Published online Jan 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.210
Peer-review started: October 10, 2022
First decision: November 11, 2022
Revised: November 25, 2022
Accepted: December 21, 2022
Article in press: December 21, 2022
Published online: January 6, 2023
Processing time: 86 Days and 14.6 Hours
Ochronosis, also known as alkaptonuria, is a rare autosomal recessive self-metabolic disease arising from deficiency of homogentisate 1,2 dioxygenase enzyme. It affects several organs and muscoskeletal structures. We herein report a case of a patient who presented with severe hip arthropathy complicated with late stage ochronosis.
A 56-year-old male patient was admitted in our department in 2019 with complaints of chronic low backache and left hip pain. After the required investigations were done, lumbar disc herniation and severe hip arthritis were the initial diagnosis. A total left hip arthroplasty was performed. Ochronotic osteoarthritis was only obtained post-surgery as confirmatory diagnosis. He was again admitted mid 2022 with the same complaints on the right hip. Subsequently, he underwent a total right hip arthroplasty. Post-operative recovery and follow-ups were deemed very satisfactory.
Ochronosis is an unusual diagnosis for a patient who presents with typical hip arthritis. Thus, unless meticulous history taking and advanced laboratory tests, the diagnosis can easily be missed by surgeons.
Core Tip: Ochronosis is not an usual diagnosis in orthopedics. Thus, unless meticulous history taking and advanced laboratory tests, the diagnosis can easily be missed by surgeons. Advanced testing should come in mind when odd physical examinations are noted and especially with peculiar radiological findings. Early diagnosis and a good communication between the two parties are primordial to obtain the best prognosis.
- Citation: Yap San Min N, Rafi U, Wang J, He B, Fan L. Ochronotic arthropathy of bilateral hip joints: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(1): 210-217
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i1/210.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.210
Ochronosis is a rare metabolic disease with an estimated incidence of about 1:1000000[1] arising from the deficiency of homogentisate 1,2 dioxygenase enzyme. Symptoms usually manifest in patients ranging from 20 to 50-year-old with a 2:1 male to female ratio[2]. The end stage of this disease can be accompanied with severe osteoarthritis, known as ochronotic osteoarthropathy[3,4]. Due to the rarity of the disease, initial diagnosis is challenging. We herein report a case of a patient who presented with severe hip arthropathy who was then diagnosed with late stage ochronosis.
A 56-year-old male patient was admitted to our hospital in 2019 with complaints of low backache, limited range of motion and pain in the left hip.
In 2019, he had low back pain accompanied with left buttock pain for 5 years and severe movement limitation in the left lower limb for 4 wk.
The patient was generally in good health and had a history of high blood pressure for several years, no history of other chronic, non-communicable and infectious diseases. He had ureterolithiasis surgery a few years back. He did not provide detailed information concerning any major trauma, blood transfusion, drug and food allergy and vaccination status. There was history of dark colored urine with no similar case in the family.
He was of Chinese Han ethnicity, married and had 1 healthy female offspring. No remarkable history was noted.
Upon general examination, the patient was looking well with no obvious abnormalities. No notable skin changes were observed; lesions, rash and erythema were absent. Cardiopulmonary and abdominal examinations were within normal range. Palpation and percussion of the spine revealed tenderness and pain in the lumbar5/Sac1 paravertebral and intervertebral space. Lordosis and Kyphosis of the spine were normal despite limited motion of the lumbar region. Flexion of the hip, extension of the knee and toes were normal in both lower limbs; Lasegue and Braqard test were both negative, pain was positive in left femoral trochanter and tenderness was felt in the left inguinal region upon palpation. Left hip “4-sign” positive, external and internal rotation with abduction and adduction of left hip were limited, posterior extension was 5 degrees and flexion was 50 degrees, Harris score of the left hip was 35.
During hospitalization, the left hip joint was thoroughly investigated and laboratory screenings indicated that, basic blood and urine tests were all within normal range. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, antistreptolysin O, rheumatoid factor and urinalysis were also normal or negative.
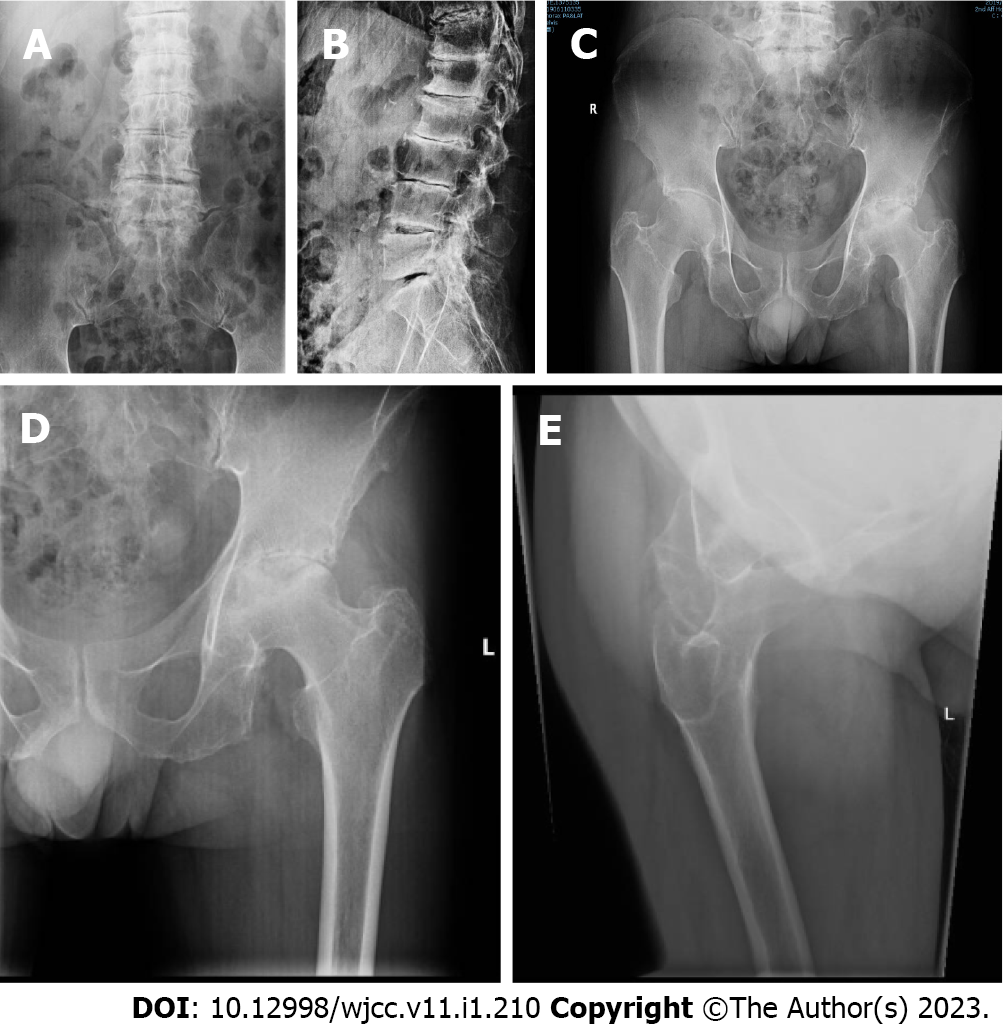
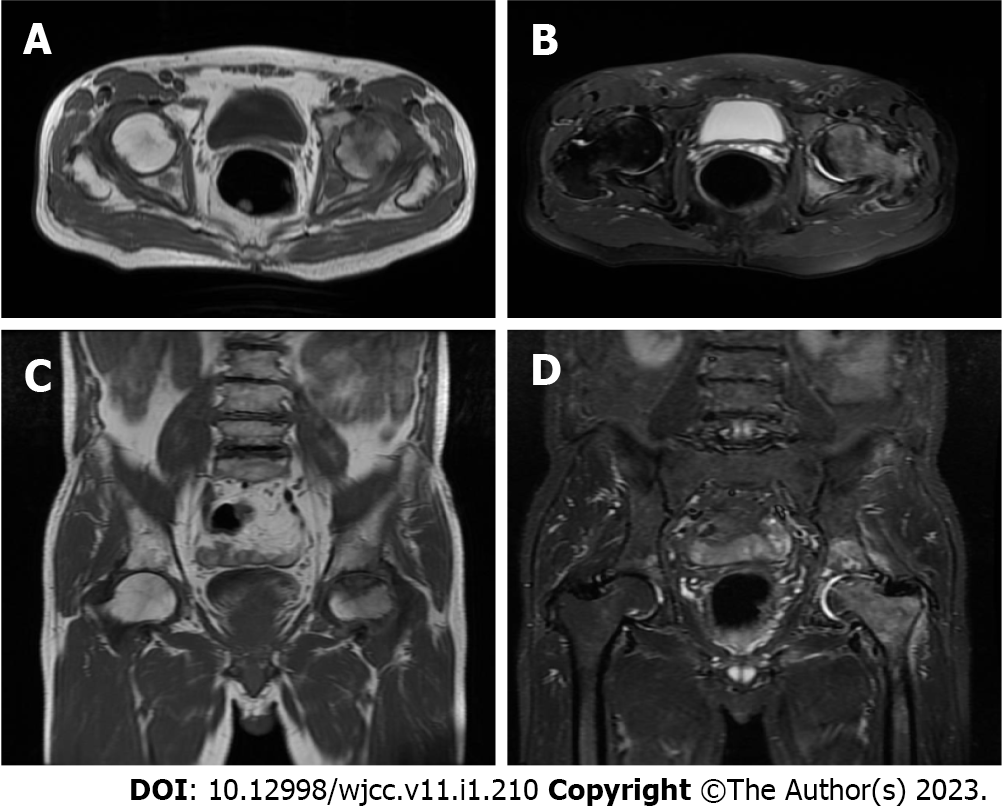
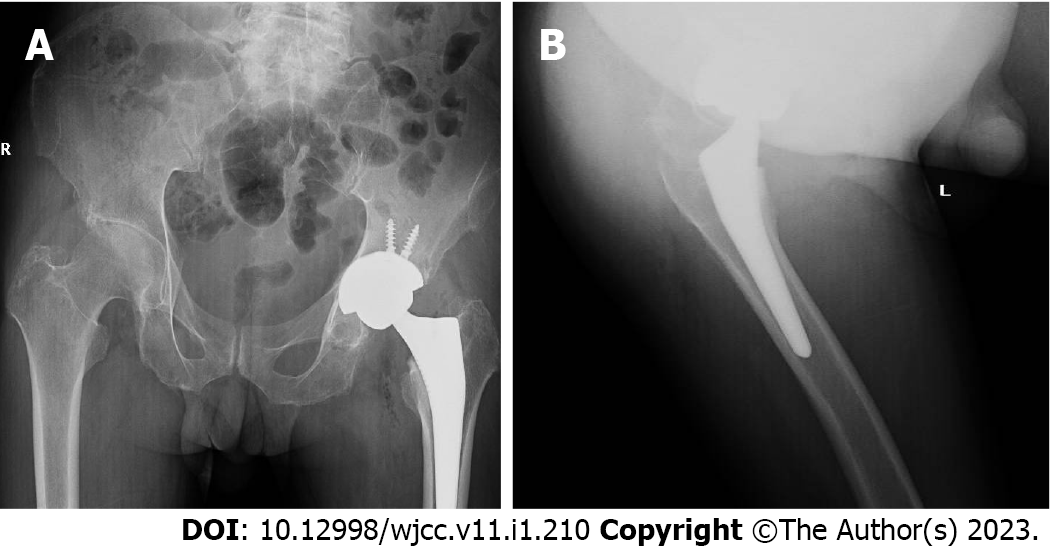
Thoracolumbar X-ray reported “spondylitis in thoracic vertebra, lumbar vertebra and pelvis, bilateral hip arthritis, aseptic necrosis of left hip joint” (Figure 1). Magnetic resonance imaging of both hips showed “aseptic necrosis of the left femoral head and left hip arthritis, edema of right femoral head and cervical bone marrow, bilateral acetabular cystic ischemia and edema in the left gluteus maximus intermuscular space” (Figure 2). Taking the patient’s history, laboratory and radiology findings into account, the following primary diagnoses were made: Bilateral hip joint osteoarthritis, aseptic necrosis of left femoral head (stage 4), lumbar disc herniation (L5/S1).
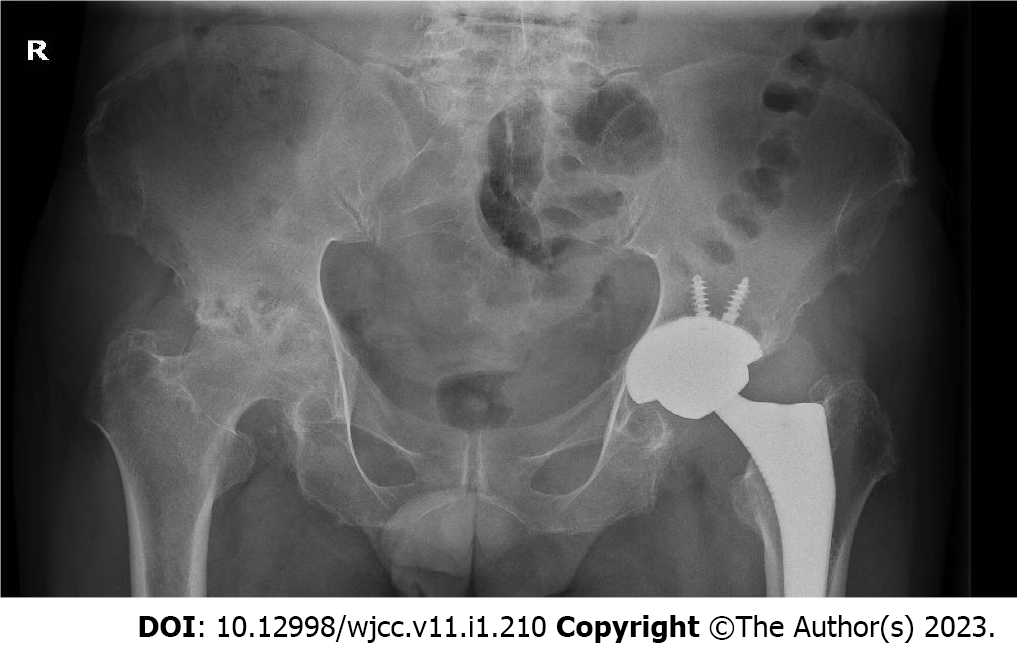
Upon these new discoveries and consultation of relevant literature, the patient was diagnosed with alkaptonuria, ochronotic osteoarthropathy of the left hip and L5/S1 disc herniation. In July 2022, patient presented himself again to our department with pain and limited range of motion in the right hip. A pelvic X-ray revealed a marked degeneration in his right hip (Figure 3). Consequently, he was admitted and scheduled for a total right hip replacement. Similar findings were noted during surgery as compared to his previous left hip replacement (Figure 4). The intervention was uneventful (Figure 5).
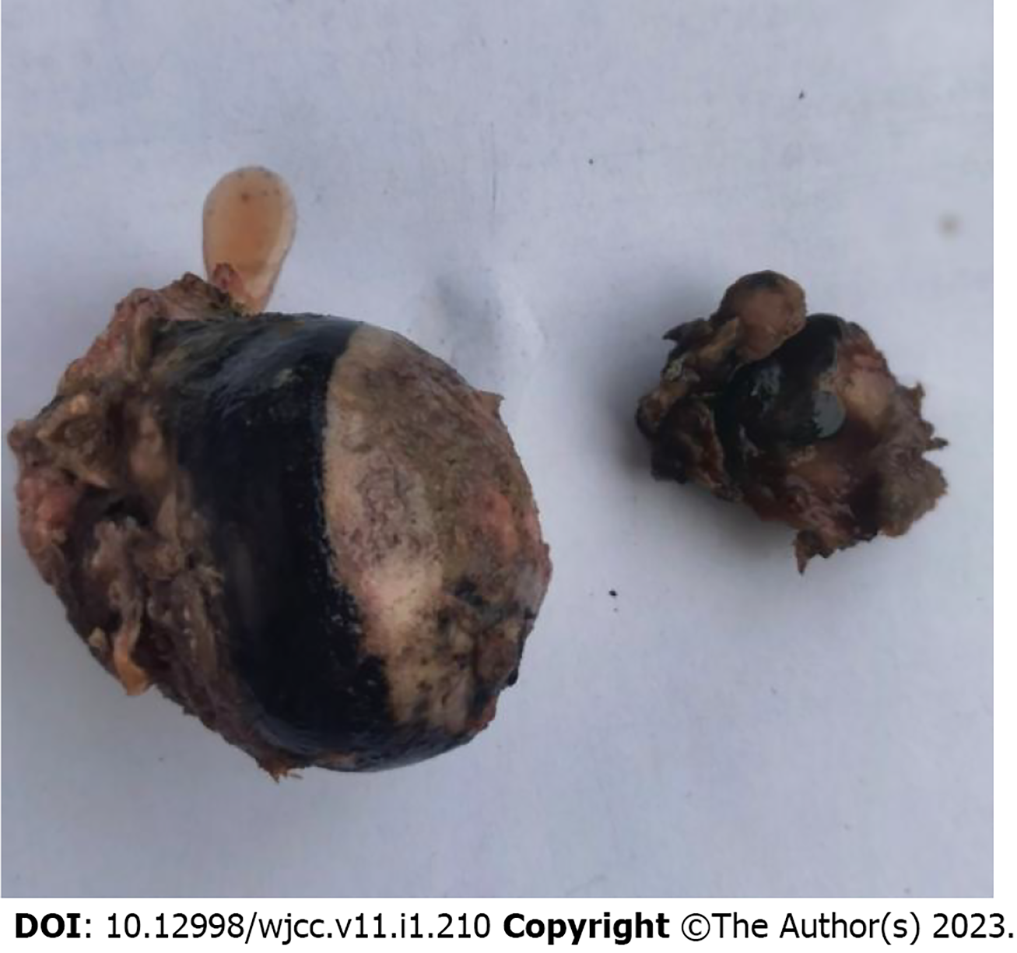
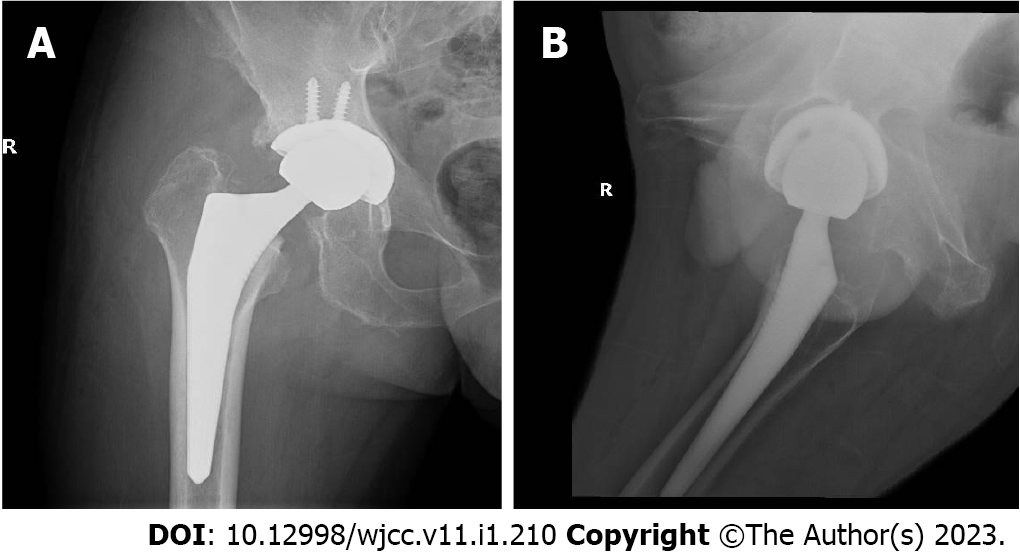
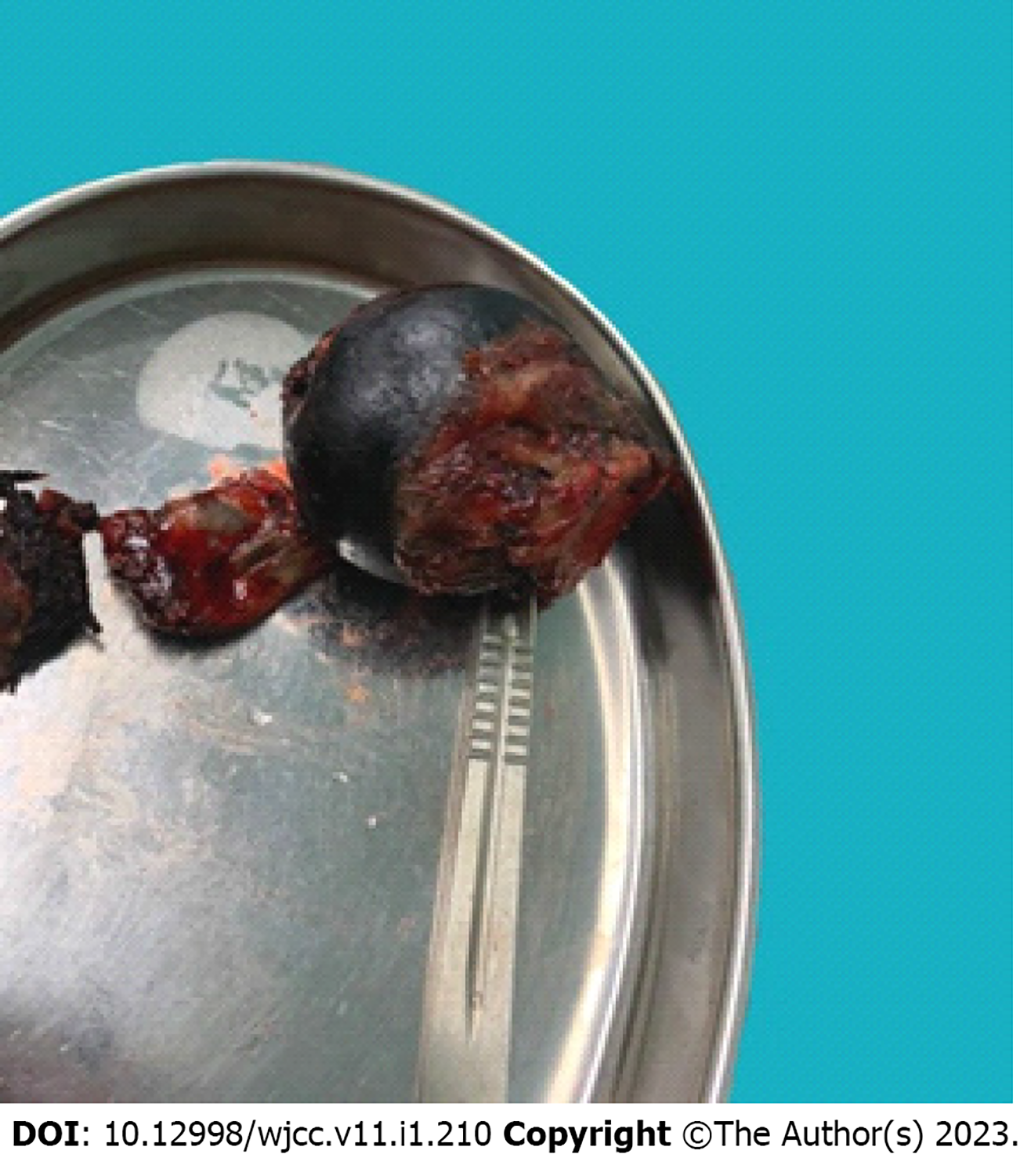
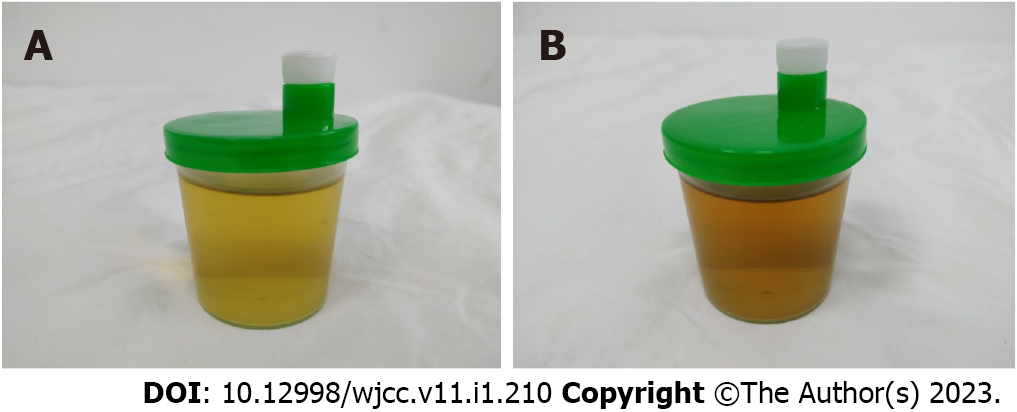
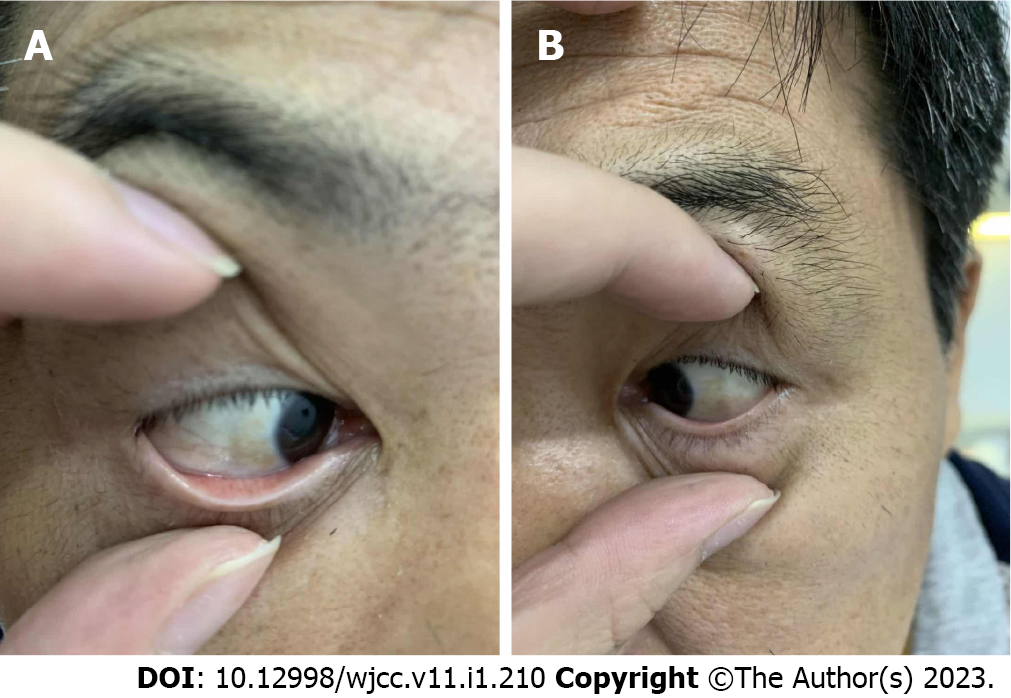
Based on these radiological and physical findings, a left total hip replacement was scheduled on the 4th d of admission. During surgery, a large amount of black and brown material deposits was seen on the surface of the joint capsule. Further incision of the joint capsule revealed that the femoral head and the whole joint capsule were black and brown (Figure 6). They were sent for histopathology. Nevertheless, surgery was successful. Post-operative X-ray of the left hip was very satisfactory (Figure 7). Taking this unusual finding into account, we decided to investigate and include new tests. Histopathology report of the femoral head and joint capsule revealed inflammatory hyperplasia of the joint capsule. A urine sample was taken in the morning and let to oxidise, specific urine tests were also ordered. The urine sample turned dark brown after a 24 h rest (Figure 8). Urine homogentisic acid (HGA) was also positive. A detailed eye examination revealed yellowish-brown plaques in both sclerae (Figure 9).
After his discharge in 2019, the patient was followed up to 6 mo with satisfying outcome. The patient reported that his left hip pain subsided and had a normal gait. The left hip joint Harris score was 88 points. In 2022, after a 3 mo follow-up, the gait was normal, right hip pain was negligible and patient stated that he was living a normal lifestyle.
Ochronosis, also known as alkaptonuria, brown yellow disease, black uricemia, was proposed and defined by Virchow through an autopsy in 1866[1] and described by Garrod in 1908 as “a metabolic error in the human body”[5]. Due to genetic deficiency of enzyme homogentisate 1,2 dioxygenase, tyrosine metabolism ends at the level of HGA and it is no longer further oxidized and decomposed into acetoacetic acid and fumaric acid. The accumulated HGA in the body is oxidized and decomposed and the product irreversibly combines with relevant tissues and organs, to form a brownish yellow polymer, leading to degeneration of brown yellow pigmentation, fragile texture and rupture of tissues caused by induced inflammatory reaction. Long-term deposition of HGA in bone tissue can cause spinal and joint diseases, and severe destruction of cartilage in late stage and can result in crippling osteoarthropathy[6,7]. Part of the excess HGA is excreted by urine and oxidized into melanin in the air, making the urine black[8]. Urine HGA is currently considered as the gold standard for the diagnosis of the disease[9].
Symptoms of ochronosis are often not typical, some doctors have insufficient understanding of the disease and many hospitals do not routinely perform urine HGA tests. Ochronotic osteoarthropathy is considered as a rare joint disease and therefore it is easily misdiagnosed as osteoarthritis or even as lumbar disc herniation. The diagnosis is often confirmed by clinical symptoms and imaging findings but is mostly diagnosed when brown yellow pigment deposits are found during surgery. It should be distinguished from osteoarthritis, hemophilia, immune diseases and other secondary arthritis in clinical settings. Ochronosis osteoarthropathy usually involves major bearing joints such as spine, hip and knee, but also the shoulder and elbow joints, presenting as early onset and rapidly progressing degenerative joint disease[10]. Symptoms often first occur in the spine, presenting as spinal canal stenosis. The clinical and imaging manifestations are similar to ankylosing spondylitis such as the absence of vertebral space and fusion. It can later involve peripheral weight-bearing joints causing similar symptoms like osteoarthritis; joint space disappearance, joint destruction and secondary femoral head necrosis may occur in severe cases.
In this case, the patient was admitted with “lumbar disc herniation”. During hospitalization, the patient was diagnosed with systemic multiple joint disease. The primary symptom was pain and restricted movement in the left hip. In addition, no remarkable skin changes were observed during his physical examination. The disease can be classified into the endogenous or exogenous group. In the latter case, it is caused by long-term local use of hydroquinone, phenol and other phenol intermediates resulting in the classic skin manifestations observed by physicians. Urinary melanic acid oxidase contains a hydrophobic group (-SH), therefore, its activity can be inhibited by certain chemicals and drugs such as phenol, phenol intermediates, resorcinol, hydroquinone, picric acid, acetaminophen, mipaline, etc. as well as by certain antimalarials drugs, resulting in the accumulation of uronic acid in the collagen fibers of the local skin. The patient, in this case, has not taken any special drugs orally. Therefore, the disease was of endogenous origin.
Surgical indication was clear because of the disappearance of joint space and necrosis of the collapsed femoral head. It was not until a large amount of black and brown deposits were found in the joint capsule and femoral head during surgery that the diagnosis was confirmed. Therefore, it is imperative to have a correct understanding of this disease to be able to find clues during history taking to give a correct diagnosis. As surgeons, it is imperative that the preoperative diagnosis matches perioperative procedures to ensure the maximum chance of success. In this case, although the surgical method was correct with satisfactory outcome, there were still medical risks in the absence of a clear preoperative diagnosis and proper dialogue with the patient.
Ochronosis is not a diagnosis that comes to the minds of orthopedic surgeons with this type of patient presentation. Thus, unless advanced medical work-up, the diagnosis can easily be omitted. Currently, there are no effective non-surgical treatments for ochronotic arthropathy. Surgical interventions seem to produce the best outcome for damaged joints. Nevertheless, early gene screening and diagnosis can drastically increase prognosis and better management in ochronotic osteoarthropathy. Therefore, it is imperative to have a thorough and early screening to uncover any rare diseases.
We would like to acknowledge and thank the patient for allowing us to share his case and pictures with the medical community.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Abbas K, Pakistan; Zhiyong S, China S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: A P-Editor: Wang JJ
| 1. | Phornphutkul C, Introne WJ, Perry MB, Bernardini I, Murphey MD, Fitzpatrick DL, Anderson PD, Huizing M, Anikster Y, Gerber LH, Gahl WA. Natural history of alkaptonuria. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:2111-2121. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 428] [Cited by in RCA: 390] [Article Influence: 17.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Davison AS, Hughes AT, Milan AM, Sireau N, Gallagher JA, Ranganath LR. Alkaptonuria - Many questions answered, further challenges beckon. Ann Clin Biochem. 2020;57:106-120. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Mazoochy H, Razi M. Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Surgery in a Patient with Ochronotic Arthropathy: Surgical Tips. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2018;6:577-581. [PubMed] |
| 4. | Evangelista P, Parente JS, Brasileiro R, Paiva JG, Freitas MV, Moreira A, Alves AP, Costa I. Secondary osteoarthritis to ochronotic arthropathy - a diagnostic challenge. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2018;64:583-585. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Zatkova A, Ranganath L, Kadasi L. Alkaptonuria: Current Perspectives. Appl Clin Genet. 2020;13:37-47. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Zanwar A, Phatak S, Misra R. Ochronosis. Postgrad Med J. 2016;92:626. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Xu H, Wang J, Chen F, Hong Z, Zhang X, Ji X, Shao D. Ochronotic arthritis of bilateral knees: a case report. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:8185-8189. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Arora S, Sodhi N, Harith AK, Kapoor U. A case of 'blue skin' and 'dark urine'. Med J Armed Forces India. 2018;74:300-303. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Thapa M, Bhatia M, Maurya VK. Alkaptonuria. Med J Armed Forces India. 2018;74:394-396. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Alkasem W, Boissiere L, Obeid I, Bourghli A. Management of a pseudarthrosis with sagittal malalignment in a patient with ochronotic spondyloarthropathy. Eur Spine J. 2019;28:2283-2289. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |