Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2021; 9(34): 10392-10399
Published online Dec 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10392
Published online Dec 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10392
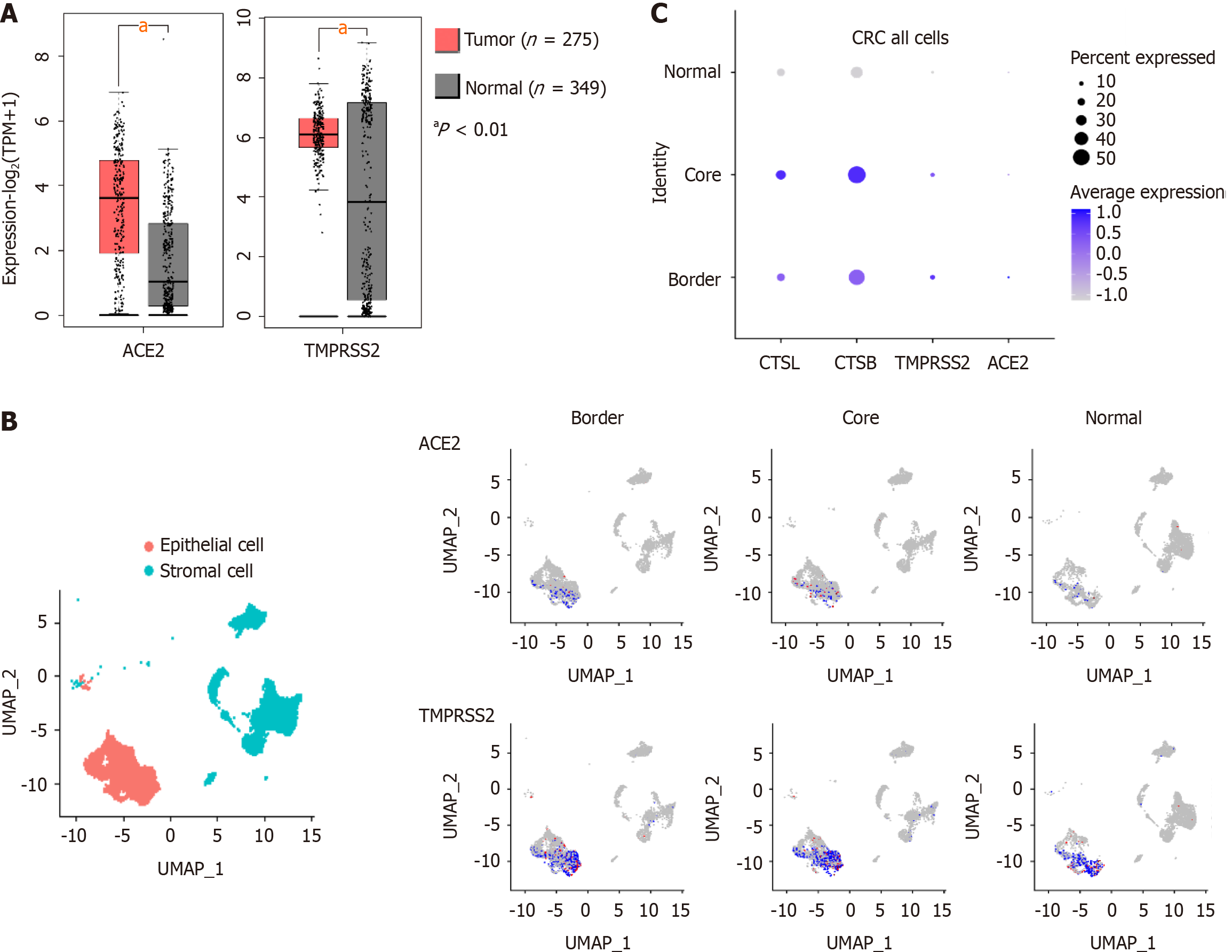
Figure 1 Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 recognition proteins are highly expressed in the tumor tissues of patients with colorectal cancer.
A: In the TCGA and GTEx databases, expression of angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) was significantly higher in in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors than in healthy tissues (P < 0.01); B: single-cell sequencing analysis of 27,414 cells from six CRC patients found that ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression was higher in CRC than in healthy tissue, and was mainly expressed in epithelial cells; C: Expression of ACE2, TMRPSS2, cathepsin B, and cathepsin L was higher in CRC than in normal tissue in both stromal and epithelial cells analysis of single-cell sequencing (Gene Expression Omnibus: GSE144735). ACE2: Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2; CRC: Colorectal cancer; CTSB: Cathepsin B; CTSL: Cathepsin L; GTEx: Genotype-tissue expression; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane serine protease 2; UMAP: Uniform manifold approximation and projection.
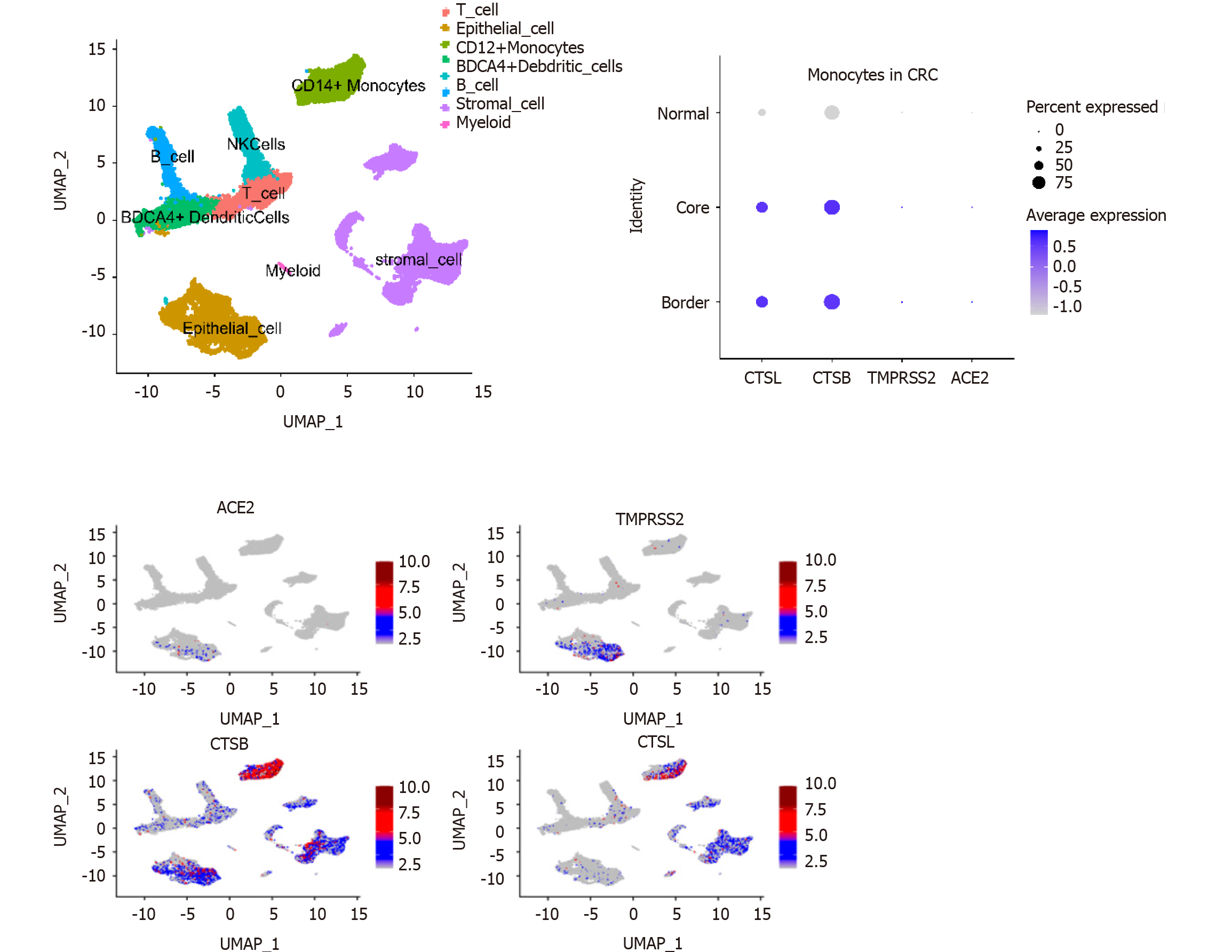
Figure 2 Infiltrating monocytes in colorectal cancer tissues express high levels of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 recognition proteins.
Analysis of single-cell sequencing of 27,414 cells in six colorectal cancer patients identified genes that were expressed in at least three cells and at least 200 genes were identified in each cell. Harmony was used to remove batch effects. The first 20 principal components were selected in Seurat to cluster the patients, and the enriched pathways in marker gene sets were found with enrichR (https://amp.pharm.mssm.edu/Enrichr/) and the expression of coronavirus disease 2019-related genes in dendritic, natural killer, myeloid, stromal, and epithelial cells; monocytes, and B cells was screened. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 recognition proteins were mainly expressed on monocytes. The expression of angiotensin I converting enzyme 2, transmembrane serine protease 2, cathepsin B, and cathepsin L in tissue-infiltrated monocytes was higher in colorectal cancer than in normal tissue. ACE2: Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2; CRC: Colorectal cancer; CTSB: Cathepsin B; CTCL: Cathepsin L; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane serine protease; UMAP: Uniform manifold approximation and projection.
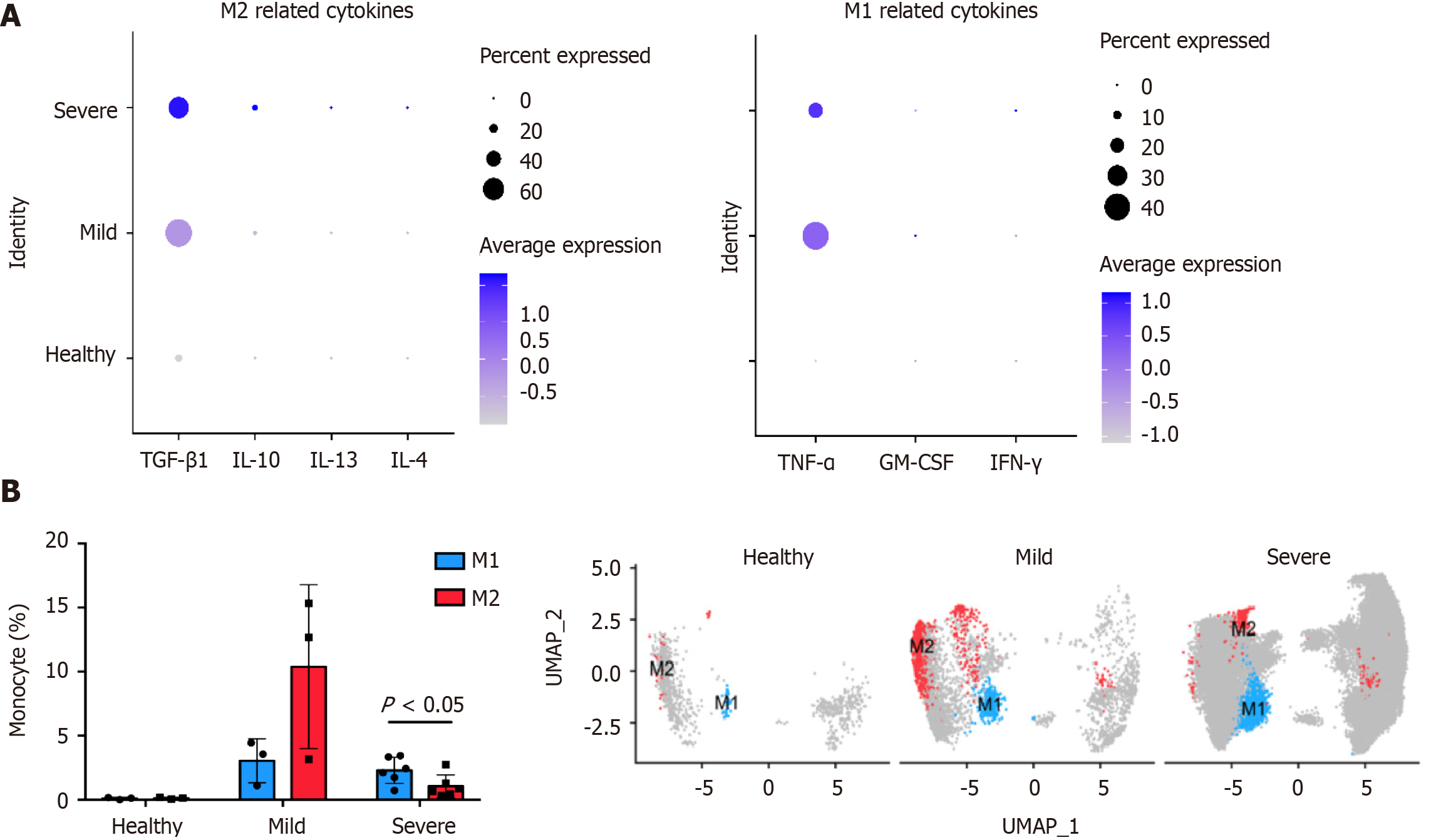
Figure 3 Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on monocytes.
A: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induces the differentiation of M1 and M2 macrophages by affecting cytokines, especially TGF-β1 and TNF-α; B: COVID-19 patients had higher macrophage infiltration than healthy people. In severe COVID-19, the M1/M2 ratio increased. GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; IL: Interleukin; M1: Type 1 macrophage; M2: Type 2 macrophage.
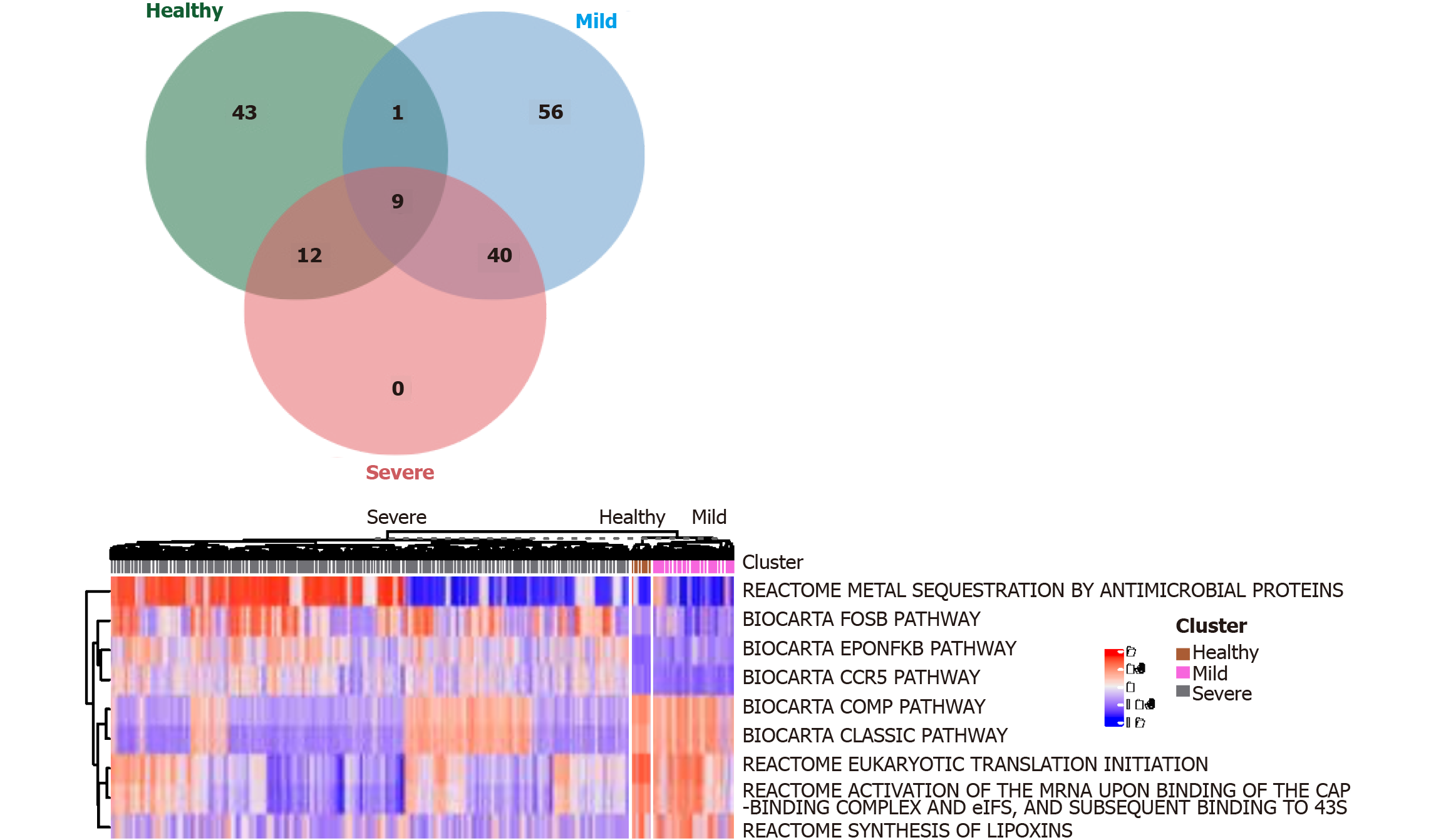
Figure 4 Coronavirus disease 2019 infection promotes the activation of NF-κB and CCR5 signaling pathways in monocytes.
The limma R package was used to identify differentially expressed pathways (DEGeneset) in severe and nonsevere Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, and healthy controls with an absolute value score > 0.35 and a false discovery rate < 0.001. Nine differential pathways were found. COVID-19 infection promoted the activation of NF-κB and CCR5 signaling pathways in monocytes. Multiple metabolic pathways were also involved.
- Citation: Bai L, Yang W, Qian L, Cui JW. Regulating monocyte infiltration and differentiation: Providing new therapies for colorectal cancer patients with COVID-19. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(34): 10392-10399
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i34/10392.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10392