Published online Feb 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i4.1357
Peer-review started: August 11, 2021
First decision: September 2, 2021
Revised: September 22, 2021
Accepted: December 23, 2021
Article in press: December 23, 2021
Published online: February 6, 2022
Processing time: 166 Days and 2.6 Hours
In mirror-image dextrocardia, the anterior-posterior position of the cardiac chambers and great vessels is maintained, but the left-right orientation of the abdominal organs is reversed. The abnormal anatomy of the heart poses surgical challenges and problems in dealing with surgical risk and monitoring complications. There are few reports on closure of the left atrial appendage (LAA) in dextrocardia and no reports on the application of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) following LAA occlusion (LAAO) procedures.
The objective for this case was to ensure perioperative safety and accelerate postoperative recovery from LAAO in a patient with mirror-image dextrocardia. ERAS was guided by the theory and practice of nursing care. Atrial fibrillation was diagnosed in a 77-year-old male patient, in whom LAAO was performed. The 2019 guidelines for perioperative care after cardiac surgery recommend that the clinical nursing procedures for patients with LAAO should be optimized to reduce the incidence of perioperative complications and ensure patient safety. Music therapy can be used throughout perioperative treatment and nursing to improve the anxiety symptoms of patients.
The procedure was uneventful and proceeded without complications. Anxiety symptoms were improved.
Core Tip: Mirror dextrocardia has typical clinical characteristics. Because of the high prevalence and mortality of atrial fibrillation of patients with mirror dextrocardia, left atrial appendage occlusion has an important role in treatment, which continues to be confirmed. Left atrial appendage occlusion is an ideal choice for patients with atrial fibrillation. Moreover, music therapy can be used throughout perioperative treatment and nursing to improve the anxiety symptoms of patients.
- Citation: Tian B, Ma C, Su JW, Luo J, Sun HX, Su J, Ning ZP. Left atrial appendage occlusion in a mirror-image dextrocardia: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(4): 1357-1365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i4/1357.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i4.1357
Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) is a multimode, interdisciplinary care model designed to improve perioperative care, including medical care before, during, and after surgery and during rehabilitation. Increasing evidence supports the use of ERAS in surgical patients. ERAS is effective in reducing gastrointestinal infections and hospital stay associated with general colon and rectum surgery. The ERAS Society has been the source of international plans for colorectal, hepatobiliary, urinary, gastric, gynecological, and cardiac surgery groups, and provided evidence-based guidelines for the perioperative treatment and nursing of patients[1-3].
In cardiac surgery, the ERAS model shows that early extubation is safe and feasible, and can significantly shorten electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring and coronary care unit (CCU) stays. However, the application of ERAS models in cardiac surgery is still at an early stage, and reports in interventional cardiology are limited. Studies have shown that ERAS regimens are feasible and safe in minimally invasive cardiac surgery, and have the potential to significantly improve patient prognosis[4,5].
The ERAS model has characteristics specific to different clinical fields, but the basic concept is common to all fields. The 2019 guidelines for accelerating postoperative rehabilitation of heart surgery include correcting malnutrition before surgery, smoking and drinking cessation, establishing a cardiac preadaptation plan including education, nutrition optimization, sports training, social support, and reducing anxiety, infection prevention, carbohydrate loading (sugar prestorage), establishment of an electronic health platform, etc. The intraoperative care package includes local nasal treatment to eliminate staphylococcus colonization, skin preparation, depilation scheme, dressing changes, prevention of hypothermia, keeping venous access open, rigid sternum fixation, and hemostasis. Whole-process management of patients in the perioperative period includes intensive glycemic control, pain management, delirium screening, drug anticoagulation, early extubation, biomarkers for early identification of high-risk patients with acute kidney injury, and goal-directed recommendations (i.e., blood pressure, cardiac index, systemic venous oxygen saturation, and urine volume). Fluid management therapy is a cooperative multiteam effort, including nutritionists, early cardiac rehabilitation therapists, and physiotherapists.
Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) is a minimally invasive intervention guided by medical imaging equipment[6]. A device is positioned in the left atrial appendage (LAA) by percutaneous venipuncture to prevent thrombi from entering the blood circulation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Medical staff are concerned about the consequences of and low compliance with long-term use of oral anticoagulants and the high risk of bleeding. Therefore, LAAO has been applied as an alternative[7,8]. At present, the two most commonly used LAAO devices worldwide are the Watchman implant system and the Amplatzer cardiac plug. The Watchman device has been approved by Federal Drug Administration as an alternative for stroke prevention and it is the most widely used LAAO closure device[9]. Studies have shown that the effectiveness of LAAO against thrombus formation is similar to that of oral warfarin, and it has advantages in preventing stroke and maintaining quality of life[10-13]. In long-term follow-up, the incidence of both bleeding and stroke decreased significantly. LAAO was also found to be suitable for patients with atrial fibrillation who cannot tolerate oral anticoagulants, have a high risk of bleeding, have anticoagulant contraindications, and for whom anticoagulation did not prevent stroke[14-16]. The Watchman device was also found to reduce the incidence of perioperative complications, hemorrhagic stroke, stroke disability and mortality, cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality, and to improve clinical outcomes and prognosis[17-20]. With ongoing advances in perioperative care, LAAO will continue to develop as an effective alternative strategy to prevent stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation.
In dextrocardia, the apex of the heart points to or is located on the right side of the chest[21,22]. Using the longitudinal axis of the heart as a reference, dextrocardia can be seen as either situs solitus, in which the abdominal organs are in their normal positions, or situs invertus, in which the abdominal organs are horizontally reversed or “mirrored”[23]. Mirror-image dextrocardia is a rare anomaly, with an incidence of about 1:10,000 in the general population[24]. There have been few published reports of LAAO in patients with dextrocardia, which is surgically challenging because of the anatomical anomalies, surgical risk, and complication monitoring that must be considered[25,26]. There have also been no reports on the application of the ERAS model to LAAO. This case describes our experience with ERAS following the 2019 accelerated cardiac surgery rehabilitation perioperative nursing guidelines for perioperative care of a patient with dextrocardiac LAAO.
The patient presented to the outpatient facility with atrial fibrillation.
The patient reported having experienced occasional palpitations and discomfort without obvious chest tightness and pain, and presented with fluent speech, unclear articulation, hearing loss, and mild activity impairment of the left lower limb.
The patient had a history of cerebral infarction, hypertension, cholecystectomy, prostatic hyperplasia surgery, and fractures of both upper limbs and the left lower limb. Long-term oral aspirin was discontinued in the previous month because of hematochezia.
No family history.
On presentation, the patient’s body temperature was 37 °C, the pulse was 89 beats/min, respiration rate was 18 breaths/min, blood pressure was 143/76 mmHg, and the numerical rating scale pain score was 0. Twelve-lead electrocardiography revealed atrial fibrillation with a change in the ST-T segment.
Twelve-lead electrocardiography revealed atrial fibrillation with a change in the ST-T segment.
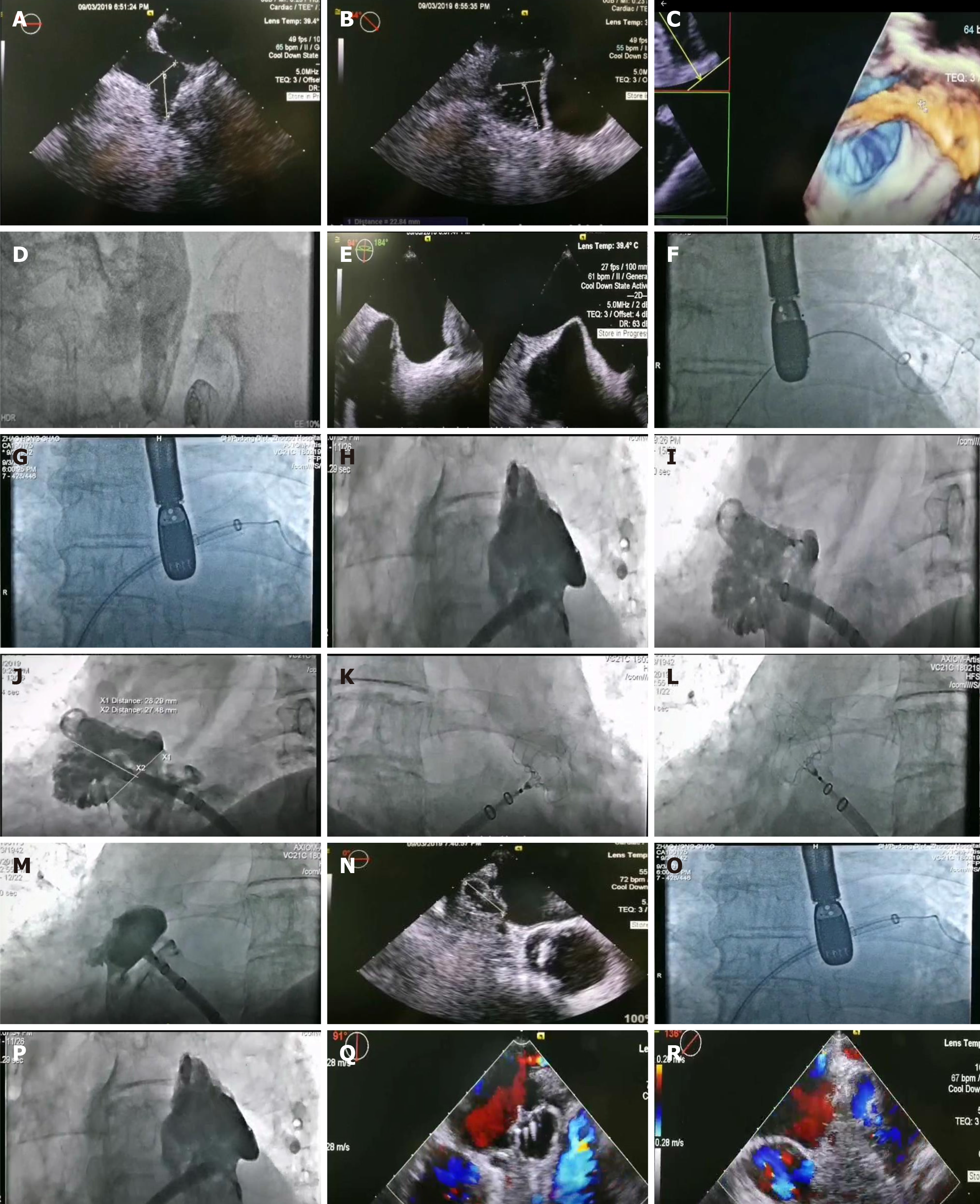
The diagnosis was arrhythmia, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, cardiac function New York Heart Association level II, level II very high-risk hypertension, sequelae of cerebral infarction, and visceral inversion (Figure 1).
Percutaneous LAAO was performed under general intravenous anesthesia (Figure 1).
After the LAAO procedure, the patient was admitted to the CCU. His vital signs were closely monitored and found to be stable following surgery. At 18 h, the heart rate was 75 beats/min, average blood pressure was 139/80 mmHg, average O2 saturation was 97%, and the urine volume was 2100 mL. At 19 h, the blood pressure was 197/99 mmHg, the heart rate was 64/min, O2 saturation was 92%, and the urine volume was 900 mL. Infusion of 0.9% normal saline 250 mL + 10 mg isosorbide nitrate was maintained at 10 mL/h, as advised by the doctor. At 19 h 15 min, the blood pressure was 190/85 mmHg, the heart rate was 64 beats/min, and the O2 saturation was 95%. At 20 h, the blood pressure was 172/94 mmHg, heart rate was 69 beats/min, O2 saturation was 97%, and the blood pressure was 135/68 mmHg.
Puncture wounds were treated by finger compression to stop bleeding. If after 20 min no bleeding had occurred, then an elastic bandage was applied for compression. A 1 kg sandbag was applied for 6 h and a right lower limb brake was applied for 12 h. The wound dressing was changed daily. TEE on the first day after the procedure showed that the position of the umbrella was good, and that the residual shunt was about 2 mm behind the lower edge of the umbrella. No procedure-associated complications occurred during hospitalization or in the 12 d after the procedure. Follow-up echocardiography on October 18, 2019, 45 d after the procedure, and November 21, 2019 found that the occluder was in a good position, with a residual shunt of 2 mm around the lower edge of the umbrella. There had been no serious arrhythmia, bleeding, or cerebrovascular accident (Figure 1).
Dextrocardia situs inversus totalis is a rare congenital cardiac anomaly[26] in which the relationship of the great arteries is normal or transposed, as in mirror dextrocardia (coordinated cardiac circulation). Uncoordinated cardiac circulation usually shows congenital transposition of great arteries[27]. In patients with mirror dextrocardia, the main challenge for surgeons is the reversal of the whole heart, and in this case, the ECG leads were placed in the mirror mode (i.e., reversed). The fluoroscopy image is reversed horizontally, and the catheter is rotated in the opposite direction from normal[28]. The risks of coronary atherosclerosis and acute myocardial infarction in those with mirror dextrocardia are not different from those in normal individuals.
LAA is a remnant of the primitive atrium in the embryo. It has pectinate and trabecular muscle a unique rough endocardium[11]. It usually has three anatomical regions, the mouth, neck, and leaf and a morphology usually described as chicken wing, cactus, windsock, and cauliflower, which are present in different proportions[29,30] and appear different when observed from different angles. Some studies have reported that the LAA regulates pressure and volume load, releases atrial natriuretic peptide and B-type natriuretic peptide, and regulates hemodynamics.
The increase of volumetric load blood pressure after cardiac interventions may be related to excess intraoperative infusion. The left ventricular cardiac ejection fraction of the patient, who weighed 79.8-80 kg, was 56%. Fluid loss was [(4 × 10) + (2 × 10) + (1 × 60)] × 9 = 1080 mL and replenishment was complete within 2 h after the start of anesthesia[31,32]. The volume of fluid replenishment at 1 h was 1080/2 + 110 = 650 mL, with an additional 650 mL at 2 h. After that, a physiological requirement of 110 mL/h was maintained. The patient was given antibiotics (0.9% normal saline 100 mL + cefuroxime 1500 mg), sodium lactate ringer injection 500 mL + 5% glucose, normal saline 500 mL + heparin 5000 U within 2 h after the start of anesthesia. The total of 2100 mL, which was more than needed, may have contributed to the postoperative elevated blood pressure. It was agreed that the total intraoperative fluid given to the patient was not likely to have exceeded 1500 mL.
The preoperative nutritional status of the patient was good; he did not smoke or drink. His hemoglobin was 136 g/L, and he was infection-free. An electronic health platform allowed for establishment of a real-time hospital community with an application for those with coronary heart disease to participate in a cardiac preconditioning plan that included education, nutrition optimization, sports training, social support, and anxiety reduction. A self-rating anxiety scale was used to assess the anxiety level of the patient when he was admitted to hospital on August 29. His score was 65, indicating moderate anxiety. International studies have shown that music therapy can improve the mood of patients, promote mental health, and reduce anxiety and depression symptoms[33-35]. Chu et al[36] and others have shown that music therapy can improve anxiety and depression in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Studies in China have shown that five-element music therapy improved the sleep quality of patients with heart failure and anxiety and that Wuxing music combined with Baduanjin had a positive effect on the psychology of patients with poor health status[37,38]. Music therapy was used in the care of this patient. Six pieces of music were selected and played at 8:00-8:30 in the morning and 20:00-20:30 in the evening. The volume was 40-60 DB. On September 6, the SAS score was 46, and the anxiety state had significantly improved. Music therapy was easy to provide and not limited by the venue, and was enjoyed by the patient (Table 1).
| Phase | Project | Level of evidence | Recommendation | Remarks |
| Preoperative | Hemoglobin | IIA, C-LD | Yes | Preoperative measurement of hemoglobin to assist risk stratification |
| Albumin | IIA, C-LD | Yes | Preoperative assessment of albumin contributes to risk stratification | |
| Correcting malnutrition | IIA, C-LD | Yes | Recommend correcting nutritional deficiencies where feasible | |
| Smoking and drinking | I, C-LD | Yes | Patients were advised to stop 4 wk prior to elective surgery | |
| Carbohydrate load | IIB, C-LD | Yes | Carbohydrate loading (sugar prestocking) can be performed 2-4 h before general anesthesia | |
| Infection prevention | IA | Yes | Cephalosporins are recommended for 30-60 min before surgery | |
| E-health platform | IIA, C-LD | Yes | Establish electronic health education platform | |
| Cardiac preconditioning program | IIA, B-NR | Yes | These include education, nutrition optimization, sports training, social support, and mindfulness stress reduction training to reduce anxiety | |
| Intraoperative | Implementation care package | I, B-R | Yes | Including local intranasal therapy to eliminate staphylococcal colonization |
| Cephalosporins were injected within 60 min before skin incision and redone in cases over 4 h | ||||
| Skin preparation, depilation plan, dressing change after every 48 h | ||||
| Recovery temperature | III, B-R | No | Avoid high temperature during cardiopulmonary bypass reheating, that is the core temperature should not be > 37.9 °C | |
| Rigid sternum fraction | IIA, B-R | No | Rigid sternum fraction is beneficial in patients undergoing sternotomy | |
| Bleeding prevention | I, A | No | Tranexamic acid or amino hexic acid is recommended for cardiopulmonary bypass | |
| Postoperative | Enhanced glycemic control | IIA, B-NR | Yes | Factors of postoperative hyperglycemia: glucose toxicity, oxidative stress, prethrombotic effect, inflammation |
| Insulin infusion to treat hyperglycemia | IIA, B-NR | No | Insulin infusion is recommended to treat perioperative hyperglycemia | |
| Pain management | I, B-NR | No | Prescription of acetaminophen, tramadol, dexmedetomidine, pregabalin, gabapentin, etc. | |
| Hypothermia | I, B-NR | Yes | Warm blankets, elevated room temperature, heat perfusion and intravenous infusion are recommended for postoperative use | |
| Delirium | I, B-NR | Yes | At least one delirium screening is recommended for each nursing class | |
| Anticoagulant drugs | IIA, C-LD | Yes | Drug anticoagulation is recommended to reduce the risk of thrombosis | |
| Early extubation | IIA, B-NR | Yes | Strategies are recommended to ensure that the tube is extubated within 6 h of surgery | |
| Acute renal injury | IIA, B-R | Yes | Biomarkers are recommended for early identification of at-risk patients early and guide the reduction of AKI | |
| Goal-directed fluid therapy | I, B-R | Yes | Goal-directed fluid therapy is recommended to reduce postoperative complications | |
| Other | Unrated | Yes | Cardiopulmonary bypass, perfusion, mechanical ventilation at low tidal volume, early postoperative enteral feeding and postoperative mobilization are recommended | |
| It is recommended that the recommendations be adjusted to achieve the goals through multiteam collaboration (dietitians, early cardiac rehabilitation therapists, and physical therapists) |
Mirror dextrocardia has typical clinical characteristics. Because of the high prevalence and mortality of atrial fibrillation of patients with mirror dextrocardia, LAAO has an important role in treatment, which continues to be confirmed[39,40]. LAAO is an ideal choice for patients with atrial fibrillation. The 2019 nursing guidelines for accelerated cardiac surgery recovery optimize the clinical nursing path of patients with LAAO and can reduce perioperative complications and ensure the patient safety. The application of music therapy can reduce patient anxiety and is suitable for the entire process of treatment and nursing care.
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Wong F, for performance of the transesophageal echocardiography assessment; to Liu YX, for serving as the patient’s anesthesiologist; and to Zheng QQ, who performed language translation activities for the case report.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Cardiac and cardiovascular systems
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Spartalis M S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: A P-Editor: Yan JP
| 1. | Engelman DT, Ben Ali W, Williams JB, Perrault LP, Reddy VS, Arora RC, Roselli EE, Khoynezhad A, Gerdisch M, Levy JH, Lobdell K, Fletcher N, Kirsch M, Nelson G, Engelman RM, Gregory AJ, Boyle EM. Guidelines for Perioperative Care in Cardiac Surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Society Recommendations. JAMA Surg. 2019;154:755-766. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 333] [Cited by in RCA: 347] [Article Influence: 57.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Kubitz JC, Schulte-Uentrop L, Zoellner C, Lemke M, Messner-Schmitt A, Kalbacher D, Sill B, Reichenspurner H, Koell B, Girdauskas E. Establishment of an enhanced recovery after surgery protocol in minimally invasive heart valve surgery. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0231378. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | McGinigle KL, Eldrup-Jorgensen J, McCall R, Freeman NL, Pascarella L, Farber MA, Marston WA, Crowner JR. A systematic review of enhanced recovery after surgery for vascular operations. J Vasc Surg. 2019;70:629-640.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Sola M, Ramm CJ, Kolarczyk LM, Teeter EG, Yeung M, Caranasos TG, Vavalle JP. Application of a Multidisciplinary Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Pathway to Improve Patient Outcomes After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Am J Cardiol. 2016;118:418-423. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Zaouter C, Imbault J, Labrousse L, Abdelmoumen Y, Coiffic A, Colonna G, Jansens JL, Ouattara A. Association of Robotic Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Associated With a Preliminary Cardiac Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Program: A Retrospective Analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2015;29:1489-1497. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Alsagheir A, Koziarz A, Belley-Côté EP, Whitlock RP. Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion: A Narrative Review. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019;33:1753-1765. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Holmes DR Jr, Doshi SK, Kar S, Price MJ, Sanchez JM, Sievert H, Valderrabano M, Reddy VY. Left Atrial Appendage Closure as an Alternative to Warfarin for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: A Patient-Level Meta-Analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2614-2623. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 366] [Cited by in RCA: 419] [Article Influence: 41.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Chow DHF, Wong YH, Park JW, Lam YY, De Potter T, Rodés-Cabau J, Asmarats L, Sandri M, Sideris E, McCaw T, Lee RJ, Sievert H, Søndergaard L, De Backer O. An overview of current and emerging devices for percutaneous left atrial appendage closure. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2019;29:228-236. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Francisco ARG, Infante de Oliveira E, Nobre Menezes M, Carrilho Ferreira P, Canas da Silva P, Nobre Â, Pinto FJ. Combined MitraClip implantation and left atrial appendage occlusion using the Watchman device: A case series from a referral center. Rev Port Cardiol. 2017;36:525-532. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Chanda A, Reilly JP. Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion for Stroke Prevention. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2017;59:626-635. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Naksuk N, Padmanabhan D, Yogeswaran V, Asirvatham SJ. Left Atrial Appendage: Embryology, Anatomy, Physiology, Arrhythmia and Therapeutic Intervention. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2016;2:403-412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Glikson M, Wolff R, Hindricks G, Mandrola J, Camm AJ, Lip GYH, Fauchier L, Betts TR, Lewalter T, Saw J, Tzikas A, Sternik L, Nietlispach F, Berti S, Sievert H, Bertog S, Meier B. EHRA/EAPCI expert consensus statement on catheter-based left atrial appendage occlusion - an update. EuroIntervention. 2020;15:1133-1180. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 208] [Article Influence: 41.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Reddy VY, Sievert H, Halperin J, Doshi SK, Buchbinder M, Neuzil P, Huber K, Whisenant B, Kar S, Swarup V, Gordon N, Holmes D; PROTECT AF Steering Committee and Investigators. Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure vs warfarin for atrial fibrillation: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;312:1988-1998. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 601] [Cited by in RCA: 732] [Article Influence: 66.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Berti S, Santoro G, Brscic E, Montorfano M, Vignali L, Danna P, Tondo C, D'Amico G, Stabile A, Saccà S, Patti G, Rapacciuolo A, Poli A, Golino P, Magnavacchi P, De Caterina A, Meucci F, Pezzulich B, Rezzaghi M, Stolcova M, Tarantini G. Left atrial appendage closure using AMPLATZER™ devices: A large, multicenter, Italian registry. Int J Cardiol. 2017;248:103-107. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Lee OH, Kim JS, Pak HN, Hong GR, Shim CY, Uhm JS, Cho IJ, Joung B, Yu CW, Lee HJ, Kang WC, Shin ES, Choi RK, Lim DS, Jang Y. Feasibility of Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion for Left Atrial Appendage Thrombus in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2018;121:1534-1539. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Lempereur M, Aminian A, Freixa X, Gafoor S, Shakir S, Omran H, Berti S, Santoro G, Kefer J, Landmesser U, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, Cruz-Gonzalez I, Kanagaratnam P, Nietlispach F, Ibrahim R, Sievert H, Schillinger W, Park JW, Gloekler S, Tzikas A. Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Previous Major Gastrointestinal Bleeding (from the Amplatzer Cardiac Plug Multicenter Registry). Am J Cardiol. 2017;120:414-420. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Price MJ. Safety and Efficacy of Transcatheter Left Atrial Appendage Closure for Stroke Prevention in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;60:542-549. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Wiebe J, Franke J, Lehn K, Hofmann I, Vaskelyte L, Bertog S, Sievert H. Percutaneous Left Atrial Appendage Closure With the Watchman Device: Long-Term Results Up to 5 Years. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:1915-1921. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Hutt E, Wazni OM, Saliba WI, Kanj M, Tarakji KG, Aguilera J, Barakat AF, Rasmussen P, Uchino K, Russman A, Hussain S, Wisco D, Kapadia S, Lindsay BD, Hussein AA. Left atrial appendage closure device implantation in patients with prior intracranial hemorrhage. Heart Rhythm. 2019;16:663-668. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Reddy VY, Doshi SK, Kar S, Gibson DN, Price MJ, Huber K, Horton RP, Buchbinder M, Neuzil P, Gordon NT, Holmes DR Jr; PREVAIL and PROTECT AF Investigators. 5-Year Outcomes After Left Atrial Appendage Closure: From the PREVAIL and PROTECT AF Trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70:2964-2975. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 485] [Cited by in RCA: 727] [Article Influence: 90.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Perloff JK. The cardiac malpositions. Am J Cardiol. 2011;108:1352-1361. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Li Y, Fang JB. Nursing strategy and complication prevention of cardiac resynchronization therapy for a patient with dextrocardia. Huli Xuebao. 2018;25:59-61. |
| 23. | Qutbi M. SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging in patients with Dextrocardia. J Nucl Cardiol. 2019;26:1197-1204. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Yilmaz S, Demirtas A, Tokpinar A, Niyazi A. Dextrocardia and Situs Inversus Totalis in a Turkish Subject: A Case Report. Int J Morphol. 2019;37:900-902. |
| 25. | González-Cordero A, López-Puebla J, Franqui-Rivera H. Implantation of a completely right sided subcutaneous cardioverter-defibrillator in a patient with situs inversus dextrocardia. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2019;19:72-74. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Onan B, Aydin U, Kahraman Z, Bakir I. Robotic atrial septal defect closure and tricuspid annuloplasty in a case of situs inversus totalis with dextrocardia. J Robot Surg. 2017;11:87-90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 27. | Zhou GB, Ma J, Zhang JL, Guo XG, Yang JD, Liu SW, Ouyang FF. Catheter ablation of supraventricular tachycardia in patients with dextrocardia and situs inversus. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019;30:557-564. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 28. | He J, Sun Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhong J, Lin F, Liu Y. Emergent percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction in patients with mirror dextrocardia: case reports and brief review. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2016;6:267-273. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Barbero U, Ho SY. Anatomy of the atria. Herzschr Elektrophys. 2017;28:347-354. |
| 30. | López-Mínguez JR, Nogales-Asensio JM, Infante De Oliveira E, De Gama Ribeiro V, Ruiz-Salmerón R, Arzamendi-Aizpurua D, Costa M, Gutiérrez-García H, Fernández-Díaz JA, Martín-Yuste V, Rama-Merchán JC, Moreno-Gómez R, Benedicto-Buendía A, Íñiguez-Romo A. Long-term Event Reduction After Left Atrial Appendage Closure. Results of the Iberian Registry II. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2019;72:449-455. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Caliskan E, Cox JL, Holmes DR Jr, Meier B, Lakkireddy DR, Falk V, Salzberg SP, Emmert MY. Interventional and surgical occlusion of the left atrial appendage. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14:727-743. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Huang WQ, Xu X. Expert consensus on fluid therapy during anesthesia operation. Annual Meeting of Anesthesiology Branch of Beijing Medical Association. 2014; 24-25. |
| 33. | Vaudreuil R, Avila L, Bradt J, Pasquina P. Music therapy applied to complex blast injury in interdisciplinary care: a case report. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;41:2333-2342. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Wood C, Cutshall SM, Wiste RM, Gentes RC, Rian JS, Tipton AM, Ann-Marie D, Mahapatra S, Carey EC, Strand JJ. Implementing a Palliative Medicine Music Therapy Program: A Quality Improvement Project. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2019;36:603-607. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Sihvonen AJ, Särkämö T, Leo V, Tervaniemi M, Altenmüller E, Soinila S. Music-based interventions in neurological rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:648-660. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 211] [Cited by in RCA: 261] [Article Influence: 32.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Chu H, Yang CY, Lin Y, Ou KL, Lee TY, O'Brien AP, Chou KR. The impact of group music therapy on depression and cognition in elderly persons with dementia: a randomized controlled study. Biol Res Nurs. 2014;16:209-217. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 11.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Gao J, Yi X, Wu CX, Bai DX, Ye Y, Zhu R, Wu S. Application effect of noon ebb flow timing five element music therapy in patients with chronic heart failure anxiety. Zhonghua Huli Zazhi. 2016;51:443-448. |
| 38. | Geng YQ. Research on the intervention effect of Baduanjin and Five-notes music on mental sub-health state. Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Dissertation), 2013. |
| 39. | Schnabel RB, Yin X, Gona P, Larson MG, Beiser AS, McManus DD, Newton-Cheh C, Lubitz SA, Magnani JW, Ellinor PT, Seshadri S, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. 50 year trends in atrial fibrillation prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the Framingham Heart Study: a cohort study. Lancet. 2015;386:154-162. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 890] [Cited by in RCA: 1210] [Article Influence: 121.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Lin JJ, Fan YQ. Nursing care of 4 patients with transcatheter closure of left atrial appendage. Zhonghua Huli Zazhi. 2015;50:629-631. |