Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2022; 10(12): 3647-3661
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i12.3647
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i12.3647
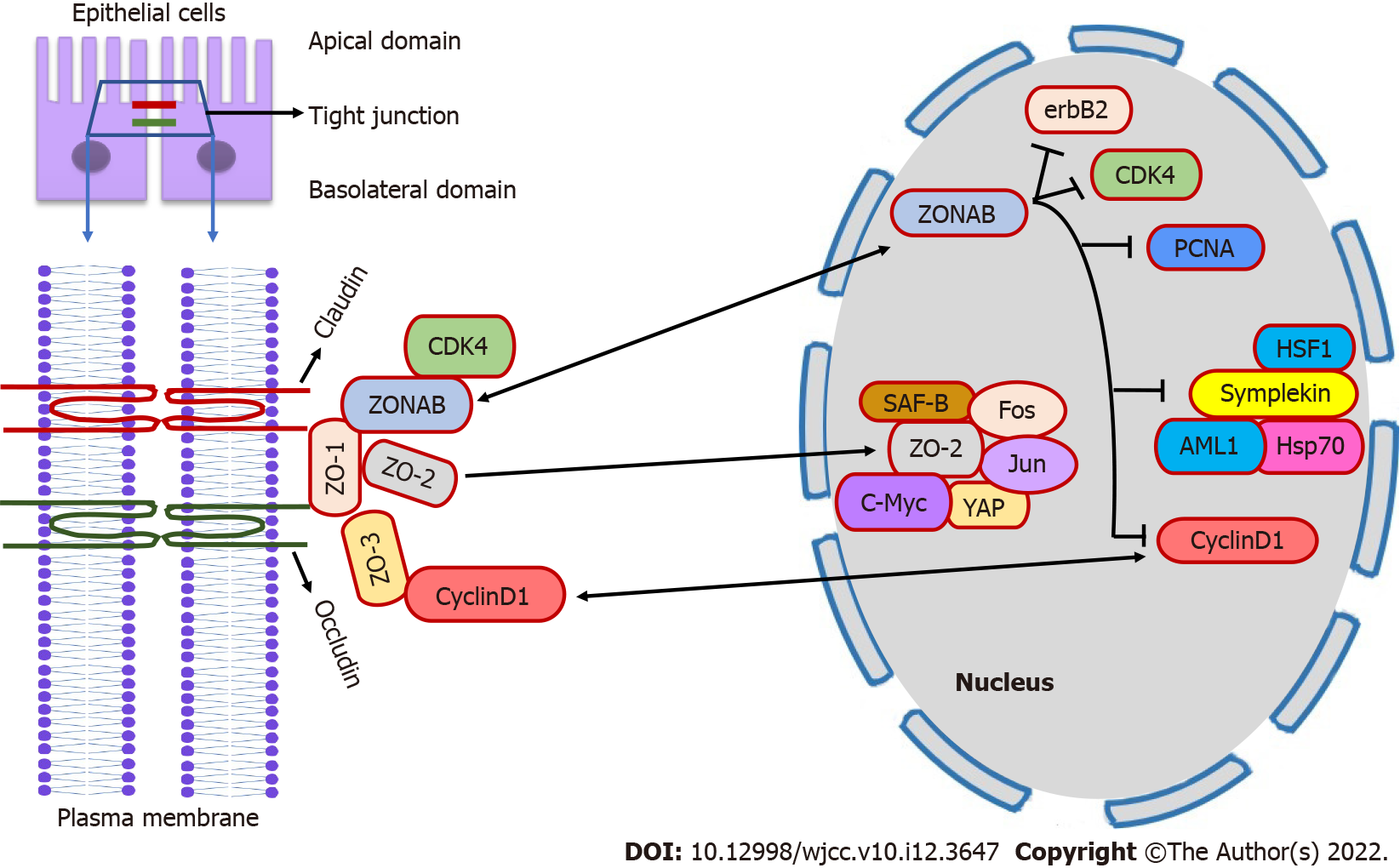
Figure 1 Mechanism by which zonula occluden 1, 2, and 3 proteins regulate cell proliferation.
Zonula occludens (ZO)-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3 localizes at the tight junction along with claudin and occludin. ZO-1 regulates cell proliferation by cytoplasmic sequestration of ZO-1 associated nucleic acid binding protein (ZONAB) from the nucleus to repress the transcription of cell cycle related genes such as cyclin dependent kinase 4, cyclin D1 (CD1), and proliferating cell nuclear antigen. ZONAB also interacts with symplekin to regulate gene expression. ZO-2 interacts with several transcription factors such as Jun, fos, c-Myc, and yes associated protein and regulates gene expression. ZO-3 degrade the protein expression of CD1 and inhibits cell cycle progression. CDK4: Cyclin dependent kinase 4; ZONAB: Zonula occludens-1 associated nucleic acid binding protein; ZO: Zonula occludens; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; YAP: Yes associated protein.
- Citation: Ram AK, Vairappan B. Role of zonula occludens in gastrointestinal and liver cancers. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(12): 3647-3661
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i12/3647.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i12.3647