Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 16, 2021; 9(5): 1139-1147
Published online Feb 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1139
Published online Feb 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1139
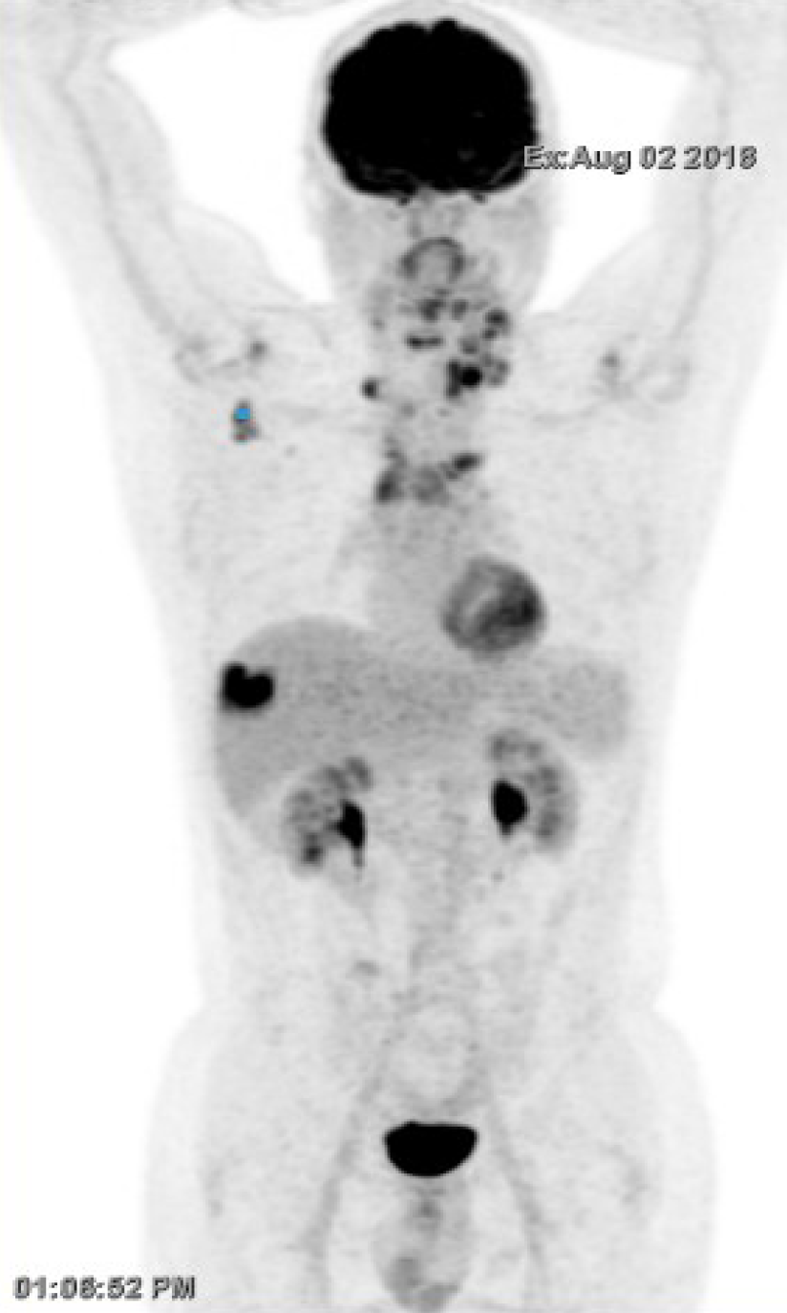
Figure 1 Disease recurrence with fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography showing cervical, right axillary, and mediastinal lymphadenopathies, and a single hepatic lesion (August 2018).
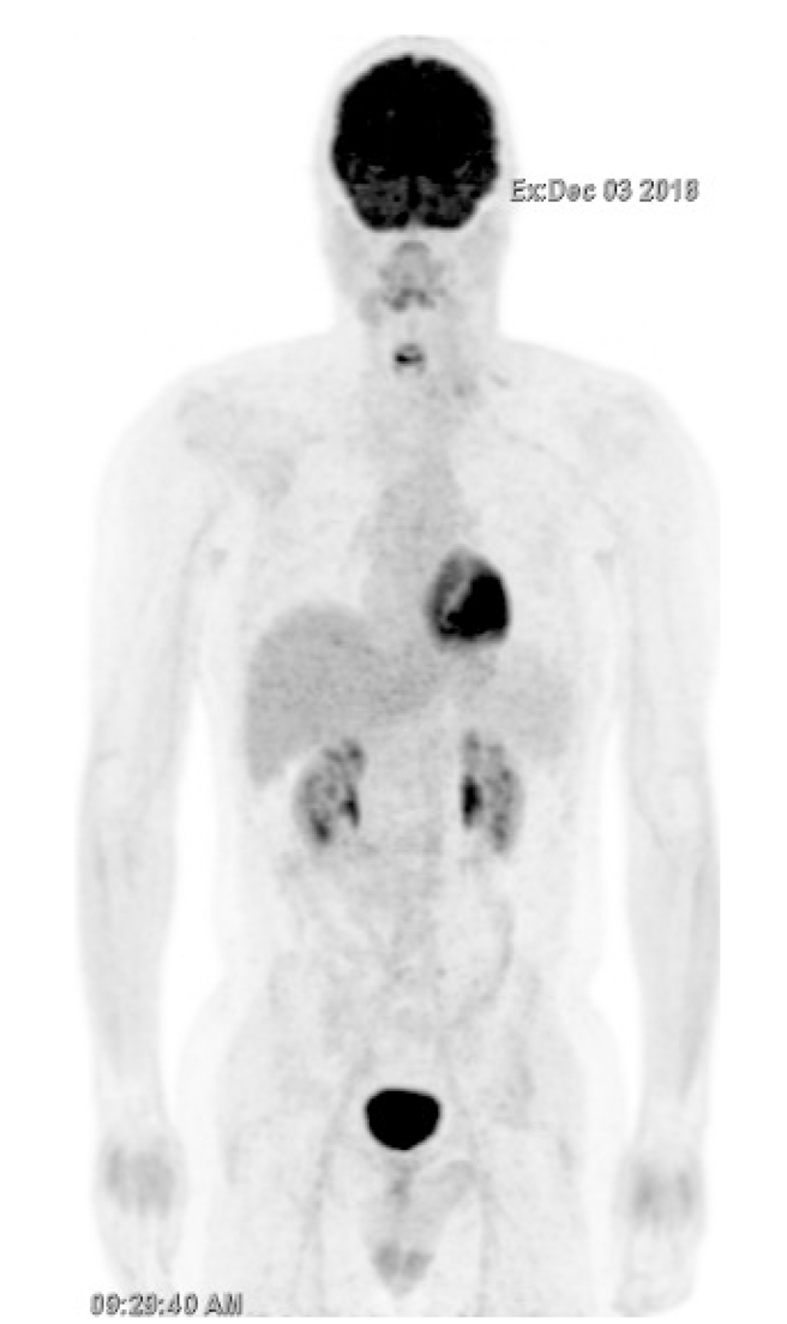
Figure 2 Response to palliative radiation therapy followed by three cycles of paclitaxel-carboplatin systemic therapy (December 2018).
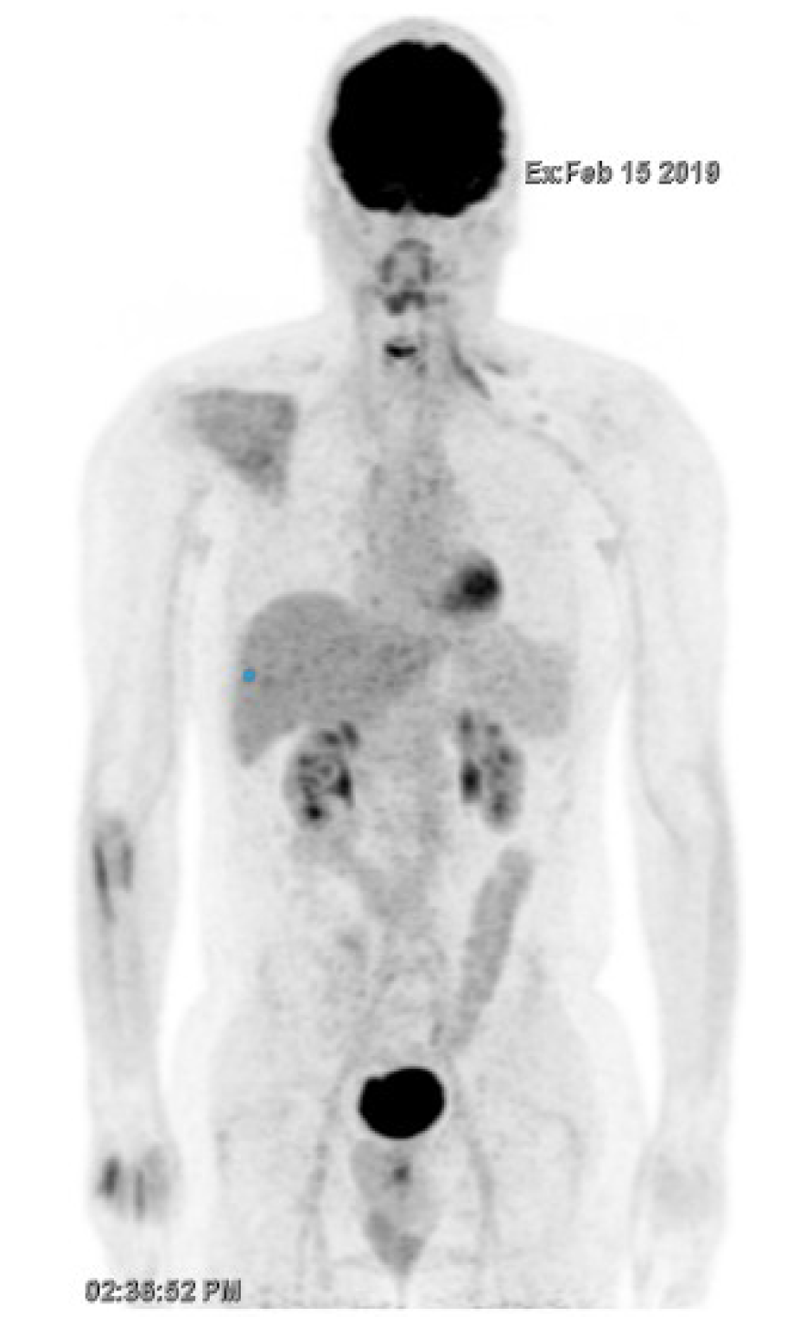
Figure 3 Confirmation of complete metabolic response by fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography (February 2019).
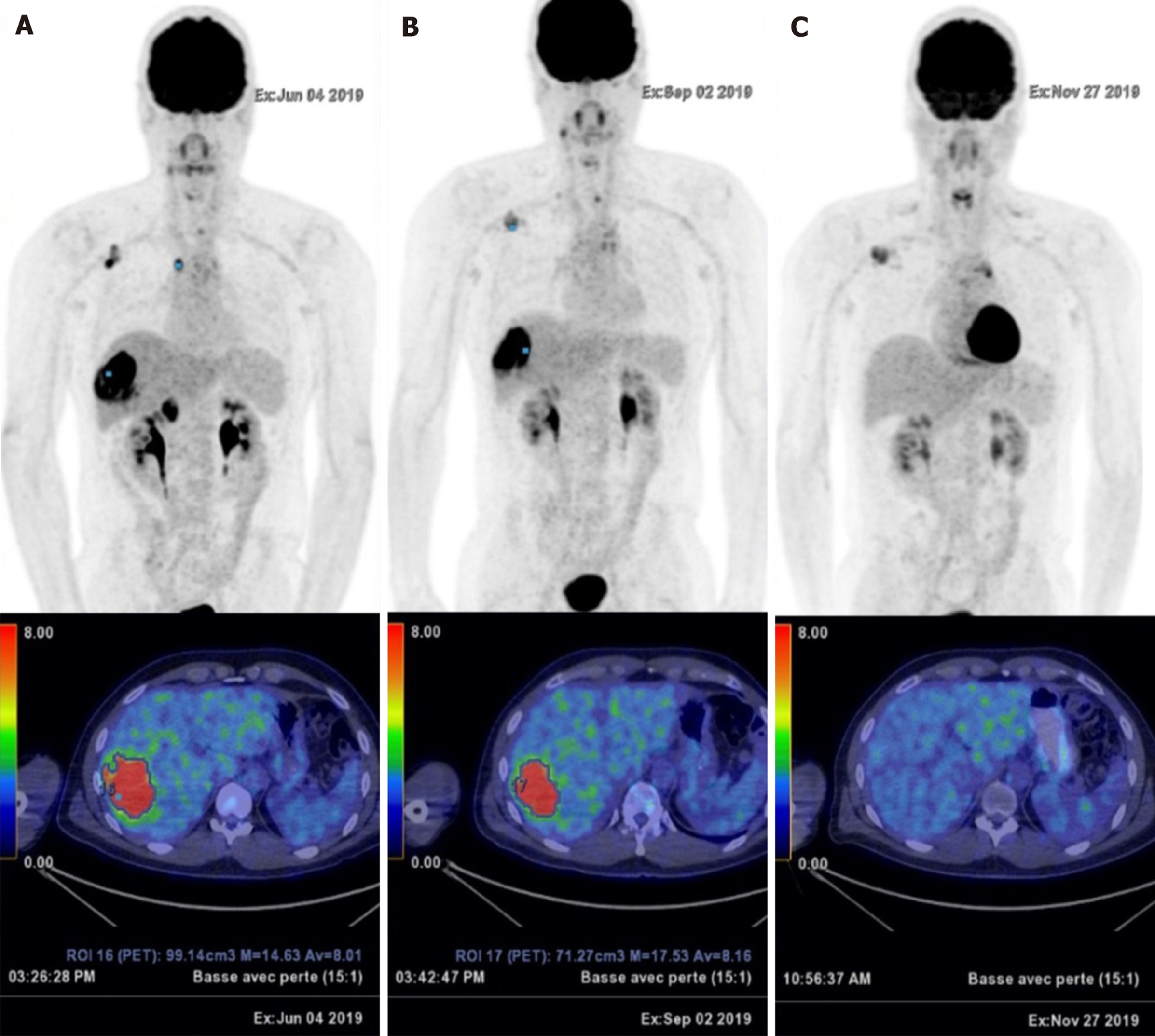
Figure 4 Disease progression.
A: Disease recurrence with a large hypermetabolic hepatic mass, mediastinal and axillary lymph nodes (June 2019); B: Dissociated response after four cycles of pembrolizumab with decrease in fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake on the axillary and mediastinal lymph nodes, but increase in FDG uptake on the liver metastasis (standardized uptake value: 14.63 to 17.53) (September 2019); C: Complete metabolic response of the liver mass and lymph nodes after eight cycles of pembrolizumab (November 2019).
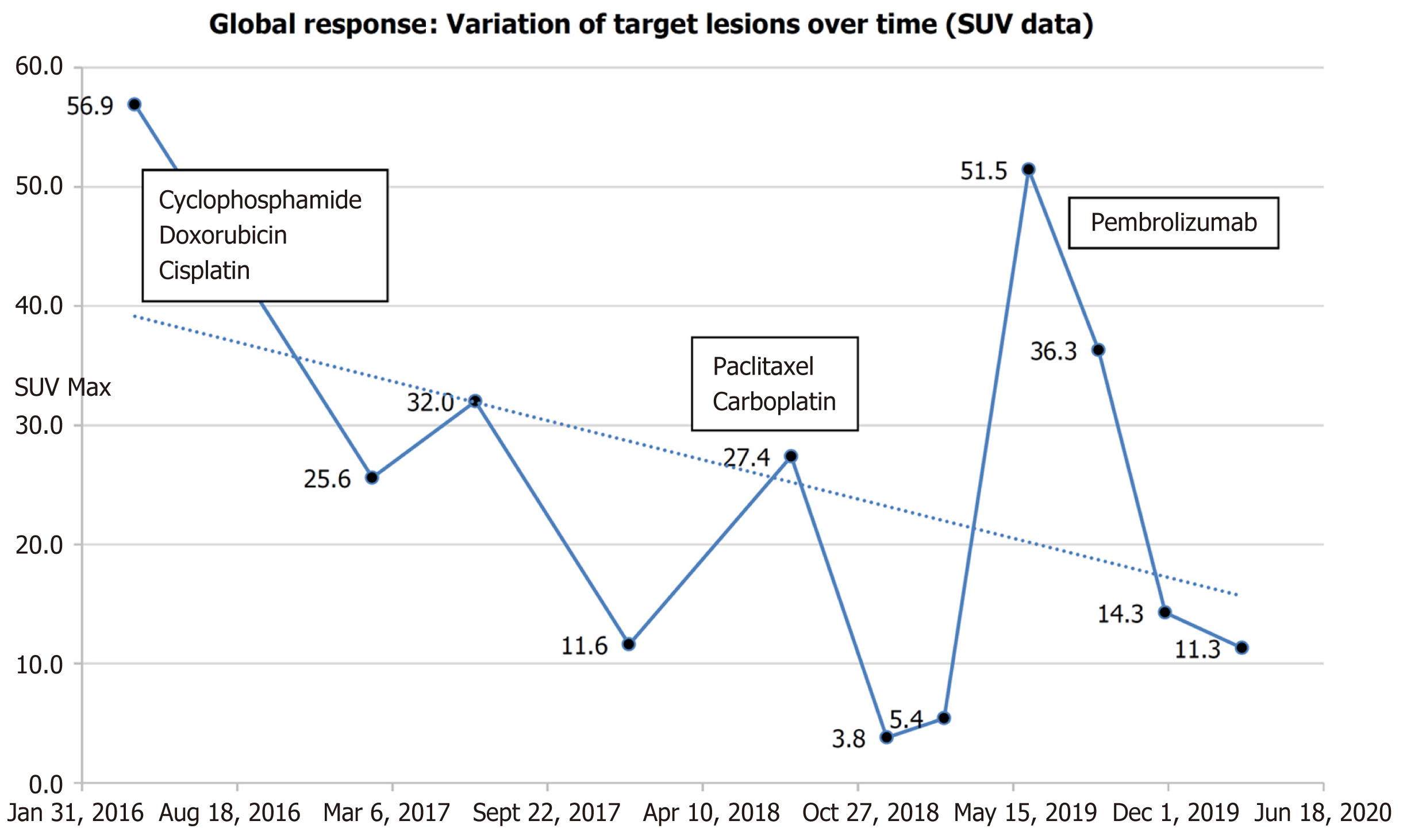
Figure 5 Global response: Variation of SUV of target lesions over time, from start of frontline systemic treatment to last follow-up.
The corresponding treatments are noted on the graph.
- Citation: Wong-Chong J, Bernadach M, Ginzac A, Veyssière H, Durando X. Pembrolizumab as a novel therapeutic option for patients with refractory thymic epithelial tumor: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(5): 1139-1147
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i5/1139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1139