Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2021; 9(25): 7535-7541
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7535
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7535
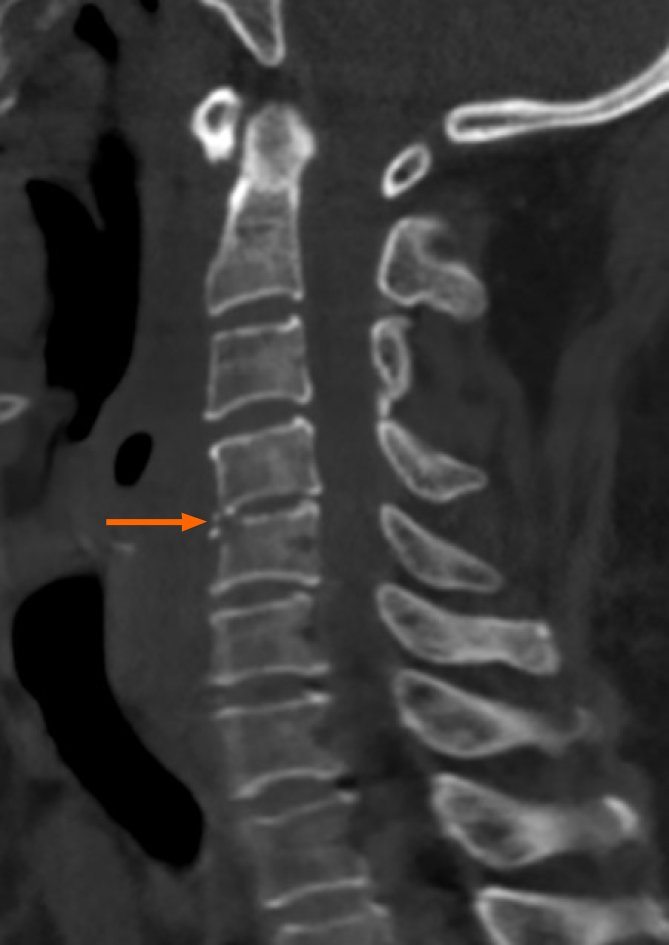
Figure 1 Preoperative computed tomography scan.
No fish bone was detected. Note the narrowing of the disc space at C4/C5 (arrow).
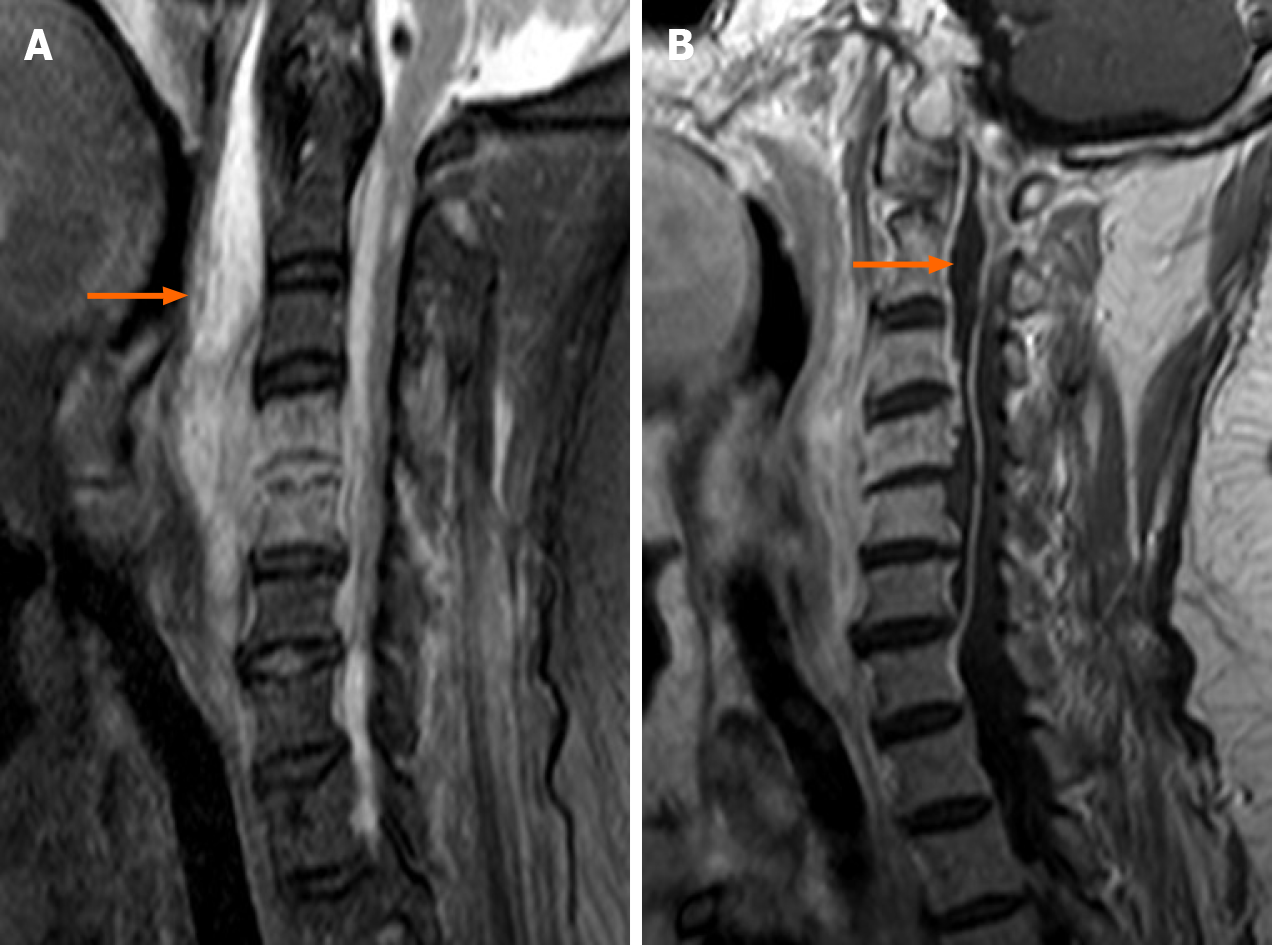
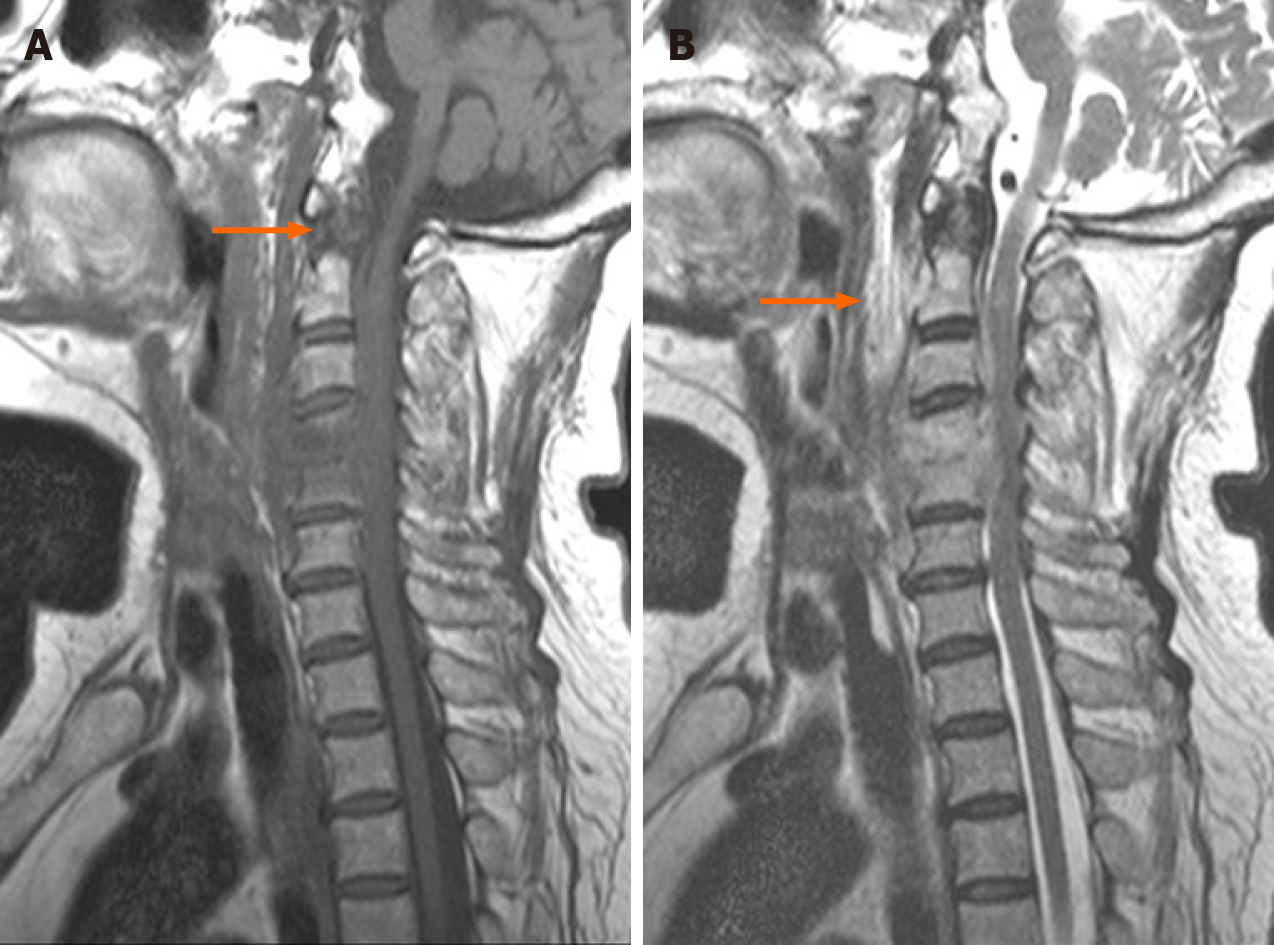
Figure 2 Preoperative magnetic resonance images.
A: Sagittal T2-weighted fat-suppressed image shows a marked fluid collection in the spatium retropharyngeum (arrow) spreading into the spinal canal through the C4/C5 disc space; B: Sagittal gadolinium-enhanced image demonstrates a well-delineated peripherally enhancing ventral epidural abscess (arrow) extending from C6 to the foramen magnum.
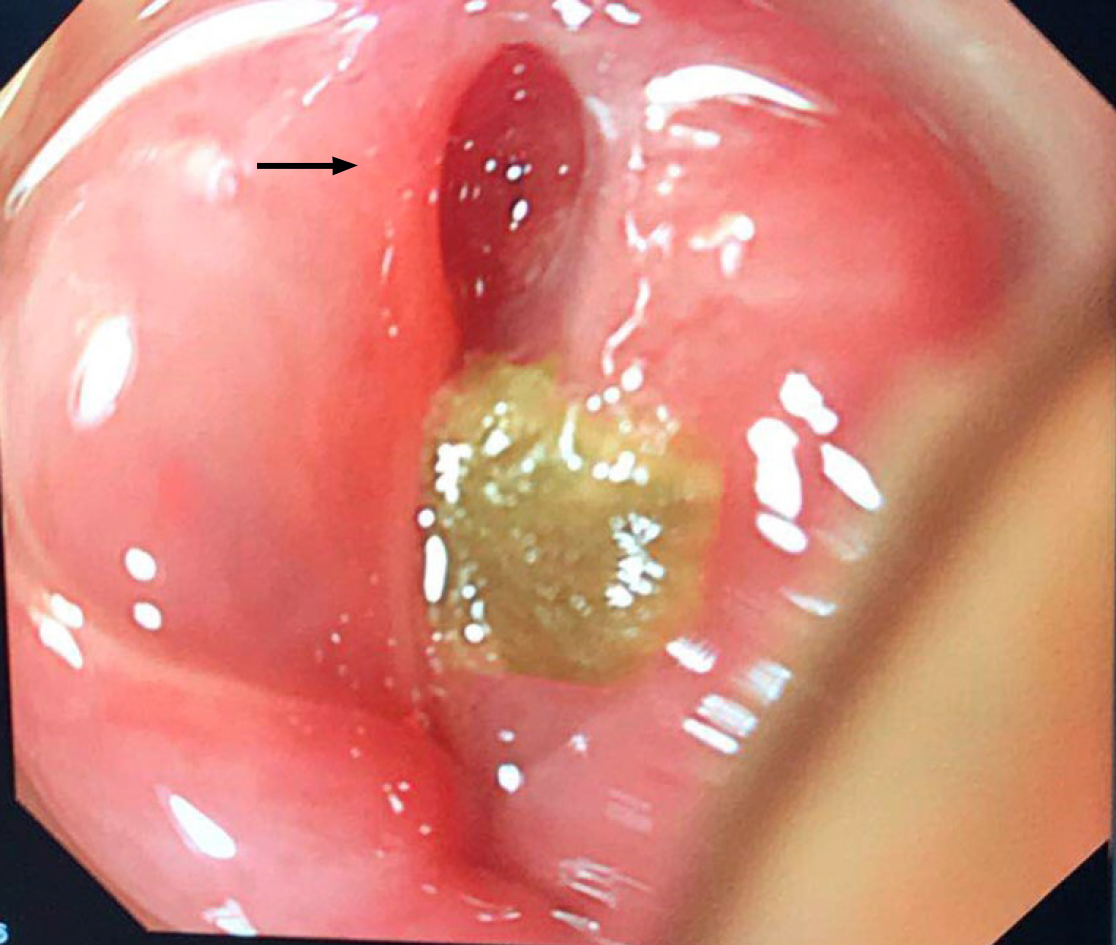
Figure 3 Endoscopic examination reveals perforation (arrow) and abscess on the posterior pharyngeal wall.
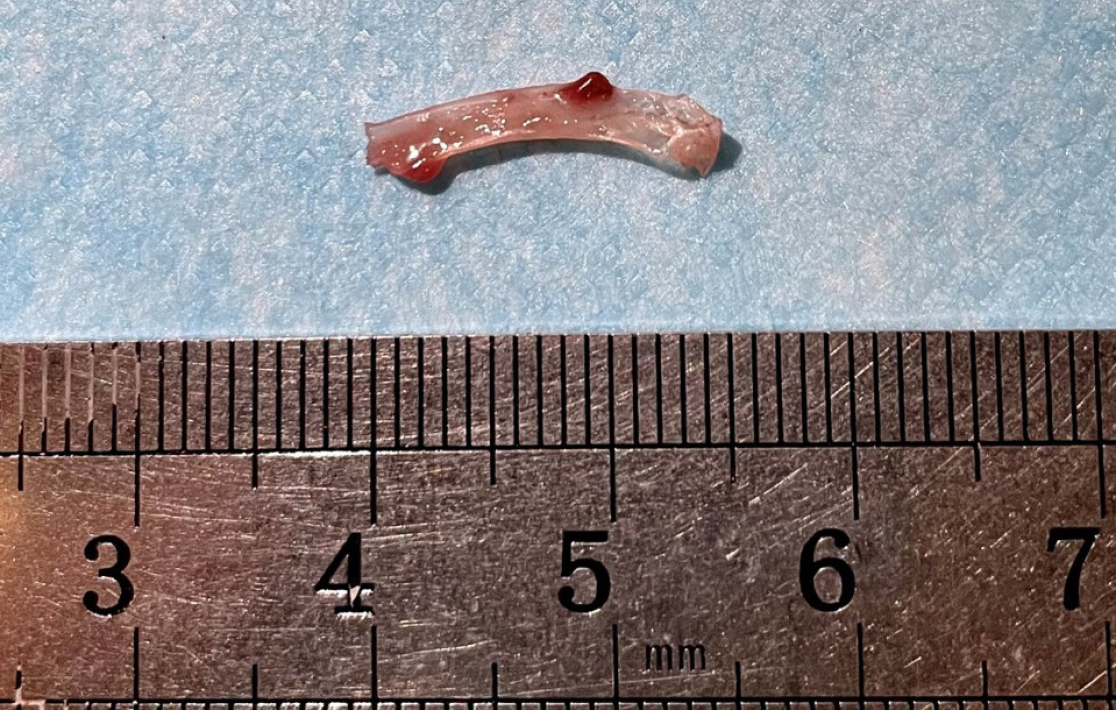
Figure 4 The fish bone was found in the irrigation fluid.
Figure 5 Postoperative magnetic resonance images.
A: Sagittal T1-weighted image shows that the epidural abscess (arrow) was less than that before surgery; B: Sagittal T2-weighted image demonstrates that the abscess in the posterior pharyngeal wall (arrow) was obviously less than that before surgery.
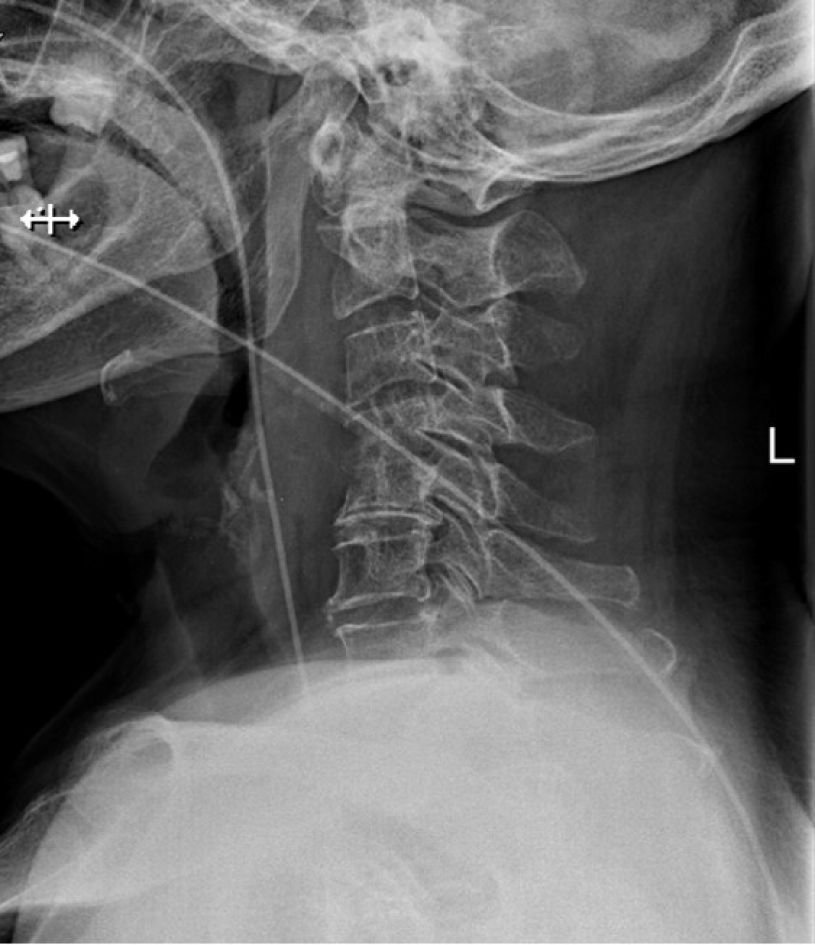
Figure 6 X-ray of cervical spine (fifth week after operation).
No fish bone was detected. The nasogastric tube was placed in the esophagus.
- Citation: Li SY, Miao Y, Cheng L, Wang YF, Li ZQ, Liu YB, Zou TM, Shen J. Surgical treatment of delayed cervical infection and incomplete quadriplegia with fish-bone ingestion: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(25): 7535-7541
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i25/7535.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7535