Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2021; 9(6): 1329-1335
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1329
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1329
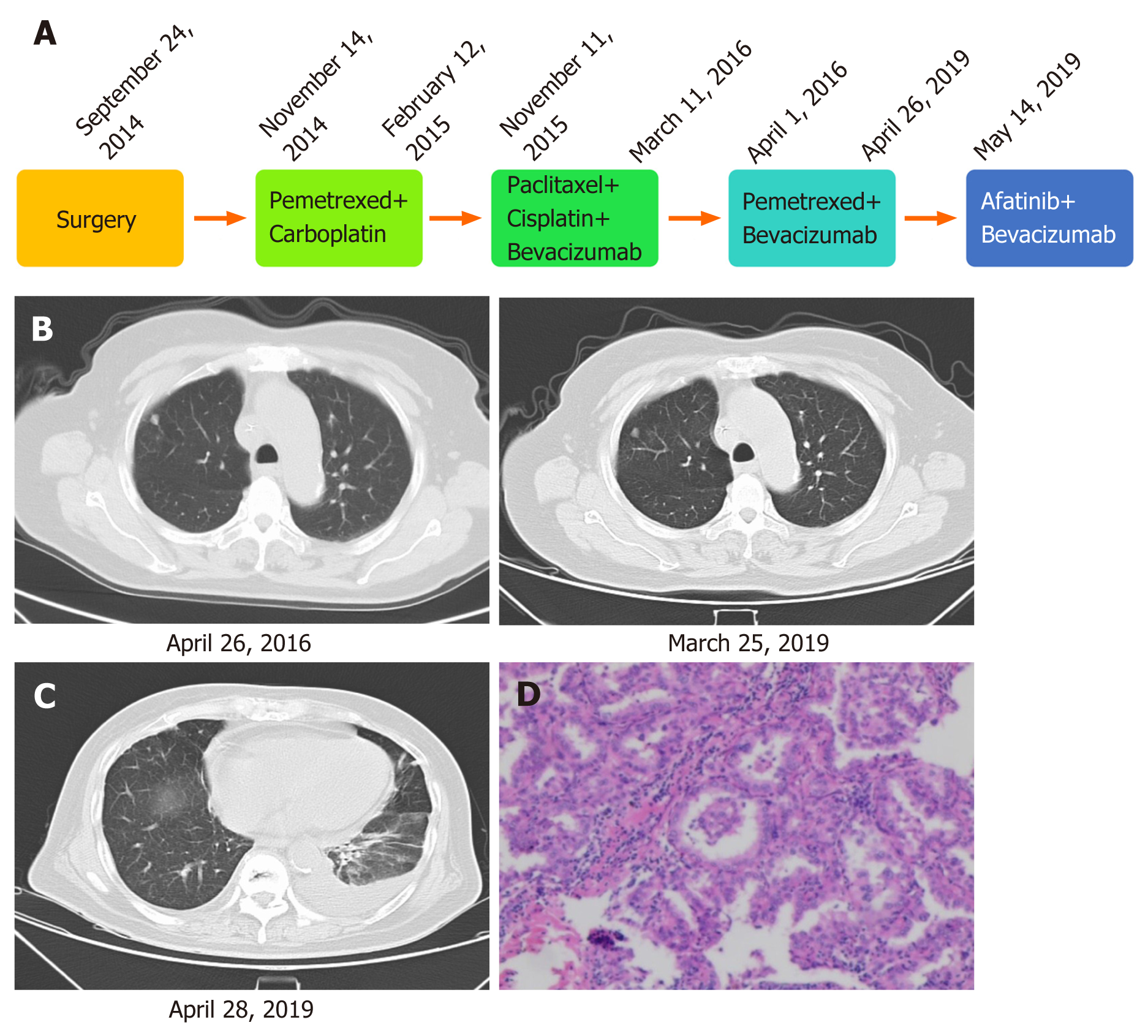
Figure 1 Diagnosis and treatment of the patient’s disease.
A: Treatment of lung adenocarcinoma using different regimens; B: Imaging diagnosis during pemetrexed plus bevacizumab treatment; C: Imaging diagnosis before afatinib therapy; D: Pathological diagnosis.
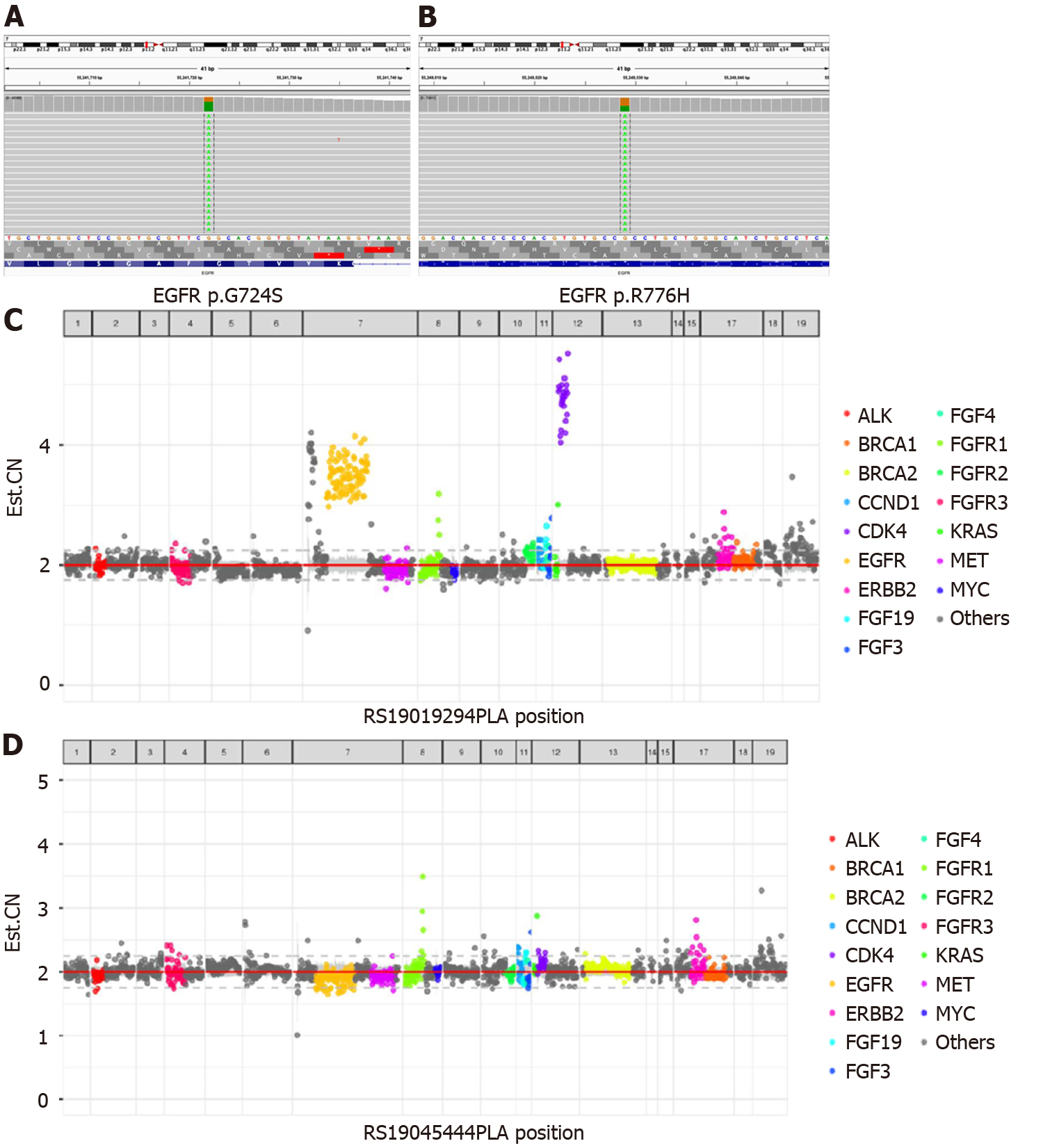
Figure 2 Next-generation sequencing results.
A: Next-generation sequencing showed G724S in EGFR exon 18; B: Next-generation sequencing showed R776H in EGFR exon 20; C: Next-generation sequencing showed EGFR amplification before treatment; D: Next-generation sequencing showed EGFR amplification after treatment.
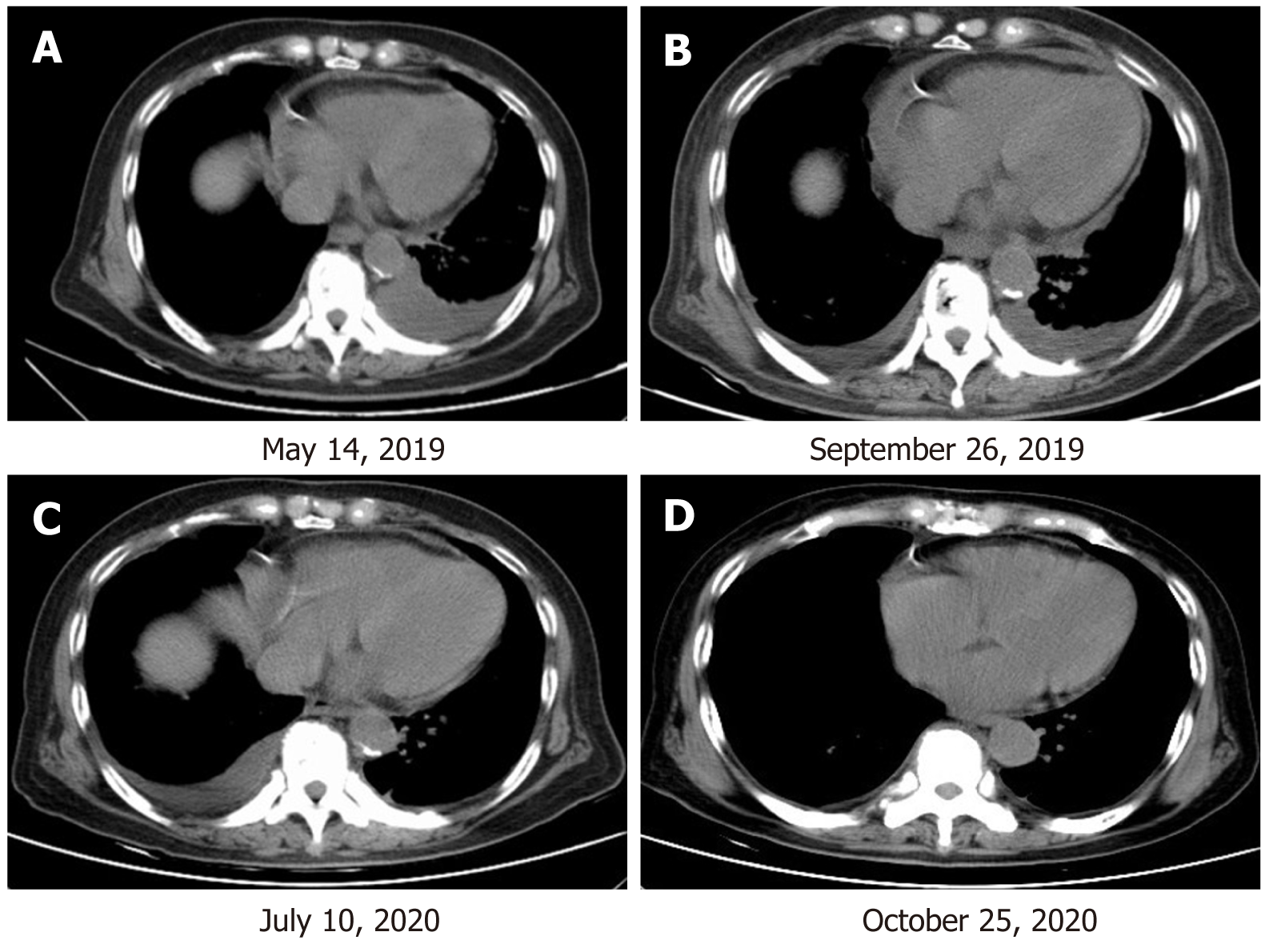
Figure 3 The patient’s clinical course including treatment history and relevant imaging studies.
A: At baseline before therapy with afatinib combined with bevacizumab; B: At 4 mo of therapy with afatinib combined with bevacizumab, with an SD response; C: At 14 mo of therapy with afatinib combined with bevacizumab, with an SD response. D: At 17 mo of therapy with afatinib combined with bevacizumab, with a progressive disease response.
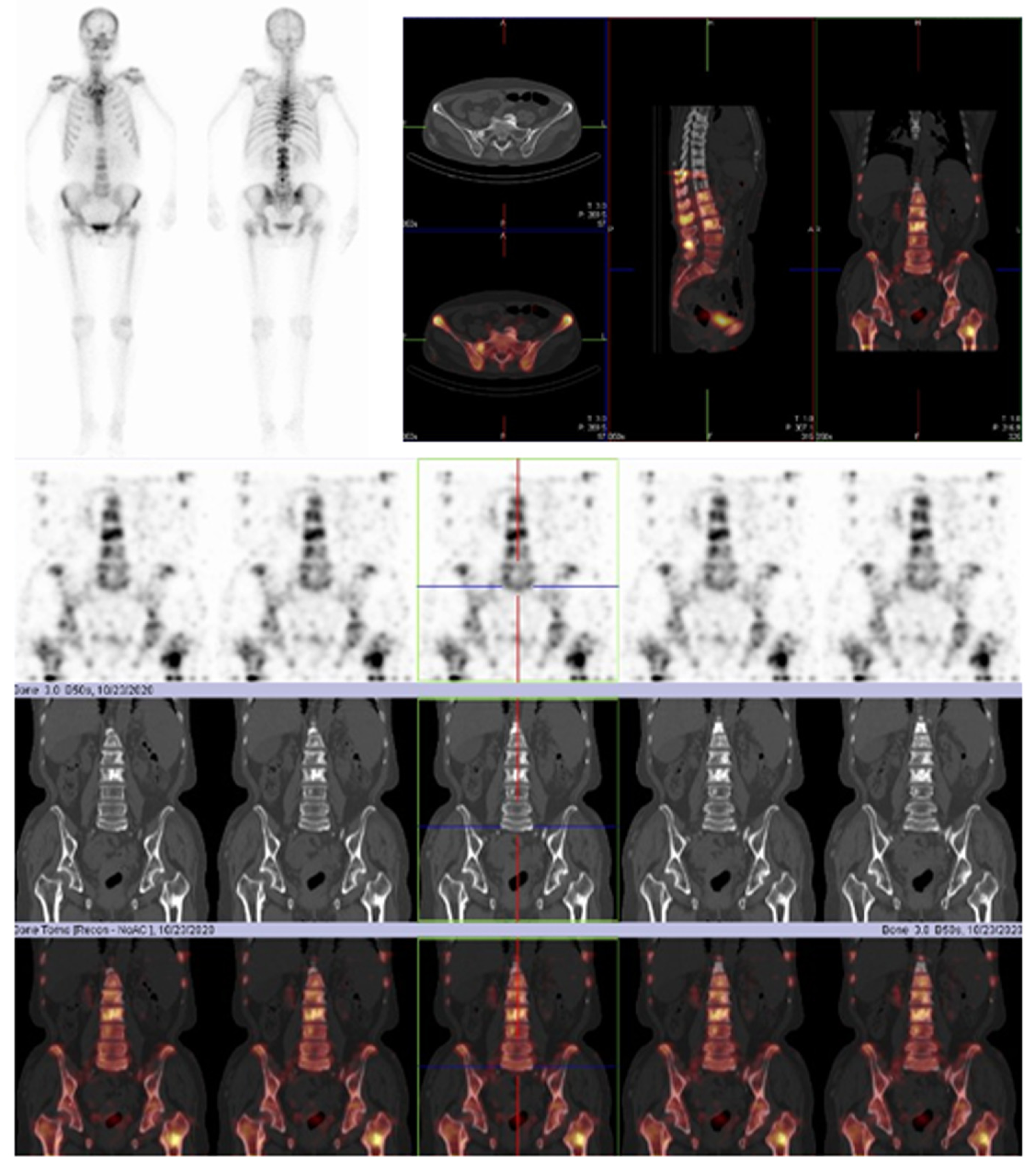
Figure 4 Diagnosis of disease progression in the patient.
Whole-body bone scan and organ tomography revealed increased uptake of multiple imaging agents in the skull, spine, ribs on both sides, pelvis composition, and upper left femur, suggesting bone metastasis of the tumor.
- Citation: He SY, Lin QF, Chen J, Yu GP, Zhang JL, Shen D. Efficacy of afatinib in a patient with rare EGFR (G724S/R776H) mutations and amplification in lung adenocarcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(6): 1329-1335
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i6/1329.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1329