Published online Sep 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i26.9276
Peer-review started: December 25, 2021
First decision: March 12, 2022
Revised: March 26, 2022
Accepted: August 5, 2022
Article in press: August 5, 2022
Published online: September 16, 2022
Processing time: 250 Days and 17.2 Hours
Postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) is one of the most common and serious complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD). To effectively reduce the incidence of POPF, we designed a new type of pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ), which was termed one-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced.
To explore the clinical application value of this new technique.
We compared 62 patients who had undergone PD by either the traditional duct-to-mucosa anastomoses or the new one-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced method at our hospital from May 2015 to September 2019. All 62 patients were operated by the same surgeon experienced in both procedures. We retrospectively analyzed patient characteristics, perioperative outcomes, and surgical results.
There was no significant difference between the two groups in basic information except the postoperative hospital stays, 14.7 ± 5.4 d in the traditional duct-to-mucosa anastomoses group and 12.0 ± 4.2 d in the one-half layer PJ group (P = 0.042). In terms of postoperative complications, the one-half layer PJ group had a lower rate of POPF than the traditional group. The overall number of cases with POPF was 8 (24.2%) in the traditional group and 2 (6.9%) in the one-half layer group (P = 0.017). Additionally, the rate of grades B and C POPF was lower in the one-half layer group (3.4%) compared with that (12.1%) in the traditional group (P = 0.010). One patient died due to hemorrhage caused by severe pancreatic fistula in the traditional group.
One-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced is a safe and feasible procedure that can successfully reduce the rate of POPF. It may be a promising technique for PJ after PD.
Core Tip: Postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) is one of the most common and serious complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy. To effectively reduce the incidence of POPF, we designed a new type of pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ). The technique that we introduce in this paper is a very new kind of PJ. Our research confirmed that this new technique is simple, safe, and easy to operate, and it can effectively reduce the occurrence of POPF.
- Citation: Wei JP, Tai S, Su ZL. One-half layer pancreaticojejunostomy with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced: A valuable anastomosis technique. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(26): 9276-9284
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i26/9276.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i26.9276
Postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) is one of the most common and serious complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD). It is also the major reason for bleeding and serious infection of the abdomen[1-3]. Some reports have shown that the morbidity of POPF ranges from 5% to 25%[4-7], and the relative mortality ranges from 10% to 50%[8-10]. Development of procedures to minimize or even avoid the occurrence of POPF has become one of the most difficult problems for surgeons worldwide. The pancreatic texture, main pancreatic duct diameter, and anastomotic technique are considered the most important factors that increase the risk of POPF[11,12]. However, the anastomotic technique is the only factor that can be modified[13,14]. Our team found that the rear wall of the pancreatic intestinal anastomosis is always involved in serious POPF occurrence. We designed a new type of pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ), called one-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced, based on this finding. To our knowledge, this method has not been reported in previous studies, and it is safe and effective in reducing the occurrence of POPF.
In this study, we retrospectively analyzed 71 patients with periampullary neoplasms, including ampullary carcinomas and carcinomas of the distal bile duct and the periampullary duodenum, who received either the traditional duct-to-mucosa anastomoses or one-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced method at our hospital from May 2015 to September 2019. After reviewing the medical records of these patients, we excluded all cases with diffused metastases in the abdomen or with severe diseases in other systems, as well as those who received preoperative neoadjuvant therapy. As a result, a total of 62 patients were classified into two groups. We analyzed the basic information of patients including age, sex, body mass index, pancreatic tissue, tumor size, and pathologic diagnosis. Likewise, perioperative outcomes and surgical results were evaluated, including operative time, anastomosis time, volume of intraoperative blood loss, duration of hospital stays, and postoperative complications. The amylase concentration was measured on the first, third, and fifth postoperative days (PODs), as well as subsequent time points, if necessary. POPF was defined as any measurable volume of drainage fluid on or after POD3 with an amylase content 3 times greater than the serum amylase activity according to the International Study Group on Pancreatic Fistula’s definition. This research was unanimously approved by our hospital medical ethics committee (No. HMUIRB20160006). All patients or their next of kin provided informed consent for surgery.
Patients were placed in a supine position and given general anesthesia with tracheal intubation. Their lower backs were elevated with cushions. The right quarter rib area by the rectus abdominis was incised, and conventional abdominal exploration was conducted, focusing on exploration of lymph nodes and distant metastasis, clearing the location, and determining the size and texture of the tumor. One-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced was used for digestive tract reconstruction.
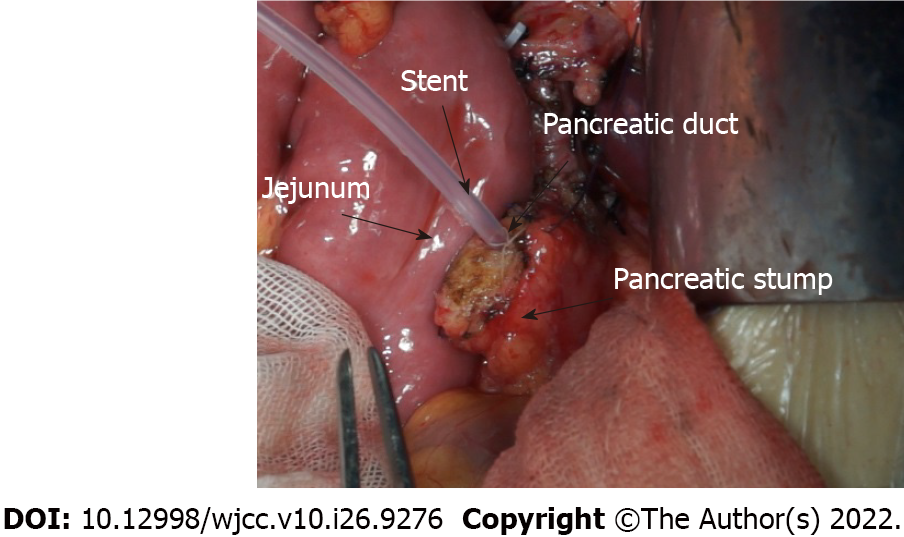
Transecting the pancreas: The pancreas was transected at the level of the portal vein. Careful hemostasis was achieved by electrocautery or sutures of the pancreatic stump. The superior and inferior borders of the reserved stump were sewn with silk sutures. For convenience, in the resection of the head of the pancreas, we ligated a 1-0 silk suture approximately 0.5 cm from the pre-cut line at the head of the pancreas and cut off the pancreas at the pre-cut line with a scalpel while focusing on the main pancreatic duct. To prevent pancreatic stump ischemia and damage, we aimed to avoid using an electrotome unless bleeding occurred. Fish mouth-shaped or mattress sutures were also avoided. The pancreatic stump surrounding tissue was dissociated, but not excessively; we simply matched the length that was required. We inserted a thin silicone tube in the pancreatic duct as a stent.
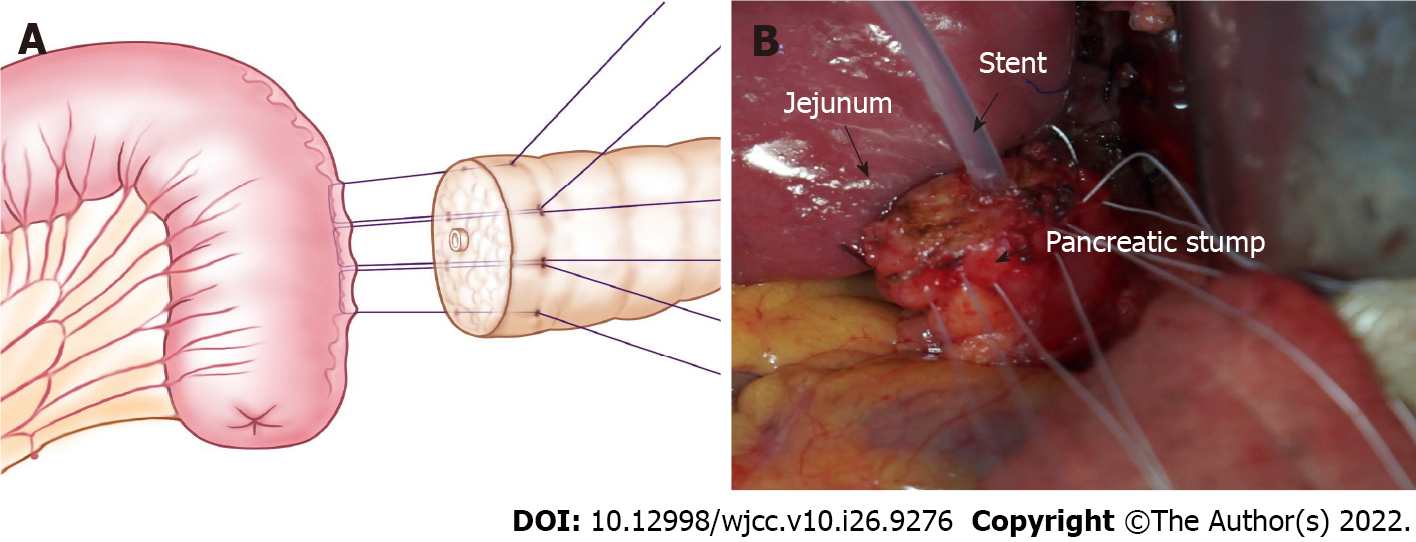
Preparation for a jejunum loop: We lifted the jejunal loop through an opening on the right side of the mesocolon and ensured that the pancreatic stump and jejunal loop were as close as possible to avoid the formation of a blind loop. An electrotome was used to cauterize the jejunal seromuscular layer to produce a pore with the same size as the main pancreatic duct. A hemostat was used to clamp and lift the jejunal mucosa to be cut by the electrotome. Then, the hemostat slightly stretched the pore on the jejunum wall.
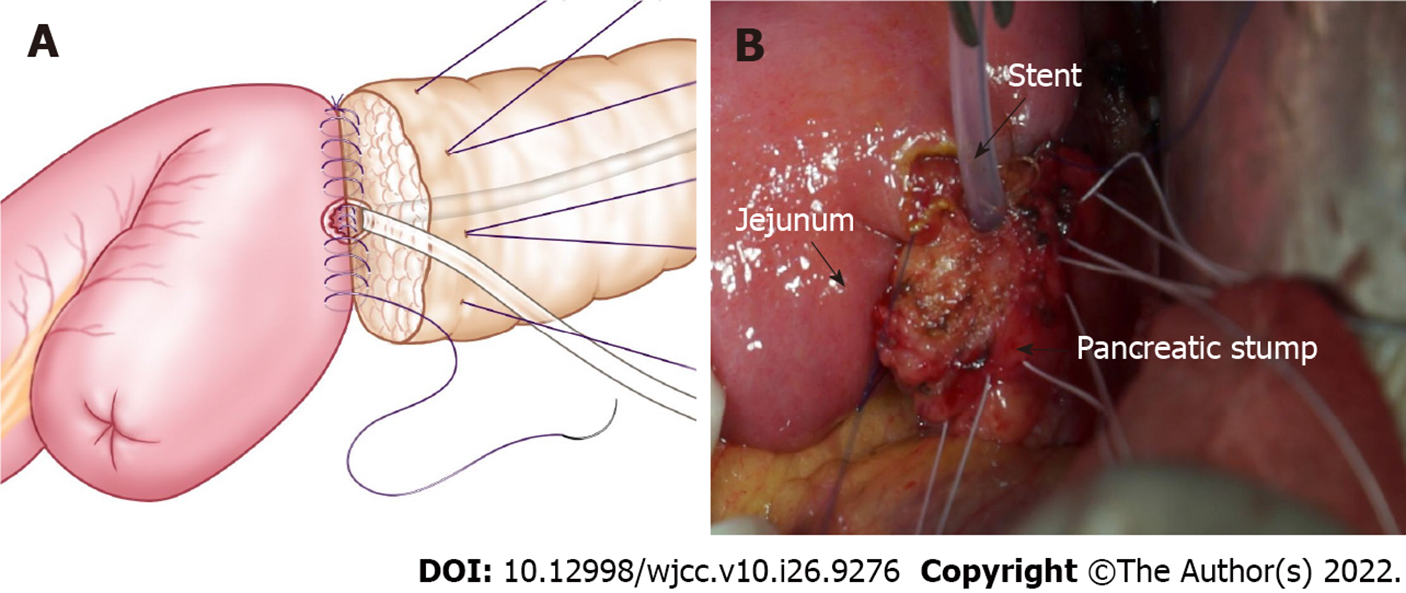
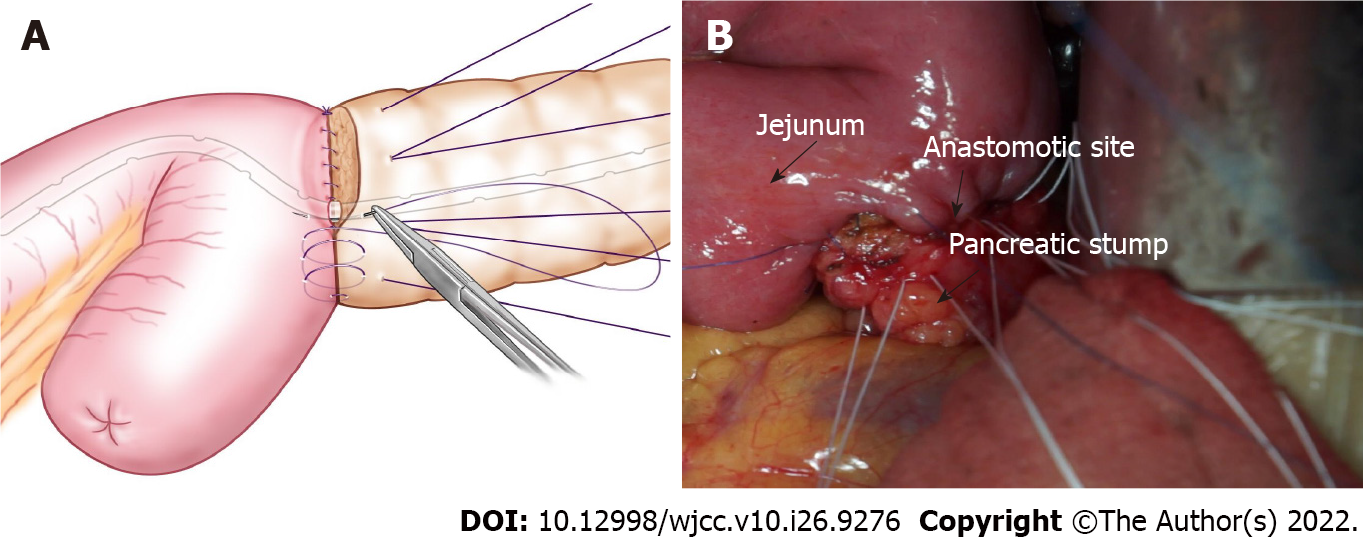
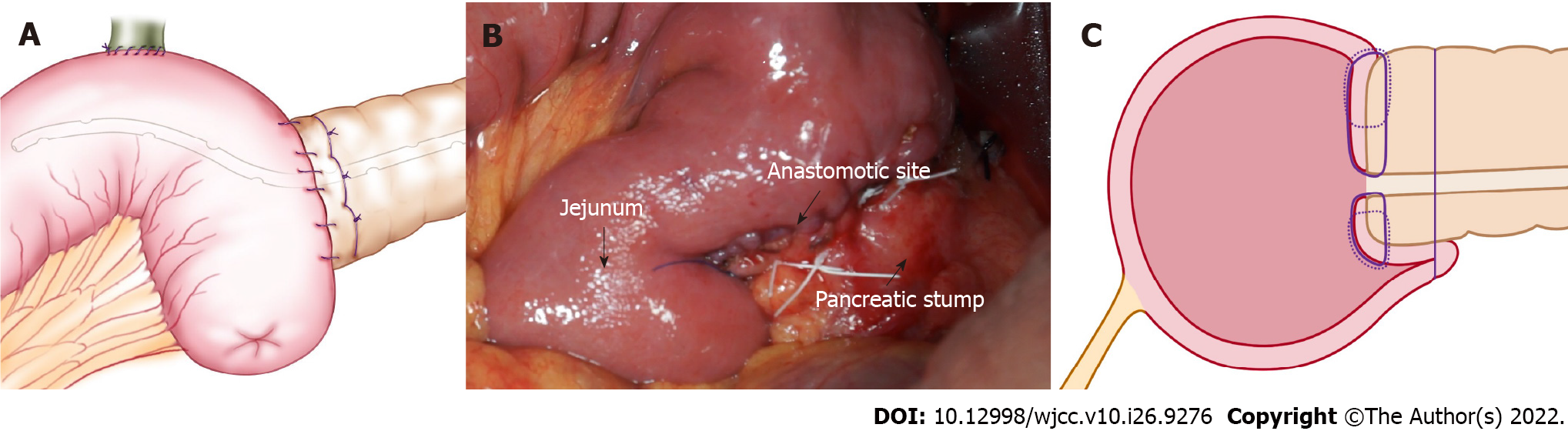
Anastomosis: Figure 1 shows the pancreatic stump and jejunum loop before anastomosis. At the place at least 1 cm from the pancreatic incisal margin, one needle with 4-0 Gore thread was inserted through the anterior wall of the pancreas. The needle pierced through the pancreas and protruded from the rear wall at the same distance from the incisal margin. Then, suturing was continued through the seromuscular layer of the jejunum loop along the direction of the intestine, which was approximately 1.5 cm beneath the anastomosis pore, and the distance was approximately 1/3 to 1/4 of the length of the pancreatic stump diameter. Finally, the needle was inserted through the pancreas again from the rear wall to the anterior wall, ensuring that the needle point distance was approximately 1/3 to 1/4 of the pancreatic stump diameter, similar to a U-shaped suture. Then, after suturing 2-3 additional stitches in the same manner, the two adjacent U-shape sutures were slightly overlapped (Figure 2). Mosquito forceps were used to hold the 3-4 U-shape sutures while waiting for the next ligation. A continuous suture was used to complete the anastomosis between the jejunum and rear wall of the pancreas stump with a 5-0 absorbable suture. When the suture was close to the pancreatic duct, we performed a pancreatic duct-to-mucosa anastomosis (Figure 3). Then, the silicone tube that was inserted into the pancreatic duct previously was placed into the jejunum anastomosis pore, ensuring that it was located in the jejunal afferent loop. We continued suturing of the anterior wall of the anastomosis to complete the first layer (Figure 4). We ligated the 3-4 U-shaped sutures so that they could hold the rear wall of the pancreas (Figure 5), and this was the half layer match. We must note that the ligation should not be too tight to ensure that the pancreatic stump has a good blood supply; a watertight closure should be achieved.
Continuous variables are expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS 21.0 computer software.
Patients were followed by outpatient examinations and telephone interviews. Outpatient examinations included color Doppler ultrasound or abdominal computed tomography evaluations. Telephone interviews included questions about whether the patients had abdominal pain, abdominal distension, or other discomfort. Diet, sleep, and other general conditions were also discussed in telephone follow-up evaluations. Follow-up was performed until March 2020.
The basic information of the patients is shown in Table 1. The mean ages of the two groups were 56.4 ± 8.8 years and 54.1 ± 11.0 years (P = 0.819). Among 62 patients, 37 were classified as having firm pancreatic tissue while 25 had soft tissue. This was not significantly different between the two groups (P = 0.281). In total, 34 cases of dilated pancreatic ducts were identified, with 18 (54.5%) in the traditional group and 16 (55.2%) in the one-half layer PJ group (P = 0.483). Fifteen patients were diagnosed with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, 22 with common bile duct ampulla area adenocarcinomas, 10 with duodenal papillary adenocarcinomas, 7 with pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, and 8 with duodenal ampullary adenocarcinomas. The histopathology distribution between the two groups was not significantly different (P = 0.288). The operative time was 262.6 ± 44.8 min in the traditional group and 271.3 ± 35.3 min in the one-half layer PJ group (P = 0.145). The mean PJ time was 12.4 ± 3.5 in the traditional group and 12.8 ± 3.0 in the one-half layer PJ group (P = 0.696). Overall mean volume of intraoperative blood loss was 425.5 ± 300.6 mL in the traditional group and 390.5 ± 275.4 in the one-half layer PJ group (P = 0.147). The mean total length of the postoperative hospital stay was 14.7 ± 5.4 d in the traditional group and 12.0 ± 4.2 d in the one-half layer PJ group (P = 0.042).
| Variable | Traditional group (n = 33) | One-half layer PJ group (n = 29) | P value |
| Age (yr) | 56.4 ± 8.8 | 54.1 ± 11.0 | 0.889 |
| Sex | 0.571 | ||
| Male | 18 | 19 | |
| Female | 15 | 10 | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.5 ± 2.9 | 22.9 ± 3.1 | 0.822 |
| Texture of pancreas | 0.281 | ||
| Firm | 20 | 17 | |
| Soft | 13 | 12 | |
| Dilated pancreatic duct | 18 (54.5%) | 16 (55.2%) | 0.483 |
| Tumor size | 2.85 ± 0.9 | 3.25 ± 1.0 | 0.176 |
| Pathological diagnosis | 0.288 | ||
| Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas | 6 | 9 | |
| Common bile duct ampulla area adenocarcinomas | 15 | 7 | |
| Duodenal papillary adenocarcinomas | 5 | 5 | |
| Pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms | 3 | 4 | |
| Duodenal ampullary adenocarcinoma | 4 | 4 | |
| Operative time (min) | 262.6 ± 44.8 | 271.3 ± 35.3 | 0.145 |
| Anastomosis time (min) | 12.4 ± 3.5 | 12.8 ± 3.0 | 0.696 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 425.5 ± 300.6 | 390.5 ± 275.4 | 0.147 |
| Postoperative hospital stay (d) | 14.7 ± 5.4 | 12.0 ± 4.2 | 0.042 |
In terms of postoperative complications (Table 2), the one-half layer PJ group had a lower rate of POPF than the traditional group. The overall number of cases with POPF was 8 (24.2%) in the traditional group and 2 (6.9%) in the one-half layer group (P = 0.017). Additionally, the rate of grades B and C POPF was lower in the one-half layer group (3.4%) compared with that (12.1%) in the traditional group (P = 0.010). There were five patients (8.1%) with delayed gastric emptying, three (9.1%) in the traditional group and two (6.9%) in the one-half layer group (P = 0.326). The number of patients with wound infections was three (9.1%) in the traditional group and three (10.3%) in the one-half layer group (P = 0.653). One patient died due to hemorrhage caused by severe pancreatic fistula in the traditional group.
| Postoperative complication | Traditional group (n = 33) | One-half layer PJ group (n = 29) | P value |
| POPF | 8 (24.2%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0.017 |
| Grade A | 4 (20.9%) | 1 (24.4%) | |
| Grade B | 3 (9.1%) | 1 (3.4%) | |
| Grade C | 1 (3.0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| DGE | 3 (9.1%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0.326 |
| Pneumonia | 0 (0%) | 1 (3.4%) | |
| Wound infection | 3 (9.1%) | 3 (10.3%) | 0.653 |
| Mortality | 1 (3.0%) | 0 (0%) |
Codivilla, who was from Italy, originally described the PD procedure in 1898. Subsequently, POPF after PD has become one of the most troubling complications for surgeons. Many factors lead to the occurrence of POPF, and a number of research results have shown that the texture of the pancreas, diameter of the main pancreatic duct, and style of the anastomosis are important factors that influence the occurrence of POPF[15-17]. Since the first two factors are not within interventional control, surgeons have focused on inventing new types of PJ or pancreaticogastrostomy (PG) to minimize the occurrence of POPF.
PJ and PG are two types of popular pancreaticoenteric anastomoses that were recently described. Although Lee et al[18] described the PG method as having feasible outcomes for POPF and as having advantages over PJ, the results of many randomized controlled trials comparing PJ and PG have shown no firm conclusions to date about the superiority of one method or the other[19-21]. The two main methods used to perform PJ anastomoses are the invagination technique and the duct-to-mucosa anastomosis technique. Chen et al[22] proposed that the invagination PJ was relatively simple technically, and necrotic tissues and secretion could be drained into the intestine in a timely manner, but the pancreatic transecting surface was exposed to the intestinal lumen, which may lead to erosion and even life-threatening hemorrhage. One-layer end-to-side anastomosis decreases the operative time and is not generally affected by a lack of familiarity with the surgical technique, but it does not actually prevent pancreatic fistula formation. In addition, Su et al[23] clearly demonstrated that triple-layer duct-to-mucosa PJ with resection of the jejunal serosa provided a safe anastomosis and was associated with a very low risk of POPF. However, Zhang et al[17] argued that by increasing the suture layer of PJ, pancreatic leakage could be caused by large numbers of needle sutures and cutting of the pancreatic parenchyma.
No standard technique exists to rebuild the digestive tract. However, regardless of the type of anastomosis, the basic principles of digestive tract reconstruction must be followed, which include good exposure and vision, a lack of tension, a suitable match pitch, obtaining good coverage, and providing an adequate blood supply to pancreas sections. These are important factors to avoid POPF[24,25]. Our team found that most POPFs, especially severe cases, occurred at the rear wall of the pancreatic anastomosis. The reasons may be as follows: First, the pancreas is a substantial glandular tissue with a soft, fragile texture. With the exception of the anterior wall, the rear wall and the upper and lower edges have no peritoneal covering. Therefore, an anastomosis on the rear wall is more fragile than an anastomosis on the anterior wall, and it is more prone to cutting injury than an anastomosis on the anterior wall of the pancreas. Second, suturing an anastomosis in the rear wall is different from suturing the anterior wall, which is under direct vision, and this leads to a relatively poor grasp of needle depth and density. Third, we also found that most of patients have primary pancreatic duct openings that are located in the lower part of the flat ends, and this leads to a rear wall anastomosis being a weak point. Furthermore, as the abdominal aorta, celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery and vein, splenic vein, inferior mesenteric vein, and other important great vessels are adjacent to the rear wall of the pancreas, a fistula resulting from the rear wall of PJ will undoubtedly lead to disastrous consequences. Therefore, we reinforced the rear wall of the anastomosis after one-layer PJ. This can reduce the occurrence of POPF, and it also helps to avoid disastrous bleeding.
Compared to other anastomoses, this anastomosis has the following advantages: First, it reduces the occurrence of POPF, including the risk of disastrous bleeding. Three or four U-shaped sutures firmly wrap the rear wall of the pancreas. Even when succus pancreaticus leaks from the rear wall of the first layer, it will be limited to the area between the rear wall of the pancreas and the jejunal serosa and will not leak into the abdominal cavity. Second, the indications are widespread. The technique can be adapted to all types of pancreases, and no special requirement exists regarding the texture of the pancreas and the diameter of pancreatic ducts. Third, it is simple, timesaving, and easy to master. There is no need to deliberately prepare a pancreas stump and jejunum before the match, unlike a telescopic or bundled anastomosis that require freeing the pancreas with sufficient length to perform the next match. A 3-pin U-shaped anastomosis is simple and requires only a single layer of continuous suturing. Moreover, a pancreatic drainage tube ensures smooth drainage and reduces the activation of trypsin. A pancreatic duct drainage tube stretches across the anastomotic stoma and avoids activation of succus pancreaticus, which will corrode the anastomotic stoma. Even if leakage of the anastomosis occurs, it will be less harmful. Finally, it is effective in reducing surgical trauma to the pancreas, avoiding the suture cutting damage to pancreatic tissue that occurs with multiple layers. It should be noted that when the rear wall is reinforced, the 3-4 pin U-shaped anastomosis should avoid piercing into the main pancreatic duct so as not to increase the risk of succus pancreaticus leakage. Due to the currently limited number of cases, multi-center prospective randomized controlled studies are needed to determine whether this anastomosis can be used as a routine additional surgical procedure for PD.
One-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced is a safe and feasible procedure that can successfully reduce the rate of POPF. It may be a promising technique for PJ after PD.
To effectively reduce the incidence of postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF), we designed a new type of pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ).
To effectively reduce the incidence of POPF.
This study was to explore the clinical application value of this new technique.
In this study, we retrospectively analyzed 62 patients who received either the traditional duct-to-mucosa anastomoses or one-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced method at our hospital from May 2015 to September 2019. They were classified into two groups. We analyzed the basic information, perioperative outcomes, and surgical results of the patients.
In terms of postoperative complications, the one-half layer PJ group had a lower rate of POPF than the traditional group. The overall number of cases with POPF was 8 (24.2%) in the traditional group and 2 (6.9%) in the one-half layer group (P = 0.017). Additionally, the rate of grades B and C POPF was lower in the one-half layer group (3.4%) compared with that (12.1%) in the traditional group (P = 0.010). One patient died due to hemorrhage caused by severe pancreatic fistula in the traditional group.
One-half layer PJ with the rear wall of the pancreas reinforced is a safe and feasible procedure that can successfully reduce the rate of POPF.
This method may be a promising technique for PJ after pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Demirli Atici S, Turkey; Shah OJ, India S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Wang JJ
| 1. | Wellner UF, Kulemann B, Lapshyn H, Hoeppner J, Sick O, Makowiec F, Bausch D, Hopt UT, Keck T. Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage--incidence, treatment, and risk factors in over 1,000 pancreatic resections. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18:464-475. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 92] [Cited by in RCA: 118] [Article Influence: 10.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Ecker BL, McMillan MT, Asbun HJ, Ball CG, Bassi C, Beane JD, Behrman SW, Berger AC, Dickson EJ, Bloomston M, Callery MP, Christein JD, Dixon E, Drebin JA, Castillo CF, Fisher WE, Fong ZV, Haverick E, Hollis RH, House MG, Hughes SJ, Jamieson NB, Javed AA, Kent TS, Kowalsky SJ, Kunstman JW, Malleo G, Poruk KE, Salem RR, Schmidt CR, Soares K, Stauffer JA, Valero V, Velu LKP, Watkins AA, Wolfgang CL, Zureikat AH, Vollmer CM Jr. Characterization and Optimal Management of High-risk Pancreatic Anastomoses During Pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 2018;267:608-616. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 19.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Bannone E, Andrianello S, Marchegiani G, Masini G, Malleo G, Bassi C, Salvia R. Postoperative Acute Pancreatitis Following Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Determinant of Fistula Potentially Driven by the Intraoperative Fluid Management. Ann Surg. 2018;268:815-822. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 107] [Article Influence: 15.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Wu W, He J, Cameron JL, Makary M, Soares K, Ahuja N, Rezaee N, Herman J, Zheng L, Laheru D, Choti MA, Hruban RH, Pawlik TM, Wolfgang CL, Weiss MJ. The impact of postoperative complications on the administration of adjuvant therapy following pancreaticoduodenectomy for adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:2873-2881. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 149] [Cited by in RCA: 174] [Article Influence: 15.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Yanagimoto H, Satoi S, Toyokawa H, Yamamoto T, Hirooka S, Yamao J, Yamaki S, Ryota H, Matsui Y, Kwon AH. Pancreaticogastrostomy following distal pancreatectomy prevents pancreatic fistula-related complications. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21:473-478. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | De Carlis L, Ferla F, Di Sandro S, Giacomoni A, De Carlis R, Sguinzi R. Pancreatico-duodenectomy and postoperative pancreatic fistula: risk factors and technical considerations in a specialized HPB center. Updates Surg. 2014;66:145-150. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Bai X, Zhang Q, Gao S, Lou J, Li G, Zhang Y, Ma T, Xu Y, Liang T. Duct-to-Mucosa vs Invagination for Pancreaticojejunostomy after Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial from a Single Surgeon. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;222:10-18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 6.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Connor S. Defining post-operative pancreatitis as a new pancreatic specific complication following pancreatic resection. HPB (Oxford). 2016;18:642-651. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 129] [Cited by in RCA: 116] [Article Influence: 12.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Kimura W, Miyata H, Gotoh M, Hirai I, Kenjo A, Kitagawa Y, Shimada M, Baba H, Tomita N, Nakagoe T, Sugihara K, Mori M. A pancreaticoduodenectomy risk model derived from 8575 cases from a national single-race population (Japanese) using a web-based data entry system: the 30-day and in-hospital mortality rates for pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 2014;259:773-780. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 268] [Cited by in RCA: 300] [Article Influence: 27.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Hoem D, Viste A. Improving survival following surgery for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma--a ten-year experience. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012;38:245-251. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Roberts KJ, Hodson J, Mehrzad H, Marudanayagam R, Sutcliffe RP, Muiesan P, Isaac J, Bramhall SR, Mirza DF. A preoperative predictive score of pancreatic fistula following pancreatoduodenectomy. HPB (Oxford). 2014;16:620-628. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | El Nakeeb A, Salah T, Sultan A, El Hemaly M, Askr W, Ezzat H, Hamdy E, Atef E, El Hanafy E, El-Geidie A, Abdel Wahab M, Abdallah T. Pancreatic anastomotic leakage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Risk factors, clinical predictors, and management (single center experience). World J Surg. 2013;37:1405-1418. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Shrikhande SV, Barreto G, Shukla PJ. Pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy: the impact of a standardized technique of pancreaticojejunostomy. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2008;393:87-91. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 72] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Lyu Y, Li T, Cheng Y, Wang B, Chen L, Zhao S. Pancreaticojejunostomy Versus Pancreaticogastrostomy After Pancreaticoduodenectomy: An Up-to-date Meta-analysis of RCTs Applying the ISGPS (2016) Criteria. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2018;28:139-146. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (35)] |
| 15. | El Nakeeb A, Hamdy E, Sultan AM, Salah T, Askr W, Ezzat H, Said M, Zeied MA, Abdallah T. Isolated Roux loop pancreaticojejunostomy versus pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a prospective randomized study. HPB (Oxford). 2014;16:713-722. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Yang X, Aghajafari P, Goussous N, Patel ST, Cunningham SC. The "Colonial Wig" pancreaticojejunostomy: zero leaks with a novel technique for reconstruction after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017;16:545-551. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Zhang L, Li Z, Wu X, Li Y, Zeng Z. Sealing pancreaticojejunostomy in combination with duct parenchyma to mucosa seromuscular one-layer anastomosis: a novel technique to prevent pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220:e71-e77. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Lee JY, Kim EY, Lee JS, Lee SH, Na GH, Hong TH, You YK, Kim DG. A novel pancreaticogastrostomy method using only two transpancreatic sutures: early postoperative surgical results compared with conventional pancreaticojejunostomy. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015;88:299-305. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Yang SH, Dou KF, Sharma N, Song WJ. The methods of reconstruction of pancreatic digestive continuity after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Surg. 2011;35:2290-2297. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Nakao A, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Kaneko T, Takeda S, Inoue S, Nomoto S, Kanazumi N. Is pancreaticogastrostomy safer than pancreaticojejunostomy? J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006;13:202-206. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | He T, Zhao Y, Chen Q, Wang X, Lin H, Han W. Pancreaticojejunostomy versus pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Surg. 2013;30:56-69. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Chen Y, Zhu X, Huang J, Zhu Y. End-to-Side Penetrating-Suture Pancreaticojejunostomy: A Novel Anastomosis Technique. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;221:e81-e86. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Su AP, Zhang Y, Ke NW, Lu HM, Tian BL, Hu WM, Zhang ZD. Triple-layer duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy with resection of jejunal serosa decreased pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Surg Res. 2014;186:184-191. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Kim JH, Yoo BM, Kim JH, Kim WH. Which method should we select for pancreatic anastomosis after pancreaticoduodenectomy? World J Surg. 2009;33:326-332. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Yoshioka R, Yasunaga H, Hasegawa K, Horiguchi H, Fushimi K, Aoki T, Sakamoto Y, Sugawara Y, Kokudo N. Impact of hospital volume on hospital mortality, length of stay and total costs after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Br J Surg. 2014;101:523-529. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 11.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |