Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2021; 9(5): 1148-1155
Published online Feb 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1148
Published online Feb 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1148
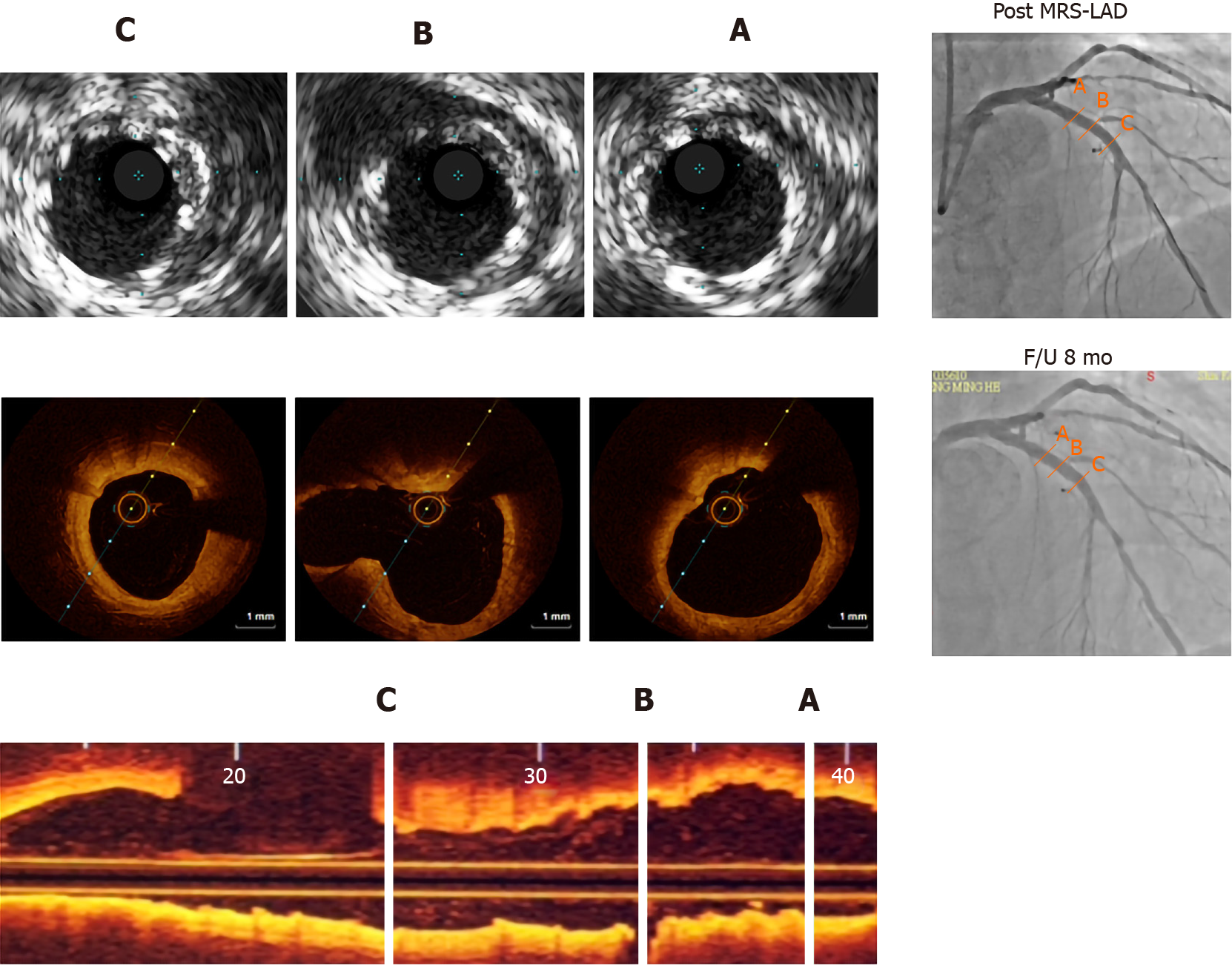
Figure 1 Intravascular ultrasound 8 mo prior, optical coherence tomography and coronary angiography findings.
A-C: The treated segments are proximal cross-section (A), middle cross-section (B), distal cross-section (C). Post-implantation intravascular ultrasound images of the magnesium-based metal scaffolds show good apposition of struts. Real-time optical coherence tomography pullbacks vividly demonstrate almost complete resorption of the struts at the 8th month. MRS: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy; LAD: Left anterior descending artery.
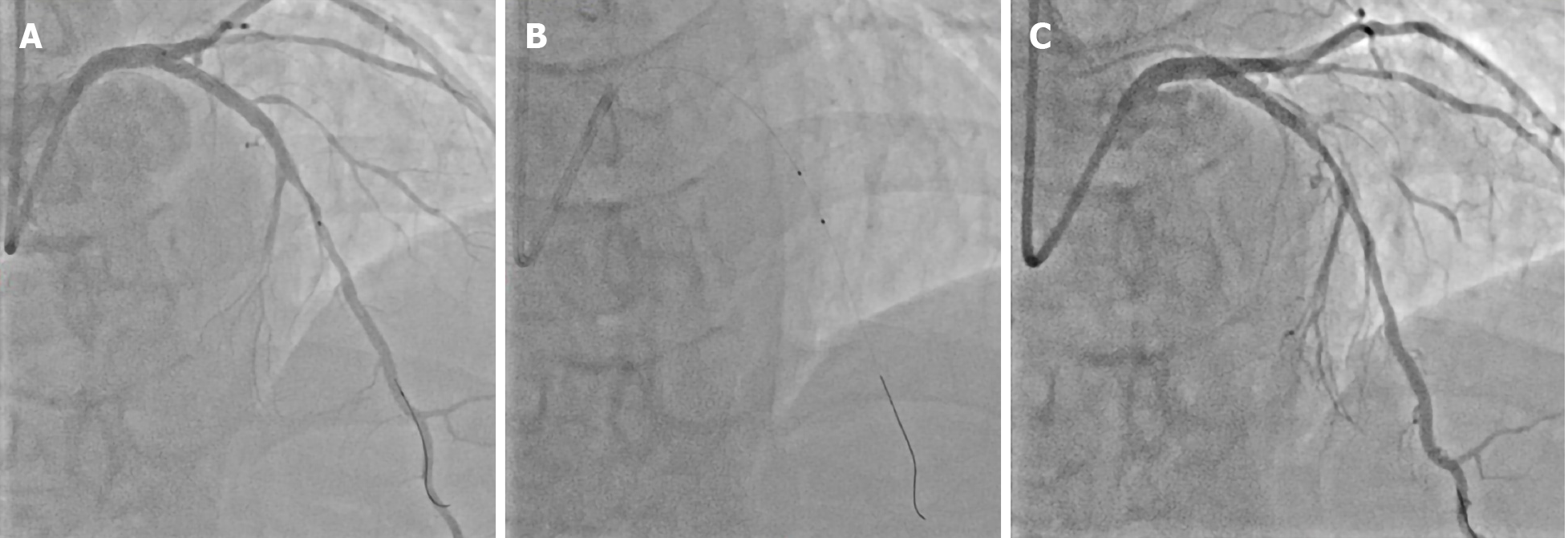
Figure 2 Coronary angiography images.
A: Edge vascular response adjacent to the distal edges after implantation of fully magnesium-based resorbable scaffold; B: Optimal balloon angioplasty; C: Coronary dissection occurs with rapid spreading out (in antero-cranial view).
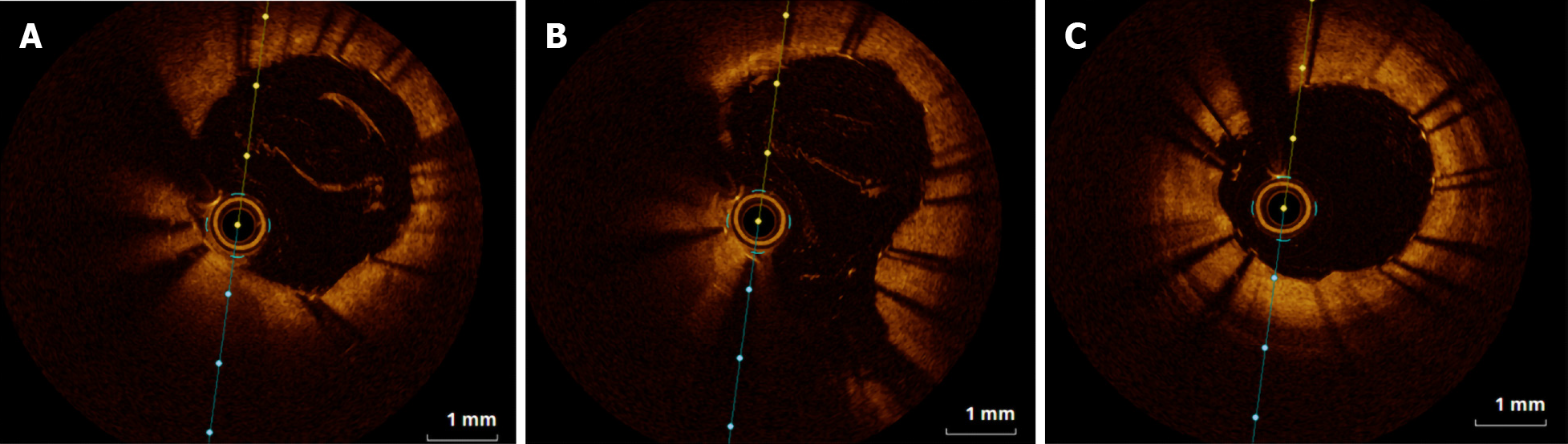
Figure 3 Optical coherence tomography images.
A: Proximal cross-section; B: Middle cross-section; C: Distal cross-section. Optical coherence tomography results are consistent with the estimates of the prior image study and showed good apposition struts.
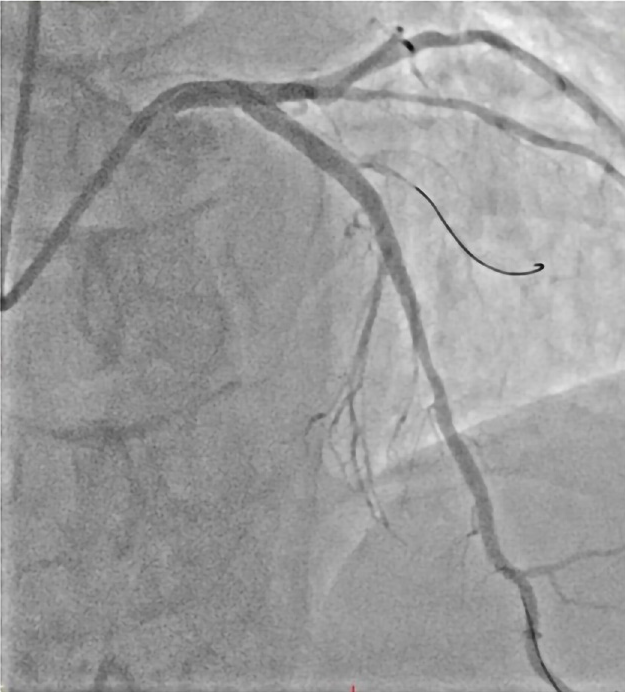
Figure 4 Coronary angiography images.
Image of percutaneous coronary intervention reveals satisfactory outcomes in the antero-cranial view.
- Citation: Liao ZY, Liou JY, Lin SC, Hung HF, Chang CM, Chen LC, Chua SK, Lo HM, Hung CF. Successful bailout stenting strategy against rare spontaneous retrograde dissection of partially absorbed magnesium-based resorbable scaffold: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(5): 1148-1155
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i5/1148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1148