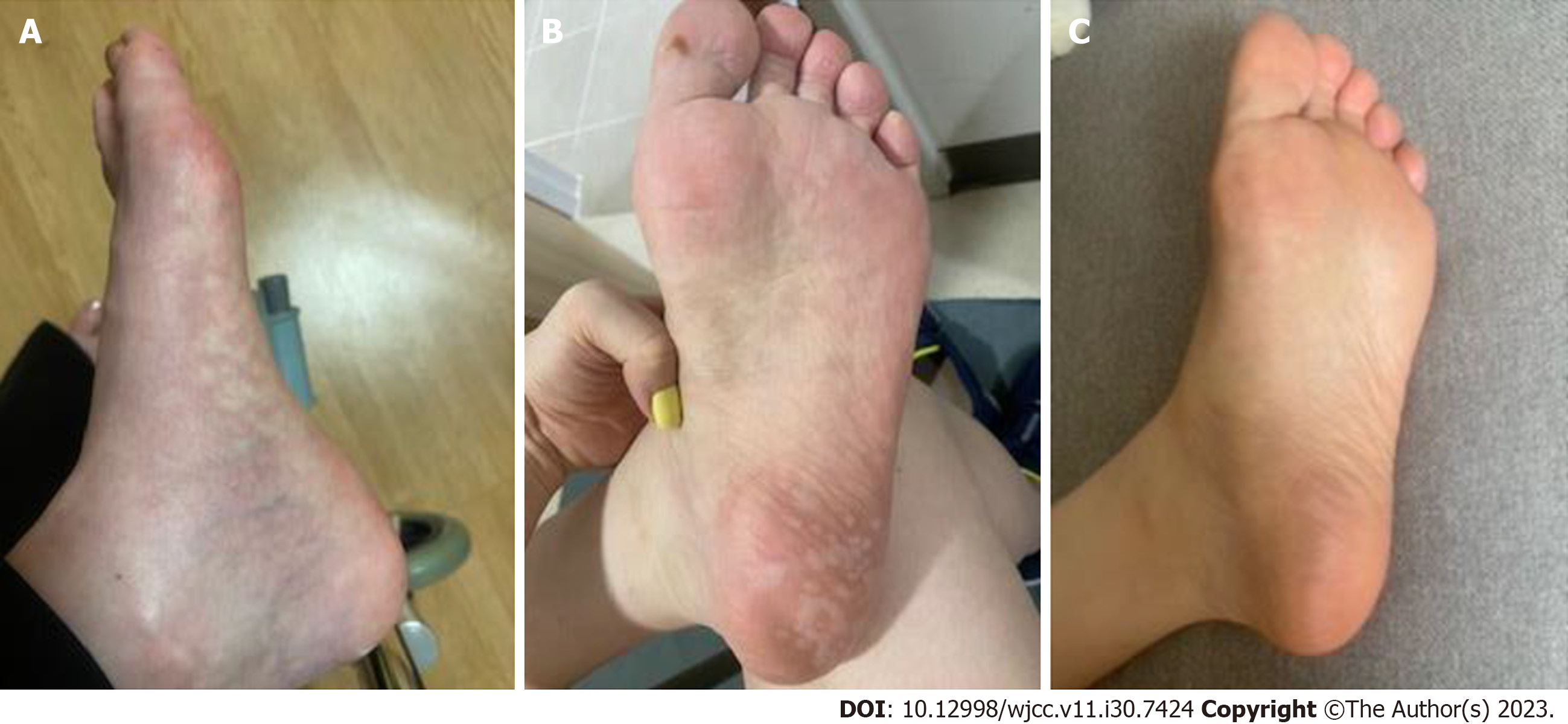
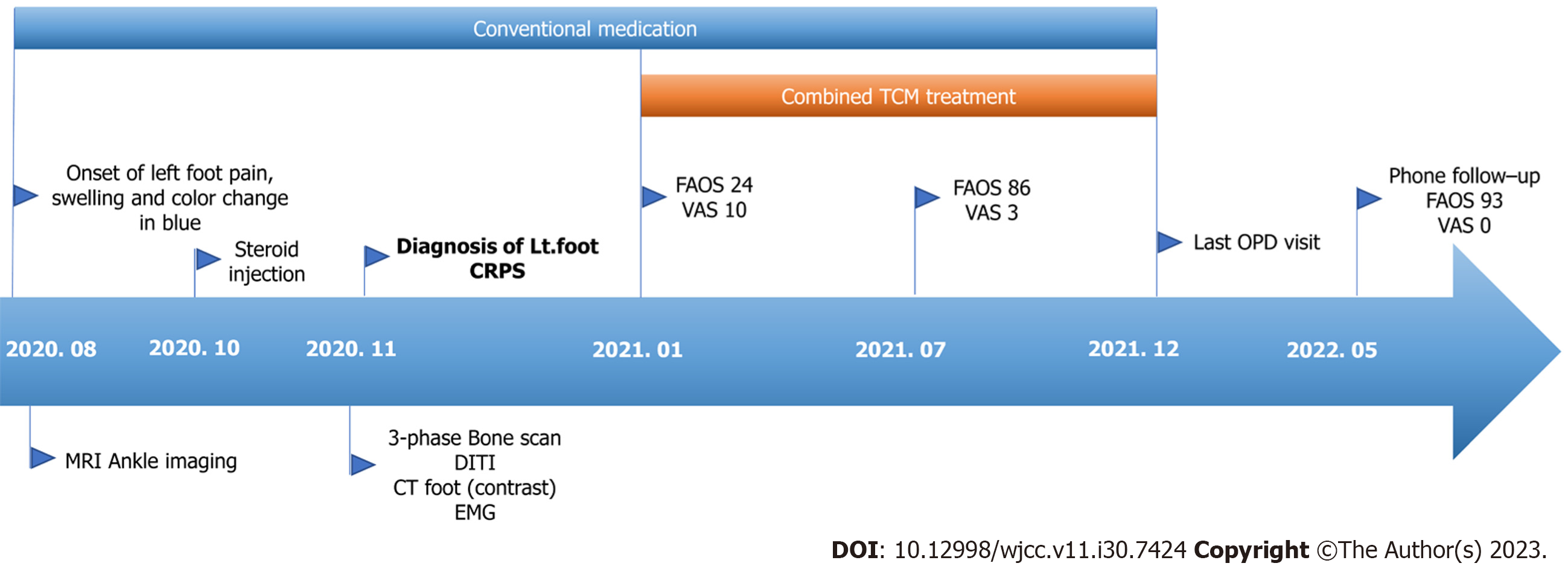
In January 2021, a 35-year-old woman visited the outpatient department (OPD) of a Korean rehabilitation medicine unit in a Korean medicine hospital for the treatment of pain and swelling in the heel and ball of her left foot. The patient was unable to walk at the time of presentation because of pain and swelling. Notably, the left foot showed a bluish skin discoloration (Video, depicting the condition of the foot, was recorded by the patient on November 11, 2020).
The patient sustained an Achilles tendon sprain on August 3, 2020, and was treated with a splint for approximately 1 wk. On August 24, 2020, the patient began experiencing pain in the heel and ball of the left foot, accompanied by redness and swelling; therefore, she visited a rehabilitation clinic in November 2020.
Imaging investigations revealed no bone or soft tissue abnormalities. The doctors diagnosed the patient with CRPS according to the revised diagnostic criteria for CRPS (Budapest criteria) and prescribed steroid injections and medicines, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (celecoxib), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (sulfasalazine), tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline hydrochloride), glucocorticoids (triamcinolone), and anticonvulsants (pregabalin). Although these medications gave the patient some relief, her symptoms still waxed and waned, and she still experienced difficulty while walking. Therefore, the patient visited the Korean Medicine Rehabilitation Clinic for further mana
The patient had no remarkable previous medical history.
The patient had no remarkable personal and family history.
The patient was able to bear only up to 30% of her body weight on the left foot upon presentation. The left ankle had limited range of motion and cutaneous discoloration. In addition, the patient had poor foot and ankle outcome scores (FAOS) of twenty-four.
No specific laboratory findings were noted.
Based on the patient’s previous medical records, an ankle computed tomography (contrast) and magnetic resonance imaging were performed, and these revealed retrocalcaneal bursitis with Haglund deformity, along with pre-Achilles fat pad inflammation. No remarkable findings were revealed by 3-phase bone scan and electromyography, including a sympathetic skin response. Digital infrared thermal imaging revealed no significant findings.
The patient self-reported continuing pain that was disproportionate to any inciting event and showed symptoms in all four categories: Sensory, vasomotor, sudomotor, edematous, motor, and trophic. After several examinations, no other diagnosis could explain the patient’s signs or symptoms; furthermore, there was no evidence of nerve damage. Based on the Budapest criteria, the patient was diagnosed with CRPS-I (Table 1).
| Budapest consensus criteria for the clinical diagnosis of CRPS | Signs and symptoms of the patient | |
| (1) Continuing pain, which is disproportionate to any inciting event | Yes | |
| (2) Report at least one symptom in three of the following four categories | ||
| -Sensory | Reports of hyperesthesia and/or allodynia | Hyperesthesia and allodynia in the left foot |
| -Vasomotor | Reports of temperature asymmetry and/or sweating changes and/or sweating asymmetry | Bluish skin discoloration |
| -Sudomotor/edema | Reports of edema and/or sweating changes | Edema of the left foot |
| -Motor/trophic | Reports of decreased ROM and/or motor dysfunction (weakness, tremor, and dystonia) and/or trophic changes (hair, nail, and skin) | Difficulty in walking and weight bearing in the left foot |
| (3) Display at least one sign at the time of evaluation in two of the four following categories | ||
| -Sensory | Evidence of hyperalgesia and/or allodynia | Hyperalgesia and allodynia in the left foot |
| -Vasomotor | Evidence of temperature asymmetry and/or skin color changes and/or asymmetry | Cyanosis in left foot and asymmetric cutaneous discoloration |
| -Sudomotor/edema | Evidence of edema and/or sweating changes and/or sweating asymmetry | Left foot edema |
| -Motor/trophic | Evidence of decreased ROM and/or motor dysfunction (weakness, tremor, and dystonia) and/or trophic changes (hair, nail, and skin) | Decrease in active ROM during left toe dorsiflexion |
| (4) There is no other diagnosis that better explains the signs and symptoms | Yes | |
The detailed treatment methods are described below. No other treatments were used in the Korean rehabilitation medicine department in addition to the presented therapy.
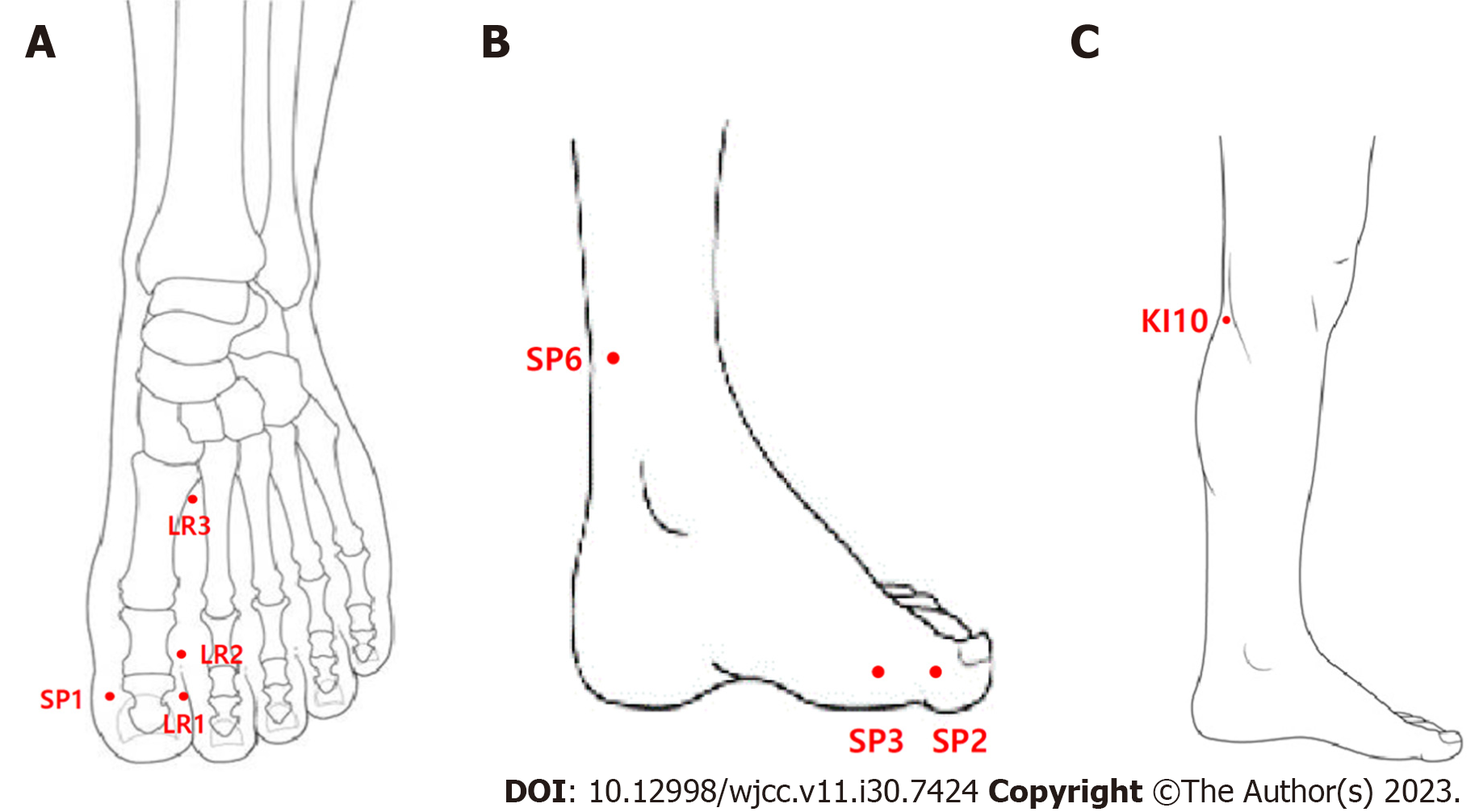
Disposable stainless-steel needles (0.25 mm × 40 mm, DongBang, Acupuncture Inc., Boryung, South Korea) were inserted during the visit to the OPD of the Korean rehabilitation medicine unit at the Korean medicine hospital. Acupuncture needles were inserted at the acupoints SP1, SP2, SP3, SP6, LR1, LR2, LR3, and KI10 (Figure 1). Infrared therapy was combined with acupuncture above the treatment site for the entire treatment session. The physiological effects of infrared rays include the enhancement of local blood flow, anti-inflammatory effects, effects on the autonomic nervous system, promotion of wound healing, and healing of damaged nerve tissues. Therefore, infrared rays are frequently used to treat pain and ischemic disease[10]. Acupuncture and infrared therapy were administered twice weekly.
Moxibustion is a TCM treatment that uses moxa (folium artemisiae argyi or mugwort) cautery at the acupoint. The effects of moxibustion have been studied in several diseases, including gastrointestinal and musculoskeletal disorders. Moxibustion exerts a therapeutic effect through three main stimuli: Heat, radiation, and the pharmacological actions of moxa and its combustion products[11]. A small amount of moxa (grain-size) was primarily placed at the LR2 acupoint. The treatment was administered twice weekly along with acupuncture.
Pharmacopuncture is a new form of therapy derived from a combination of herbal medicine and acupuncture, in which herbal extracts are used as a stimulus measure at the meridian point[12]. Panax Ginseng (P. ginseng) pharmacopuncture distilled from P. ginseng was injected at acupoint LR2 at a dose of 0.1-0.2 cc. Pharmacopuncture was administered twice weekly.
Two types of herbal decoction were used in accordance with TCM theories (Table 2).
| Name | Formula | Dose-length |
| Baekhaoleejung-tang | Cynanchi Wilfordii Radix, Cinnamomi Ramulus, Zingiberis Rhizoma, Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba, Paeoniae Radix, Citri Unshius Pericarpium,Glycyrrhizae, Radix et Rhizoma | January 2 to 12 (11 d) |
| Hyangsayangwi-tang | Ginseng Radix, Paeoniae Radix, Pinelliae Tuber, Citri Unshius Pericarpium, Crataegi Fructus, Amomi Fructus Rotundus, Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba, Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma, Cyperi Rhizoma, Zingiberis Rhizoma, Amomi Fructus, Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens, Zizyphi Fructus | February 16 to 25 (10 d) |
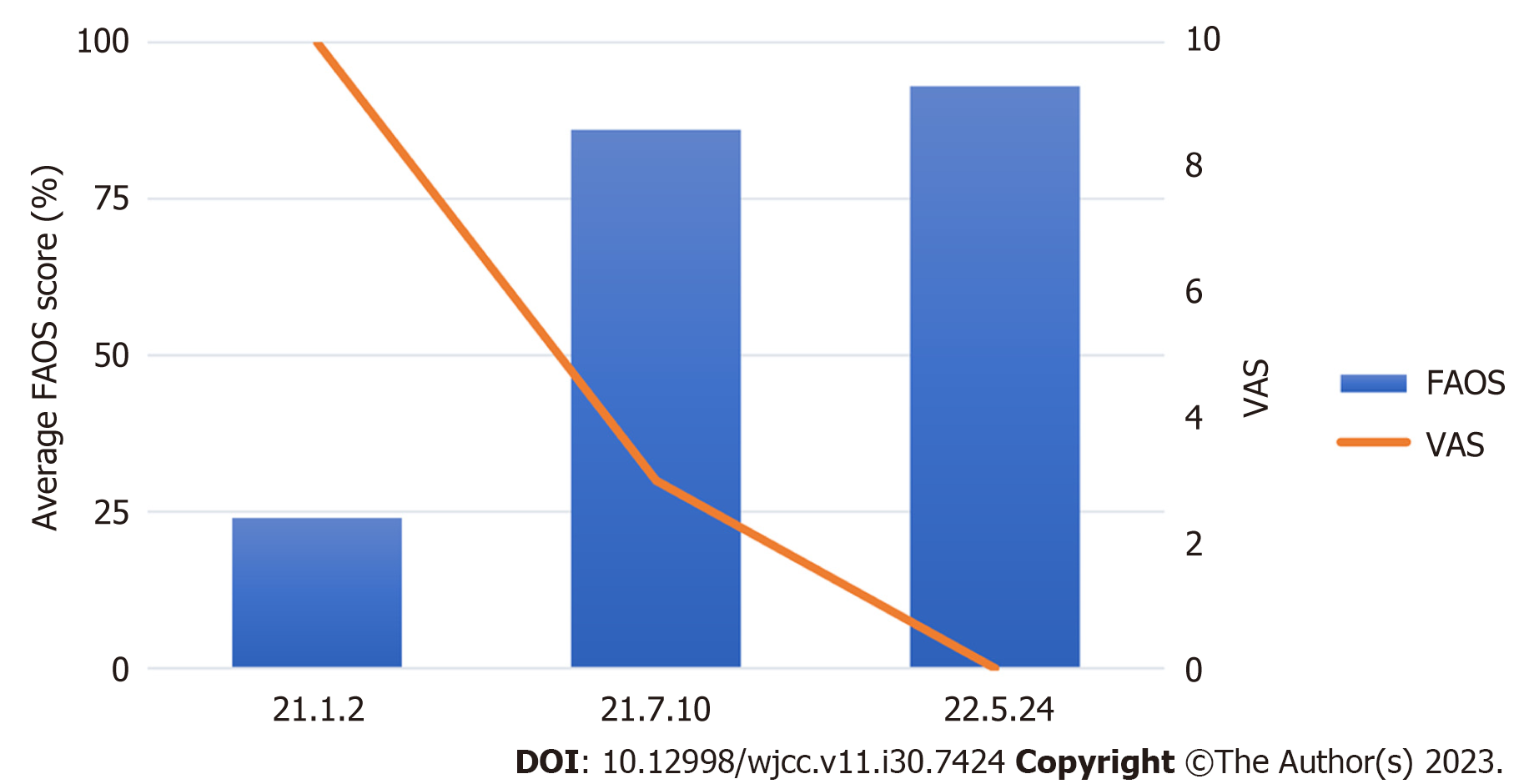
Starting from January 2, 2021, the patient was treated twice a week with acupuncture, pharmacopuncture, moxibustion, and herbal decoctions at the OPD. The FAOS and visual analog scale (VAS) were used to evaluate overall pain, function, and quality of life. The FAOS, which comprises five subscales: Pain, other symptoms, function in daily living, function in sports and recreation, and foot- and ankle-related quality of life, was also used to evaluate various foot- and ankle-related problems. The percentage score for the FAOS was calculated using a website program (https://orthotoolkit.com/faos/). The FAOS and VAS scores were assessed twice throughout the treatment, and phone follow-up was conducted 5 mo after the last visit (December 11, 2021). The percentage score for FAOS improved and was maintained at follow-up. The VAS score for pain decreased from 10 to 3, and at the phone follow-up, the VAS score for pain was 0 (Figure 2). The patient’s walking ability was also assessed during treatment. During the patient’s first visit, she arrived in a wheelchair because unaided walking was impossible due to excessive pain. After 2 mo of treatment, ambulation with the aid of a cane was possible for 30 min, and after 2 more months of treatments (a total of 4 mo of treatment), the patient was able to walk without a cane for approximately 10 min. Finally, at the end of treatment, the patient could walk unaided for up to 3 h. At follow-up, the patient had no ambulation symptoms. Additionally, the swelling and discoloration of the left foot resolved (Figure 3). No adverse events were observed during the treatment. The timeline of the case report is shown in Figure 4.
CRPS is a disorder that usually affects the distal limbs and can significantly lead to the deterioration of the quality of life of patients due to several symptoms, mostly pain. Given the uncertainty and complexity of its pathophysiology, optimal diagnostic tests and treatment methods are yet to be established. Although the exact pathology of CRPS remains unclear, most researchers agree that it involves multiple mechanisms, including peripheral and central sensitization, and neurogenic inflammation.
In this case, prior to combined TCM treatment, the patient received conventional medications and injection therapy at several medical clinics, but did not experience distinct improvement; moreover, the pain and disability persisted. Combined TCM treatment with acupuncture, moxibustion, pharmacopuncture, and herbal decoction significantly reduced pain and resolved the left foot swelling and discoloration, along with functional improvements. TCM treatment for CRPS has been reported in several studies with a focus on acupuncture[7,8]. Compared to other TCM treatments, the curative effect of acupuncture and its mechanisms have been thoroughly studied[13]. Acupuncture exerts its analgesic effect via the local specificity of acupoints, anti-inflammatory effects, and comprehensive neurophysiological mechanisms in the spinal cord and brain, which comprise the descending pain modulation system and the brain region relevant to pain modulation. These mechanisms are mediated by multiple transmitters and modulators, including endogenous opioids, cholecystokinin, serotonin, noradrenaline, dopamine, glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid, acetylcholine, and orexin A[14,15]. Additionally, acupuncture can aid chronic pain by altering pain perception in the central nervous system through the modulation of endogenous opioids, serotonin, and norepinephrine[16]. Another advantage of acupuncture is that it has relatively few adverse effects and has been proven safe in several studies[17]. This overall mechanism may explain the therapeutic effects of acupuncture in patients with CRPS.
Several diagnostic criteria have been proposed to define and diagnose CRPS, one of which classifies it into two subgroups, cold and warm[18]. The cold type is associated with decreased skin temperature and cutaneous discoloration (usually a bluish discoloration), which are suggestive of a vasomotor disorder. The patient in this report complained of pain in the left foot and edematous changes associated with bluish skin discoloration, which fulfilled the criteria for cold-type CRPS. Moxibustion, one of the main methods of TCM treatment, usually exerts its therapeutic effect through thermal stimulation, thereby stimulating blood circulation[19]. Moxibustion has been used to treat various diseases, including chronic pain-associated symptoms, and has shown analgesic effects in various pain models[20]. Its analgesic effect is predicted to occur through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediators. While the warm type of CRPS is conventionally associated with the inflammatory mechanism, one study has shown no significant difference between the warm and cold type CRPS on inflammatory mediator[21]. Among the moxibustion techniques, grain-sized moxibustion involves lighting a moxa at an acupoint or a specific area of the body for a few seconds and subsequently removing it to prevent skin burning. Recent studies have reported that grain-sized moxibustion has better therapeutic effects on inflammatory pain and significantly reduces the level of pro-inflammatory mediators[22]. Therefore, grain-sized moxibustion could be a favorable and safe treatment option, particularly for cold-type CRPS.
Pharmacopuncture is a novel treatment that combines the effects of acupuncture and herbal medicine. The pharmacopuncture used in this case consisted of P. ginseng, also known as Asian or Korean ginseng. P. ginseng is primarily used as a tonic in traditional medicine to boost various functions. Additionally, ginsenosides, the main active components of P. ginseng, are known for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects[23]. A recent study reviewed the mechanism of action of P. ginseng at the systemic level using network pharmacology, and concluded that P. ginseng influences blood circulation and immune system processes. In terms of disease, P. ginseng is effective in the treatment of ischemia- and pain-related diseases. Therefore, P. ginseng pharmacopuncture may relieve pain and vasomotor disorders in patients with CRPS.
This case report had several limitations. Because of the combination of treatments, it is difficult to clearly distinguish the effects of individual treatments. It is also not possible to determine whether the effects observed are due to the simple sum of the treatments or the amplification of the treatments. Further clinical trials are needed to compare the effects of individual treatments on CRPS. Second, the administration of conventional medications was continued during TCM treatment. Therefore, although significant improvements were seen after the utilization of TCM treatments, the therapeutic effects observed cannot be conclusively judged to be the effects of TCM alone; however, the effects observed could be the combined or cumulative therapeutic effects of conventional and complementary medicine. Moreover, this was a single case report, and further large, high-quality clinical trials are needed to investigate the effects of TCM treatment on CRPS. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report on the treatment effects of various TCM modalities, especially for lower-extremity CRPS.
Despite the limitations of a single case report, the findings of this case recommend the use of combined TCM treatment as adjuvant therapy for patients with CRPS, as it produced significant improvements in symptoms and had no significant adverse effects. The combination of conventional medicine and TCM is promising and can improve the overall quality of life of patients with CRPS. Therefore, the TCM approach should be considered a safe supplementary treatment for CRPS. Further research is needed to verify the effect of the treatment modality of TCM and validate the efficacy of the treatment.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: South Korea
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): E
P-Reviewer: Mezian K; Shibata Y, Japan S-Editor: Qu XL L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Kessler A, Yoo M, Calisoff R. Complex regional pain syndrome: An updated comprehensive review. NeuroRehabilitation. 2020;47:253-264. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Bruehl S. Complex regional pain syndrome. BMJ. 2015;351:h2730. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 198] [Cited by in RCA: 241] [Article Influence: 24.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Taylor SS, Noor N, Urits I, Paladini A, Sadhu MS, Gibb C, Carlson T, Myrcik D, Varrassi G, Viswanath O. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Pain Ther. 2021;10:875-892. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 26.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Duong S, Bravo D, Todd KJ, Finlayson RJ, Tran Q. Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: an updated systematic review and narrative synthesis. Can J Anaesth. 2018;65:658-684. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Cossins L, Okell RW, Cameron H, Simpson B, Poole HM, Goebel A. Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome in adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials published from June 2000 to February 2012. Eur J Pain. 2013;17:158-173. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 89] [Cited by in RCA: 70] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Żyluk A, Puchalski P. Effectiveness of complex regional pain syndrome treatment: A systematic review. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2018;52:326-333. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Liu S, Zhang CS, Cai Y, Guo X, Zhang AL, Xue CC, Lu C. Acupuncture for Post-stroke Shoulder-Hand Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Neurol. 2019;10:433. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Lei S, Dai F, Xue F, Hu G, Zhang Y, Xu X, Wang R, Zhang X, Cong D, Wang Y. Acupuncture for shoulder-hand syndrome after stroke: An overview of systematic reviews. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101:e31847. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Wei X, He L, Liu J, Ai Y, Liu Y, Yang Y, Liu B. Electroacupuncture for Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy after Stroke: A Meta-Analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019;28:1388-1399. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Kim SG, Shin IH, Choi CH, Choe JY. [Anti-inflammatory effect of near-infrared irradiated cell culture media]. Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29:338-344. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Deng H, Shen X. The mechanism of moxibustion: ancient theory and modern research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:379291. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 145] [Article Influence: 12.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Byun DY, Kim H, Han SH, Kim KW, Lee JH, Chung WS, Song MY, Cho JH. Pharmacopuncture for lumbar herniated intervertebral disc: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2021;43:101369. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Kaptchuk TJ. Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136:374-383. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 614] [Cited by in RCA: 575] [Article Influence: 25.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Chen T, Zhang WW, Chu YX, Wang YQ. Acupuncture for Pain Management: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48:793-811. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Lin JG, Kotha P, Chen YH. Understandings of acupuncture application and mechanisms. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14:1469-1481. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Kelly RB, Willis J. Acupuncture for Pain. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100:89-96. [PubMed] |
| 17. | He Y, Guo X, May BH, Zhang AL, Liu Y, Lu C, Mao JJ, Xue CC, Zhang H. Clinical Evidence for Association of Acupuncture and Acupressure With Improved Cancer Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:271-278. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 243] [Article Influence: 48.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Bruehl S, Maihöfner C, Stanton-Hicks M, Perez RS, Vatine JJ, Brunner F, Birklein F, Schlereth T, Mackey S, Mailis-Gagnon A, Livshitz A, Harden RN. Complex regional pain syndrome: evidence for warm and cold subtypes in a large prospective clinical sample. Pain. 2016;157:1674-1681. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Xiang W, Jiang J, Hu T, Deng X, Chen C, Chen Z. The efficacy and safety of moxibustion for pressure injury: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101:e28734. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Zhou W, Lei R, Zuo C, Yue Y, Luo Q, Zhang C, Lv P, Tang Y, Yin H, Yu S. Analgesic Effect of Moxibustion with Different Temperature on Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain Mice: A Comparative Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:4373182. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Dirckx M, Stronks DL, van Bodegraven-Hof EA, Wesseldijk F, Groeneweg JG, Huygen FJ. Inflammation in cold complex regional pain syndrome. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2015;59:733-739. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Zhang CS, Zuo CY, Lv P, Zhang HX, Lin SR, Huang RZ, Shi G, Dai XQ. The role of STIM1/ORAI1 channel in the analgesic effect of grain-sized moxibustion on inflammatory pain mice model. Life Sci. 2021;280:119699. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Park SY, Park JH, Kim HS, Lee CY, Lee HJ, Kang KS, Kim CE. Systems-level mechanisms of action of Panax ginseng: a network pharmacological approach. J Ginseng Res. 2018;42:98-106. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |