Published online Sep 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i27.6631
Peer-review started: July 2, 2023
First decision: August 9, 2023
Revised: August 15, 2023
Accepted: August 23, 2023
Article in press: August 23, 2023
Published online: September 26, 2023
Processing time: 80 Days and 13.8 Hours
Polypoid endometriosis (PEM) is a rare and unique type of endometriosis. To date, no article has provided a systematic report of this disease. The current article provides a complete report on rare PEM based on ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, intraoperative findings and postoperative pathology data.
A 38-year-old female patient was admitted to our hospital after complaining of “vague pain in the right lower quadrant with an aggravated menstrual period for 8 mo”. The patient underwent laparoscopic exploratory surgery on January 7, 2022. The postoperative pathology revealed extensive PEM.
PEM is a type of endometriosis that is a benign disease but has biological properties similar to malignant tumours.
Core Tip: Polypoid endometriosis (PEM) is a rare and unique type of endometriosis that is a benign disease but has biological properties similar to those of malignant tumours. We reported a case of rapidly growing PEM possibly attributed to the discontinuation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist. We provide complete ultrasound findings, magnetic resonance imaging findings, intraoperative pictures and postoperative pathology data. We conducted a systematic review of the clinical features, imaging features, and pathology of PEM by reviewing the literature.
- Citation: Zhang DY, Peng C, Huang Y, Cao JC, Zhou YF. Rapidly growing extensive polypoid endometriosis after gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist discontinuation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(27): 6631-6639
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i27/6631.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i27.6631
Polypoid endometriosis (PEM) is the overgrowth of localized ectopic endometrium on the basis of endometriosis, and it is characterized by an endometrial polypoid, which can be located on the serosal surface, mucosal surface or endometriotic cyst cystic wall[1]. PEM is a rare, special type of endometriosis and is a benign disease, but it has biological properties similar to malignant tumours[2]. In this article, we described a case involving the accelerated growth of PEM, which could be linked to the discontinuation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRH) (GnRH-a). We provide complete ultrasound findings, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings, intraoperative pictures and postoperative pathology data. We conducted a systematic review of the clinical features, imaging features, and pathology of PEM by reviewing the literature. We believe that our report will broaden the diagnostic thinking for similar cases and improve diagnostic accuracy.
A 38-year-old female patient was admitted to our hospital after complaining of “vague pain in the right lower quadrant with an aggravated menstrual period for 8 mo”.
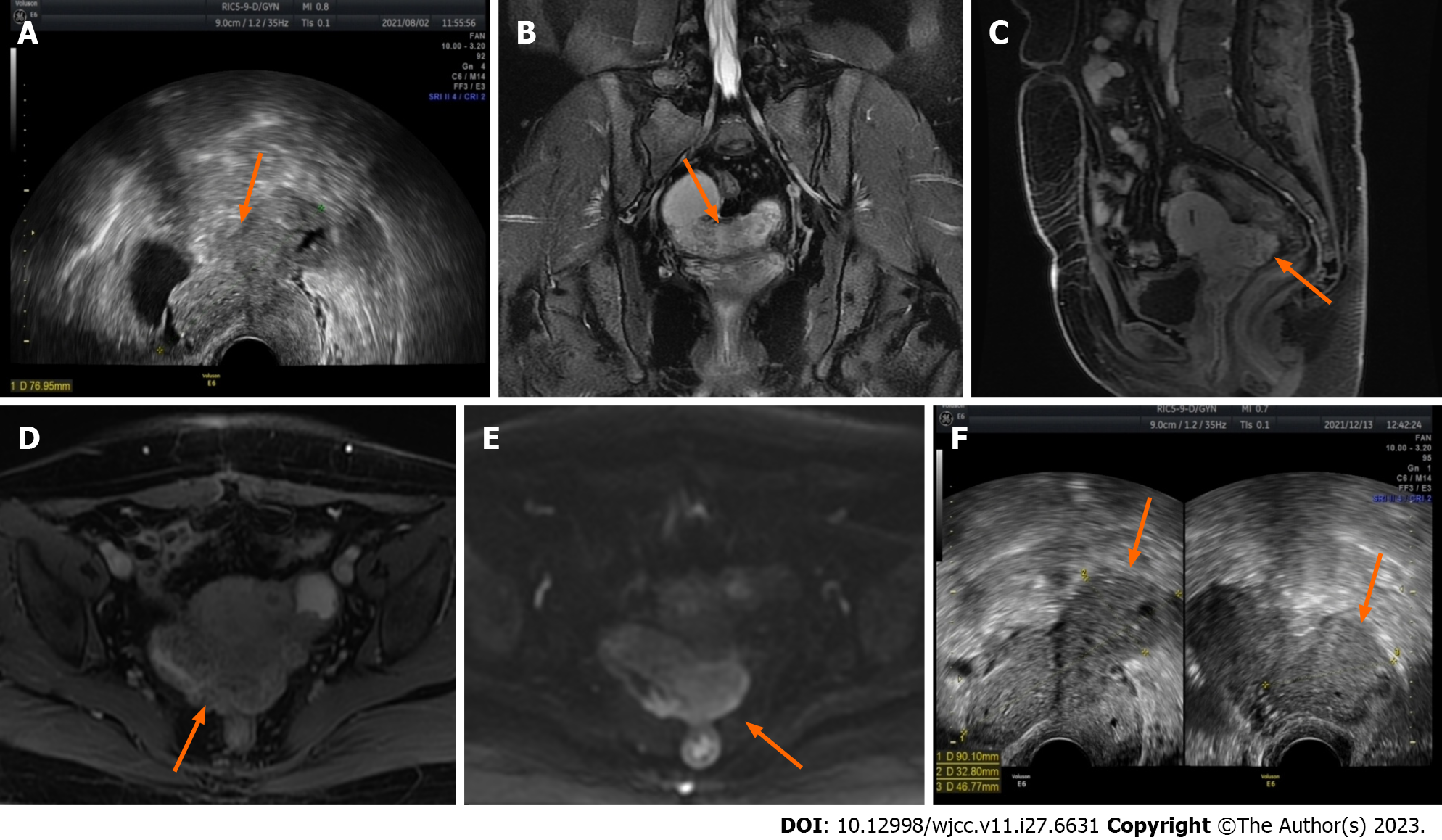
The patient experienced right lower quadrant pain with menstrual aggravation on April 29, 2021, with no apparent cause. Gynaecological ultrasonography revealed a double adnexal tubular mass, with an irregular cyst of approximately 5 cm in diameter near the left ovary and a solid cystic mass of approximately 5 cm in diameter below the right ovary, both of which were adherent. In the case of pelvic inflammatory disease, the symptoms were relieved after two weeks of anti-infective treatment with moxifloxacin hydrochloride tablets. During a re-examination of the ultrasound on July 26, 2021, the double adnexal cyst was found to be an endometriotic cyst, and the patient was referred to our hospital. Gynaecological ultrasound (Figure 1A) revealed a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass in the pelvis measuring approximately 7.5 cm × 7.7 cm × 5.0 cm in size, with anechoic areas of varying sizes, the nature of which will be investigated. Contrast-enhanced pelvic MRI (Figure 1B-E) indicated bilateral adnexal chocolate cysts and abnormal lamellar signals in the uterine and rectal depressions. The patient was diagnosed with endometriosis, which appeared to be associated with bilateral chocolate cysts and an unclear demarcation between the posterior uterine wall and the anterior rectum wall. The outpatient clinic advised the patient to undergo three cycles of GnRH-a treatment before undergoing surgery. On August 16, 2021, and September 6, 2021, the patient received two cycles of 3.75 mg of Differin. Due to personal reasons, the third cycle of treatment could not be completed. During this time (on December 13, 2021), the patient underwent a repeat gynaecological ultrasound (Figure 1F), and the results revealed that the lesion had grown in size.
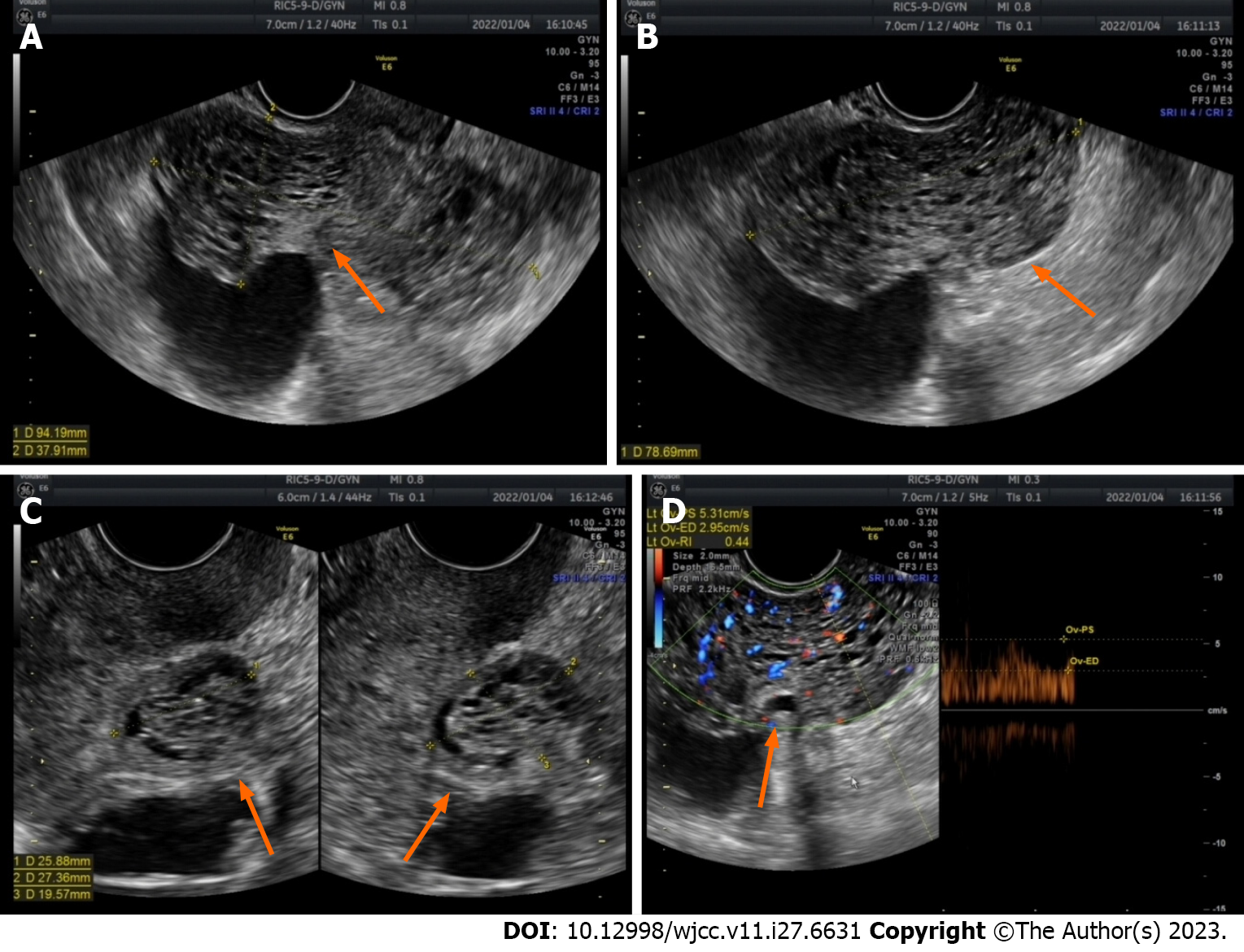
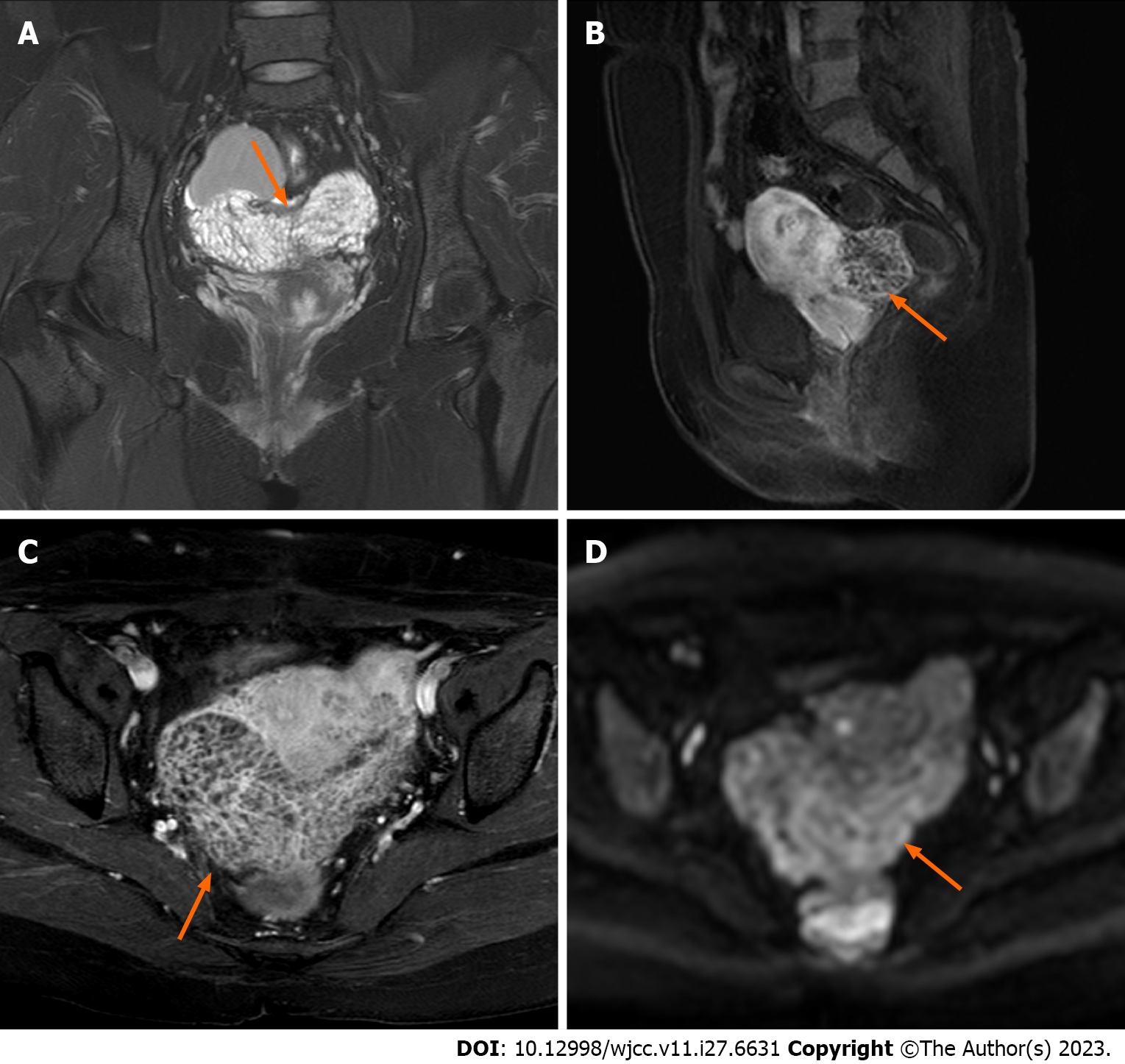
The patient was admitted to the hospital for surgery on January 2, 2022. Preoperative gynaecological ultrasound revealed heterogeneous hypoechoic masses behind the isthmus of the uterus, approximately 9.1 cm × 7.9 cm × 3.8 cm in size, and echogenic areas of varying sizes inside the uterus, which were honeycomb-shaped (Figure 2). Enhanced pelvic MRI (Figure 3) showed that the endometriosis lesions were larger than those observed on August 11, 2021, with diffuse grid-like changes in the interior, unclear boundaries with the uterus, bilateral appendages, and anterior wall of the rectum, including new lesions on the left anterior wall of the uterus.
The patient underwent combined hysteroscopy and laparoscopy on May 29, 2019, for “secondary infertility”, during which the bilateral ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids were removed. The left ovarian cyst revealed an endometriotic cyst after surgery. Four months after the operation, the patient became pregnant on her own. Due to a “scarred uterus”, a caesarean section of the lower uterine segment was performed on July 12, 2020, during which the endometrioma cyst of the left ovary was removed. The intraoperative revised classification of the American Fertility Society staging was stage III (40 points), and no medication was used for long-term postoperative management.
The patient had no pertinent personal or family history of PEM.
No abnormalities were found during physical examination of the external genitalia, vagina, or cervix. Poor uterine mobility. Bilateral adnexal thickening without tenderness. Anal examination indicated that the anterior wall of the rectum was fixed to the left sacral ligament.
Antigen 125, antigen 199, carcinoembryonic antigen and alpha-fetoprotein were normal.
Initially, gynaecological ultrasound revealed a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass in the pelvis measuring approximately 7.5 cm × 7.7 cm × 5.0 cm in size, with anechoic areas of varying sizes, the nature of which will be investigated (Figure 1A). Contrast-enhanced pelvic MRI (Figure 2) indicated bilateral adnexal chocolate cysts and abnormal lamellar signals in the uterine and rectal depressions. After discontinuation of the GnRH-a, gynaecological ultrasound revealed heterogeneous hypoechoic masses behind the isthmus of the uterus, approximately 9.1 cm × 7.9 cm × 3.8 cm in size, and echogenic areas of varying sizes inside the uterus, which were honeycomb-shaped. Enhanced pelvic MRI (Figure 3) showed that the endometriosis lesions were larger than those observed on August 11, 2021, with diffuse grid-like changes in the interior, unclear boundaries with the uterus, bilateral appendages, and anterior wall of the rectum, including new lesions on the left anterior wall of the uterus.
Considering the clinical symptoms, physical exam findings, laboratory and radiographic findings, ultrasound and MRI findings, intraoperative findings and postoperative pathology, a final diagnosis of PEM was made.
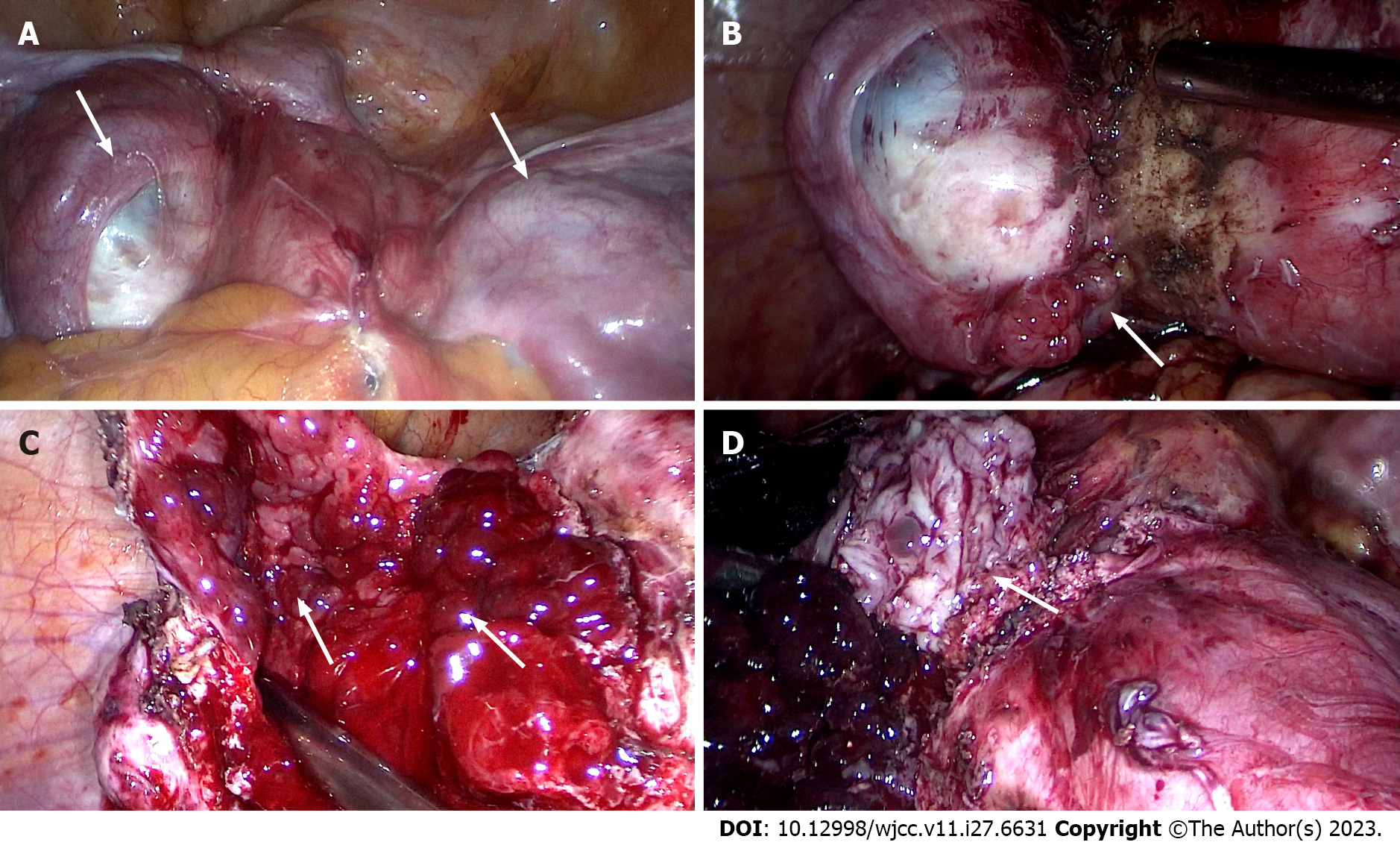
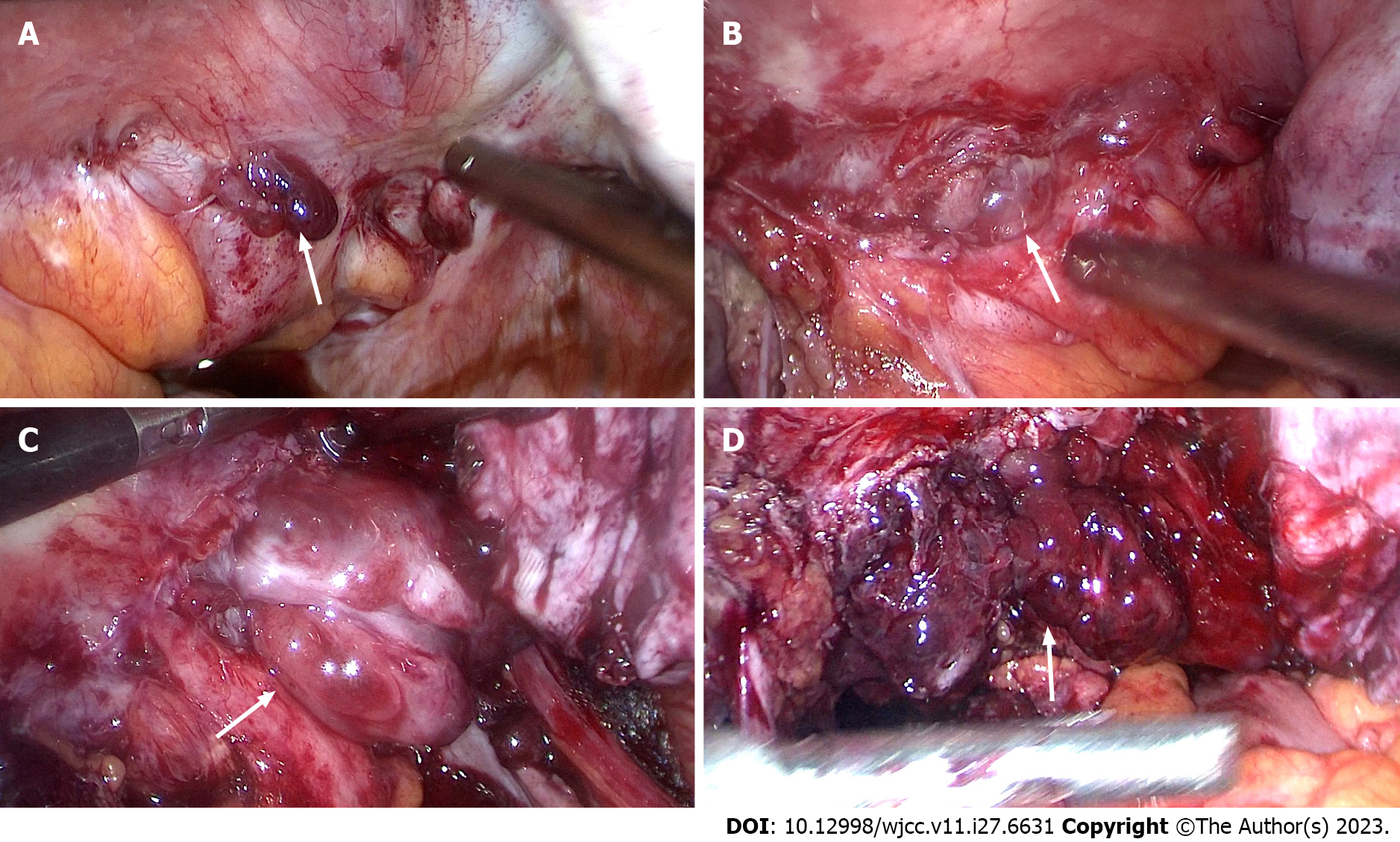
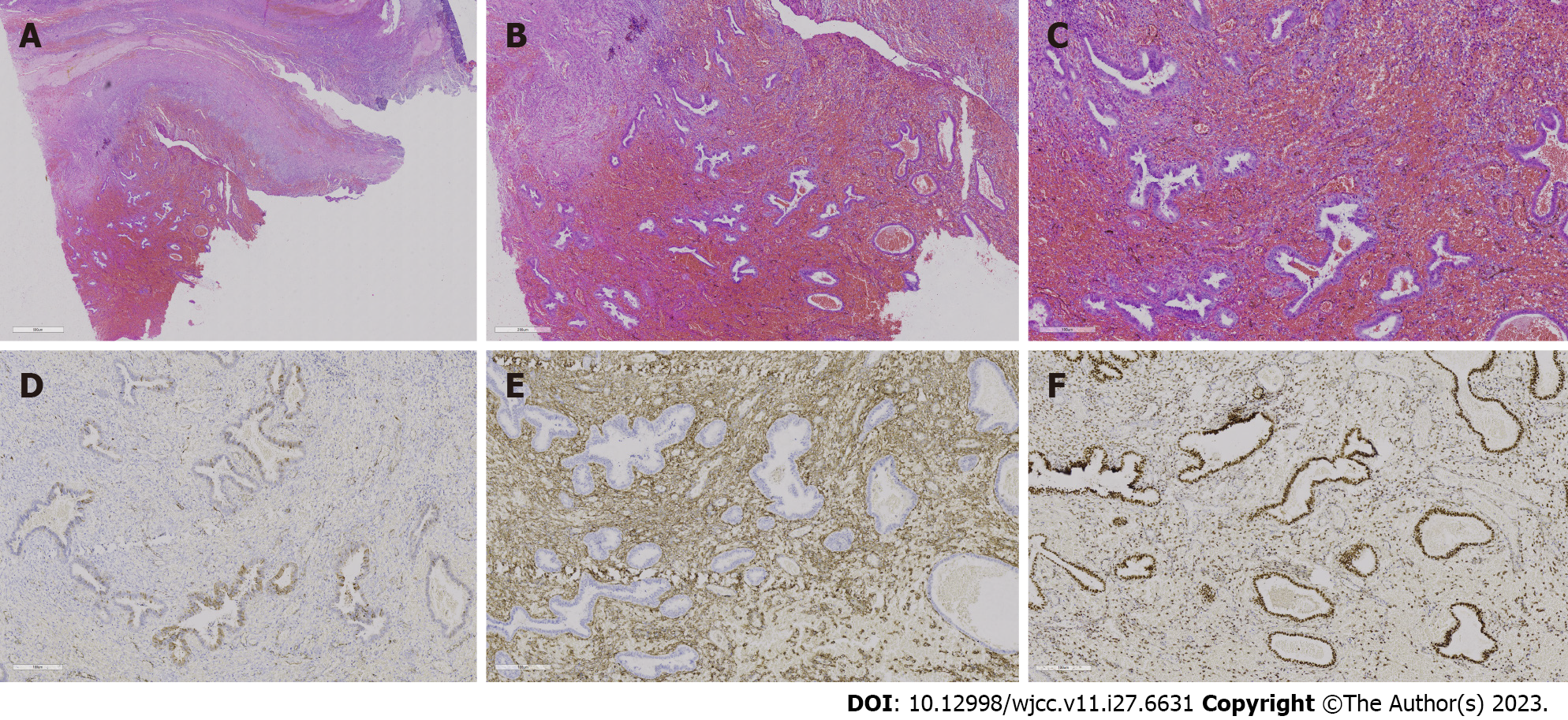
The patient underwent laparoscopic exploratory surgery on January 7, 2022. The entire uterus, right adnexa, left fallopian tube, right ovarian cyst, rectovaginal septum endometriosis lesions, and rectal surface endometriosis lesions were removed during the surgery. Furthermore, cystic enlargement of the right ovary with a diameter of 9 cm was observed, and chocolate-like fluid was aspirated by a puncture, as shown in Figures 4 and 5. After incision, the lower segment of the left anterior wall of the uterus and the left wall were found to have 1-cm and 2.5-cm bulging masses covered with red polypoid endometrial tissue. The rectum and posterior wall of the uterus were extensively densely adhered, with the cysts on the two lateral walls adhered to the posterior and pelvic walls, respectively. After separating the adhesions, extensive red polypoid intimal tissue was found. All adhesions were dissected and consistent with MRI findings, indicating that the double adnexal lesions were linked to the pelvic lesions. Six days after the operation, the patient recovered and was discharged from the hospital. After intense deliberations among the pathologists, the final pathological consideration was extensive PEM devoid of atypical cellular presence (Figure 6).
The patient’s pain symptoms disappeared after surgery, and he was treated with GnRH-a for 4 cycles. Regular follow-up examinations revealed no recurrence.
Endometriosis is the presence of endometrial-like glands and stroma outside the uterus[3]. PEM is a rare subtype of endometriotic lesions exhibiting a polypoid growth pattern. Benz et al[4] reported the first case of colonic PEM in 1952. Mostoufizadeh and Scully[5] formally coined the term PEM in 1980. Parker et al[2] reported 24 cases of PEM to date, with a mean age of 52.5 years and 60% of patients older than 50 years. Yamamoto et al[6] reported 34 cases from 11 articles and found that the average age was 50.2 years old, with an overall younger trend.
The clinical manifestations of PEM depend on the growth site. The susceptible sites include the colorectum, ovary, uterine serosal surface, cervical or vaginal mucosa, ureter, omentum, bladder, paraurethral, paravaginal, and retroperitoneal[2,7]. Intestinal PEM can cause abdominal cramps, blood in the stool, intestinal obstruction, and, in rare cases, perforation or malignant degeneration[8]. Physical examination may reveal lower abdominal pain or a pelvic mass if it occurs on the serosal surface of the ovary and uterus[9]. In this case, the patient had right lower quadrant pain with no apparent cause and menstrual aggravation, and gynaecological ultrasound revealed a pelvic mass. Vaginal bleeding and increased vaginal discharge after intercourse are symptoms of PEM of the cervix or vaginal mucosa[10]. Cervical polyps can even infiltrate the parametrium, causing ureteral obstruction and secondary hydronephrosis, as well as ureter-like cervical cancer[11].
The exact pathogenesis of PEM is still unclear. In 1999, Schlesinger and Silverberg[12] found a link between tamoxifen and PEM. Tamoxifen has been linked to the stimulation and exacerbation of PEM in several case reports[13-15]. Tamoxifen is a selective oestrogen receptor (ER) modulator with different effects on different tissues and is one of the chemotherapy drugs for breast cancer. Tamoxifen can act as an oestrogen antagonist, primarily in the breast. Simultaneously, tamoxifen can also occupy the hypothalamic ER, block the negative feedback effect of oestrogen on the hypothalamus, increase the secretion of GnRH, and then make the pituitary gland secrete gonadotropin to promote follicle growth. Oestrogen in the blood increases as the follicle enlarges, and it also has a weak oestrogenic effect on the endometrium, resulting in endometrial thickening. However, oestrogen was used after menopause in 11 of the 24 cases reported by Parker et al[2]. Therefore, we speculate that oestrogen stimulation is one of the causes of PEM. Two other case reports stated that patients developed PEM after the discontinuation of GnRH-a[16,17]. They considered a rebound phenomenon after stopping GnRH-a inhibition, a rare complication of GnRH-a. In this case, the patient's imaging data before the use of GnRH-a suggested that the patient had PEM. Due to personal reasons, the drug was stopped after two uses for more than three months, and an ultrasound and MRI examination revealed that the cyst had grown in size. The mass also displayed typical PEM changes. Therefore, we can speculate that this case may be a rare complication after discontinuing GnRH-a.
Presently, few imaging data related to PEM are available. The clinical and imaging manifestations of PEM are similar to those of malignant tumours, which can be easily misdiagnosed and deserve our attention[11]. Ultrasound images of PEM are diverse and related to the disease site, with each having its own set of characteristics. The mass contains many heterogeneous echogenic masses that have a honeycomb appearance. On ultrasound images, PEM of the ovary is typical of endometriotic cysts, with papillary and solid echoes in the cyst wall. The tumour, in this case, had a typical honeycomb shape, but due to the rarity of the disease and doctors’ inexperience, the possibility of the disease could not be considered before surgery. Normal endometriotic cysts have old haemorrhages in the cysts; thus, the cysts in the pelvic MRI showed a high signal on T1 weighted images (T1WI) and a low signal on T2 weighted images (T2WI)[18]. However, if PEM coexists with common endometriosis, typical endometriosis imaging features may appear, resulting in imaging features of polypoid lesions. The polypoid area was similar to the endometrial signal, with moderate to high intensity on T2WI, and the mass margins were surrounded by T2 hypointensity. However, small haemorrhagic foci in the mass are hyperintense on T1WI and slightly increased on diffusion-weighted imaging, and no imaging features of malignancy, such as lymphadenopathy, are present[19,20]. A few larger lesions may exhibit diffuse, uniform, finely divided-like changes. This patient’s second MRI revealed both typical imaging features of endometriosis and PEM.
PEM is characterized by polypoid nodules that can be single or multiple, approximately one-third of which are multiple, and can be scattered or closely arranged like 19, ranging in size from 0.4 cm to 20 cm[4,11]. Cysts come in a variety of colours, including red, pink, reddish-brown, grey-white, and others, and can be soft, solid, or cystic-solid, with small cystic cavities on some of the cut surfaces. PEM is similar to normal endometriosis in appearance, with visible endometrial stroma and glands but thick-walled blood vessels. In some cases, extensive haemorrhagic foci can be seen. The glands have a variety of structural features, including multiple cysts. Metaplastic changes in the glands, such as squamous metaplasia, mucinous metaplasia, or mucosal metaplasia, are common. Simple hyperplasia is the most common focal-like endometrial hyperplasia, followed by atypical hyperplasia. The endometrial glands were positive for ER and progesterone receptor, while the endometrial stroma was positive for CD10 and vimentin when the lesions were immunohistochemically stained. This is a typical case of those mentioned above, accompanied by an irregular proliferation of endometrial glands. Stewart and Bharat[20] classified it into two subtypes based on whether immunohistochemical p16 was positive or negative. The first is an endometriosis-like change with only the gross appearance of polypoid and normal microscopically, p16 is not expressed or is only weakly expressed, and the patient’s age of onset is comparable to that of the normal. The other is that endometrial polyps have a similar appearance to endometrial polyps. Typical thick-walled vessels can be seen, and p16 expression is higher than that in the former subtype. The patients’ onset age was older, and most of them were postmenopausal with endometrial polyps. Based on the above pathological description, this case is more aligned with the former subtype.
Polypoid endometriosis is a rare endometriosis, and its occurrence may be related to the use of hormone drugs. The clinical manifestations of the disease depend on the location of the disease. The ultrasonography often indicates that the lesion is honeycomb-like and the blood flow is slightly rich. Enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance often indicates that the lesion has uneven enhancement, and it is easy to be misdiagnosed as a malignant disease. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the awareness of this disease, to reduce misdiagnosis and avoid excessive surgical resection.
We thank the Medical Imaging Department of Peking University First Hospital for providing us with valuable imaging materials.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Naem AA, Germany S-Editor: Qu XL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Yuan YY
| 1. | Parker RL, Dadmanesh F, Young RH, Clement PB. Polypoid endometriosis: a clinicopathologic analysis of 24 cases and a review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:285-297. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 124] [Cited by in RCA: 95] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Ghafoor S, Lakhman Y, Park KJ, Petkovska I. Polypoid endometriosis: a mimic of malignancy. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020;45:1776-1782. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Laganà AS, Naem A. The Pathogenesis of Endometriosis: Are Endometrial Stem/Progenitor Cells Involved?. Stem Cells in Reproductive Tissues and Organs. Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine 2022; 70: 193-216. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 4. | Benz EJ, Dockerty MB, Dixon CF. Polypoid endometrioma of the colon: report of case in which unusual pathologic features were present. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1952;27:201-208. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Mostoufizadeh M, Scully RE. Malignant tumors arising in endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1980;23:951-963. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Yamamoto A, Usami T, Kondo E, Kato K, Motoyama T. Huge polypoid endometriosis: report of a case and review of the literature. Int Cancer Conf J. 2016;5:31-35. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Marguerie M, Howell J, Belland L. Vaginal polypoid endometriosis. CMAJ. 2023;195:E620-E621. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Ramai D, Linn S, Murphy T, Reddy M. Transmural Polypoid Endometriosis of the Sigmoid Colon. J Gastrointest Surg. 2018;22:2184-2186. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Tsai C, Huang SH, Huang CY. Polypoid endometriosis - A rare entity of endometriosis mimicking ovarian cancer. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;58:328-329. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Ling R, Jin H, Yang Y, Cheng L. Polypoid Endometriosis of the Rectum and Vagina in an Adolescent. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2020;33:581-585. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Kwek JW, H'ng MW, Chew SH, Tay EH. Florid polypoid endometriosis of the cervix with left ureteric obstruction: a mimic of cervical malignancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2010;36:252-254. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Schlesinger C, Silverberg SG. Tamoxifen-associated polyps (basalomas) arising in multiple endometriotic foci: A case report and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 1999;73:305-311. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Choi IH, Jin SY, Jeen YM, Lee JJ, Kim DW. Tamoxifen-associated polypoid endometriosis mimicking an ovarian neoplasm. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2015;58:327-330. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Kraft JK, Hughes T. Polypoid endometriosis and other benign gynaecological complications associated with Tamoxifen therapy-a case to illustrate features on magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Radiol. 2006;61:198-201. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Chang CK, Chen P, Leu FJ, Lou SM. Florid polypoid endometriosis exacerbated by tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102:1127-1130. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Othman NH, Othman MS, Ismail AN, Mohammad NZ, Ismail Z. Multiple polypoid endometriosis--a rare complication following withdrawal of gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist for severe endometriosis: a case report. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996;36:216-218. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Marugami N, Hirohashi S, Kitano S, Takahama J, Ito T, Torimoto K, Hirao Y, Kichikawa K. Polypoid endometriosis of the ureter mimicking fibroepithelial polyps. Radiat Med. 2008;26:42-45. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Bulut E, Peker M, Kupeli A, Danisan G, Bulut AC. The efficiency of susceptibility-weighted MRI in the differentiation of endometriomas from haemorrhagic ovarian cysts. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021;46:5337-5343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Miyoshi S, Yamaguchi K, Chigusa Y, Sunada M, Yamanoi K, Horie A, Hamanishi J, Kondoh E, Mandai M. Fertility preservation of polypoid endometriosis: Case series and literature review. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2022;48:502-509. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Stewart CJ, Bharat C. Clinicopathological and immunohistological features of polypoid endometriosis. Histopathology. 2016;68:398-404. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |