Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2021; 9(6): 1483-1489
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1483
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1483
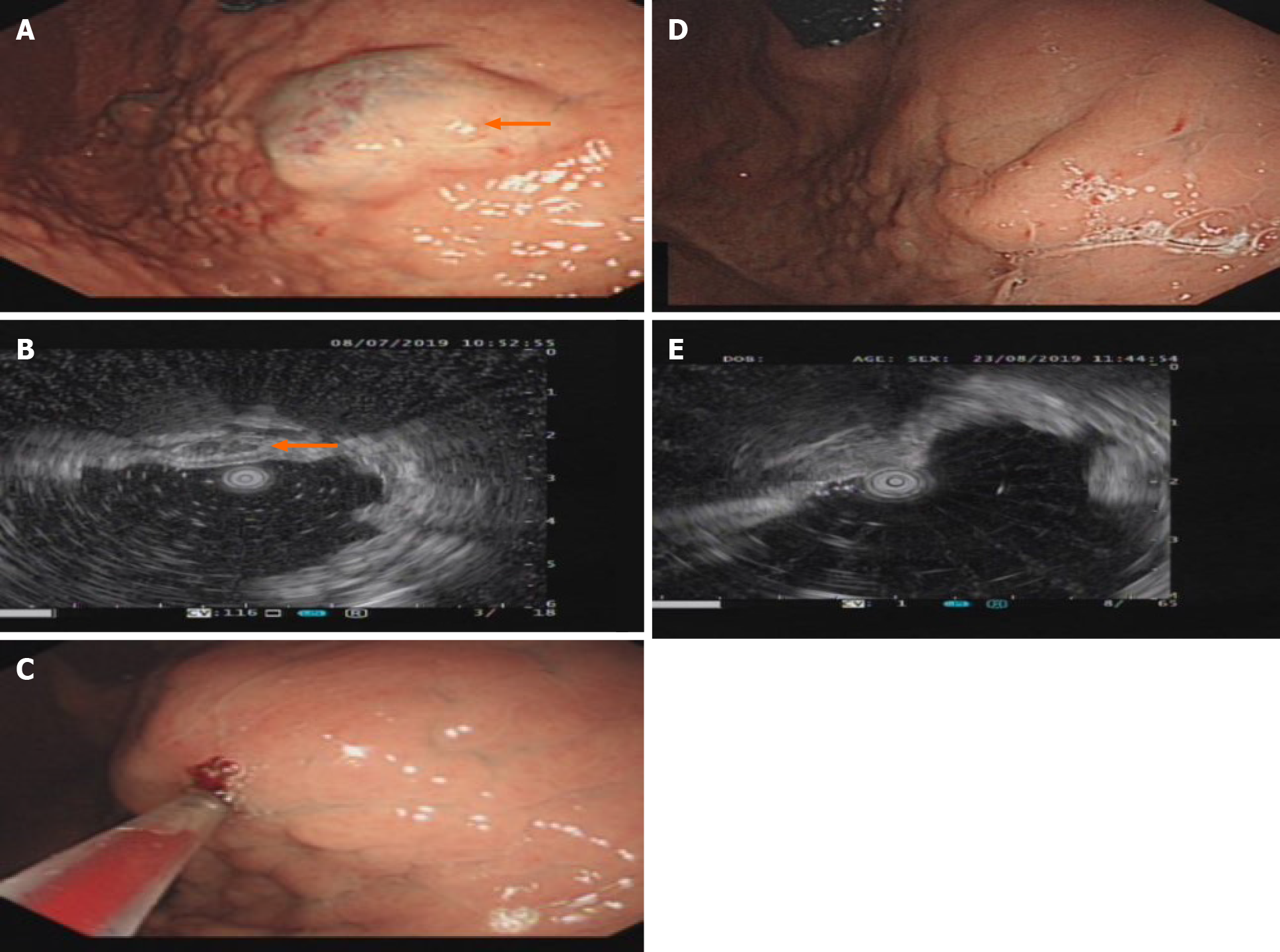
Figure 1 Gastroscopy and ultrasound images of the lower esophagus.
A: Gastroscopy showing a bulge of about 4.0 cm × 4.5 cm × 2 cm in the lower esophagus. The mucosa was smooth and blue (as shown by the arrow in the picture); B: Endoscopic ultrasound showing lesions with multiple grids without echo structures and clear boundaries (as shown by the arrow in the picture); C: Twenty milliliters of polidocanol was injected into the hemangioma under a transparent cap with a 25G needle endoscope; D: The hemangioma at the esophageal lesion disappeared, and the mucosa was pink after treatment with polidocanol; E: Ultrasound showing that the non-echo structure disappeared after submucosal treatment with polidocanol.
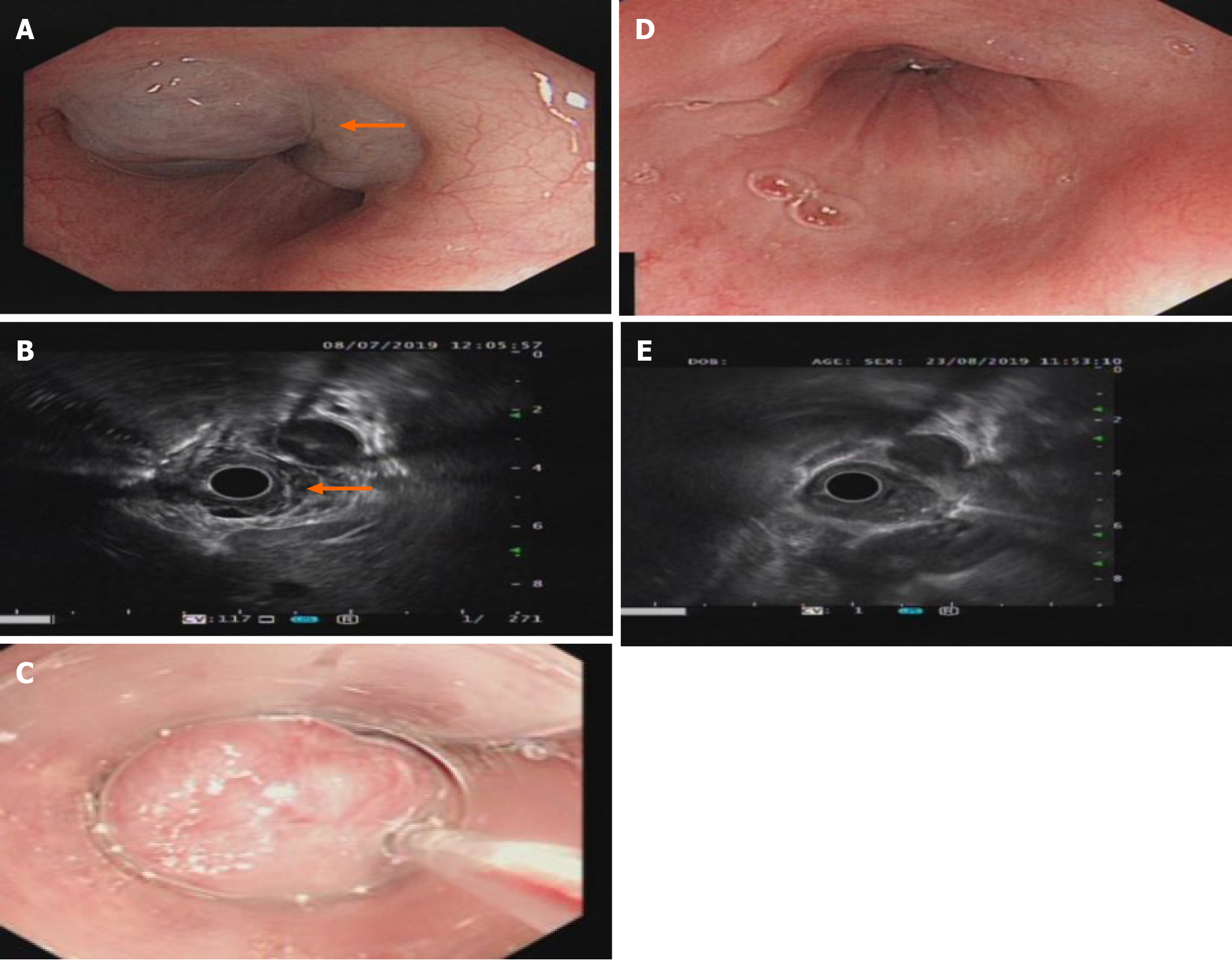
Figure 2 Gastroscopy and ultrasound images of the posterior wall of the bottom of the stomach.
A: A 2.5 cm × 3.0 cm × 2 cm submucosal bulge of the posterior wall of the bottom of the stomach was seen on gastroscopy. The mucosa was smooth and the top of the mucosa was pale blue-purple (as shown by the arrow in the picture); B: Endoscopic ultrasound showing grid-like echoless structure with clear borders (as shown by the arrow in the picture); C: Fifteen milliliters of polidocanol was injected into the hemangioma under a transparent cap with a 25G needle endoscope; D: The submucosal bulge disappeared, and the mucosa color returned to normal on gastroscopy after treatment with polidocanol; E: The echoless structure of the lesions disappeared on endoscopic ultrasound after treatment with polidocanol.
- Citation: Yao H, Xie YX, Guo JY, Wu HC, Xie R, Shi GQ. Polidocanol sclerotherapy for multiple gastrointestinal hemangiomas: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(6): 1483-1489
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i6/1483.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1483