Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2021; 9(7): 1619-1630
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1619
Published online Mar 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1619
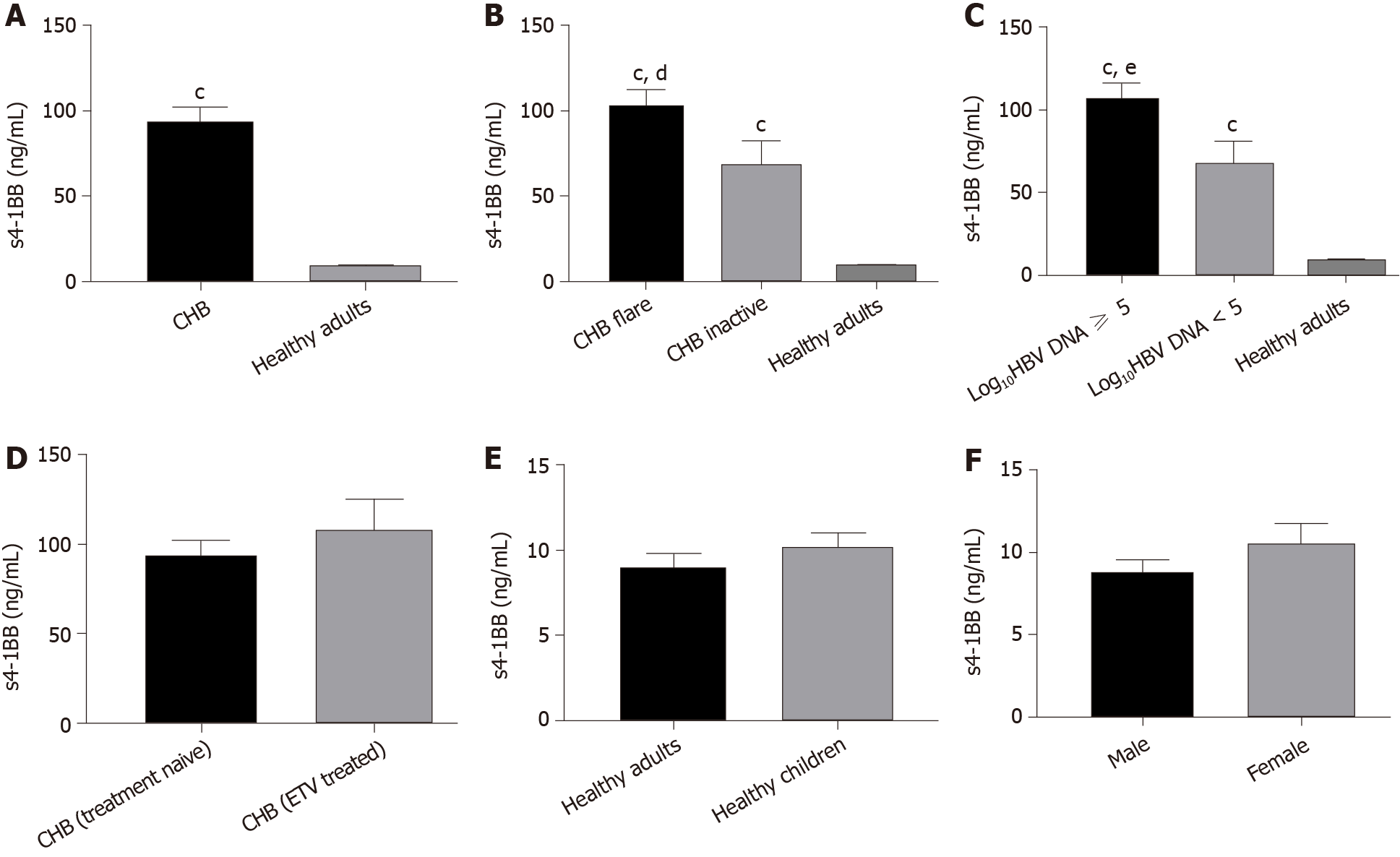
Figure 1 Plasma soluble 4-1BB levels in various groups of treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B (except for the comparison between treatment naïve group and entecavir treated group).
A: Soluble 4-1BB (s4-1BB) levels in healthy adults and chronic hepatitis B (CHB); B and C: s4-1BB levels in patients with CHB in various phases of disease (CHB flare means infection exhibiting a disease flare up, elevated alanine aminotransferase; CHB inactive means patients with inactive disease, normal alanine aminotransferase); D: s4-1BB levels before and after treatment in patients with hepatitis B virus; E: Plasma s4-1BB levels in healthy adults and healthy children; F: Plasma s4-1BB levels in healthy male donors and healthy female donors. P values were obtained by the Mann–Whitney U test or unpaired t test according to the characteristics of the data. cP < 0.001 vs healthy adult group; dP < 0.05 vs chronic hepatitis B inactive group; eP < 0.05 vs log10HBV DNA < 5 group. CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; s4-1BB: Soluble 4-1BB; ETV: Entecavir.
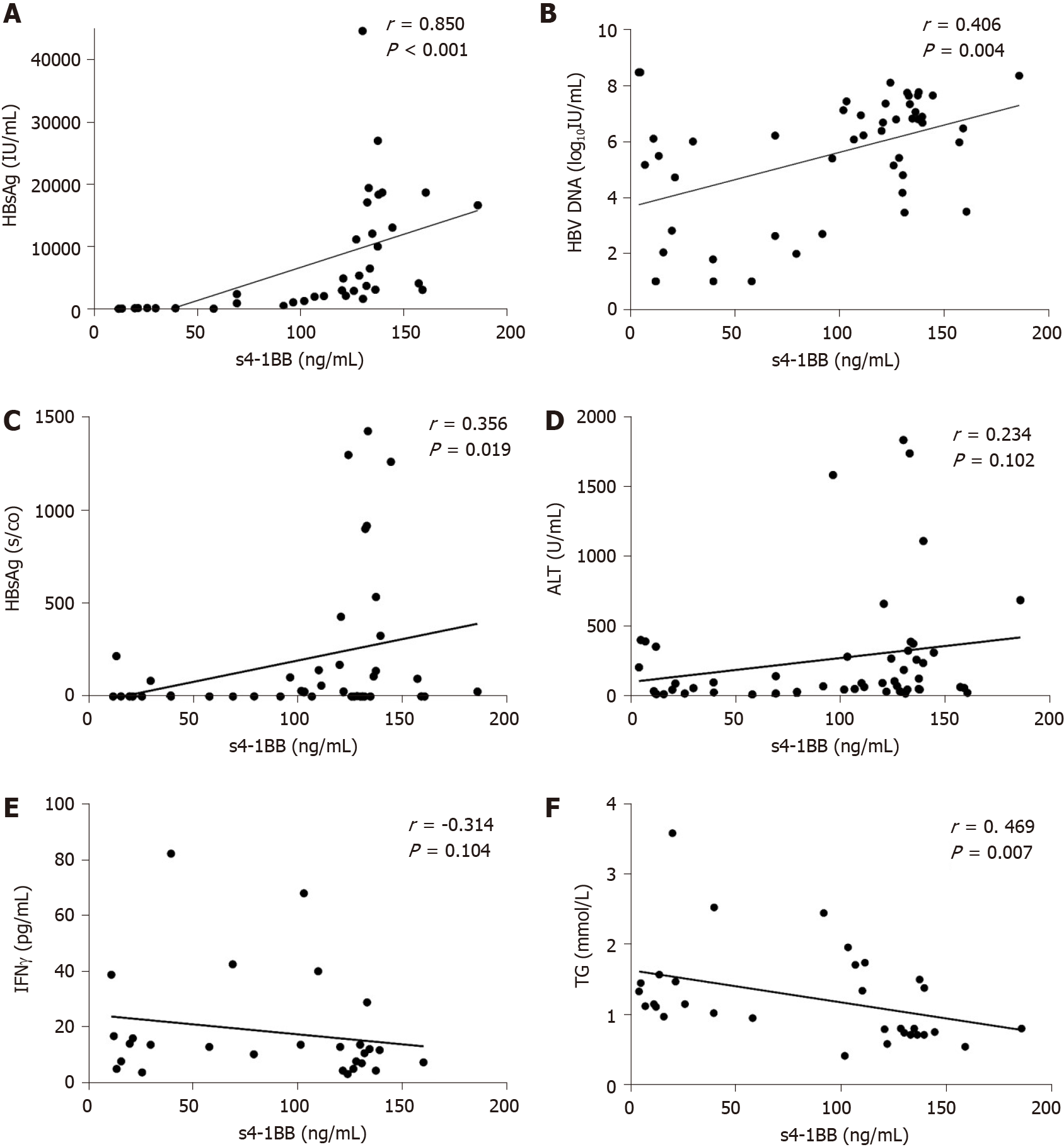
Figure 2 Association between plasma soluble 4-1BB levels and hepatitis B virus markers as well as clinical parameters in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B.
A-C: The positive correlations of plasma soluble 4-1BB (HBsAg) levels with quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B virus DNA, and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg); D-F: The correlations of plasma s4-1BB levels with alanine aminotransferase (ALT), IFNγ, and triglyceride (TG). Correlations were tested by Spearman’s rho (r), and the level of significance was expressed as the P value (P). CHB: Chronic hepatitis B.
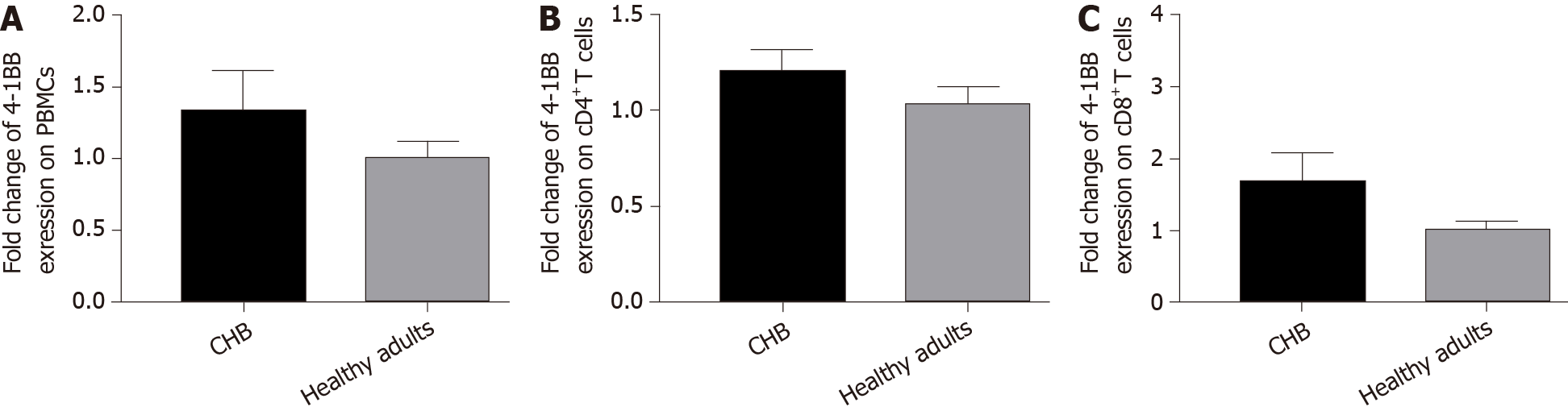
Figure 3 Expression of 4-1BB in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B and healthy adults.
A-C: Soluble 4-1BB (s4-1BB) mRNA levels of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells in peripheral blood were compared between patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and healthy adults. Horizontal lines indicate the median values ± standard error of the mean, and P values were obtained by the Mann–Whitney U test or unpaired t test according to the characteristics of the data.
- Citation: Zhan MR, Gao XZ, Wang C, Peng F, Wang XM, Xu HQ, Niu JQ. Elevated soluble 4-1BB is associated with serum markers of hepatitis B virus in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(7): 1619-1630
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i7/1619.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1619