Published online Jul 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4504
Peer-review started: April 1, 2023
First decision: April 13, 2023
Revised: May 17, 2023
Accepted: June 6, 2023
Article in press: June 6, 2023
Published online: July 6, 2023
Processing time: 90 Days and 7.4 Hours
Dietary imbalance and overeating can lead to an increasingly widespread disease - obesity. Aesthetic considerations aside, obesity is defined as an excess of adipose tissue that can lead to serious health problems and can predispose to a number of pathological changes and clinical diseases, including diabetes; hypertension; atherosclerosis; coronary artery disease and stroke; obstructive sleep apnea; depression; weight-related arthropathies and endometrial and breast cancer. A body weight 20% above ideal for age, gender and height is a severe health risk. Bariatric surgery is a set of surgical methods to treat morbid obesity when other treatments such as diet, increased physical activity, behavioral changes and drugs have failed. The two most common procedures currently used are sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass. This procedure has gained popularity recently and is generally considered safe and effective. Although current data show that perioperative mortality is low and better control of comorbidities and short-term complications is achieved, more randomized trials are needed to evaluate the long-term outcomes of bariatric procedures. This review aims to synthesize and summarize the growing evidence on the long-term effectiveness, outcomes and complications of bariatric surgery.
Core Tip: The method of bariatric surgery is associated with dramatic weight loss, overall health improvement and, in many cases curing obesity-related comorbidities (i.e., diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, asthma and other breathing disorders, arthritis, cholesterol problems, gastroesophageal reflux disease, fatty liver, urinary stress incontinence, brain pseudotumor, and more). Furthermore, in cases with a high degree of obesity, undergoing this type of surgical intervention also decreases overall mortality. Simultaneously, physical quality of life improved faster than mental quality of life.
- Citation: Gulinac M, Miteva DG, Peshevska-Sekulovska M, Novakov IP, Antovic S, Peruhova M, Snegarova V, Kabakchieva P, Assyov Y, Vasilev G, Sekulovski M, Lazova S, Tomov L, Velikova T. Long-term effectiveness, outcomes and complications of bariatric surgery. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(19): 4504-4512
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i19/4504.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4504
An imbalance in dietary patterns and excessive nutritional intake may give rise to ailments such as obesity. Despite any purely aesthetic considerations, obesity can be described as an excess of adipose tissue that endangers a person's health; specifically, a body weight exceeding 20% of the ideal weight determined by age, gender, and height is deemed to pose a significant health risk[1].
Bariatric surgery is a set of surgical methods for treating morbid obesity. This procedure has gained popularity recently and is generally considered safe and effective. In addition, some of the authors in recent scientific studies claim that it is effective in the short term, although long-term complications have not been described or are rare[1].
The method is associated with dramatic weight loss, improvement and, in many cases curing obesity-related comorbidities. These diseases include diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, bronchial asthma and other respiratory disorders, arthritis, cholesterol-related disorders, gastroesophageal reflux disease, fatty liver disease, urinary stress incontinence, brain pseudotumor, and more. Furthermore, in cases with a high degree of obesity, undergoing this type of surgical intervention also decreases overall mortality[2]. Because of this, the term "metabolic surgery" is becoming more and more critical.
There are many different causes of obesity, but it is a fact that the number of people suffering from obesity is constantly increasing. According to the World Health Organization, obesity has tripled in many countries of the European region since 1980, with overweight and obesity affecting 50% of the population in most European countries. Furthermore, it is projected that a significant portion of the global population, precisely 60%, or 3.3 billion individuals, may suffer from the effects of excessive weight gain, with 2.2 billion individuals deemed overweight and an additional 1.1 billion individuals classified as obese, by the year 2030[3].
Bariatric surgery is applied to people who cannot lose weight with diets and sports; have a body mass index (BMI) of 35 or higher, and have accompanying diseases such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, and others; as well as people who have an index above 40 but do not have accompanying diseases. Generally speaking, bariatric surgery aims at one single thing - to reduce the volume of food taken in and its absorption[3].
The global guidelines for bariatric surgery were established after a National Institutes of Health consensus conference in 1991. Even then, early bariatric procedures such as jejunoileal bypass were recognized to carry substantial long-term risks. However, the idea of surgical obesity treatment was primarily rejected. Over the next several years, the limited evidence regarding the safety and effectiveness of bariatric surgery was denied. Subsequently, a consensus panel decided that procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and vertical banded gastroplasty (VGB) are safe and effective for patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥ 40 kg/m2 or with BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 and concomitant medical complications of obesity[4].
In this way, a practice standard was established that had previously been lacking, and at the same time, this type of surgery was legitimized as a surgical discipline. Since then, the clinical evidence base for bariatric surgery has grown tremendously.
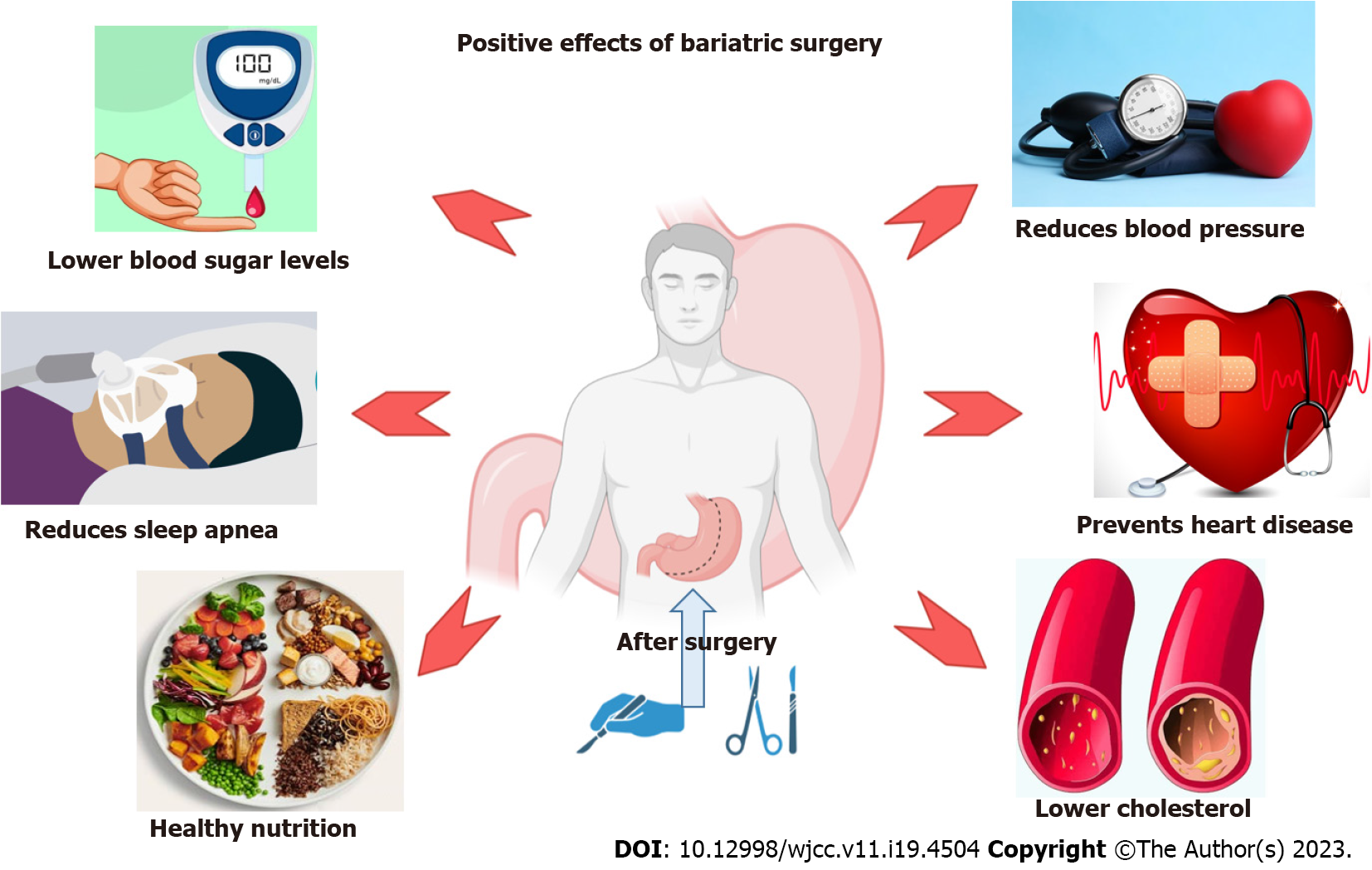
Bariatric surgery has significant health benefits, such as lowering hyperglycemia or normalizing blood glucose levels, lowering blood pressure and cholesterol, and improving obstructive sleep apnea and diabetes-related micro- and macrovascular complications. The surgical techniques involved in bariatric interventions are varied and involve different interventions[5]. When they include "bypassing" the duodenum, there is also a decrease in the hormone ghrelin and an increase in GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide 1) and PYY (Gut hormone peptide, tyrosine-tyrosine peptide), which improves insulin sensitivity, as well as other metabolic parameters. Two recently published meta-analyses of studies following patients for up to 5 years also showed reasonable glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery[5-8].
During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), most surgical procedures, especially elected, were postponed because of the health crisis and public health measures[9], including bariatric surgery.
Studies have shown that bariatric surgery leads to more significant weight loss and is more effective in treating type 2 diabetes in obese patients than non-surgical treatments. Long-term observations have also shown that these benefits persist for over five years after the surgery. However, the predicting factors of long-term complications, long-term survival, and the impact on patient mental health and costs must be constantly updated[10].
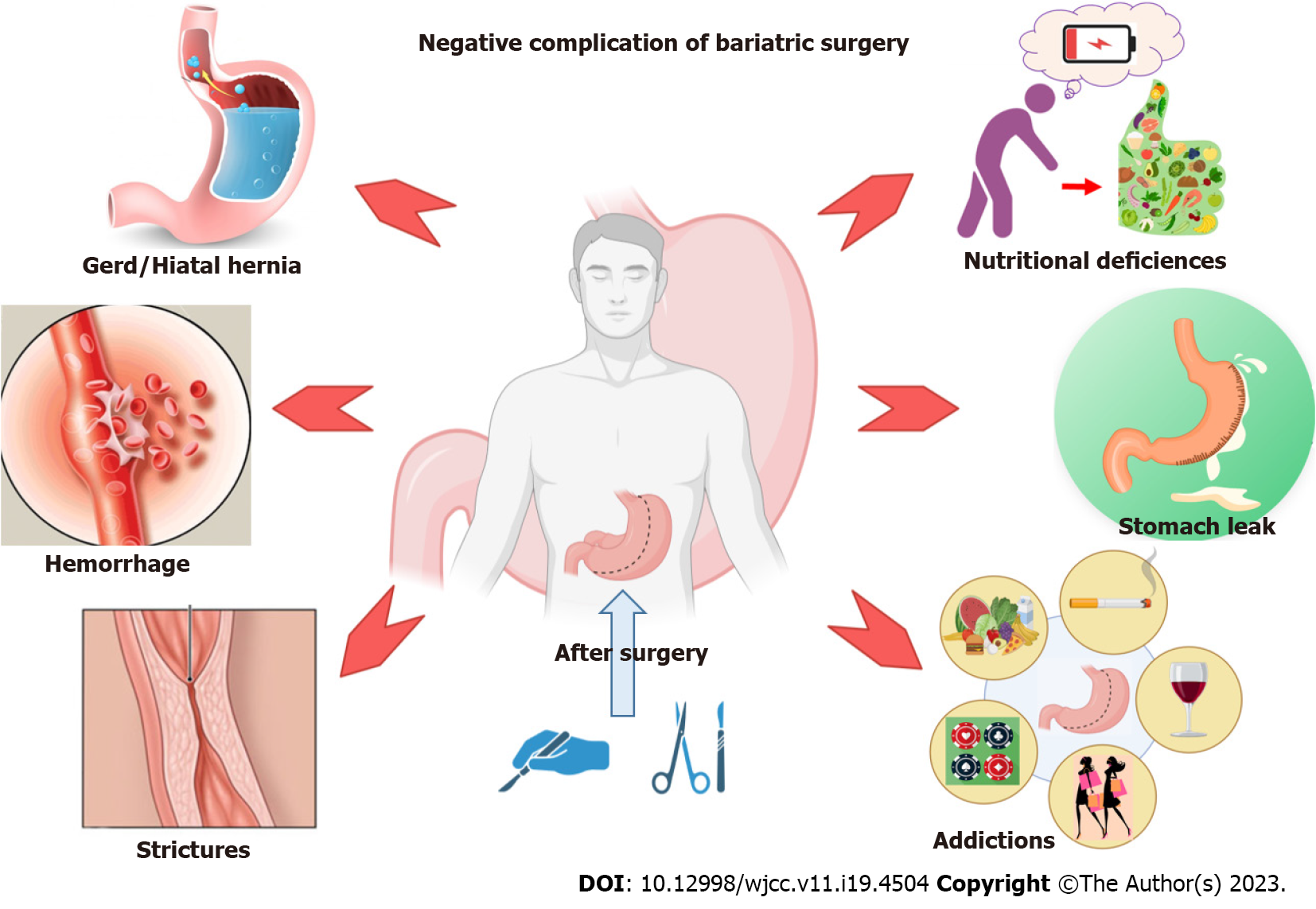
Nevertheless, like any other surgical procedure, this one hides its own risks, some of which are life-threatening, long-term nutritional complications. Often after this procedure, patients develop anemia and have calcium and vitamin losses, which must be compensated by taking substitutes throughout their lives. Some of the potentially severe complications of bariatric surgery are micro- and macronutrient deficiencies. In addition, stenosis and ulceration of the anastomosis, reflux esophagitis, cholelithiasis, steatohepatitis, and altered pharmacokinetics and dynamics may occur[11-13].
Two additional risks are often overlooked: recurrent calcium oxalate urolithiasis and osteoporosis. Both complications are described more often after RYGB, which bypasses the duodenum, where the calcium is mainly absorbed. Unfortunately, an elevated oxalate excretion after RYGB was described, which is usually challenging to treat. Consistent with calcium malabsorption is the low level of urine calcium. Even so, RYGB-related osteoporosis is not associated with changes in weight or vitamin D metabolism[14].
In this review, we focus on the long-term outcomes, complications – rates and management, and quality of life (QoL) and psychological aspects in patients after bariatric surgery.
A systematic review by O'Brien et al[15] reviewed 33 datasets reporting data beyond 10 years after bariatric surgery. There were no surgical fatalities. At 20 years, the weight reduction was 30.1 kg, excess weight loss (EWL) was 48.9%, and total weight loss (%TWL) was 22.2%. Although the reoperation rate was first high, currently, it is significantly lowered with a better band and aftercare follow-up.
They included 18 gastric bypass reports, 16 of which were RYGB and two for the laparoscopic One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) version. At 10 years or longer, the mean %EWL for all gastric bypass combinations was 56.7%, with a mean of 55.4% EWL (for RYGB), 80.9% EWL (for OAGB) and 45.9% (for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, LAGB). In addition, the mean weight reduction in the two randomized control trials (RCTs) with LAGB was 55.9% EWL [15].
While long-term efficacy was encouraging, most studies exerted inadequate quality, with typically absent controls and several data gaps (incl. missing % follow-up, reoperation rates, perioperative mortality and morbidity, etc.) in most publications. Just two RCTs were included[16,17]. Angrisani et al[17] found 69% EWL and 46% EWL in RYGB and LAGB, respectively. At 10 years in Australian research comparing LAGB to optimum medical care, the LAGB group had 63% EWL. Three noteworthy RCTs of 5-year results with RYGB vs SG have been reported[18-20]. In 5 years, the SLEEVEPASS research[18] revealed 57% and 49% EWL for RYGB and SG, respectively. The SM BOSS research[19] found that RYGB had a 68% excess BMI loss (EBMIL), and the SG had a 61% EBMIL. Finally, the STAMPEDE research[20] found that RYGB had a TWL of 21.7% and SG had a TWL of 18.5%. We anticipate a lengthier follow-up from this and other similar research. Likely, widespread adoption of bariatric surgery will not occur until more high-quality evidence is released.
Van Veldhuisen et al[21] also performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular diseases and bariatric surgery. They include 39 prospective or retrospective cohort studies, but no RCTs. Bariatric surgery lowered the risk of all-cause death [pooled hazard ratio (HR) of 0.55, P < 0.001 vs controls] and cardiovascular mortality [HR 0.59, P < 0.001]. Moreover, bariatric surgery lowered the incidence of heart failure [HR 0.50, P < 0.001], myocardial infarction [HR 0.58, P < 0.001], and stroke [HR 0.64, P < 0.001], but not atrial fibrillation (HR 0.82, P = 0.12) [21].
The extent to which the favorable impact of bariatric surgery is related to total weight loss or if additional ancillary benefits also play a role is an essential consideration. According to a new small mechanistic investigation, the advantages of bariatric surgery are entirely connected to weight loss, with no additional objective benefits[22]. However, numerous other studies have shown that ancillary aspects of the surgery, such as a changed gut hormone production, increased insulin sensitivity, and altered gut microbiome[23], impact the outcomes. Therefore, bariatric surgery is referred to as metabolic surgery[20].
Nonetheless, there is no doubt that the degree of weight loss is critical. For example, one study demonstrated that in non-surgical obese patients, a 20% weight loss was required though rarely achieved, to decrease the long-term major cardiovascular events rate. In contrast, at least 10% weight loss was needed in surgical patients, which is usually easily accomplished[23] and supports the hypothesis that additional metabolic processes improve the benefits of surgery[21]. Despite the potential benefits of bariatric surgery for preventing (and maybe treating) cardiovascular illness, no randomized controlled trials have primarily studied the influence of surgery on cardiovascular events or outcomes.
According to the European Society of Cardiology's newly issued guideline for cardiovascular disease prevention, "bariatric surgery for obese high-risk people should be considered when lifestyle adjustment does not result in maintained weight loss," i.e., it is a 2A recommendation[24]. This is a significant departure from the former guideline of 2016[25], in which diet and lifestyle changes were encouraged as mainstay therapeutic choices, and bariatric surgery was not formally recommended. Therefore, preventing or treating cardiovascular illness has had little effect on surgical recommendations thus far[26]. The most significant advice for metabolic surgery is for individuals with obesity and Type 2 diabetes. It is currently regarded as a suitable adjunct to existing conventional care in this patient population[27].
In summary, the findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrate that bariatric surgery, compared to non-surgical therapy, lowers mortality and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases in individuals with obesity. Therefore, in some instances, bariatric surgery should be explored[21].
In their systematic review and meta-analysis, Buchwald et al[28] focused on the 30-d surgical mortality of 0.1%, 0.5% and 1.1% for simply restrictive surgeries, gastric bypass, and biliopancreatic diversion or duodenal switch, respectively. Diabetes, sleep apnea and hypertension were cured in 76.8%, 85.7% and 61.7%, and improved in 86.0%, 83.6% and 78.5% of patients, respectively. Seventy percent or more of individuals observed an improvement in their hyperlipidemia. The authors concluded that after bariatric surgery, morbidly obese people lost weight effectively. Furthermore, most individuals with diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obstructive sleep apnea had their symptoms entirely resolved or improved[28].
Kang et al's systematic review and meta-analysis examined the efficacy and safety of the three most popular bariatric surgery procedures: RYGB, SG, and LAGB[29]. The findings revealed that BMI reduction and %EWL differed substantially between RYGB and LAGB but not between RYGB and SG. No significant difference in weight loss between RYGB and SG was demonstrated, even though they showed superiority to LAGB. While less efficient in weight reduction, LAGB caused fewer problems than the other two surgical techniques[29].
Still, the outcomes of bariatric surgery depend primarily on the multidisciplinary approach[30]. The desirable outcomes following bariatric surgery are presented in Figure 1.
Bariatric surgery is generally safe and, in most cases, effective, but this type of surgical procedure can be associated with severe complications, some of which can be fatal[31].
In general, the complications of bariatric surgery are divided into two major groups: early and late. Early postoperative complications include leaks, stenoses, bleeding, and venous thromboembolic events, while late complications include band erosion, acute obstruction, gallstone disease, Dumping syndrome, ischemia, and megaesophagus or pseudoachalasia and death. Regarding the complications of this type of operative manipulation, many scientific groups work in the field, and publications are increasing yearly. One of the most detailed publications on this topic is the following.
Chang et al[32] evaluated 30-d significant complications related to bariatric surgeries. This study comprised 71 American studies from 2003 to 2014 and 107874 patients with a mean age of 44 years and a pre-surgery BMI of 46.5 kg m-2. They received gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding, or SG[32]. The rate of less than 30-day anastomotic leak was 1.15%, of myocardial infarction - 0.37%; and of pulmonary embolism - 1.17%, where the death rates were 0.12%, 0.37%, and 0.18%, respectively, among all patients[33]. Although, among surgical procedures, SG had a greater anastomotic leak rate (1.21%) than gastric bypass (1.14%), gastric bypass exerted a higher risk for myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism than other techniques. However, we discovered that complication reporting is poorer than other outcomes. The 30-d rates of the three primary problems following each operation vary from 0% to 1.55%, and the mortality rate after these complications ranges from 0% to 0.64%. Future research documenting issues following bariatric surgery should increase the quality of their reporting[32].
On the other hand, in the scientific work of Stone et al[33], a fascinating relationship between the skin color of the patients, respectively the nationality, with the complications that have occurred. They demonstrated that most studies revealed that Black patients had higher 30-d mortality, morbidity, and duration of stay than White patients. The differences between White and Hispanic patients were mainly non-significant in these outcomes. In conclusion, during 30-d of bariatric surgery, black individuals may encounter a greater risk of adverse events than white patients. Explanations for this discrepancy were limited due to the limits of large multicenter datasets. Longer-term studies that cover additional races and ethnicities and take socioeconomic considerations might help future studies[33].
Chierici et al[34] included 39 papers in their systematic review and meta-analysis to demonstrate that biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch provides the best weight loss results (total weight loss on the 1st and 3rd year, %TWL 12.38 and 28.42), followed by single-anastomosis duodenoileal bypass (%TWL 9.24 and 19.13), one-anastomosis gastric bypass (%TWL 7.16 and 13.1), and RYGB (%TWL 4.68 and 7.3) were all superior to re-SG. Furthermore, compared to re-SG, duodenal switch and RYGB are linked with an increased risk of late morbidity (OR: 3.07 and 2.11, respectively). However, no significant difference was seen for the other surgeries. In addition, weight recidivism is most common after re-SG; individuals receiving single-anastomosis duodenal bypass had the lowest rate[34].
Poole et al[35] conducted a survey completed by 138/715 eligible surgeons (19.3%) to evaluate the management of bariatric surgery complications. Approximately 54.3% of respondents had not received training in bariatric surgery during their residency or fellowship. Among the 108 respondents, 66.7% believed that general surgeons should handle post-bariatric surgery complications, while 25.9% lacked confidence in addressing such issues. Most respondents (65.7%) expressed interest in pursuing additional continuing professional development options for managing these complications. The most preferred educational modalities for this purpose included hands-on workshops, online resources, and live webinars, with 67.1% of the participants willing to invest 1-3 h and 42.9% ready to pay over $100 for such resources[35].
Some of the complications following bariatric surgery are presented in Figure 2.
A systematic review by Hachem and Brennan revealed that bariatric surgery improved QoL more than other obesity therapies. There were significant disparities in QoL improvements across various forms of bariatric surgery. Improvements in QoL were more likely to happen within the first 2 years after surgery, with physical QoL improving faster than mental QoL[36].
According to the study of 18 identified papers by Sierżantowicz et al[37], bariatric therapy appears to produce a long-term advantage in health-related (HRQOL), particularly its physical component score. However, due to psychological predispositions, certain individuals are less likely to benefit from bariatric therapy, whether in terms of HRQOL or weight loss. In addition, studies with inconsistent and imprecise designs may limit the usefulness of the conclusions. Therefore, the author concluded that early identification of such individuals and providing physical and psychological counseling would improve bariatric treatment results[37].
The first systematic evaluation to present data from all quantitative designs on studies that assessed personality traits was conducted by Summerville et al[38]. Overall, neuroticism appeared to be related to worse HRQOL, whereas extraversion was shown to be associated with greater HRQOL. However, null relationships for these two qualities were also detected.
Many authors claim that patients frequently rated bariatric surgery as a life-changing intervention that reduces weight, improves obesity-related comorbidities, and improves the QoL. Yet, many poll respondents considered bariatric surgery hazardous or harmful. Patients from racial minority groups expressed more anxiety about mortality risk, lower weight reduction goals, and varied reasons for pursuing bariatric surgery. Female patients were likelier to have good impressions of bariatric surgery and higher weight loss aspirations[39]. The research revealed a disparity between patient views and bariatric surgery's clinical safety and effectiveness profile. Overestimation of the hazards, false expectations, and unfamiliarity with the outcomes of bariatric surgery were all prevalent findings. These negative attitudes toward bariatric surgery may contribute to its underutilization among eligible patients. In addition, views and motives frequently differed by race, location, gender, and age, highlighting the importance of patient-centered education during the prereferral stage. The literature also revealed widespread misunderstandings about bariatric surgery. More studies should be conducted to investigate the influence of education on patient and public attitudes[39].
Despite the good results of bariatric procedures, the current data show that in a small part of all cases, the most severe complication is a fatal outcome. Perioperative mortality rates improved significantly since the early 2000s, ranging from 0.03% to 0.2%[40]. However, as Chang et al[32] maintained, the mortality rate after late complications ranges from 0% to 0.64%. Based on the meta-analysis by Robertson and colleagues and their studies involving over 3.6 million patients, the deaths were 4707. The pooled analysis showed an overall mortality of 0.08 percent. They found no statistically significant difference between overall, 30-d, 90-d, or in-hospital mortality. However, they found a relationship between the types of surgical interventions and mortality, such as 0.03% for gastric band, 0.05% for SG, 0.09% for one-anastomosis gastric bypass, 0.09% for RYGB, and 0.41% for duodenal switch[41].
Studies demonstrate that bariatric surgery, compared to non-surgical therapy, lowers mortality and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases in individuals with obesity. Most individuals with diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obstructive sleep apnea had their symptoms entirely resolved or improved. At the same time, the mortality rate after these complications ranges from 0% to 0.64%. QoL improvements, especially mental health.
In conclusion, we could say that, according to the literature, bariatric surgery is relatively safe. However, there is still a lack of data describing the frequency of obesity recurrences and persistent conditions. We believe there should be an individual selection of a surgical approach for different patients, according to the degree of obesity, because, as we have seen, some procedures have a much higher risk of complications. But following the analyzes described in detail regarding the ratio of long-term complications and mortality, it becomes clear that these complications have decreased to the extent that the benefit of the manipulation itself is greater than the risks involved. That is the main reason why bariatric surgery is increasingly used every year as a means of choice for patients with morbid obesity.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Surgery
Country/Territory of origin: Bulgaria
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Emran TB, Bangladesh; Gupta R, India S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: A P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. |
Alfonso Enrique Martínez-Núñez, Oscar Ernesto Gamboa-López, Montserrat Bacardí-Gascón, Arturo Jiménez-Cruz Long-term complications and side effects of bariatric surgery: a systematic review.
|
| 2. | Frigolet ME, Dong-Hoon K, Canizales-Quinteros S, Gutiérrez-Aguilar R. Obesity, adipose tissue, and bariatric surgery. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2020;77:3-14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 3. | Courcoulas AP, Yanovski SZ, Bonds D, Eggerman TL, Horlick M, Staten MA, Arterburn DE. Long-term outcomes of bariatric surgery: a National Institutes of Health symposium. JAMA Surg. 2014;149:1323-1329. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 196] [Cited by in RCA: 245] [Article Influence: 24.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 4. | Finks JF, Dimick JB. An updated National Institutes of Health consensus panel on bariatric surgery. JAMA Surg. 2014;149:1329-1330. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Sheng B, Truong K, Spitler H, Zhang L, Tong X, Chen L. The Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Type 2 Diabetes Remission, Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications, and Mortality: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes Surg. 2017;27:2724-2732. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 91] [Cited by in RCA: 160] [Article Influence: 20.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Wu GZ, Cai B, Yu F, Fang Z, Fu XL, Zhou HS, Zhang W, Tian ZQ. Meta-analysis of bariatric surgery versus non-surgical treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Oncotarget. 2016;7:87511-87522. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Heneghan HM, Nissen S, Schauer PR. Gastrointestinal surgery for obesity and diabetes: weight loss and control of hyperglycemia. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012;14:579-587. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | El Khoury L, Chouillard E, Chahine E, Saikaly E, Debs T, Kassir R. Metabolic Surgery and Diabesity: a Systematic Review. Obes Surg. 2018;28:2069-2077. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Gulinac M, Novakov IP, Antovic S, Velikova T. Surgical complications in COVID-19 patients in the setting of moderate to severe disease. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2021;13:788-795. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Crozet J, Pasquer A, Pelascini E, Robert M. Factors influencing bariatric surgery outcomes. J Visc Surg. 2023;160:S7-S11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Nuzzo A, Czernichow S, Hertig A, Ledoux S, Poghosyan T, Quilliot D, Le Gall M, Bado A, Joly F. Prevention and treatment of nutritional complications after bariatric surgery. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:238-251. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 12.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Chevallier JM. [From bariatric to metabolic surgery: 15 years experience in a French university hospital]. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2010;194:25-36; discussion 36. [PubMed] |
| 13. | Koch TR, Finelli FC. Postoperative metabolic and nutritional complications of bariatric surgery. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2010;39:109-124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 14. | Weiss D. Long-term Complications of Bariatric Surgery. JAMA. 2021;325:186. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | O'Brien PE, Hindle A, Brennan L, Skinner S, Burton P, Smith A, Crosthwaite G, Brown W. Long-Term Outcomes After Bariatric Surgery: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Weight Loss at 10 or More Years for All Bariatric Procedures and a Single-Centre Review of 20-Year Outcomes After Adjustable Gastric Banding. Obes Surg. 2019;29:3-14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 279] [Cited by in RCA: 476] [Article Influence: 95.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | O'Brien PE, Brennan L, Laurie C, Brown W. Intensive medical weight loss or laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of mild to moderate obesity: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomised trial. Obes Surg. 2013;23:1345-1353. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Angrisani L, Cutolo PP, Formisano G, Nosso G, Vitolo G. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding versus Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 10-year results of a prospective, randomized trial. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9:405-413. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Salminen P, Helmiö M, Ovaska J, Juuti A, Leivonen M, Peromaa-Haavisto P, Hurme S, Soinio M, Nuutila P, Victorzon M. Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss at 5 Years Among Patients With Morbid Obesity: The SLEEVEPASS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2018;319:241-254. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 729] [Cited by in RCA: 711] [Article Influence: 101.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Peterli R, Wölnerhanssen BK, Peters T, Vetter D, Kröll D, Borbély Y, Schultes B, Beglinger C, Drewe J, Schiesser M, Nett P, Bueter M. Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss in Patients With Morbid Obesity: The SM-BOSS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2018;319:255-265. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 693] [Cited by in RCA: 875] [Article Influence: 125.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Aminian A, Brethauer SA, Navaneethan SD, Singh RP, Pothier CE, Nissen SE, Kashyap SR; STAMPEDE Investigators. Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical Therapy for Diabetes - 5-Year Outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:641-651. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1626] [Cited by in RCA: 1885] [Article Influence: 235.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | van Veldhuisen SL, Gorter TM, van Woerden G, de Boer RA, Rienstra M, Hazebroek EJ, van Veldhuisen DJ. Bariatric surgery and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. 2022;43:1955-1969. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 157] [Article Influence: 52.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Yoshino M, Kayser BD, Yoshino J, Stein RI, Reeds D, Eagon JC, Eckhouse SR, Watrous JD, Jain M, Knight R, Schechtman K, Patterson BW, Klein S. Effects of Diet versus Gastric Bypass on Metabolic Function in Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:721-732. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 164] [Cited by in RCA: 180] [Article Influence: 36.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Aminian A, Zajichek A, Tu C, Wolski KE, Brethauer SA, Schauer PR, Kattan MW, Nissen SE. How Much Weight Loss is Required for Cardiovascular Benefits? Insights From a Metabolic Surgery Matched-cohort Study. Ann Surg. 2020;272:639-645. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Visseren FLJ, Mach F, Smulders YM, Carballo D, Koskinas KC, Bäck M, Benetos A, Biffi A, Boavida JM, Capodanno D, Cosyns B, Crawford C, Davos CH, Desormais I, Di Angelantonio E, Franco OH, Halvorsen S, Hobbs FDR, Hollander M, Jankowska EA, Michal M, Sacco S, Sattar N, Tokgozoglu L, Tonstad S, Tsioufis KP, van Dis I, van Gelder IC, Wanner C, Williams B; ESC National Cardiac Societies; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3227-3337. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3739] [Cited by in RCA: 3266] [Article Influence: 816.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, Albus C, Brotons C, Catapano AL, Cooney MT, Corrà U, Cosyns B, Deaton C, Graham I, Hall MS, Hobbs FDR, Løchen ML, Löllgen H, Marques-Vidal P, Perk J, Prescott E, Redon J, Richter DJ, Sattar N, Smulders Y, Tiberi M, van der Worp HB, van Dis I, Verschuren WMM, Binno S; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts) Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2315-2381. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5080] [Cited by in RCA: 4699] [Article Influence: 522.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 26. | Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, Ard JD, Comuzzie AG, Donato KA, Hu FB, Hubbard VS, Jakicic JM, Kushner RF, Loria CM, Millen BE, Nonas CA, Pi-Sunyer FX, Stevens J, Stevens VJ, Wadden TA, Wolfe BM, Yanovski SZ. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(Pt B):2985-3023. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1717] [Cited by in RCA: 2025] [Article Influence: 168.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Cummings DE, Rubino F. Response to Comment on Rubino et al. Metabolic Surgery in the Treatment Algorithm for Type 2 Diabetes: A Joint Statement by International Diabetes Organizations. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:e202-e203. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K, Schoelles K. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724-1737. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5073] [Cited by in RCA: 4706] [Article Influence: 224.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 29. | Kang JH, Le QA. Effectiveness of bariatric surgical procedures: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e8632. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 134] [Article Influence: 16.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. |
Grozdev K, Khayat N, Arabadzhiev A, Kamenov Zdr, Handjieva-Darlenska T, Ivanova E, Georgiev Ognian, Angelov Kostadin.
Multidisciplinary approach in bariatric surgery: initial experience for the Bulgarian Public Health System. Khirurgiia 2018; |
| 31. | Lim R, Beekley A, Johnson DC, Davis KA. Early and late complications of bariatric operation. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2018;3:e000219. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 15.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Chang SH, Freeman NLB, Lee JA, Stoll CRT, Calhoun AJ, Eagon JC, Colditz GA. Early major complications after bariatric surgery in the USA, 2003-2014: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2018;19:529-537. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 64] [Cited by in RCA: 95] [Article Influence: 13.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Stone G, Samaan JS, Samakar K. Racial disparities in complications and mortality after bariatric surgery: A systematic review. Am J Surg. 2022;223:863-878. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Chierici A, Chevalier N, Iannelli. Postoperative morbidity and weight loss after revisional bariatric surgery for primary failed restrictive procedure: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2022;102:106677. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 35. | Poole M, Fasola L, Zevin B. Management of Complications After Bariatric Surgery: a Survey of Comfort and Educational Needs of General Surgeons in Ontario, Canada. Obes Surg. 2022;32:2407-2416. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Hachem A, Brennan L. Quality of Life Outcomes of Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review. Obes Surg. 2016;26:395-409. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 122] [Cited by in RCA: 103] [Article Influence: 11.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Sierżantowicz R, Ładny JR, Lewko J. Quality of Life after Bariatric Surgery-A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Summerville S, Kirwan E, Sutin AR, Fortune D, O'Súilleabháin PS. Personality trait associations with quality-of-life outcomes following bariatric surgery: a systematic review. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2023;21:32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Rajeev ND, Samaan JS, Premkumar A, Srinivasan N, Yu E, Samakar K. Patient and the Public's Perceptions of Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review. J Surg Res. 2023;283:385-406. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Arterburn DE, Telem DA, Kushner RF, Courcoulas AP. Benefits and Risks of Bariatric Surgery in Adults: A Review. JAMA. 2020;324:879-887. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 649] [Cited by in RCA: 680] [Article Influence: 136.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Robertson AGN, Wiggins T, Robertson FP, Huppler L, Doleman B, Harrison EM, Hollyman M, Welbourn R. Perioperative mortality in bariatric surgery: meta-analysis. Br J Surg. 2021;108:892-897. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 12.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |