Published online Jul 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6417
Peer-review started: August 13, 2021
First decision: November 11, 2021
Revised: November 23, 2021
Accepted: April 21, 2022
Article in press: April 21, 2022
Published online: July 6, 2022
Processing time: 314 Days and 23.8 Hours
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare inflammatory disorder in children. However, there is still no standard guideline in the treatment of pediatric eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
To report our experience with the diagnosis and treatment of children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
From January 2017 to December 2019, a total of 22 children were diagnosed with eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
Endoscopic examination showed eosinophil infiltration in the duodenum [mean number of eosinophils/high-power field (HPF) = 53.1 ± 81.5], stomach (mean number of eosinophils/HPF = 36.8 ± 50.5), and terminal ileum (mean number of eosinophils/HPF = 49.0 ± 24.0). All 18 children with low eosinophil infiltration (< 14%) responded well to the initial drug treatment without relapse, while two of four children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) relapsed after initial methylprednisolone/montelukast treatment. In addition, children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) showed symptomatic relief and histological remission without further relapse after receiving budesonide/methylprednisolone as initial or relapse treatment.
Methylprednisolone/montelukast is still the best treatment for children with low eosinophil infiltration (< 14%). Budesonide can be considered as the initial or relapse treatment for children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%).
Core Tip: Pediatric eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare inflammatory disorder, and there is still no standard treatment guideline. Based on our treatment experience and analysis, the level of eosinophil infiltration may be an important factor affecting the treatment outcome. Methylprednisolone/montelukast is still the best treatment for children with lower eosinophil percentage (< 14%). Budesonide can be considered as the initial or relapse treatment for children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%).
- Citation: Chen Y, Sun M. Preliminary evidence in treatment of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children: A case series. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(19): 6417-6427
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i19/6417.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6417
Eosinophilic gastritis/gastroenteritis is a rare inflammatory disorder in adult and children, characterized by diffuse or patchy eosinophilic infiltration of the stomach, intestine, and colon[1-4]. In recent years, the incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic gastroenteritis have gradually increased, especially in Western countries. The prevalence of eosinophilic gastritis in the United States is estimated to be 6.3 per 100000 cases, with the highest prevalence in children under 5 years old[5]. Although epidemiologic studies regarding eosinophilic gastroenteritis in Asia are very limited, the clinical, endoscopic, and histopathological characteristics of patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis in Asia are mostly similar to those reported in Western countries[6-9].
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis in adult and children may present different gastrointestinal symptoms, depending on the location of the affected gastrointestinal tract and the extension of eosinophilic inflammation. Generally, the most common symptoms of eosinophilic gastroenteritis include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, bloating, burping, and intestinal obstruction[6,9-11]. Some patients may also experience loss of appetite, general weakness, foreign body sensation in the pharynx, dysphagia, focal mass, and massive ascites[12,13]. Moreover, eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children and adolescents may severely cause growth retardation, delayed puberty, and amenorrhea. The diagnosis of eosinophilic gastroenteritis generally includes the appearance of abnormal gastrointestinal symptoms, the presence of ≥ 20 eosinophils per high-power field (HPF), and exclusion of other secondary causes such as parasite or tuberculosis infection[14]. However, there is still no validated guideline for the clinical management of patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis, let alone standard guideline for children. Some evidence in the case report/series suggests that dietary restrictions (or elemental diet therapy) and the use of corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents such as prednisone and montelukast are effective as first-line treatments[2,15]. Considering the rarity of this disease in China and the limited understanding of its diagnosis and treatment, the aim of this study was to report our experience with the diagnosis and treatment outcome of 22 children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis in China.
From January 2017 to December 2019, 22 children with histologically confirmed eosinophilic gastroenteritis were enrolled in the study. Inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease were excluded by biopsies on colonoscopy and fecal calprotectin examination. Clinical data of the children including demographics, allergic histories, and laboratory and endoscopic examination were retrospectively reviewed and analyzed. The diagnosis of eosinophilic gastroenteritis was based on Talley’s diagnostic criteria[16]: (1) The presence of gastrointestinal symptoms; (2) Histological evidence of eosinophil infiltration in one or more areas of the gastrointestinal tract; and (3) No parasites or extraintestinal disease. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of our hospital, and the requirement for written informed consent was waived by the IRB due to the respective nature of this study.
The data collected for analysis in this study includes demographic characteristics (age, gender, and weight), laboratory parameters [white blood cell (WBC) count, absolute eosinophil count (AEC), hemoglobin, C-reactive protein (CRP), albumin, and immunoglobulin E (IgE)], history of atopic disease (asthma, eczema, urticaria, etc.), allergy history, physical examination results, clinical symptoms, medications, and endoscopic and imaging results. For statistical analysis, continuous variables are presented as the mean ± SD, and categorical variables are presented as numbers and percentages.
A total of 22 children (17 males and 5 females) were diagnosed with eosinophilic gastroenteritis, with a mean age of 9.3 ± 3.2 years and a mean weight of 32.0 ± 13.8 kg (Table 1). In all the 22 pediatric patients, the results of tuberculosis testing and parasite stool testing (larvae, cyst, and ova) were negative. The mean WBC count was (11.7 ± 8.9) × 109 cells/L. The mean AEC was 1692.9 ± 3845.6 cells/μL, and the converted eosinophil percentage was 9.5% ± 14.5%. Except for patient #19, the hemoglobin levels of the remaining 21 patients were within the standard range. The mean hemoglobin level of the 22 patients was 126.2 ± 15.2 g/L. Except for patients #7, #19, and #21, the albumin levels of the remaining 19 patients were within the normal range. The mean albumin level was 39.9 ± 8.4 g/L. Among the 22 patients, 15 (68.2%) had abnormal CRP levels, with a mean value of 11.5 ± 12.1 mg/dL. The serum IgE levels of nine patients (40.9%) exceeded the normal IgE level of children for the corresponding age, with a mean value of 520.3 ± 351.2 kU/L. All the 22 patients had a history of allergies or atopy disorders. Among them, 11 patients (50.0%) were allergic to food (wheat, egg, milk, etc.), and 6 (27.3%) were allergic to environmental allergies (house dust, dust mite, mold, etc.). In addition, three (13.6%), two (9.1%), and one (4.5%) patient had a history of asthma, eczema, and urticaria, respectively. The most common symptoms on admission included abdominal pain in 17 children (77.3%), vomiting in 9 (40.1%), diarrhea in 3 (13.6%), and nausea in 2 (9.1%).
| Characteristic | |
| Age (yr) | 9.3 ± 3.2 |
| Gender | |
| Male (n, %) | 17 (77.3) |
| Female (n, %) | 5 (22.7) |
| Weight (kg) | 32.0 ± 13.8 |
| WBC count (× 109/L) | 11.7 ± 8.9 |
| AEC (/μL) | 1692.9 ± 3845.6 |
| Eosinophilia percentage (%) | 9.5 ± 14.5 |
| Hemoglobin | 126.2 ± 15.2 |
| Albumin (outside the normal range) | |
| Number (%) | 3 (13.6) |
| Value (g/L) | 21.9 ± 5.0 |
| CRP (outside the normal range) | |
| Number (%) | 15 (68.2) |
| Value (mg/dL) | 11.5 ± 12.1 |
| Total IgE (outside the normal range) | |
| Number (%) | 9 (40.9) |
| Value (kU/L) | 520.3 ± 351.2 |
| Allergy history (n, %) | |
| Food allergies | 11 (50.0) |
| Environmental allergies | 6 (27.3) |
| Asthma | 3 (13.6) |
| Eczema | 2 (9.1%) |
| Urticaria | 1 (4.5) |
| Clinical symptoms (n, %) | |
| Abdominal pain | 17 (77.3) |
| Vomiting | 9 (40.1) |
| Diarrhea | 3 (13.6) |
| Nausea | 2 (9.1) |
| HPF | |
| Duodenum | 53.1 ± 81.5 |
| Stomach | 36.8 ± 50.5 |
| Ileum | 49.0 ± 24.0 |
The symptoms of eosinophilic gastroenteritis are heterogeneous, mainly depending on the region and layer of the intestinal wall affected by the eosinophilic infiltration. According to the location of eosinophil infiltration in the gastrointestinal tract[17], eosinophilic gastroenteritis can be further classified into mucosal/sub-mucosal pattern, muscle layer pattern, and serosal/sub-serosal pattern. In this study, most children (21/22, 95.5%) were diagnosed as having mucosal pattern. Only one child (4.5%) was diagnosed as having serosal pattern with unusual presentation of eosinophilic ascites.
Gastrointestinal endoscopy depicted that 20 children (95.2%) had erythematous exudative gastritis and a rough gastric antrum, accompanied by scattered erosion of the duodenal mucosa and hyperemia. Histological examinations showed that all the 22 children (100%) had eosinophilic gastroenteritis infiltration in the duodenum (mean number of eosinophils/HPF = 53.1 ± 81.5), while 20 children (90.9%) had eosinophilic gastroenteritis infiltration in the stomach (mean number of eosinophils/HPF = 36.8 ± 50.5). Only two children (9.1%) had eosinophilic gastroenteritis infiltration in the terminal ileum (mean number of eosinophils/HPF = 49.0 ± 24.0). The molecular examination of FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene in the peripheral blood cells of all the 22 patients was negative.
Table 2 shows the clinical characteristics and treatments of 22 children with eosinophilic colitis. All the 22 children (100%) received dietary restrictions. Except for patient #4, the remaining 21 children (95.5%) received initial drug treatment, including methylprednisolone, montelukast (Singulair), budesonide, and lansoprazole. Three children relapsed after initial treatment, including patient #4 who did not receive drug treatment and two patients (2/21, 9.5%) who received initial drug treatment. It is worth noting that 17 children (17/17, 100%) with low eosinophil percentage (< 14%) responded very well to the above-mentioned medications without relapse. Two of the four children (#20 and #21) with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) and CRP levels (> 1 mg/dL) relapsed after treatment with methylprednisolone and montelukast. Moreover, for children with high eosinophil infiltration and CRP levels (#19, #21, and #22), budesonide as a first-line and relapse treatment relieved the clinical symptoms and endoscopic appearance of eosinophils.
| Patient | Age/gender | Symptoms | Eosinophil (%) | HB (g/L) | CRP (mg/dL) | Albumin (g/L) | IgE (IU/mL) | HPF | Initial treatment | Relapse | Relapse treatment | ||
| Duodenum | Stomach | Ileum | |||||||||||
| 1 | 7/male | Vomiting | 0.59 | 111 | < 1 | 44 | 31 | 10 | 40 | Lansoprazole | N | ||
| 2 | 9/male | Loss of appetite, difficulty swallowing, foreign-body sensation in pharynx | 0.76 | 119 | 4.3 | 43.7 | 58 | 36 | 10 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | N | ||
| 3 | 12/male | Abdominal pain | 1.00 | 142 | 2 | 43 | 156 | 30 | 4 | 66 | Methylprednisolone | N | |
| 4 | 7/male | Abdominal pain, vomiting | 1.02 | 137 | < 1 | 43 | 54 | 25 | Y | Montelukast | |||
| 5 | 13/male | Abdominal pain, vomiting | 1.14 | 135 | 32 | 41.3 | 624 | 21 | 21 | Methylprednisolone | N | ||
| 6 | 9/male | Abdominal pain, vomiting | 1.19 | 121 | < 1 | 43.1 | 37 | 30 | 28 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | N | ||
| 7 | 3/male | Abdominal pain | 1.24 | 104 | 24 | 27 | 21.9 | 40 | 10 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | N | ||
| 9 | 7/female | Abdominal pain, vomiting | 1.63 | 135 | 21.5 | 37.6 | 64 | 40 | 10 | Lansoprazole. Montelukast | N | ||
| 10 | 11/male | Abdominal pain | 2.73 | 141 | < 1 | 47.4 | 112 | 26 | 9 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | N | ||
| 11 | 10/female | Abdominal pain | 3.25 | 132 | 3.7 | 41.8 | 35 | 8 | 22 | Methylprednisolone | N | ||
| 12 | 10/male | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, burping | 4.88 | 110 | 6 | 50 | 1113 | 90 | 5 | Montelukast | N | ||
| 13 | 11/male | Abdominal pain, vomiting | 4.95 | 132 | 4.09 | 41 | 121 | 53 | 8 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | N | ||
| 14 | 13/male | Abdominal pain, vomiting | 5.12 | 151 | 2.78 | 46.5 | 1001 | 21 | 6 | Lansoprazole. Montelukast | N | ||
| 15 | 13/male | Abdominal pain, nausea, acid regurgitation | 8.38 | 121 | 11.8 | 37 | 26 | 28 | 4 | Montelukast | N | ||
| 16 | 11/female | Abdominal pain | 9.20 | 127 | 39 | 48 | 317 | 60 | 70 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | N | ||
| 17 | 11/male | Abdominal pain, black stool | 10.63 | 123 | < 1 | 37 | 155 | 40 | 60 | Lansoprazole. Montelukast | N | ||
| 18 | 14/male | Vomiting, diarrhea | 11.83 | 155 | < 1 | 45 | 54 | 30 | 3 | 32 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | N | |
| 19 | 3/male | Periorbital edema, limb swelling | 14.66 | 92 | 2.25 | 17 | 337 | 30 | 200 | Methylprednisolone. Budesonide | N | ||
| 20 | 10/male | Abdominal pain | 14.89 | 122 | 3.67 | 41.4 | 80 | 48 | Methylprednisolone | Y | Methylprednisolone | ||
| 21 | 5/male | Periorbital edema, limb swelling | 41.63 | 116 | 13.7 | 21.7 | 649 | 400 | 70 | Methylprednisolone. Montelukast | Y | Methylprednisolone. Budesonide | |
| 22 | 7/female | Abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea | 58.50 | 125 | 1.88 | 40.9 | 331 | 50 | 120 | Methylprednisolone. Budesonide | N | ||
Due to the rare prevalence of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in Asia, the diagnosis and treatment of the disease can only be understood through a few case reports. In addition, there is currently no standard guideline for the treatment of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children due to the lack of prospective study[4]. The treatment of eosinophil gastroenteritis is still empirical. Current treatments for eosinophilic gastroenteritis include restricted diet/elemental diet therapy, corticosteroids, and steroid-sparing agents[2,15,18,19]. Although dietary therapy was reported to be effective in relieving allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis[20,21], low patient compliance limits its usefulness, especially in adolescents and adults. The only patient in our study who received restrictive diet therapy relapsed (case 4). The patient was advised to avoid exposure to allergens and not to receive steroid treatment because of low eosinophil count (0.06 × 109 cells/μL, AEC = 60 cells/μL), low eosinophilic infiltration (25/HPF), low eosinophil percentage (1.02%), and normal hemoglobin, albumin, CRP, and total IgE levels. However, the child relapsed with increased eosinophilic infiltration in the ileum (40/HPF), stomach (20/HPF), and duodenum (55/HPF). Following montelukast (5 mg/d) treatment for 1 mo, his abdominal pain and vomiting were relieved. After discussing with the child’s parents, the relapse may be the actual difficulty of restricting diet at home. It may also be because it is difficult to accurately identify disease-causing foods through allergen testing. In clinical practice, the effect of eliminating diets based on allergen testing may be different. Therefore, corticosteroids are still the best treatment if dietary restrictions are not feasible or symptoms cannot be relieved. Based on the results of our study, methylprednisolone/montelukast is an effective first-line treatment, especially for children with lower eosinophil percentage (< 14%).
Glucocorticoids (methylprednisolone) are considered to be effective drugs for the treatment of eosinophil gastroenteritis, and about 90% of adult patients respond to glucocorticoids[22]. A recent single-center study in China reported that increased eosinophil infiltration count is the predictive factor for glucocorticoid therapy in children with eosinophil gastroenteritis[23]. However, long-term use of methylprednisolone/prednisolone has been shown to cause Cushing syndrome, weight gain, growth retardation, and hypertension, as well as increased susceptibility to infection[24]. Although budesonide is also a topical glucocorticoid, the metabolized budesonide has less than 1% of its original activity. Thus, systemic exposure can be minimized. In addition to effectively alleviating Crohn’s disease, autoimmune hepatitis, and ulcerative colitis in adults[25-27], a recent small-scale retrospective study showed that budesonide is effective in children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis[28]. In our clinical practice of the 22 children, methylprednisolone/montelukast and budesonide did be effective in the clinical and pathological remission of eosinophil gastroenteritis in children.
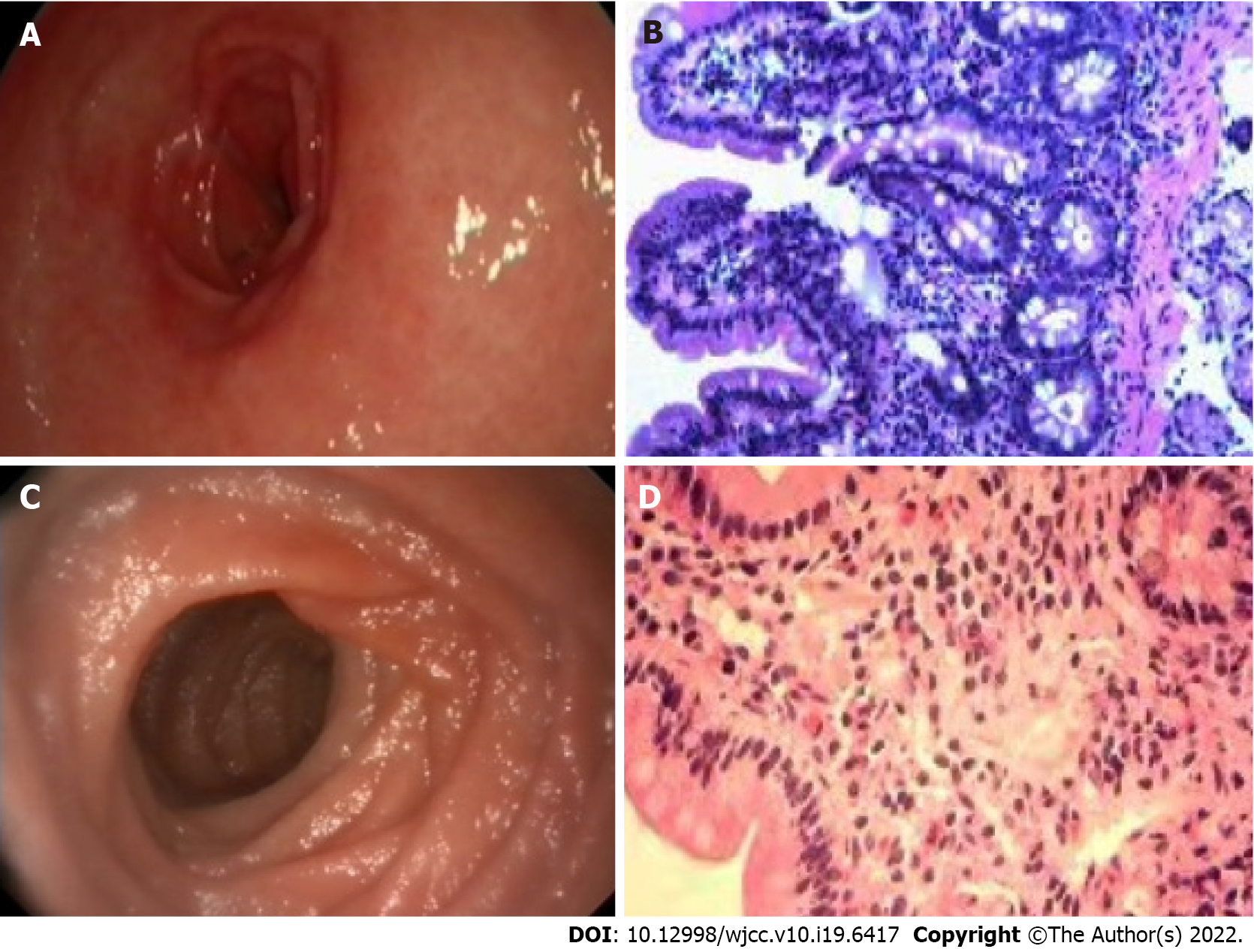
However, methylprednisolone/montelukast appears to be ineffective for children with high eosinophil infiltration and CRP levels. In this study, two patients with high eosinophil infiltration and CRP levels relapsed after receiving initial methylprednisolone/montelukast treatment. Case #21 is a 5-year-old boy with a history of asthma and food allergies, presenting with periorbital edema and swelling of his limbs. His hemoglobin level (116 g/L) was normal, and the results of tuberculosis and parasite stool examination were negative. Moreover, the patient showed elevated CRP level (13.7 mg/dL), increased serum IgE level (649 IU/mL), and low albumin level (21.7 g/L). Gastrointestinal endoscopy depicted erythematous, exudative and erosive gastritis, and congestion (Figure 1A). In addition, obvious hyperemia and edema were observed in the anterior wall of the duodenal mucosa. Histopathological examination (Figure 1B) depicted a high degree of eosinophilic infiltration. High eosinophil counts were observed in the duodenum (400/HPF) and stomach (70/HPF). The eosinophil percentage was as high as 41.63%. The patient was prescribed a dose of 2 mg/kg methylprednisolone and 5 mg/kg of montelukast for 1 wk, followed by a maintenance dose of 0.5 mg/kg of montelukast for 1 wk. Although a rapid response to methylprednisolone/montelukast was observed, the patient still relapsed four times. Finally, the treatment regimen was changed to methylprednisolone (2 mg/kg) and then maintained on budesonide (3 mg/d). The symptoms were completely relived. No symptoms of eosinophilic gastroenteritis were further observed at the revisit 2 mo later.
On the other hand, two other patients with high eosinophil infiltration and high CRP levels were initially treated with budesonide and methylprednisolone, and clinical remission was achieved without recurrence. In this study, case #19 is a 3-year-old boy with a history of asthma and food allergies, presenting with periorbital edema and swelling of his limbs. Although the gastric mucosa was normal under gastrointestinal endoscopy (Figure 1C), mucosal biopsy revealed a high degree of eosinophilic infiltration (Figure 1D). There were inflammatory infiltrations with high eosinophil count in the duodenum (30/HPF) and stomach (200/HPF). The eosinophil percentage was as high as 14.66%. The child had no oral ulcer or perianal lesions and was negative for fecal calprotectin, ruling out the possibility of inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, endoscopic biopsy examination also excluded intestinal lymphangiectasia. Since the patient showed elevated CRP level (2.25 mg/dL), raised serum IgE level (337 IU/mL), and low albumin level (17 g/L), methylprednisolone was prescribed for 1 wk, and budesonide, azathioprine, and thalidomide were used as a maintenance therapy for 1 wk. The symptoms were relived and the eosinophil counts improved rapidly. A 3-mo follow-up showed no symptoms. Although there are not many cases of using budesonide to treat children with high eosinophil infiltration and high CRP levels in this study, our clinical experience suggests that budesonide can be considered as the first-line or relapse treatment for children with high eosinophil infiltration and CRP levels. In the future, large-scale prospective randomized controlled studies should be designed to confirm whether budesonide is better than methylprednisolone/montelukast regimen in the treatment of pediatric eosinophilic gastroenteritis with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) and high CRP levels.
Compared with adults, eosinophilic gastroenteritis may cause growth retardation, failure to thrive, delayed puberty, and amenorrhea in children[29]. The diagnosis of eosinophilic gastroenteritis mainly depends on the clinical manifestations and endoscopic and radiographic examinations. Endoscopic abnormalities include erythema, mucosal hyperemia, thickened folds, fragile, rough areas, whitish spots, erosions, superficial ulcers, and nodules[30]. Because patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis do not always have the characteristics of peripheral eosinophilia, it is very important to confirm the infiltration of eosinophils by histological biopsy. Eosinophils usually exist in the lamina propria of the intestinal mucosa, gradually increasing from the duodenum to the cecum, and gradually decreasing from the right colon to the rectum. Although there is no consensus on the diagnostic threshold of eosinophil count in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract for eosinophilic gastroenteritis[31], most of the current case reports/series have suggested a threshold of > 20 eosinophils/HPF under microscopic examination[7]. In addition, degranulation of eosinophils, degeneration and regeneration of epithelial cells, and eosinophil cryptitis/abscess may also be observed. In this study, all the 22 patients showed eosinophil infiltration in the duodenum, stomach, and/or ileum, but only seven patients (31.8%) had abnormal peripheral eosinophilia counts. In addition, eosinophil infiltration does not always occur in sites where abnormalities are found by endoscopy or radiography. Instead, eosinophil infiltration is often found in normal mucosa due to patchy in distribution. Therefore, we recommended that multiple biopsies be examined to avoid misdiagnosis. It should be noted that endoscopic biopsy is mainly limited to the mucosa and submucosa. For patients with eosinophil infiltration in muscle layer or serosal pattern, mucosal biopsy may be negative. If eosinophilic gastroenteritis is highly suspected, a full-thickness surgical biopsy may be required but this is not feasible in pediatric patients.
The pathology of eosinophilic gastroenteritis is still unclear. In addition to the esophagus, eosinophils are often found in the lamina propria of various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, the number of eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract varies, with the highest count in the cecum and appendix[31]. However, the number of eosinophils also tends to increase in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory processes, including parasitic infections and allergic diseases. Activated eosinophils can release a variety of inflammatory mediators with high biological activity. Meanwhile, the degranulation of mast cells and the release of cytokines, chemokines, and lipid mediators are not only cytotoxic to the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract, but also trigger the Th2 immune responses and intestinal inflammation[32,33]. On the other hand, anatomical malformations and intestinal dysbiosis play a role in the pathophysiological mechanism of eosinophilic gastroenteritis[2]. In this study, only one pediatric patient (#20) showed abnormal superior mesenteric artery and intestinal malrotation on abdominal ultrasound examination.
There are some limitations in this study. Since this was a retrospective study of 22 patients, the accurate incidence of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children remains unclear. In addition, there may be a diagnostic bias on patients because there is still no consensus on the diagnostic threshold of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children. Despite the promising preliminary evidence of budesonide in the relapse treatment of children with high eosinophil infiltration, multicenter prospective or retrospective studies with a large sample size should be conducted to further validate the correlation between eosinophil percentage and budesonide in the treatment of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children.
For children with recurrent or persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and increased peripheral eosinophils, gastrointestinal endoscopy and endoscopic biopsy examinations should be performed multiple times to confirm the diagnosis of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Although there are currently no standard treatment guidelines for pediatric eosinophilic gastroenteritis, we recommend corticosteroids as the first-line treatment, especially when dietary restriction is not feasible or ineffective. Budesonide can be considered as the first-line or relapse treatment for children with high eosinophil infiltration and CRP levels. In the future, large-scale prospective studies are needed to explore the efficacy of budesonide and other corticosteroids in the treatment of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children with high eosinophil infiltration and CRP levels.
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare inflammatory disorder in children. Children with eosinophilic gastritis may severely cause growth retardation, delayed puberty, and amenorrhea. The diagnosis of eosinophilic gastroenteritis generally includes the appearance of abnormal gastrointestinal symptoms, the presence of ≥ 20 eosinophils per high-power field (HPF), and exclusion of other secondary causes such as parasite or tuberculosis infection. However, there is still no validated guideline for the clinical management of children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
Although some studies recommend dietary restrictions and the use of corticosteroids as first-line treatment, our clinical practice shows some different diagnosis and treatment findings.
Considering the rarity of pediatric eosinophilic gastroenteritis in China and the limited understanding of its diagnosis and treatment, the objective of this study was to report our experience with the diagnosis and treatment of 22 children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis in China.
A total of 22 children with histologically confirmed eosinophilic gastroenteritis were enrolled in the study. The diagnosis of eosinophilic gastroenteritis was based on Talley’s diagnostic criteria. Clinical data of the children including demographics, allergic histories, and laboratory and endoscopic examination were retrospectively reviewed and analyzed.
All children received dietary restrictions. First-line drug treatment included methylprednisolone, montelukast, budesonide, and lansoprazole. All children with low eosinophil percentage (< 14%) responded very well to first-line drug treatment without relapse. Half of children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (> 1 mg/dL) relapsed after treatment with methylprednisolone and montelukast. However, budesonide is an effective first-line and relapse treatment for children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) and CRP levels.
Based on our clinical practice, we recommend corticosteroids as the first-line treatment for low eosinophil infiltration (< 14%). Budesonide is recommended as the first-line or relapse treatment for children with high eosinophil infiltration and CRP levels.
Although our clinical practice showed the promising preliminary evidence of budesonide in the relapse treatment of children with high eosinophil infiltration, multicenter prospective or retrospective studies with a large sample size should be conducted to further validate the findings.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: El-Shabrawi MH, Egypt; Pop TL, Romania; Sahin Y, Turkey S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Wang JJ
| 1. | Chen B, Yang Z, Lu H, Wei C, Wang F, Liu C. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis presenting as upper gastrointestinal hematoma and ulcers after endoscopic biopsy: A case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e8075. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Licari A, Votto M, D'Auria E, Castagnoli R, Caimmi SME, Marseglia GL. Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases in Children: A Practical Review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2020;16:106-114. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Grandinetti T, Biedermann L, Bussmann C, Straumann A, Hruz P. Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: Clinical Manifestation, Natural Course, and Evaluation of Treatment with Corticosteroids and Vedolizumab. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2231-2241. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Chen PH, Anderson L, Zhang K, Weiss GA. Eosinophilic Gastritis/Gastroenteritis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2021;23:13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Jensen ET, Martin CF, Kappelman MD, Dellon ES. Prevalence of Eosinophilic Gastritis, Gastroenteritis, and Colitis: Estimates From a National Administrative Database. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016;62:36-42. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 157] [Cited by in RCA: 227] [Article Influence: 25.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 6. | Ishihara S, Kinoshita Y, Schoepfer A. Eosinophilic Esophagitis, Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis, and Eosinophilic Colitis: Common Mechanisms and Differences between East and West. Inflamm Intest Dis. 2016;1:63-69. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Tien FM, Wu JF, Jeng YM, Hsu HY, Ni YH, Chang MH, Lin DT, Chen HL. Clinical features and treatment responses of children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Pediatr Neonatol. 2011;52:272-278. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Kinoshita Y, Furuta K, Ishimaura N, Ishihara S, Sato S, Maruyama R, Ohara S, Matsumoto T, Sakamoto C, Matsui T, Ishikawa S, Chiba T. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and eosinophilic gastroenteritis. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:333-339. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 109] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Lee K, Choe BH, Kang B, Kim S, Kim JY, Shim JO, Lee YM, Lee EH, Jang HJ, Ryoo E, Yang HR. Nationwide Multicenter Study of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Korean Children. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2020;23:231-242. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Müller M, Keller KM, Stallmann S, Eckardt AJ. Clinicopathologic Findings in Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: A German Case Series. J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2014;5. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Sasaki Y, Kajino H. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with persistent abdominal pain: a case report. J Rural Med. 2020;15:44-46. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Menon J, Venkatesh V, Bhatia A, Rana SS, Lal SB. Ascites: an unusual presentation of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in a child. Trop Doct. 2020;50:277-279. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Manrriquez A, Alharbi O, Braskett M, Bhardwaj V. Mural Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disease in 2 Pediatric Patients Presenting as Focal Mass. Pediatrics. 2020;145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Sunkara T, Rawla P, Yarlagadda KS, Gaduputi V. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: diagnosis and clinical perspectives. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:239-253. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 13.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Higuchi T, Tokunaga M, Murai T, Takeuchi K, Nakayama Y. Elemental diet therapy for eosinophilic gastroenteritis and dietary habits. Pediatr Int. 2022;64:e14894. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Talley NJ, Shorter RG, Phillips SF, Zinsmeister AR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a clinicopathological study of patients with disease of the mucosa, muscle layer, and subserosal tissues. Gut. 1990;31:54-58. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 506] [Cited by in RCA: 513] [Article Influence: 14.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Klein NC, Hargrove RL, Sleisenger MH, Jeffries GH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 1970;49:299-319. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 434] [Cited by in RCA: 406] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Hogan SP, Rothenberg ME. Review article: The eosinophil as a therapeutic target in gastrointestinal disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20:1231-1240. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Madison JM, Bhardwaj V, Braskett M. Strategy for Food Reintroduction Following Empiric Elimination and Elemental Dietary Therapy in the Treatment of Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2020;22:25. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Lucendo AJ, Serrano-Montalbán B, Arias Á, Redondo O, Tenias JM. Efficacy of Dietary Treatment for Inducing Disease Remission in Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;61:56-64. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 7.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Chehade M, Sicherer SH, Magid MS, Rosenberg HK, Morotti RA. Multiple exudative ulcers and pseudopolyps in allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis that responded to dietary therapy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007;45:354-357. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Wong GW, Lim KH, Wan WK, Low SC, Kong SC. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: Clinical profiles and treatment outcomes, a retrospective study of 18 adult patients in a Singapore Tertiary Hospital. Med J Malaysia. 2015;70:232-237. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Ren L, Li HW, Xiong LY, Chen PY, Geng LL. Predictive factors for glucocorticoid therapy in children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021;23:1149-1153. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Aljebab F, Choonara I, Conroy S. Systematic Review of the Toxicity of Long-Course Oral Corticosteroids in Children. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0170259. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 74] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 12.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Rezaie A, Kuenzig ME, Benchimol EI, Griffiths AM, Otley AR, Steinhart AH, Kaplan GG, Seow CH. Budesonide for induction of remission in Crohn's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;CD000296. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 5.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Peiseler M, Liebscher T, Sebode M, Zenouzi R, Hartl J, Ehlken H, Pannicke N, Weiler-Normann C, Lohse AW, Schramm C. Efficacy and Limitations of Budesonide as a Second-Line Treatment for Patients With Autoimmune Hepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16:260-267.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Sherlock ME, MacDonald JK, Griffiths AM, Steinhart AH, Seow CH. Oral budesonide for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;CD007698. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Fang S, Song Y, Zhang S, Li C. Retrospective study of budesonide in children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Pediatr Res. 2019;86:505-509. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Agrawal N, Rani UK, Sridhar R, Dhamayanthi S. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a diagnosis behind the curtains. J Clin Diagn Res. 2012;6:1789-1790. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Zhang L, Duan L, Ding S, Lu J, Jin Z, Cui R, McNutt M, Wang A. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: clinical manifestations and morphological characteristics, a retrospective study of 42 patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:1074-1080. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Collins MH, Capocelli K, Yang GY. Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders Pathology. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017;4:261. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 70] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Caldwell JM, Collins MH, Stucke EM, Putnam PE, Franciosi JP, Kushner JP, Abonia JP, Rothenberg ME. Histologic eosinophilic gastritis is a systemic disorder associated with blood and extragastric eosinophilia, TH2 immunity, and a unique gastric transcriptome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:1114-1124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 100] [Cited by in RCA: 135] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Zhang M, Li Y. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: A state-of-the-art review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32:64-72. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 12.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |