Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2021; 9(25): 7572-7578
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7572
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7572
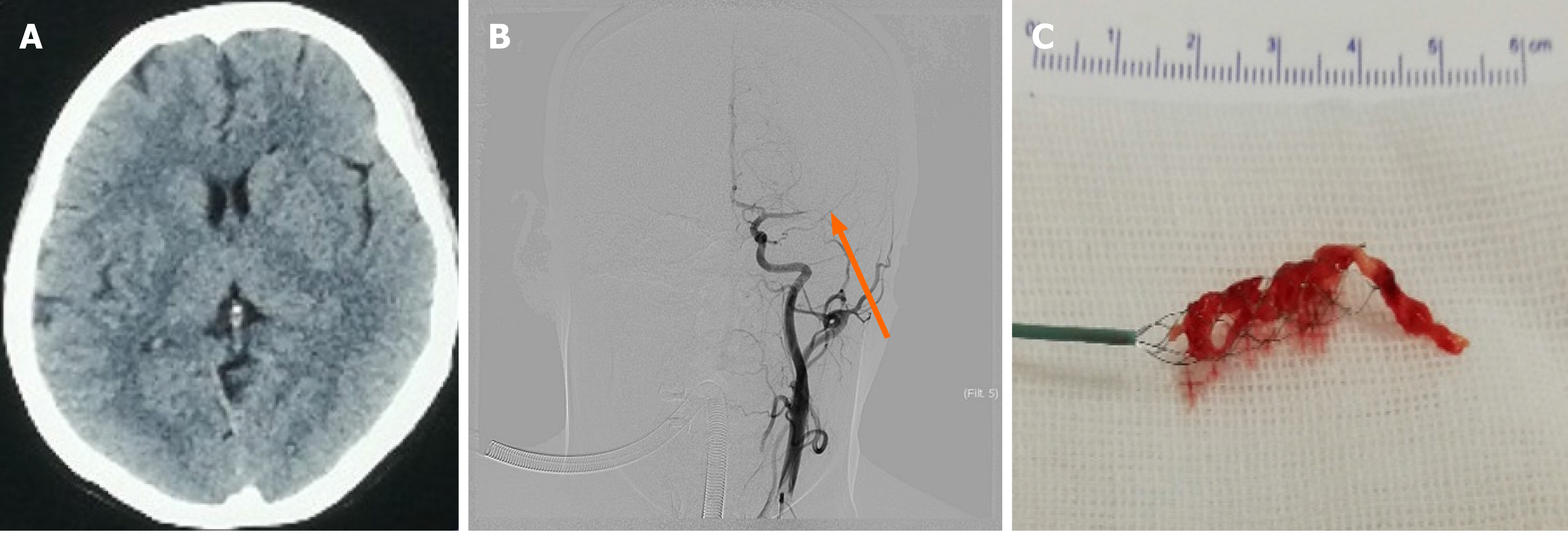
Figure 1 Head computed tomography before operation, intraoperative angiography, and stent embolectomy.
A: Head computed tomography showed no abnormalities; B: Cerebral angiography showed that the left middle cerebral artery was occluded (orange arrow); C: Thrombus removed with a stent (Solitaire FR 4.0 mm × 20 mm).
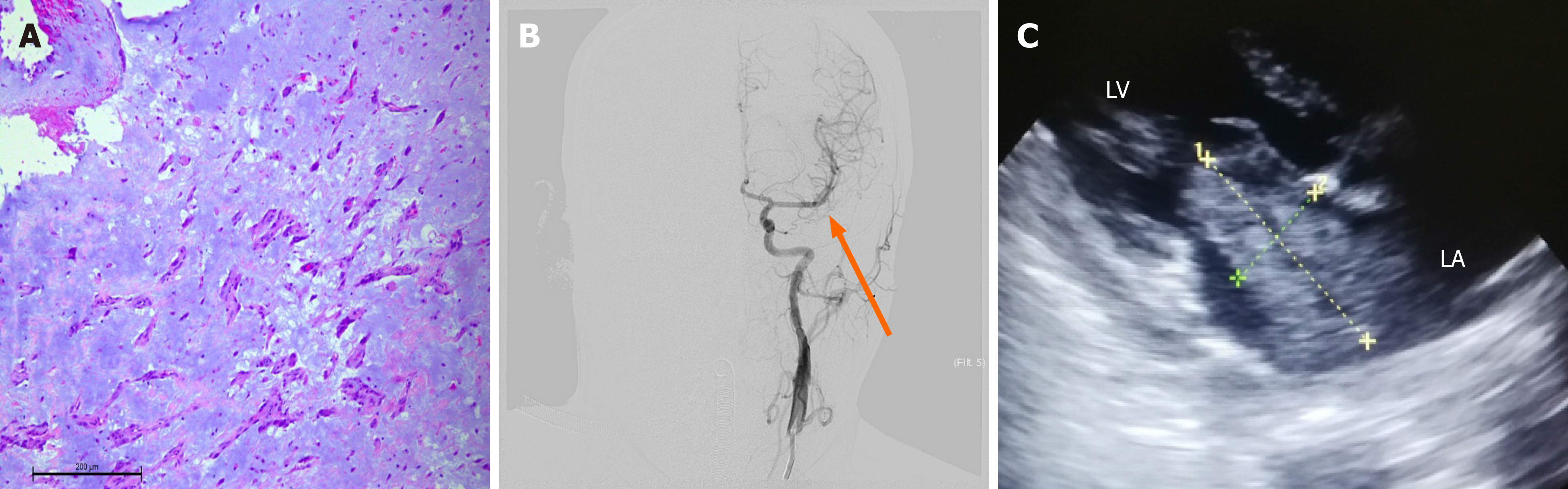
Figure 2 Arterial thrombosis pathology, angiography, and echocardiography.
A: Histopathological image showing scattered mucinous tumor cells and streaked polygonal eosinophil stromal cells in a mucinous-like matrix (hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification, 10 × 10); B: Cerebral angiography showing that the left middle cerebral artery was patent (orange arrow); C: Pre-operative transthoracic echocardiogram showing that the internal diameter of the left atrium and left ventricle were abnormal but an irregular, space-occupying mass was visible in the left atrium, with a pedicle in the atrial-septal space with marked motion.
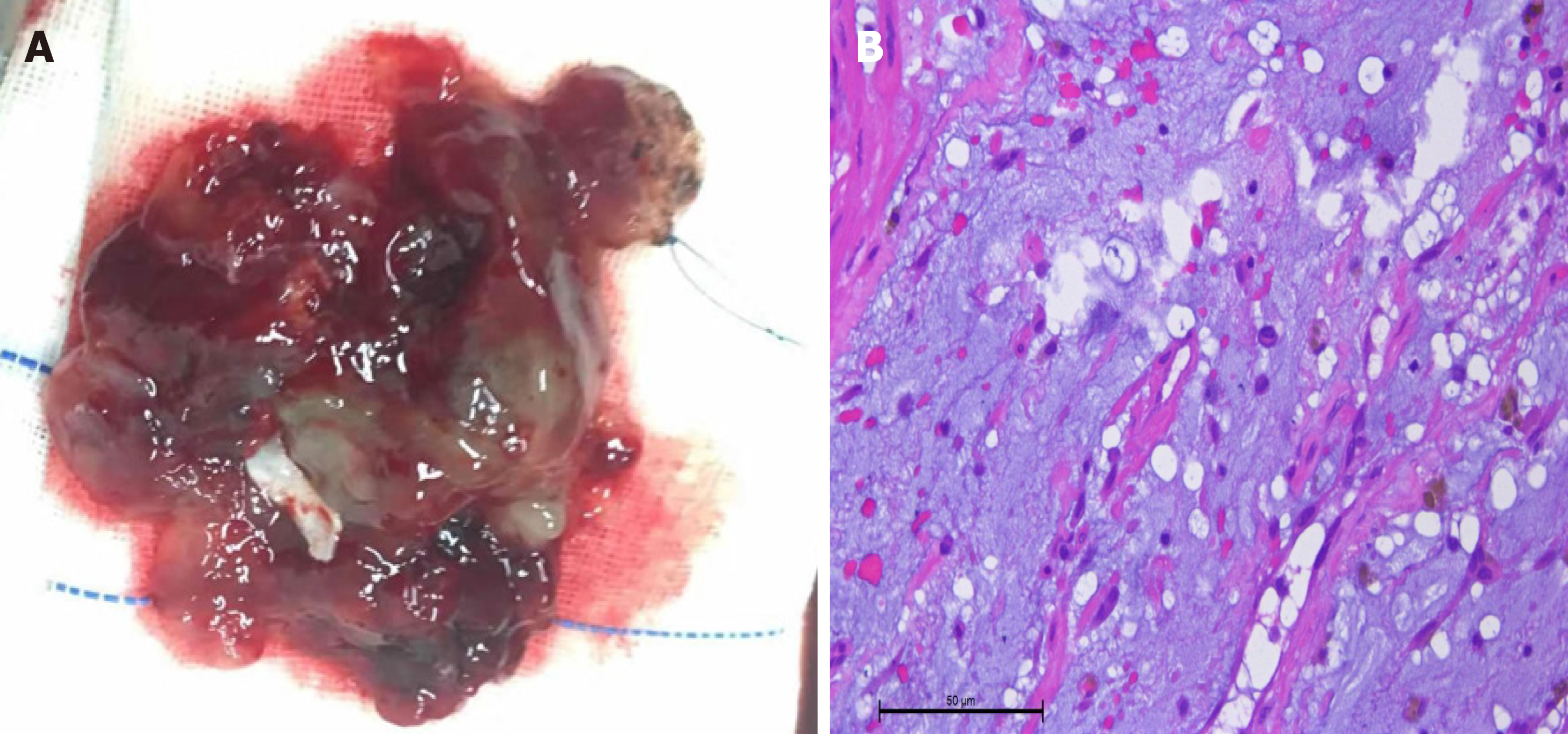
Figure 3 Appearance and microscopic display of the myxoma.
A: Gross pathology. The excised myxoma measured 6.5 cm × 6.0 cm × 5.0 cm. On macroscopic examination, the excised tumor was reddish brown jelly-like with an irregular surface and mucus; B: Histological examination of the surgically removed cardiac mass showing [hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE), scale bar: × 200] mucinous tumor cells that were scattered, shuttle-shaped or stellate, with medium amounts of cytoplasm, eosinophilic, oval nuclei, and no nuclear divisions seen in the mucinous-like matrix (HE, magnification 10 × 40).
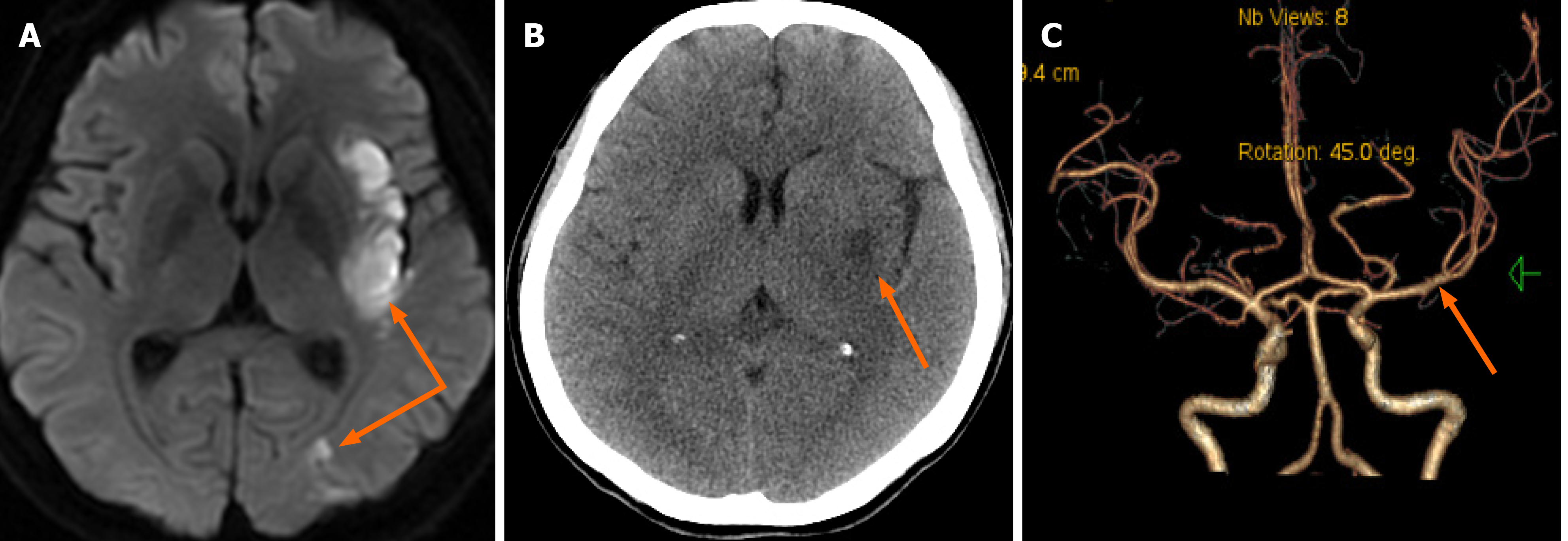
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and computed tomographic angiography of the head.
A: Diffusion-weighted imaging showed an area of hyperintensity in the left insular lobe, frontal lobe, parietal lobe, and occipital lobe consistent with acute infarction (orange arrow); B: A small left basal ganglia infarction and no signs of intracranial bleeding were found on further computed tomographic scan (orange arrow); C: Computed tomographic angiography imaging showed left middle cerebral artery patency and no stenosis (orange arrow).
- Citation: Chang WS, Li N, Liu H, Yin JJ, Zhang HQ. Thrombolysis and embolectomy in treatment of acute stroke as a bridge to open-heart resection of giant cardiac myxoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(25): 7572-7578
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i25/7572.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7572