Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2021; 9(4): 912-918
Published online Feb 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.912
Published online Feb 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.912
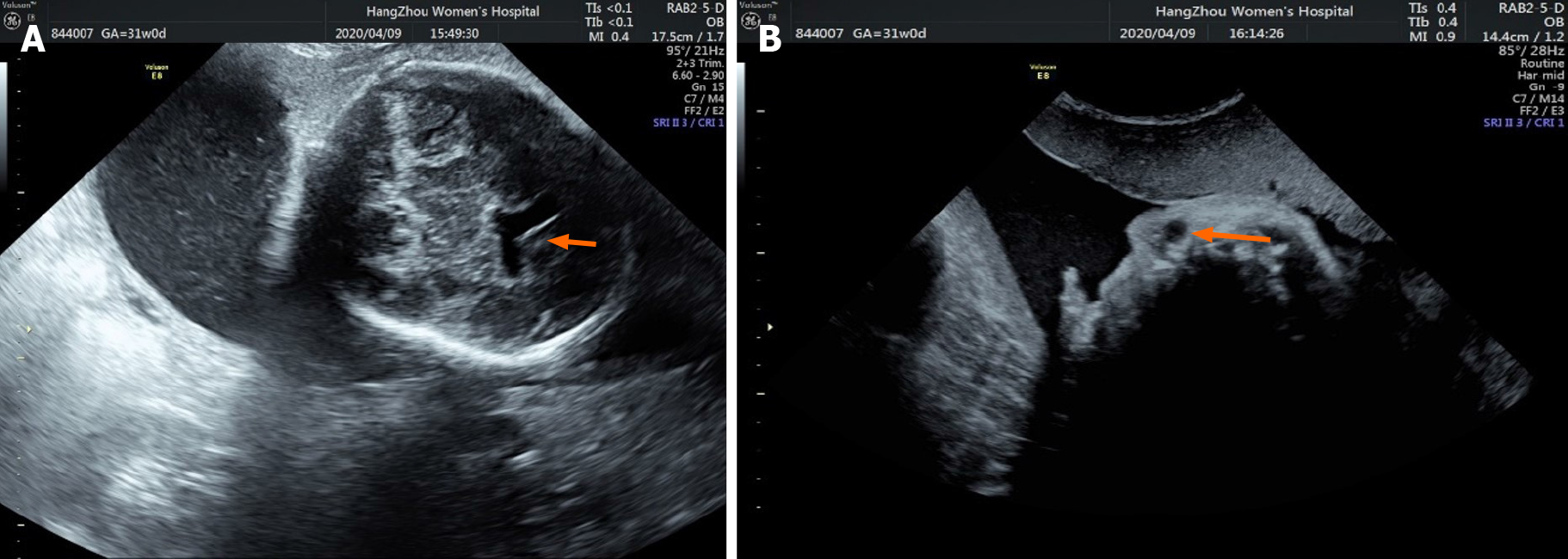
Figure 1 Fetal ultrasound performed at 30, 2/7 wk of pregnancy showed the following: A: Widened anterior horn of the lateral ventricle; B: Nasolacrimal duct cyst.
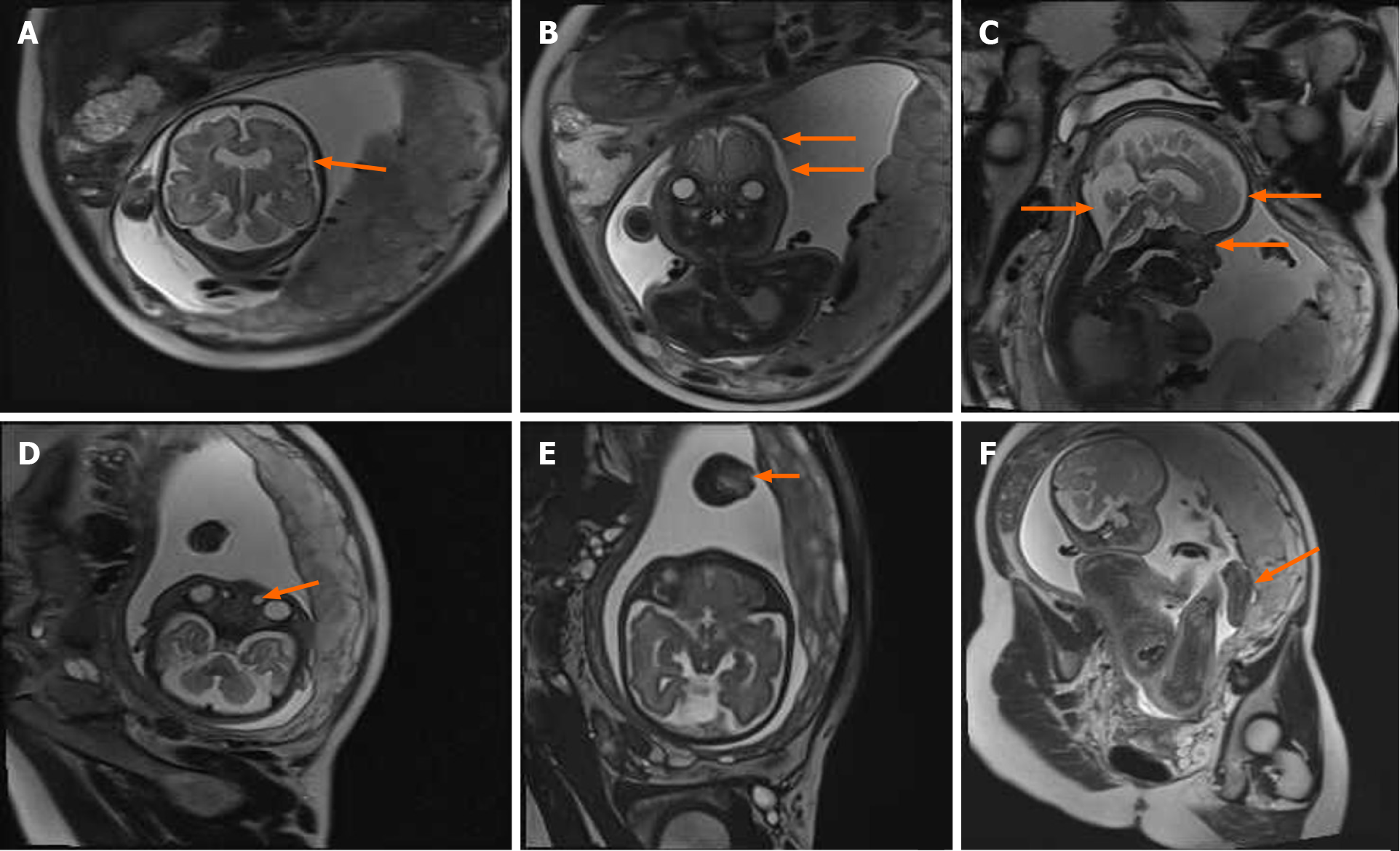
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging performed at 31, 1/7 wk of pregnancy showed the following: A: Acrocephalia; B: Craniosynostosis, widened eye distances; C: Protruding forehead, concave nasal root, widened anterior horn of the lateral ventricle and the posterior cranial fossa; D: Nasolacrimal duct cyst; E: Syndactyly of hands; and F: Syndactyly of feet.
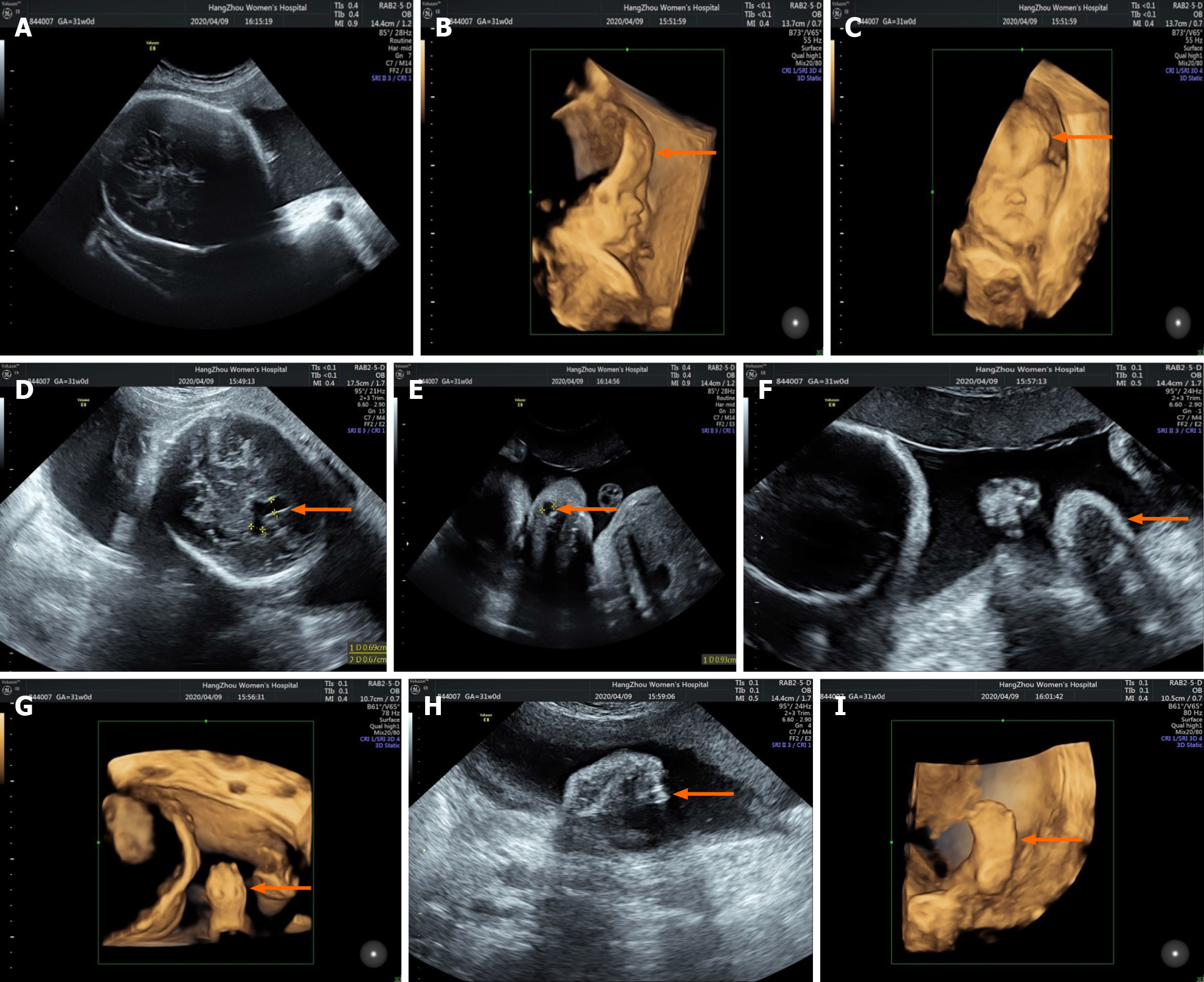
Figure 3 Three-dimensional prenatal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging showed the following: A: Craniosynostosis; B and C: Forehead protrusion; D: Widened anterior horns of the lateral ventricle; E: Nasolacrimal duct cyst; F-I: Syndactyly.
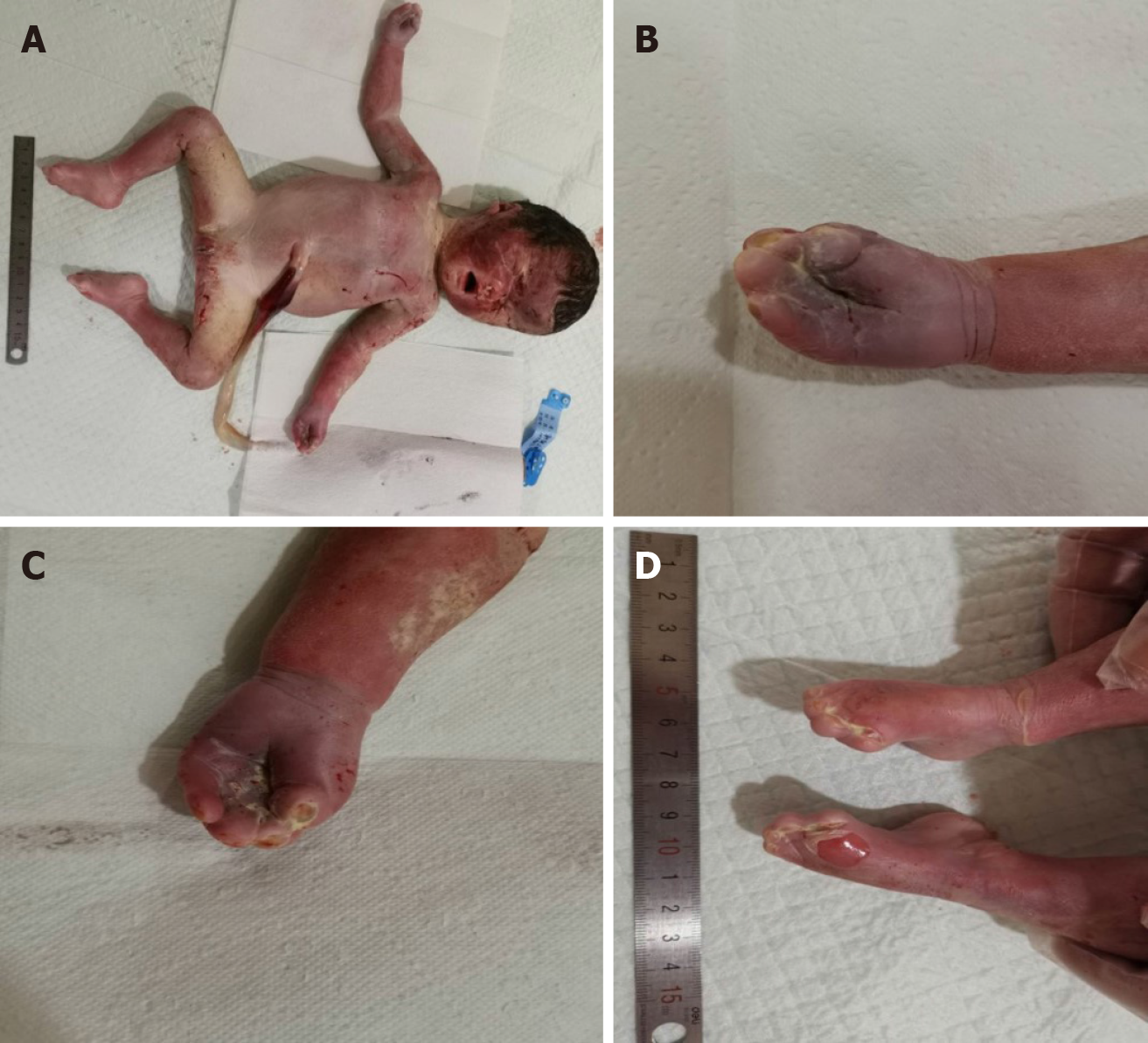
Figure 4 The fetus was stillborn 2 d after Rivanol injection.
A: Whole stillborn infant; B and C: Complete syndactyly of the hands; D: Complete syndactyly of the feet.
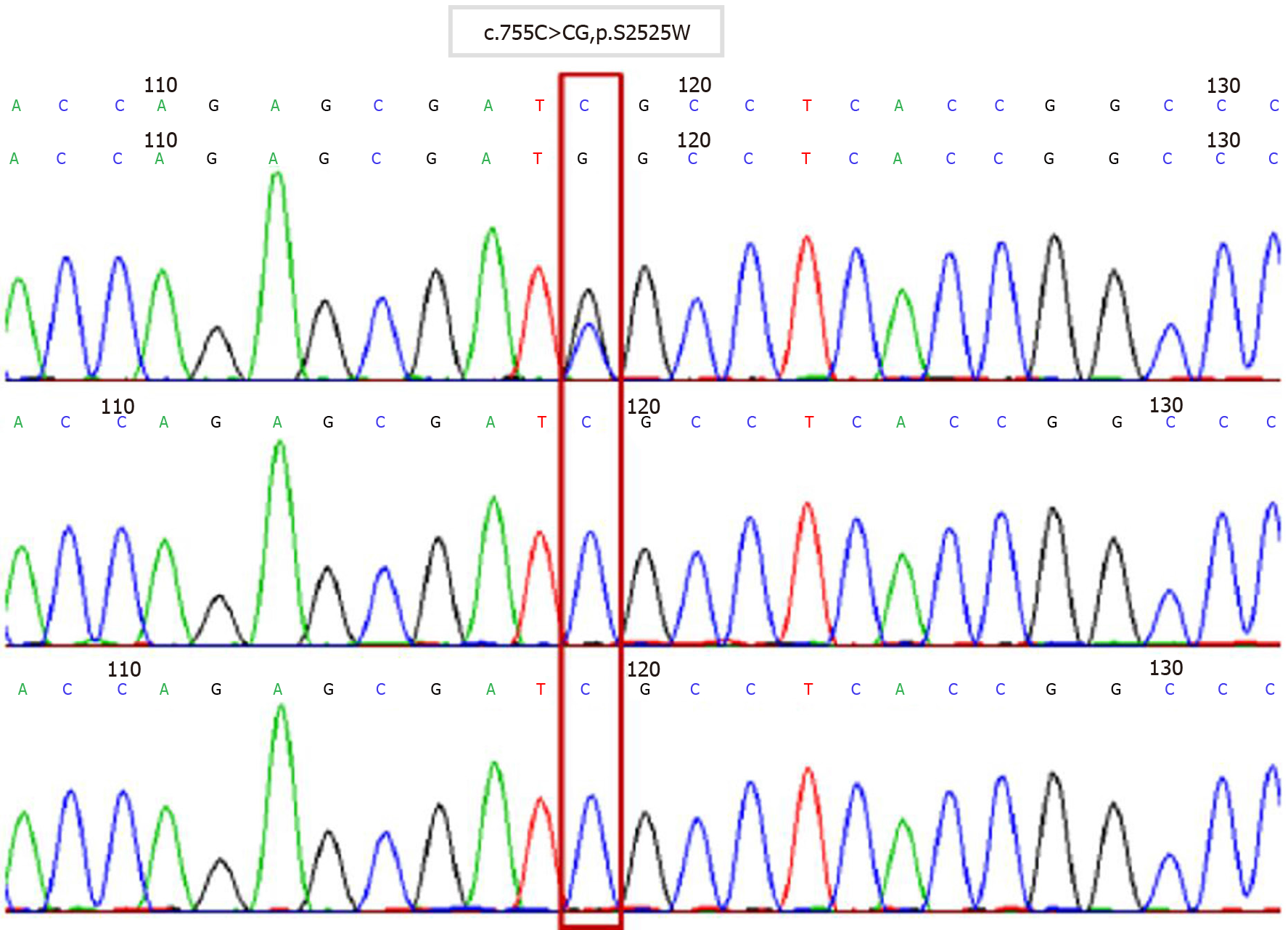
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of Sanger sequencing verification results of the tested subject and parents with FGFR2 gene variation (whole exome sequencing was performed at Hangzhou Jinnuo Medical Laboratory).
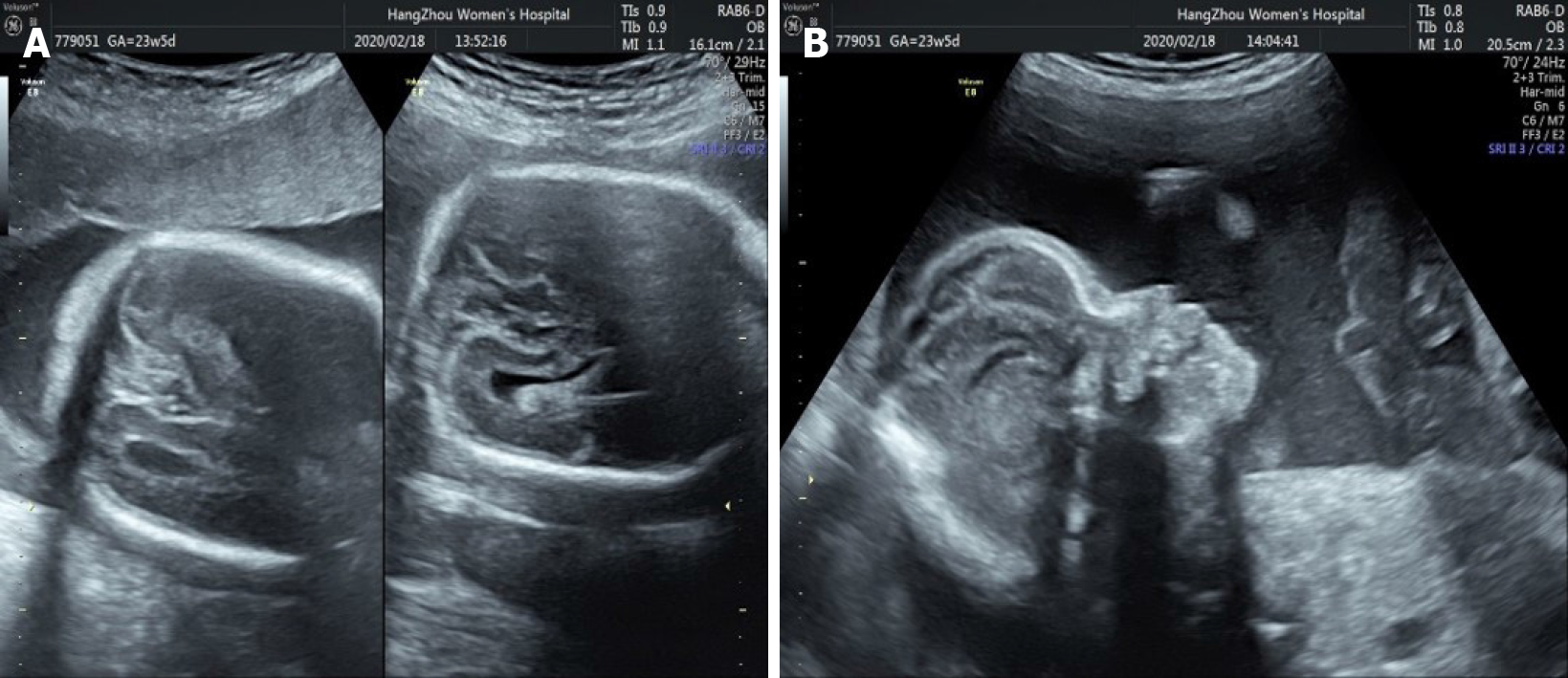
Figure 6 Three-dimensional fetal ultrasound at 23, 5/7 wk of gestation.
A: Craniosynostosis; B: Raised forehead.
- Citation: Chen L, Huang FX. Apert syndrome diagnosed by prenatal ultrasound combined with magnetic resonance imaging and whole exome sequencing: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(4): 912-918
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i4/912.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i4.912