Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2021; 9(4): 935-942
Published online Feb 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.935
Published online Feb 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.935
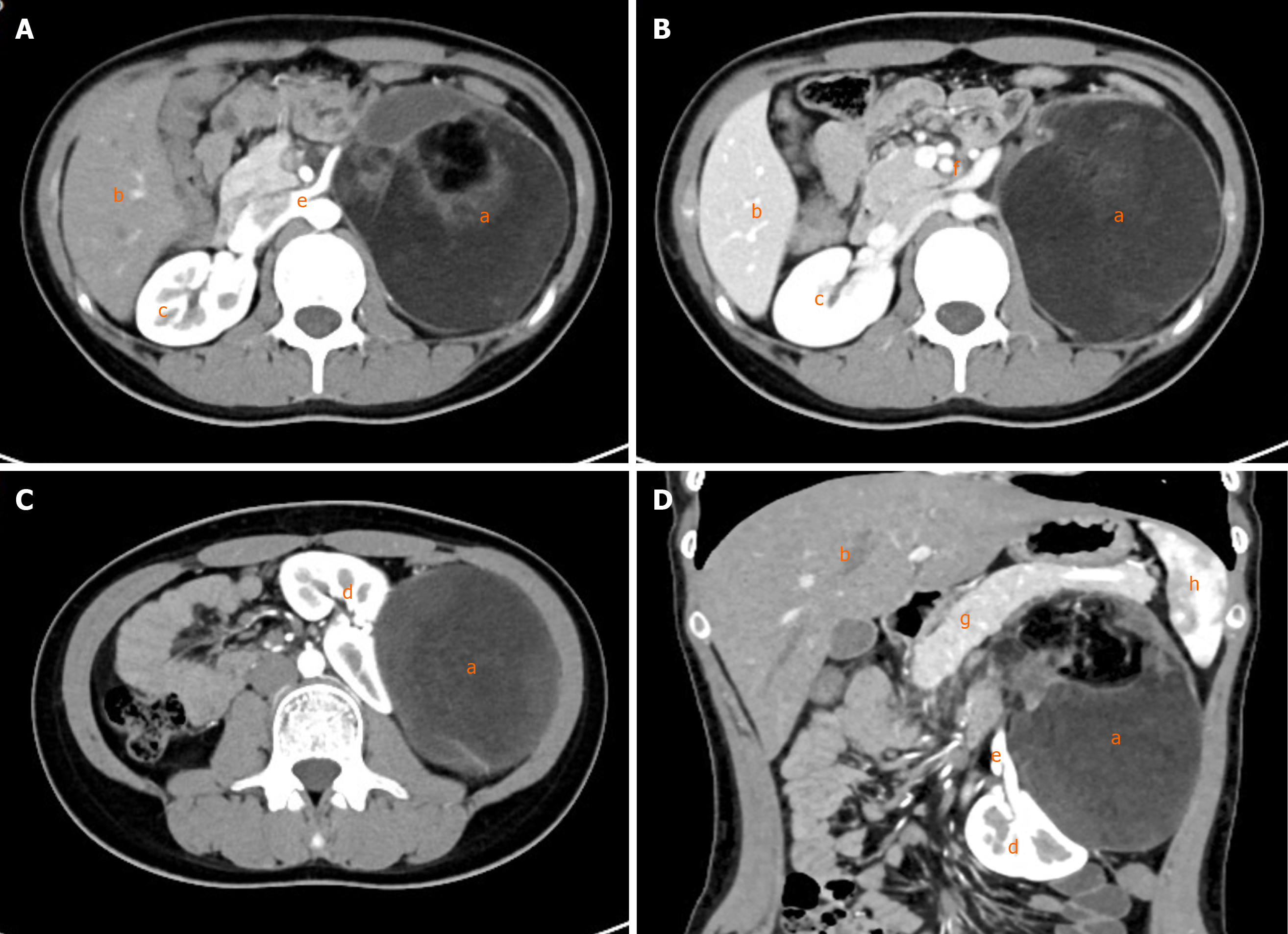
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography.
A: Transverse view, arterial phase; B: Transverse view, venous phase; C: Transverse view, arterial phase; D: Coronal view, arterial phase. a: Tumor; b: Liver; c: Right kidney; d: Left kidney; e: Renal artery; f: Renal vein; g: Pancreas; h: Spleen.
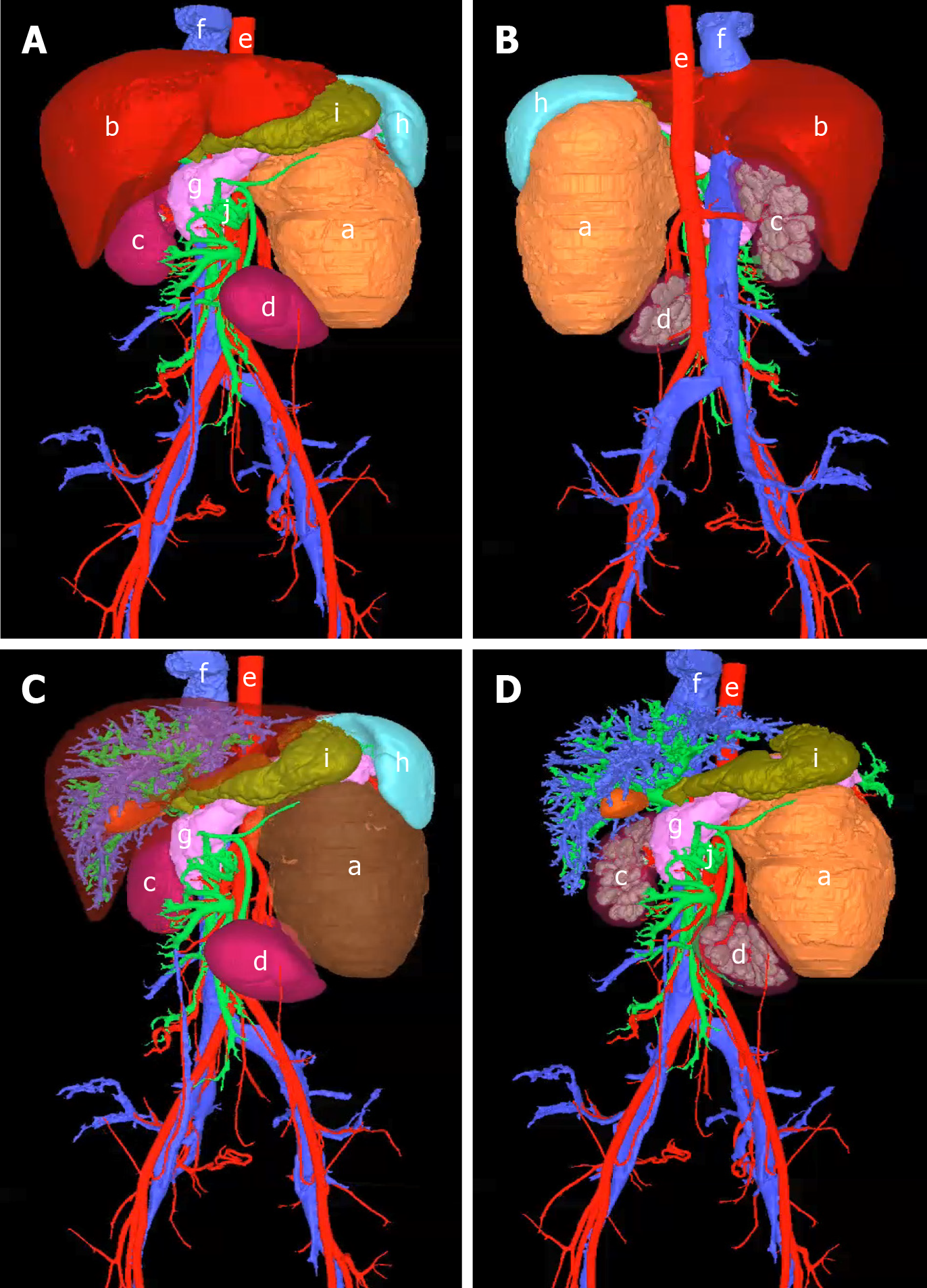
Figure 2 Three-dimensional reconstruction and visualization of the tumor and surrounding vessels and organs.
A: Frontal view; B: Dorsal view; C: Tumor visualization; D: After removal of surrounding normal organs. a: Tumor; b: Liver; c: Right kidney; d: Left kidney; e: Artery; f: Vein; g: Pancreas; h: Spleen; i: Stomach; j: Portal vein.
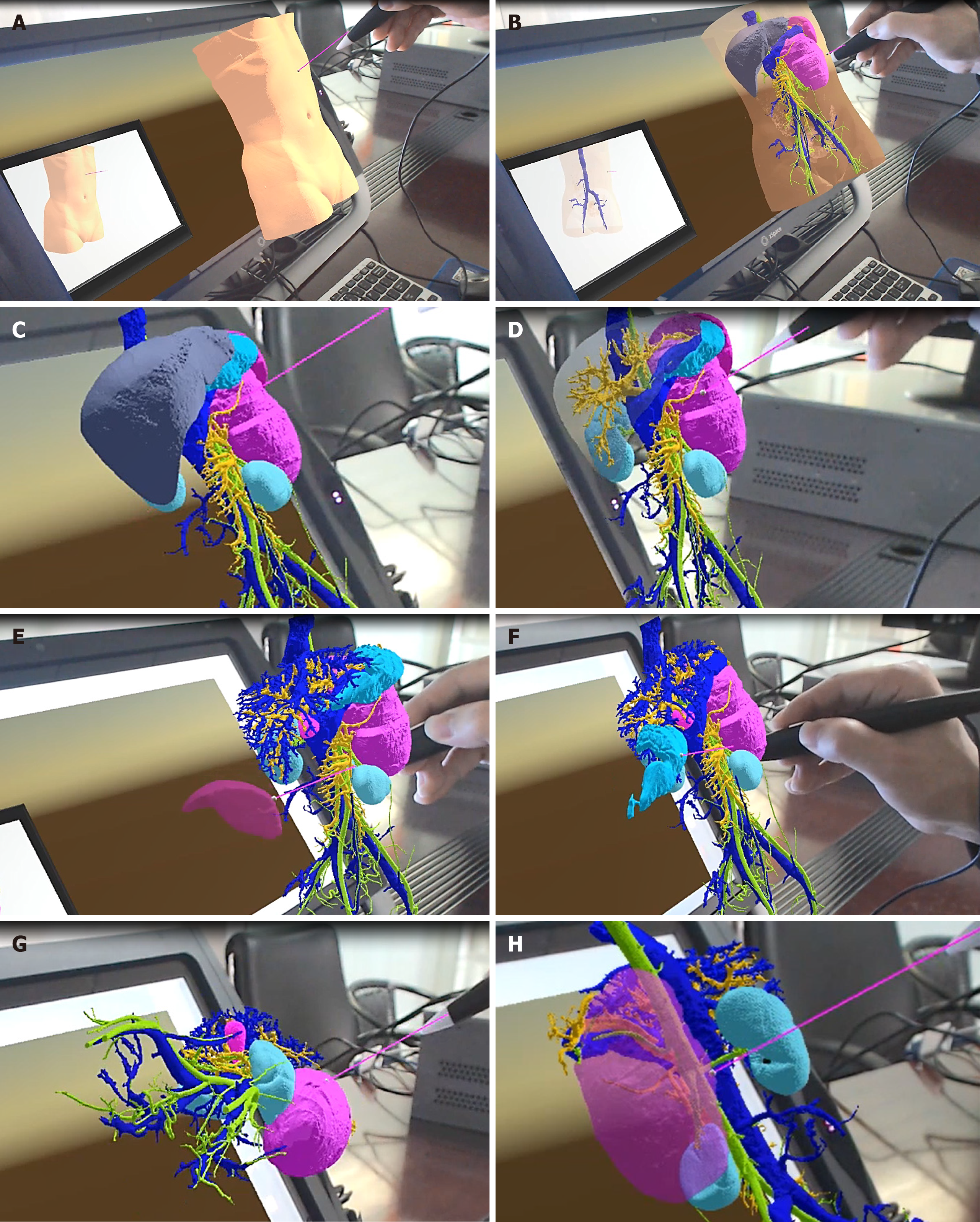
Figure 3 Virtual reality simulation of tumor excision.
A: Initial state; B: Virtual torso, revealing organs; C: Virtual removal of torso and examination of organs; D: Virtual removal of liver; E: Virtual removal of spleen; F: Virtual removal of stomach; G: Virtual removal of organs next to the tumor and examination of the tumor from multiple angles; H: Virtual removal of the tumor to examine its relationship to blood vessels.
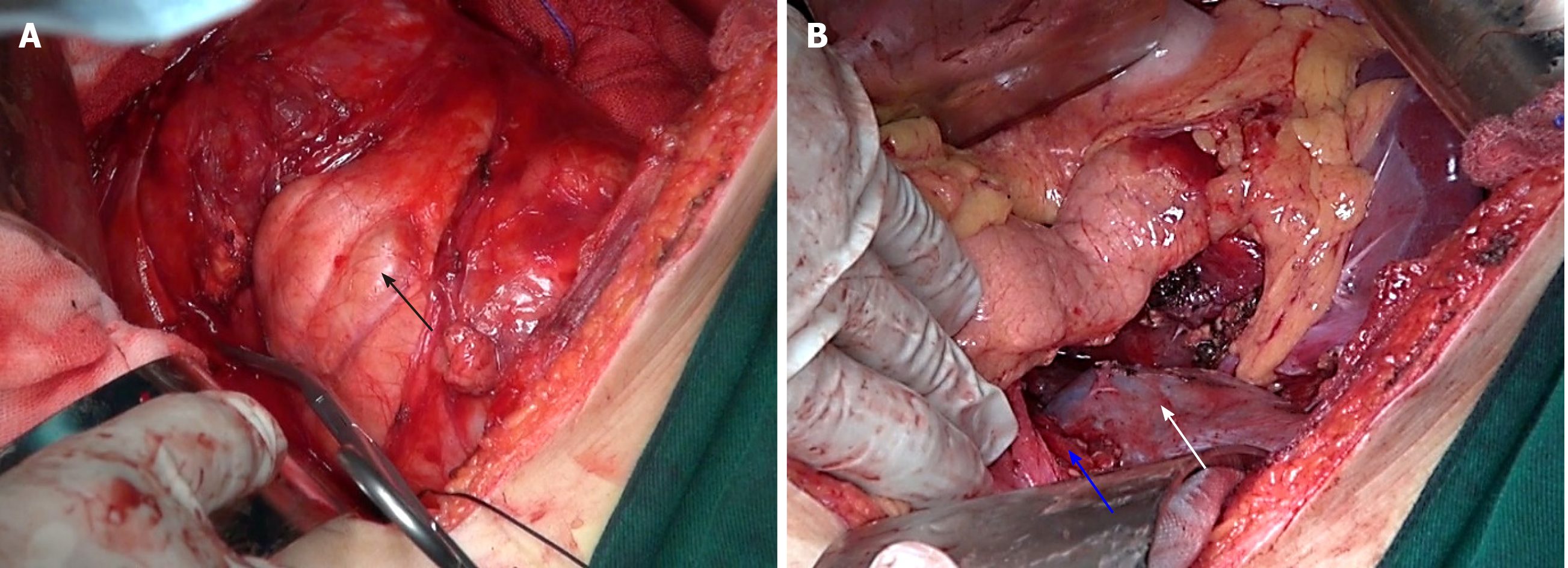
Figure 4 Intraoperative state.
A: Image of the tumor (black arrow); B: Image of the left renal vessel (blue arrow) and left kidney (white arrow).
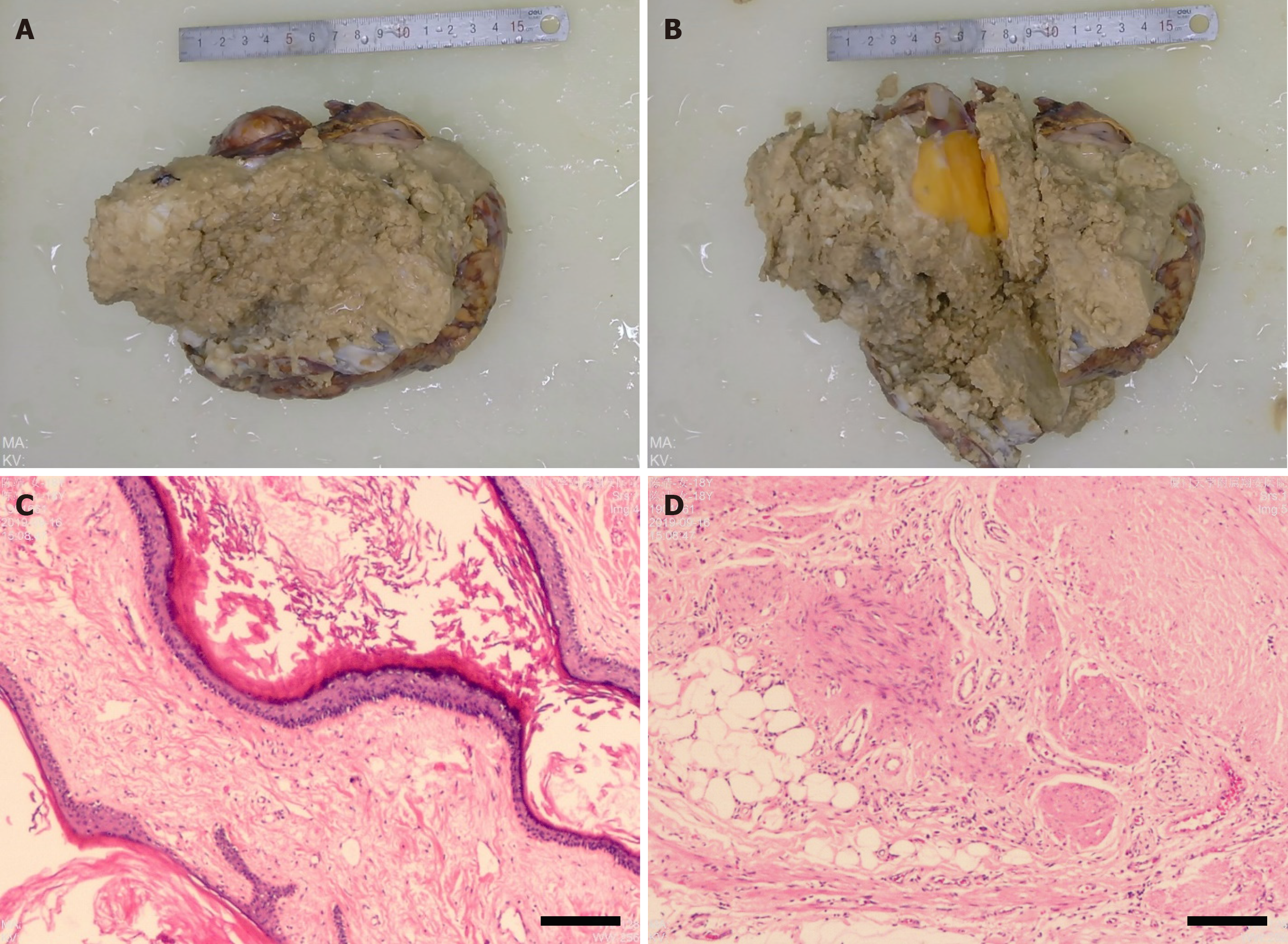
Figure 5 Postoperative pathologic examination.
A and B: Formalin-fixed tumor tissues; C and D: Representative images of tumor tissue stained with hematoxylin and eosin (100 × magnification).
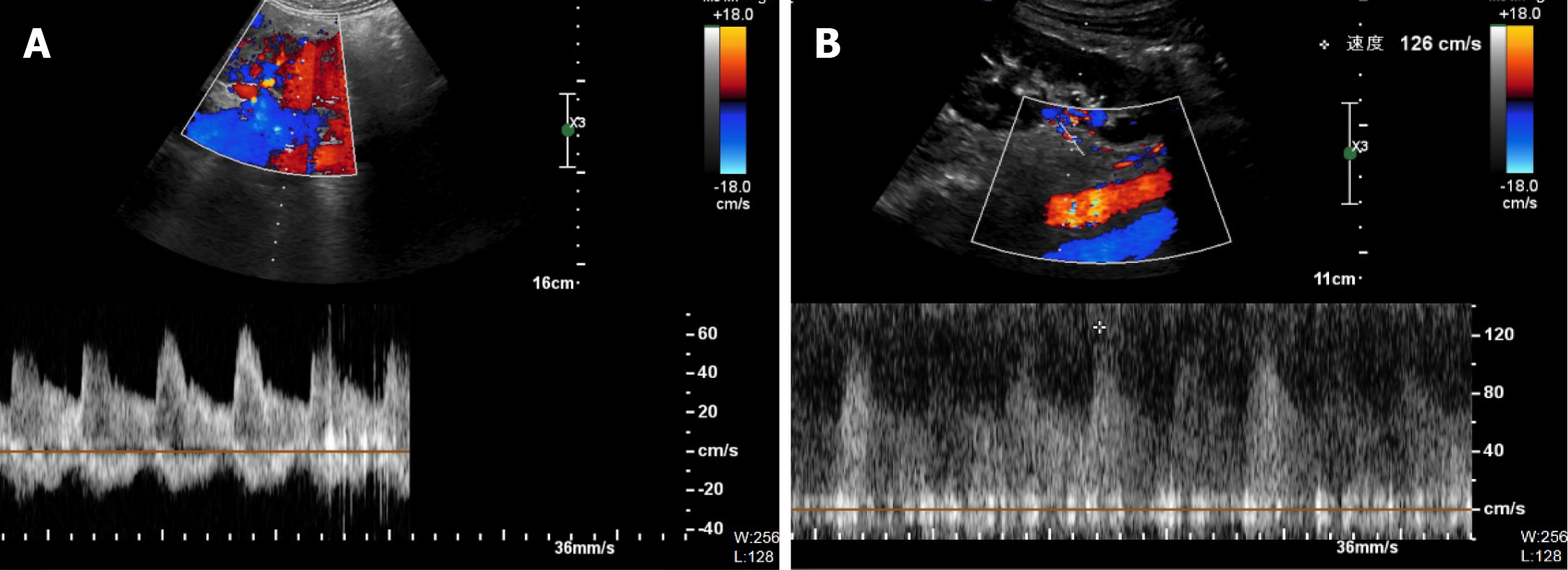
Figure 6 Postoperative color Doppler ultrasound examination.
A: Right kidney; B: Left kidney.
- Citation: Liu T, Chen K, Xia RM, Li WG. Retroperitoneal teratoma resection assisted by 3-dimensional visualization and virtual reality: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(4): 935-942
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i4/935.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.935