Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11529
Peer-review started: June 28, 2022
First decision: August 1, 2022
Revised: August 26, 2022
Accepted: September 29, 2022
Article in press: September 29, 2022
Published online: November 6, 2022
Processing time: 122 Days and 22.4 Hours
Malignant tumors of the ileocecal region often cause intestinal obstruction. Emergency surgery is the main treatment for patients presenting with an obstruction. However, this procedure is associated with a high mortality rate and frequent complications. The placement of colon stents is commonly performed for obstructions in the distal colon and is a less invasive and safer procedure. However, obstructions in the proximal colon are more challenging to treat by stent placement due to the increased distance from the anus.
This case report concerns an 88-year-old man with malignant intestinal obstruction in the ileocecal region. He was contraindicated for general anesthesia and surgical enterostomy. The placement of a self-expandable metallic stent seems an alternative to surgery, although stenting in this area is thought to be difficult and few studies have been reported so far. After three attempts at different interventional approaches, a stent was successfully placed in the obstructed segment under fluoroscopic guidance. After the procedure, the patient's abdo
For patients with proximal colonic obstruction, self-expandable metallic stent placement under fluoroscopic guidance could be considered as a feasible treat
Core Tip: This report concerns the case of an 88-year-old man with malignant intestinal obstruction in the ileocecal region whose condition improved after successful the placement of the self-expandable metallic stent under fluoroscopic guidance.
- Citation: Wu Y, Li X, Xiong F, Bao WD, Dai YZ, Yue LJ, Liu Y. Malignant obstruction in the ileocecal region treated by self-expandable stent placement under the fluoroscopic guidance: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(31): 11529-11535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i31/11529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11529
The ileocecal region is the site of many common and frequent diseases, among which malignant tumors of the colon are one of the most prevalent. In turn, the tumors are highly susceptible to malignant colonic obstruction (MCO), with approximately 8%-29% of patients presenting with acute intestinal obstruction as a clinical symptom[1,2]. In recent years, placement of a self-expandable metallic stent (SEMS) under the guidance of fluoroscope or endoscope has been more widely used in treating intestinal malignant obstruction.
However, most colon stents were deployed in distal areas, such as the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectal colon. They were hardly used in proximal colonic obstructions due to the large distance from the anus and the tortuous colonic contours, making this procedure difficult for radi
This report concerns the case of an 88-year-old man with intestinal obstruction in the ileocecal region whose condition improved after the successful placement of SEMS under fluoroscopic guidance. Few studies have been reported to date on the placement of stents in this region under fluoroscopy.
An 88-year-old male patient presented with abdominal distension for 10 d.
The patient complained of generalized abdominal pain and distension with associated nausea, vomiting, and constipation for 10 d. On admission, computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen suggested acute intestinal obstruction, otherwise no significant metastases were detected. To make a definite diagnosis, endoscopic examination was considered; however, the family members refused. In combination with the abdominal CT, the patient was considered to have a high probability of malignant obstruction and was recommended to undergo ileostomy. However, after a multidisciplinary discussion, the anesthesiologist advised against the surgical operation, in view of the patient's advanced age and underlying diseases, such as coronary heart disease and frequent premature atrial beats as suggested by an electrocardiogram. Furthermore, systemic chemotherapy was not recommended because the patient was weak, was bed-ridden, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score was 3. Moreover, palliative treatment was the only choice to improve the patient's quality of survival. Therefore, SEMS placement was considered for this patient, although the distance from the anus to the obstruction site was long, and the procedure was considered extremely difficult.
He had been diagnosed with hypertension for 28 years, coronary heart disease for 20 years, and diabetes for 3 years. He had experienced previous occasional abdominal pain, change in stool pattern for 10 mo, and weight loss of 5 kg in the last 3 mo.
The patient denied any family history of malignant tumors.
His vital signs were stable. The abdomen was distended, gastrointestinal type visible, and diffusely tender. There was no rebound tenderness, but abdominal auscultation revealed hyperactive bowel sounds.
The blood work at admission showed moderate normocytic anemia. The levels of the following serum tumor markers were elevated: carcinoembryonic antigen, 50.9 ng/mL and carbohydrate antigen 19-9, < 2 U/mL.
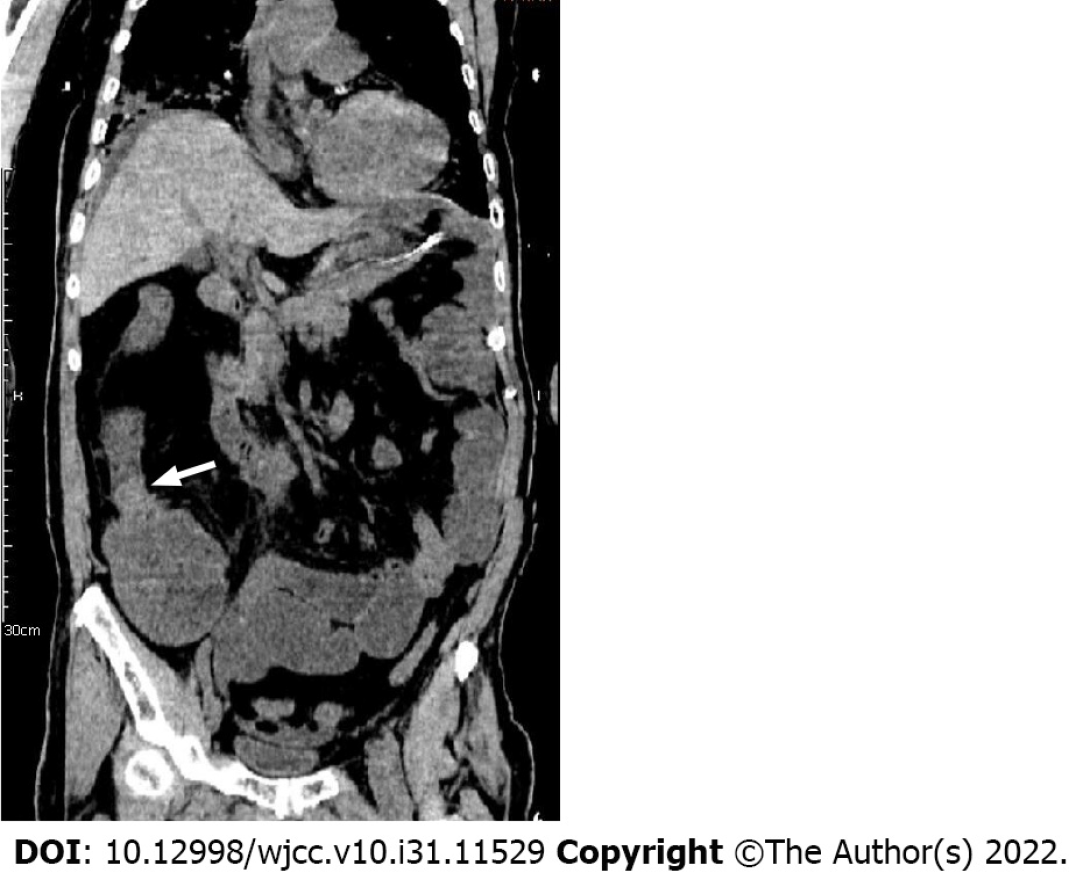
An admission CT scan of the whole abdomen showed thickening of the wall of the ascending colon with significant dilatation of the small intestine with air-fluid flattening. The distal colon was empty, and a malignant colon tumor with acute intestinal obstruction was considered (Figure 1).
The patient’s clinical diagnosis was considered to be malignant intestinal obstruction in the ileocecal region by the tumor board, according to the CT findings as well as the elevated serum tumor markers.
The procedure was performed under fluoroscopic guidance without the assistance of a colonoscope. The patient was placed in the supine position. After lubrication and anesthesia of the anus with lidocaine slurry, a hydrophilic guide wire (0.035 inch by 260 cm, Radiation Focus, Terumo, Tokyo, Japan) and a vertebral angiographic catheter (5F, 100 cm, Terumo, Tokyo, Japan) were introduced through the anus coaxially.
A water-soluble contrast medium (Iodixanol, Hengrui, Jiangsu, China) and room air were injected through the catheter during the procedure to distend and outline the colon.
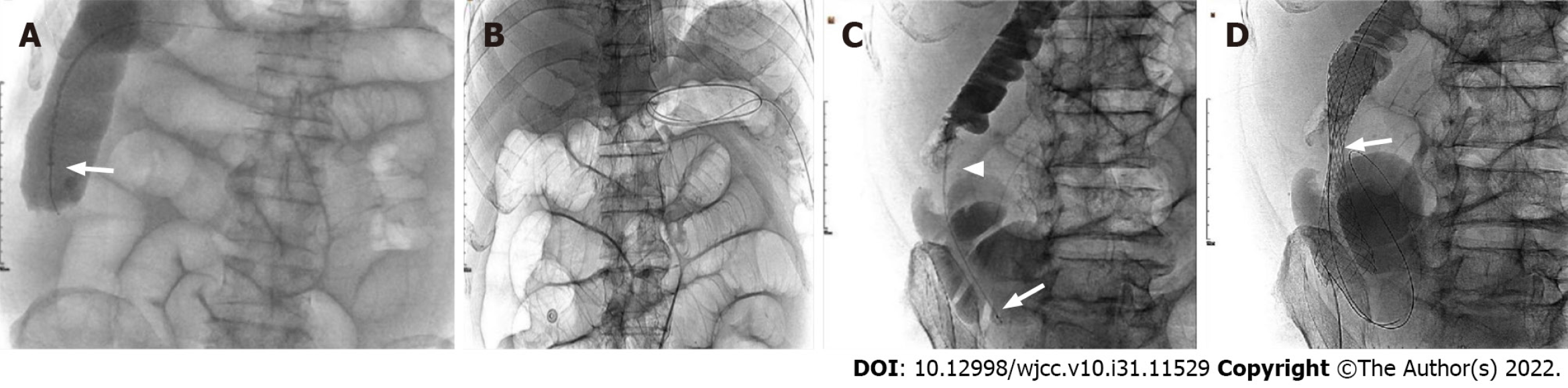
Under fluoroscopic guidance, the vertebral catheter was rotated, advanced, walked up, and intermittently traveled over the guidewire through the rectum into the sigmoid colon and, finally, to the hepatic flexure of the colon. The catheter was too short of reaching the ileocecal region. After the injection of contrast, the persistent occlusion of the ileocecal region was seen, with no apparent bowel movement on repeated observation. We managed to push the wire through the lesion but failed because the vertebral cater was not close to the lesion, and the wire did not have enough backup.
Then, a colonic stent delivery system (WallFlex Colonic stent, Boston Scientific/Medical Technology, Watertown, MA, United States) was used as a support catheter and reached the ileocecal region under the fluoroscopic guidance. But the wire could not be freely moved ahead or back and rotated, and we failed to pass the obstructed segment after many tries (Figure 2A).
The next day, an endoscopist managed to put the guide wire through the lesion under the guidance of a colonoscope in the endoscopy suite. However, the visibility was not good because of residual stool, and the procedure was not going well. Finally, it seemed successful. The patient was immediately transferred to the interventional suite to complete the next steps. To our surprise, the guide wire was located in the mid-transverse colon and far from the ileocecal region displayed by fluoroscopy image (Figure 2B).
On the third day, a Tandem contrast catheter (7F proximal and 5.5F distal, 120 cm, Boston Scientific/Medical Technology, Watertown, Mass. United States), which is usually used in Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, was used in the procedure under the fluoroscopic guidance.
When the Tandem catheter reached the obstruction site, a multi-angle view was carried out, and the contrast medium was injected to outline and fill a thin line-like lumen (Figure 2C). The guidewire was easily pushed toward the direction indicated by this lumen, which passed through the occluded section and into the upper end of the obstructed bowel. Once the position was determined, a 25 mm × 90 mm uncovered stent (WallFlex Colonic stent, Boston Scientific/Medical Technology, Watertown, MA, United States) was introduced. After accurate positioning, the stent was slowly released (Figure 2D). The stent was fully dilated at both ends and stenosed in the middle by tumor compression in a satisfactory position. The procedure went well, and the patient returned to the ward safely.
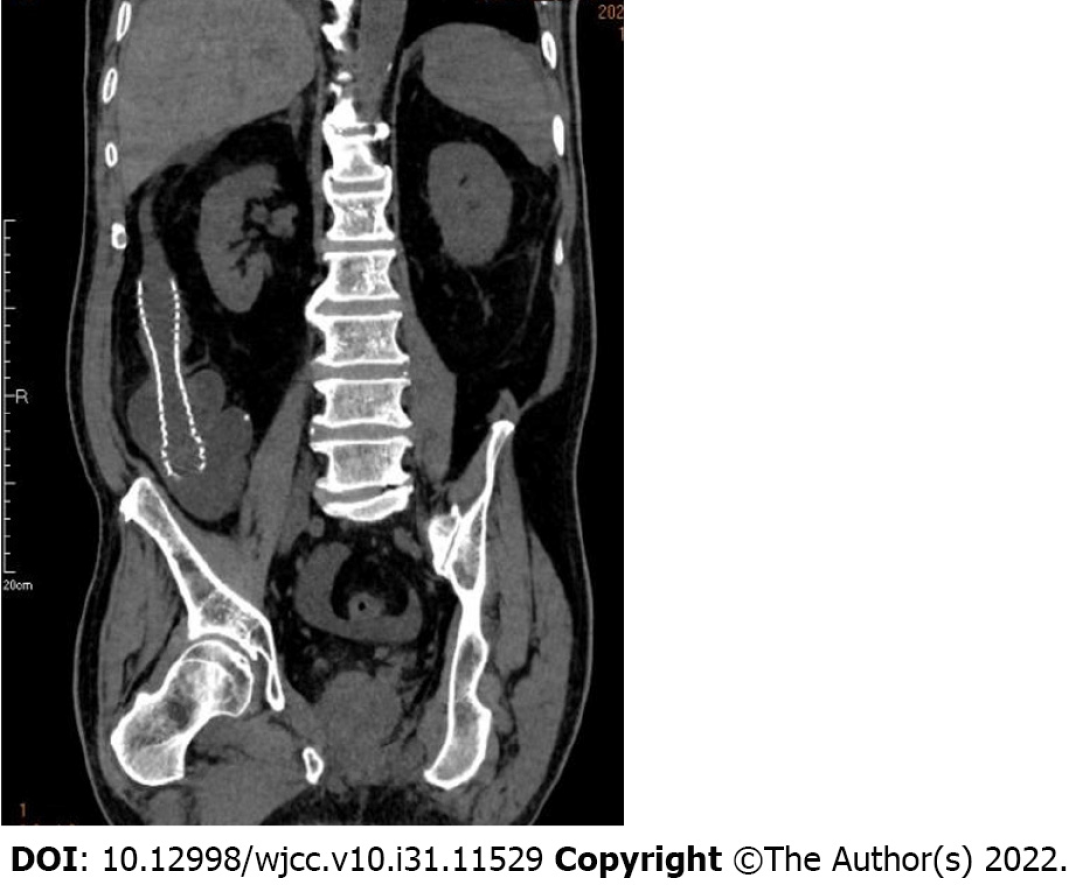
On postoperative day one, the patient's abdominal distension and abdominal pain were significantly better than before, the stool was clear, and the symptoms of intestinal obstruction were relieved. On the second postoperative day, a repeat abdominal CT indicated changes after stent placement, and the stent was in place (Figure 3). On the fourth postoperative day, the patient was discharged from the hospital.
As we all know, MCO due to colorectal cancer (CRC) requires urgent decompression as a malignant gastrointestinal emergency. If not adequately treated, MCO can lead to fluid and electrolyte imbalance, colonic necrosis, bacterial translocation, and death[3]. It is generally accepted that right side obstructive CRC can best be treated by right hemicolectomy with ileocolic anastomosis[4]. Still, in this case, the patient was too old and had too many underlying diseases to tolerate emergency surgery. Internal stenting could be an alternative to relieve the patient's symptoms of intestinal obstruction in view of the following understanding.
SEMS insertion for obstructive colon cancer enables patients to avoid emergency surgery and to recover from the acute status with a reduced risk of postoperative complications and mortality. SEMS also enables mechanical bowel preparation, which lessens proximal bowel edema[5]. In addition, it avoids the inconvenience of temporary or permanent ileostomy and improves patients' quality of life. Implantation of a permanent internal stent to treat patients who are unable to undergo surgery or do not have surgical conditions can avoid the risk of palliative surgical treatment[6]. According to previous studies, SEMS as a bridge to surgery, has no deleterious effect on the long-term oncological prognosis of patients with CRC obstruction and can achieve similar results to direct surgery[7].
Many studies have been published within the last 20 years regarding the efficacy and safety of SEMS in colon cancer. Khot et al[8] reported a systematic review of case series between January 1990 and December 2000, in which 598 patients were analyzed. Technical success, expressed as stent placement and deployment, was achieved in 92% (551 stent placement attempts). Clinical success, defined as a colonic decompression within 96 h without surgical or endoscopic intervention, was attained in 88% (n = 525)[9]. Pattarajierapan et al[10] reported a systematic review of case series between 2009 and 2019. Although the patency of SEMS reported was shorter than for stoma creation; however, SEMS patency was not much different from that of stoma within the first year (88.9% vs 93.2% in 6 mo; 84.1% vs 90.5% in 12 mo). Furthermore, the 1-year re-intervention rates did not differ between SEMS insertion and stoma creation. Despite the lower SEMS patency rate after 1 year, 84% of the patients who underwent SEMS placement did not require any re-intervention until death. This finding suggests a short overall survival of patients with incurable metastatic disease. On the other hand, palliation for malignant gastro-intestinal and biliary obstruction with SEMS deployment show a long-term outcome of 70% stent patency until death[11,12], which is considered acceptable.
For patients with MCO who cannot undergo emergency surgery, stent installation should be performed under the assistance of colonoscopy. But, in this case, the site of malignant obstruction was located in the ileocecal region, which is a special anatomical and physiological location farthest from the anus for colonoscopy, and is not a relatively indicated area for colonic stenting. Since it has been reported that stents can be successfully placed in the ascending colon for malignant obstruction under fluoroscopic guidance[13], the procedure was elected for this patient.
Unlike the typical site of stent placement, the site of obstruction in this patient was exactly in the ileocecal region, which is far away from the anus; also, the catheter used was of normal length and could not reach this area. Under this circumstance, the catheter did not provide enough backup for the wire and could not pass through the obstructed bowel segment. Although the stent release system was long enough to reach the lesion, its lumen is tight and small, and would not allow the wire to move and rotate freely. Because the stent release system is not designed like a contrast catheter, the lumen of which is usually designed to be much larger; therefore, the above mentioned limits the operation of the guide wire during the procedure and prevented us from getting the wire through the lesion. The endoscope is often used in the implantation procedure in many medical centers. However, its application is limited mainly due to the pain experienced by the patients, unclear vision by the residual stool, tortuous bowel, and the low success rate. These were proved again in this case. Finally, with the help of the Tandem contrast catheter (7F proximal and 5.5F distal), which has a large enough lumen, the wire was rotated and controlled freely, to successfully get it through the obstructed lesion. Using the Tandem catheter allowed the procedure to proceed smoothly and provided a new way of thinking about stent placement for more distant bowel segments.
To the best of our knowledge, until now, few cases of malignant terminal ileal stricture with metallic stent placement have been reported. Compared with endoscopic stenting, fluoroscopic stenting has the characteristics of high safety and high patient tolerance. In addition, the site of obstruction, in this case, was just beyond the direct reach of colonoscopy in the ileocecal region, which provides a new direction for the future treatment of intestinal obstruction.
For patients with proximal colonic obstruction, SEMS placement under fluoroscopic guidance could be considered as a feasible treatment to relieve abdominal distension and pain in patients with acute bowel obstruction. It has the characteristics of high safety and high patient tolerance. However, further study is still needed.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Oncology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D, D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ferreira GSA, Brazil; Tan JK, Malaysia S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: A P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Makhejani KR, Haq MMU, Iqbal J, Zahid N. Self-expanding Metallic Stent Placement in Malignant Terminal Ileal Stricture. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2019;29:S89-S91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Deans GT, Krukowski ZH, Irwin ST. Malignant obstruction of the left colon. Br J Surg. 1994;81:1270-1276. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 388] [Cited by in RCA: 362] [Article Influence: 11.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Saida Y. Current status of colonic stent for obstructive colorectal cancer in Japan; a review of the literature. J Anus Rectum Colon. 2019;3:99-105. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Atsushi I, Mitsuyoshi O, Kazuya Y, Syuhei K, Noriyuki K, Masashi M, Akira W, Kentaro S, Nobuyuki K, Natsuko S, Jun W, Yasushi I, Chikara K, Itaru E. Long-term outcomes and prognostic factors of patients with obstructive colorectal cancer: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:5237-5245. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Ji WB, Kwak JM, Kang DW, Kwak HD, Um JW, Lee SI, Min BW, Sung NS, Kim J, Kim SH. Clinical benefits and oncologic equivalence of self-expandable metallic stent insertion for right-sided malignant colonic obstruction. Surg Endosc. 2017;31:153-158. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Wang ZM, Gung K. Treatment of malignant obstruction of the left hemi-colon with self-expanding endoprosthesis. Chinese Interv Imaging Ther. 2006;3:278-279. |
| 7. | Haraguchi N, Ikeda M, Miyake M, Yamada T, Sakakibara Y, Mita E, Doki Y, Mori M, Sekimoto M. Colonic stenting as a bridge to surgery for obstructive colorectal cancer: advantages and disadvantages. Surg Today. 2016;46:1310-1317. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Khot UP, Lang AW, Murali K, Parker MC. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of colorectal stents. Br J Surg. 2002;89:1096-1102. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 479] [Cited by in RCA: 418] [Article Influence: 18.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Feo L, Schaffzin DM. Colonic stents: the modern treatment of colonic obstruction. Adv Ther. 2011;28:73-86. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Pattarajierapan S, Manomayangoon C, Tipsuwannakul P, Khomvilai S. Comparison of colonic stenting and stoma creation as palliative treatment for incurable malignant colonic obstruction. JGH Open. 2022;. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Ishii T, Minaga K, Ogawa S, Ikenouchi M, Yoshikawa T, Akamatsu T, Seta T, Urai S, Uenoyama Y, Yamashita Y. Effectiveness and safety of metallic stent for ileocecal obstructive colon cancer: a report of 4 cases. Endosc Int Open. 2017;5:E834-E838. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | ASGE Technology Committee; Varadarajulu S, Banerjee S, Barth B, Desilets D, Kaul V, Kethu S, Pedrosa M, Pfau P, Tokar J, Wang A, Song LM, Rodriguez S. Enteral stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:455-464. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 70] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Yoon J, Kwon SH, Lee CK, Park SJ, Oh JY, Oh JH. Radiologic Placement of Uncovered Stents for the Treatment of Malignant Colonic Obstruction Proximal to the Descending Colon. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40:99-105. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |