Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2261
Peer-review started: July 20, 2021
First decision: September 5, 2021
Revised: September 17, 2021
Accepted: January 22, 2022
Article in press: January 22, 2022
Published online: March 6, 2022
Processing time: 224 Days and 16 Hours
Intestinal intussusception caused by intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas is extremely rare in the clinic and has not been reported previously.
A 29-year-old man was admitted to the hospital for chronic abdominal pain and bloating. The preoperative diagnosis was intestinal obstruction and intussusception. Then, laparotomy, partial small intestinal resection and extraintestinal decompression were performed. Postoperative pathology confirmed intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas. After surgery, the patient recovered well with no complications. No recurrence was observed after more than 5 mo of follow-up.
We report a new case of a young male with intussusception caused by intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas. Surgery is the main treatment for these conditions. This study aimed to raise awareness and provide information to improve the clinical management of this rare yet serious condition.
Core Tip: We present a new case of a young man with intussusception caused by intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas. This case highlights that intestinal duplication and heterotopic pancreas should be considered causes of intestinal obstruction associated with intussusception.
- Citation: Wang TL, Gong XS, Wang J, Long CY. Intestinal intussusception caused by intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(7): 2261-2267
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i7/2261.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2261
Intestinal intussusception refers to intestinal tube insertion into the connected intestinal lumen, which causes obstruction of the intestinal contents. Adult intussusception only accounts for 5% of the total incidence[1]. The average age of adult patients is 50 years, and the male-to-female ratio is 1:5[2]. Adult intussusception has no specific clinical manifestations and lacks the classic triad of pediatric intussusception symptoms: abdominal pain, vomiting, and jam-like stool. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) is considered the most useful examination, but most specific causes still require intraoperative detection or postoperative pathology for clarification. Ninety percent of adult intussusception is caused by tumors, polyps, diverticulum, etc.[3-6]. Thus, 70% to 90% of adult intussusception requires surgical treatment[7]. However, to date, there are no case reports on intussusception caused by small intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas.
We report a new case of a young man with intussusception caused by intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas. Informed consent for the publication of these data was obtained from the patient.
A 29-year-old man was admitted to the hospital for repeated abdominal pain and bloating for more than 2 mo that had been aggravated for 2 d.
The patient had repeated abdominal pain and abdominal distension for 2 mo and had been treated in many hospitals. The symptoms could be relieved by symptomatic treatments, such as rehydration and pain relief. Due to aggravation of the above symptoms for 2 d, the patient was admitted to our hospital to consider the possibility of intestinal obstruction. Since onset, the patient’s anal exhaust and defecation had decreased, with no additional vomiting, chills, fever or other discomfort. A yellow-brown stool was discharged once on the day of admission, and no mucous or blood was present in the stool.
The patient had no relevant previous medical history.
The patient’s family history was unremarkable.
The physical examination findings were as follows: slight abdominal bulge, no obvious tension of the abdominal muscles, right lower abdominal tenderness, slight rebound pain, negative Murphy sign, and no obvious palpable abdominal mass.
Initial laboratory data revealed a white blood cell count of 8.3 × 109/L, neutrophil count of 6.67 × 109/L, neutrophil percentage of 83.1% and C-reactive protein of 13.9 mg/L. Liver and kidney parameters were normal.
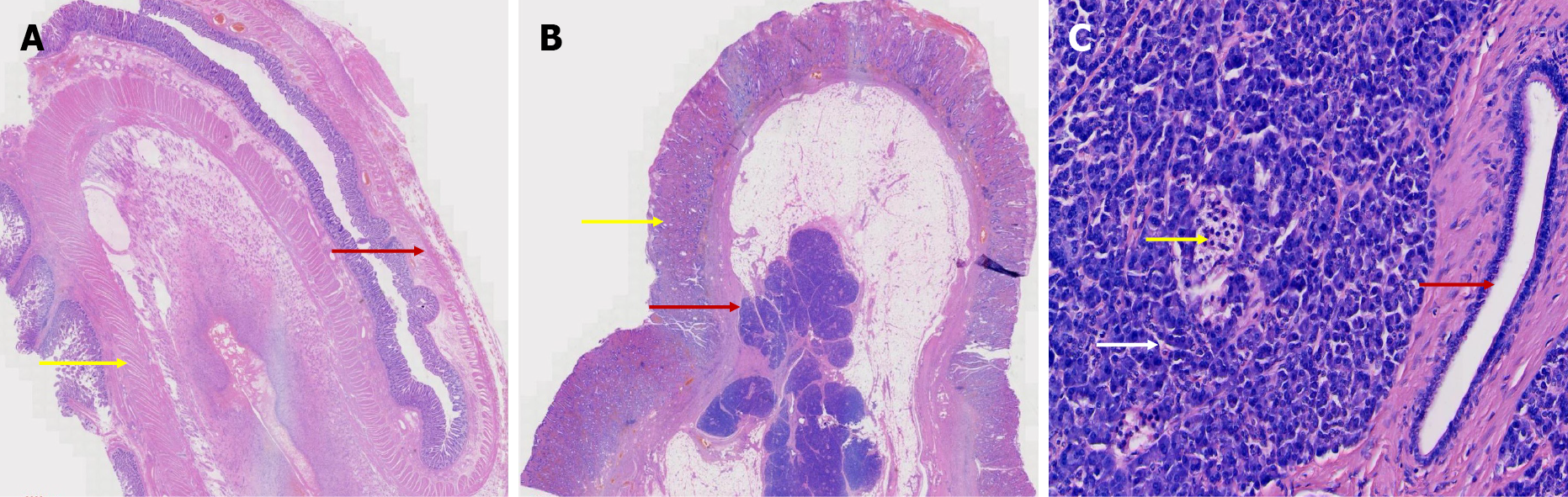
The postoperative pathology results were as follows: Two intestinal canal-like structures were observed in the mesentery-side lumen, measuring approximately 6 cm in length and 2.5 cm in diameter and 2.5 cm in length and 2 cm in diameter. The intestinal canals were observed directly after incision (Figure 1). Microscopically, the intestinal mucosa, submucosa, muscular layer and serosal layer were observed in both intestinal canals. The muscular layer of the short intestinal wall was significantly thickened, and local dysplasia of the external longitudinal muscle was accompanied by disordered growth of the muscular bundle (Figure 2A). The serosal surface of the long intestinal canal showed fatty tissue hyperplasia with ectopic pancreas, and pancreatic acinar and islet tissue and pancreatic duct cells were observed (Figure 2B and C).
Abdominal enhanced CT showed an annular bowel shadow in the lower left abdomen, indicating the possibility of intussusception, intestinal wall thickening, and inflammatory edema (Figure 3).
The following diagnoses were made: Intestinal obstruction, intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas, and intussusception.
The patient underwent emergency exploratory laparotomy, partial small intestinal resection and extraintestinal decompression.
During the operation, the proximal small intestine was found to be inserted into the distal small intestine on the ileum approximately 80 cm away from the ileocecal valve. The lesion length was approximately 20 cm, and the proximal small intestine was dilated to a diameter of approximately 8 cm. The distal small intestine was empty, and the small intestine at the site of intussusception was edematous. Some of the intestinal wall was thickened and hardened, resulting in complete obstruction of the intestinal cavity. Exploration and manual reduction of a mass measuring approximately 3 cm × 2.5 cm at the site of intussusception were difficult. Small intestinal tumors, intestinal intussusception and intestinal obstruction were considered. Partial small intestinal resection and extraintestinal decompression were performed.
The patient recovered well with no complications. No recurrence was found after more than 5 mo of follow-up.
Intussusception is a special form of intestinal obstruction, accounting for approximately 1%-5% of cases[1]. The exact cause of approximately 8%-12% of adult intussusception is unclear[1,7,8]. Any intestinal disease that changes the normal peristalsis of the intestine increases the risk of intussusception[9]. Adult intussusception is often secondary to intestinal tumors, polyps, diverticulum, etc. Therefore, for suspected adult intussusception patients, digestive tract radiography, CT, magnetic resonance imaging and other examinations should be actively performed to clarify the etiology, and active surgery is needed to treat the primary disease and relieve the obstruction. For patients with adult intussusception that can be reduced, subsequent resection of the organic lesions remains the preferred treatment.
Intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas are two independent congenital defects. The incidence of ectopic pancreas according to autopsy reports is 0.5%-13%[10]. The etiology of ectopic pancreas is still unclear. Studies have shown that during embryonic development, pancreatic primordia adhere to or penetrate the intestinal wall of the embryo and continue to develop and form in various abnormal locations with the movement of intestinal transposition[11,12]. Ectopic pancreas is mainly composed of pancreatic duct and acinar tissue and usually lacks islet tissue. There are no anatomical or vascular connections between the ectopic pancreas and normal pancreas[13]. It most commonly occurs in the duodenum but can also appear in the jejunum and, rarely, in the ileum[14]. Ectopic pancreas is generally considered asymptomatic[15]. In a few case reports, intestinal obstruction, abdominal pain and bleeding were also mentioned[16,17]. Due to the diverse locations and lack of specific lesions, early ectopic pancreas diagnosis is difficult, easily leading to misdiagnoses or missed diagnosis. We searched the literature on PubMed for adult intussusception and ectopic pancreas, and the results are summarized in Table 1.
| Ref. | Gender | Age | Location |
| Ganapathi et al[22], 2011 | Male | 26 | Ileo-ileal |
| Sciannamea et al[23], 2020 | Female | 33 | Ileo-ileal |
| Gold et al[24], 2020 | Female | 23 | Intestinal |
| Giordano et al[25], 2017 | Male | 29 | Jejunojejunal |
| Chuang et al[26], 2010 | Female | 26 | Ileo-ileal |
| Abe et al[27], 2020 | Female | 43 | Ileo-ileal |
| Daniel et al[28], 2021 | Female | 78 | Jejunojejunal |
The incidence rate of intestinal duplication is 1 in 10000 newborns, and it is rare in adults[18]. We retrieved the literature on adult intussusception caused by intestinal duplication from PubMed, and the publications are listed in Table 2. The differences between intestinal duplication and Meckel’s diverticulum are as follows: (1) Intestinal duplication shares a blood supply with the surrounding intestine, while diverticulum has an independent blood supply; and (2) well-developed smooth muscle is present in intestinal duplication but not in Meckel’s diverticulum[19]. Studies suggest that there is a direct communication hole between intestinal duplication and the normal intestinal wall for unknown reasons[20,21]. With the closure of the hole, the muscular layer becomes discontinuous, and feces form a mucosal bridge after passing through the hole, which leads to the occurrence of adult intussusception.
| Ref. | Gender | Age | Location |
| Kimura et al[21], 2018 | Male | 19 | Colon |
| Ho[29], 2012 | Male | 25 | Terminal ileum, appendix, colon and rectum |
| Li et al[30], 2013 | Male | 25 | Ileum |
| Al-Qahtani[31], 2016 | Female | 32 | Ileum |
| Kyo et al[32], 2016 | Male | 20 | Colon |
| Kim et al[33], 2014 | Female | 19 | Ileal |
| Reiser-Erkan et al[34], 2010 | Male | 25 | Colon |
| Kusnierz et al[35], 2014 | Unknown | 31 | Duodenal |
| Nadatani et al[36], 2016 | Male | 73 | Ileal |
| O'Connor et al[37], 1999 | Female | 32 | Duodenal |
Although adult intussusception, ectopic pancreas and intestinal duplication have been reported separately, our case was unique, as intussusception caused by intestinal duplication and heterotopic pancreas has not been reported previously.
In this case, the patient had been treated in many hospitals for repeated abdominal pain and received symptomatic treatments, such as fluid infusion and pain relief. However, because the fundamental cause of the disease was not determined, the symptoms persisted, and intussusception inevitably occurred, leading to complete intestinal obstruction. Therefore, we speculate that due to the abnormal anatomical position, when intestinal duplication is combined with ectopic pancreatic tissue, the ectopic pancreatic tissue is accompanied by the continuous growth of adipose tissue. Because of the compensatory ability of the body, increased intestinal peristalsis occurs, resulting in intussusception and complete intestinal obstruction. Therefore, early correct diagnosis and timely treatment are critical for adult intussusception.
This is the first reported case of intestinal intussusception caused by intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas. Therefore, intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas should be considered in the differential diagnosis of intussusception. Although modern diagnostic technology has greatly progressed, diagnosis of intestinal duplication and ectopic pancreas remains difficult. Definitive diagnosis usually depends on postoperative pathology.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Limaiem F S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: A P-Editor: Yan JP
| 1. | Azar T, Berger DL. Adult intussusception. Ann Surg. 1997;226:134-138. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 648] [Cited by in RCA: 666] [Article Influence: 23.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Honjo H, Mike M, Kusanagi H, Kano N. Adult intussusception: a retrospective review. World J Surg. 2015;39:134-138. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 170] [Article Influence: 17.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Eisen LK, Cunningham JD, Aufses AH Jr. Intussusception in adults: institutional review. J Am Coll Surg. 1999;188:390-395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 225] [Cited by in RCA: 243] [Article Influence: 9.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Weilbaecher D, Bolin JA, Hearn D, Ogden W 2nd. Intussusception in adults. Review of 160 cases. Am J Surg. 1971;121:531-535. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 239] [Cited by in RCA: 213] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Stubenbord WT, Thorbjarnarson B. Intussusception in adults. Ann Surg. 1970;172:306-310. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Akçay MN, Polat M, Cadirci M, Gencer B. Tumor-induced ileo-ileal invagination in adults. Am Surg. 1994;60:980-981. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Begos DG, Sandor A, Modlin IM. The diagnosis and management of adult intussusception. Am J Surg. 1997;173:88-94. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 365] [Cited by in RCA: 384] [Article Influence: 13.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Erkan N, Haciyanli M, Yildirim M, Sayhan H, Vardar E, Polat AF. Intussusception in adults: an unusual and challenging condition for surgeons. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2005;20:452-456. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 106] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Takeuchi K, Tsuzuki Y, Ando T, Sekihara M, Hara T, Kori T, Kuwano H. The diagnosis and treatment of adult intussusception. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;36:18-21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 126] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Gokhale UA, Nanda A, Pillai R, Al-Layla D. Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach: a case report and a brief review of the literature. JOP. 2010;11:255-257. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Liu YM, Shen HP, Li X, Gong JP. Heterotopic pancreas: a clinical analysis of nine patients and review of literature. Am Surg. 2012;78:E141-E143. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Heretsch P, Tzagkaroulaki L, Giannis A. Modulators of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010;18:6613-6624. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Sathyanarayana SA, Deutsch GB, Bajaj J, Friedman B, Bansal R, Molmenti E, Nicastro JM, Coppa GF. Ectopic pancreas: a diagnostic dilemma. Int J Angiol. 2012;21:177-180. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Tanaka K, Tsunoda T, Eto T, Yamada M, Tajima Y, Shimogama H, Yamaguchi T, Matsuo S, Izawa K. Diagnosis and management of heterotopic pancreas. Int Surg. 1993;78:32-35. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Armstrong CP, King PM, Dixon JM, Macleod IB. The clinical significance of heterotopic pancreas in the gastrointestinal tract. Br J Surg. 1981;68:384-387. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 130] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Serrano JS, Stauffer JA. Ectopic Pancreas in the Wall of the Small Intestine. J Gastrointest Surg. 2016;20:1407-1408. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Kilius A, Samalavicius NE, Danys D, Zaldokas G, Seinin D. Asymptomatic heterotopic pancreas in Meckel's diverticulum: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2015;9:108. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Iyer CP, Mahour GH. Duplications of the alimentary tract in infants and children. J Pediatr Surg. 1995;30:1267-1270. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Huang ZH, Wan ZH, Vikash V, Vikash S, Jiang CQ. Report of a rare case and review of adult intestinal duplication at the opposite side of mesenteric margin. Sao Paulo Med J. 2018;136:89-93. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Tamvakopoulos GS, Sams V, Preston P, Stebbings WS. Iron-deficiency anaemia caused by an enterolith-filled jejunal duplication cyst. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2004;86:W49-W51. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Kimura S, Iida H, Gunji N, Gohongi T, Ogata T. Stool filling of an intestinal duplication cyst at the ileocecal valve triggers colonic intussusception: a case report. Surg Case Rep. 2018;4:116. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Ganapathi S, Villa F, Perera R, Wan A. Ectopic pancreas, intussusception, and a ruptured mesenteric band: an unusual association. Clin Anat. 2011;24:128-132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Sciannamea A, Vaccari S, Marasco G, Dalla Via B, Lauro A, Marino IR, Vasuri F, Cervellera M, D'Andrea V, Tonini V. Concomitant Heterotopic Pancreas and Endometriosis as a Rare Cause of Ileo-Ileal Intussusception in a Young Woman with Spina Bifida: Case Report and Literature Review. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65:2800-2804. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Gold D, Nawass M, Imam R, Pillar N, Appelbaum L, Pikarsky A, Khalaileh A, Imam A. Intussusception in a pregnant patient caused by an ectopic pancreatic mass. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020;13:209-213. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Giordano A, Alemanno G, Bergamini C, Prosperi P, Bruscino A, Valeri A. The Role of Laparoscopy in the Management of a Diagnostic Dilemma: Jejunal Ectopic Pancreas Developing into Jejunojejunal Intussusception. Case Rep Surg. 2017;2017:8452947. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Chuang MT, Tsai KB, Ma CJ, Hsieh TJ. Ileoileal intussusception due to ileal ectopic pancreas with abundant fat tissue mimicking lipoma. Am J Surg. 2010;200:e25-e27. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Abe I, Saito M, Ikeda T, Fukuda R, Tanaka A, Rikiyama T. Ileectomy performed on a case of adult intussusception due to inversion of Meckel's diverticulum. J Surg Case Rep. 2020;2020:rjz367. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Daniel NE, Rampersad FS, Naraynsingh V, Barrow S, David S. Jejunal Intussusception Due to Heterotopic Pancreas: A Case Report. Cureus. 2021;13:e14586. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Ho YC. Total colorectal and terminal ileal duplication presenting as intussusception and intestinal obstruction. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:6338-6340. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Li BL, Huang X, Zheng CJ, Zhou JL, Zhao YP. Ileal duplication mimicking intestinal intussusception: a congenital condition rarely reported in adult. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:6500-6504. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Al-Qahtani HH. Enteric duplication cyst as a leading point for ileoileal intussusception in an adult: A rare cause of complete small intestinal obstruction. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2016;8:472-475. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Kyo K, Azuma M, Okamoto K, Nishiyama M, Shimamura T, Maema A, Shirakawa M, Nakamura T, Koda K, Yokoyama H. Laparoscopic resection of adult colon duplication causing intussusception. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:2398-2402. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Kim HS, Sung JY, Park WS, Kim YW. An ileal duplication cyst manifested as an ileocolic intussusception in an adult. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2014;25 Suppl 1:196-198. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Reiser-Erkan C, Erkan M, Ulbrich E, Nährig J, Kleeff J. Cystic colon duplication causing intussusception in a 25-year-old man: report of a case and review of the literature. BMC Surg. 2010;10:19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Kusnierz K, Pilch-Kowalczyk J, Gruszczynska K, Baron J, Lucyga M, Lampe P. A duodenal duplication cyst manifested by duodenojejunal intussusception and chronic pancreatitis. Surgery. 2014;156:742-744. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Nadatani Y, Watanabe T, Sugawa T, Eguchi S, Shimada S, Otani K, Yamagami H, Tanigawa T, Shiba M, Tominaga K, Fujiwara Y, Arakawa T. Double-balloon endoscopy WAS effective in diagnosing small intestinal duplication: a case report. Springerplus. 2016;5:1598. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | O'Connor PA, McGrath FP, Lane BE. Duodenal intussusception secondary to an internal duodenal duplication. Clin Radiol. 1999;54:69-70. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |