Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2021; 9(25): 7527-7534
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7527
Published online Sep 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7527
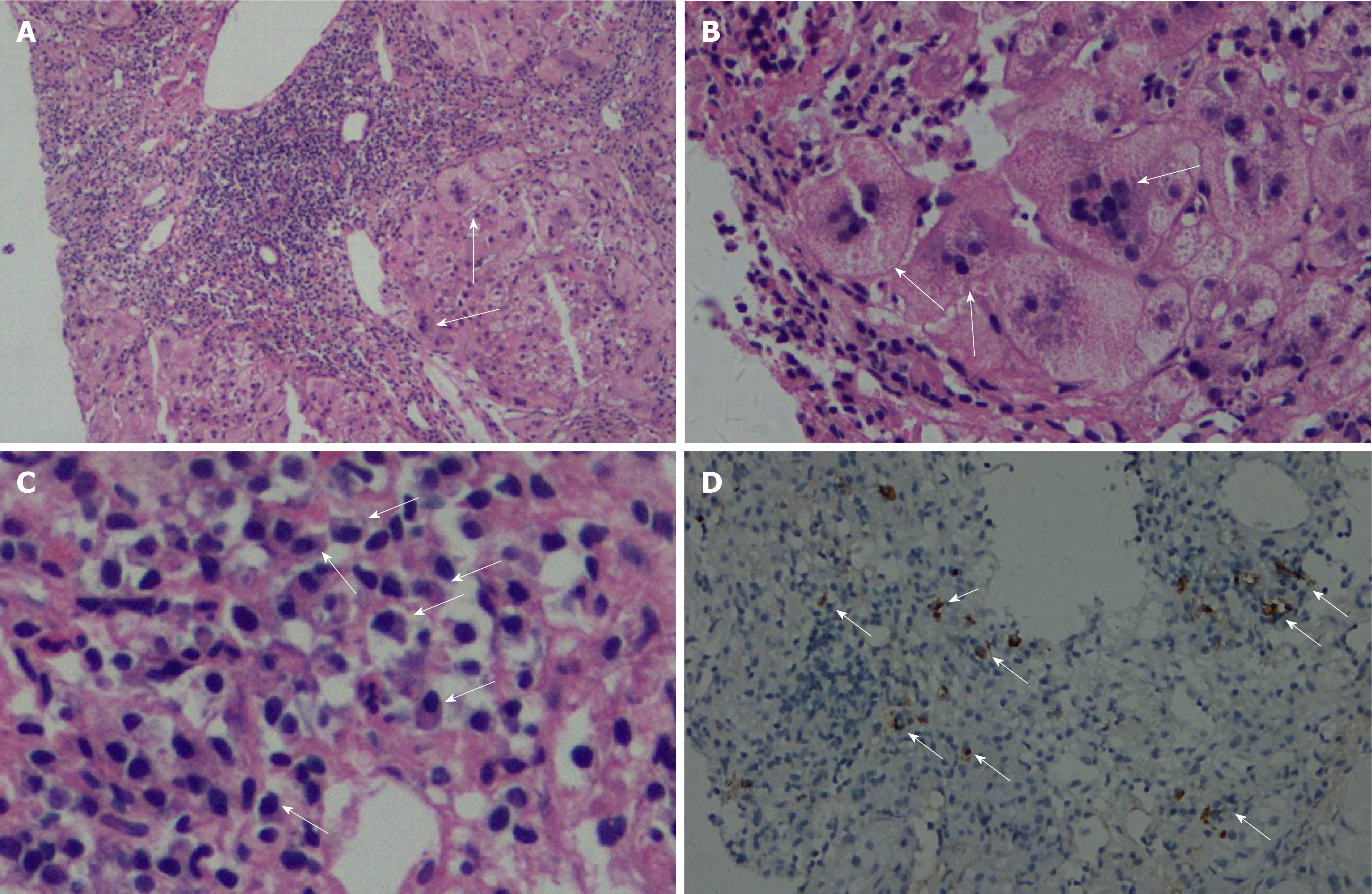
Figure 1 Histological characteristics of the first liver biopsy.
A: Severe portal inflammation and interface inflammation (arrow) are visible. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, 200 × magnification; B: Giant-cell hepatitis (arrow). HE, 400 × magnification; C: Plasma cell infiltration (arrow). HE, 400 × magnification; D: IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration (arrow). IgG4 immunohistochemical staining, 200 × magnification.
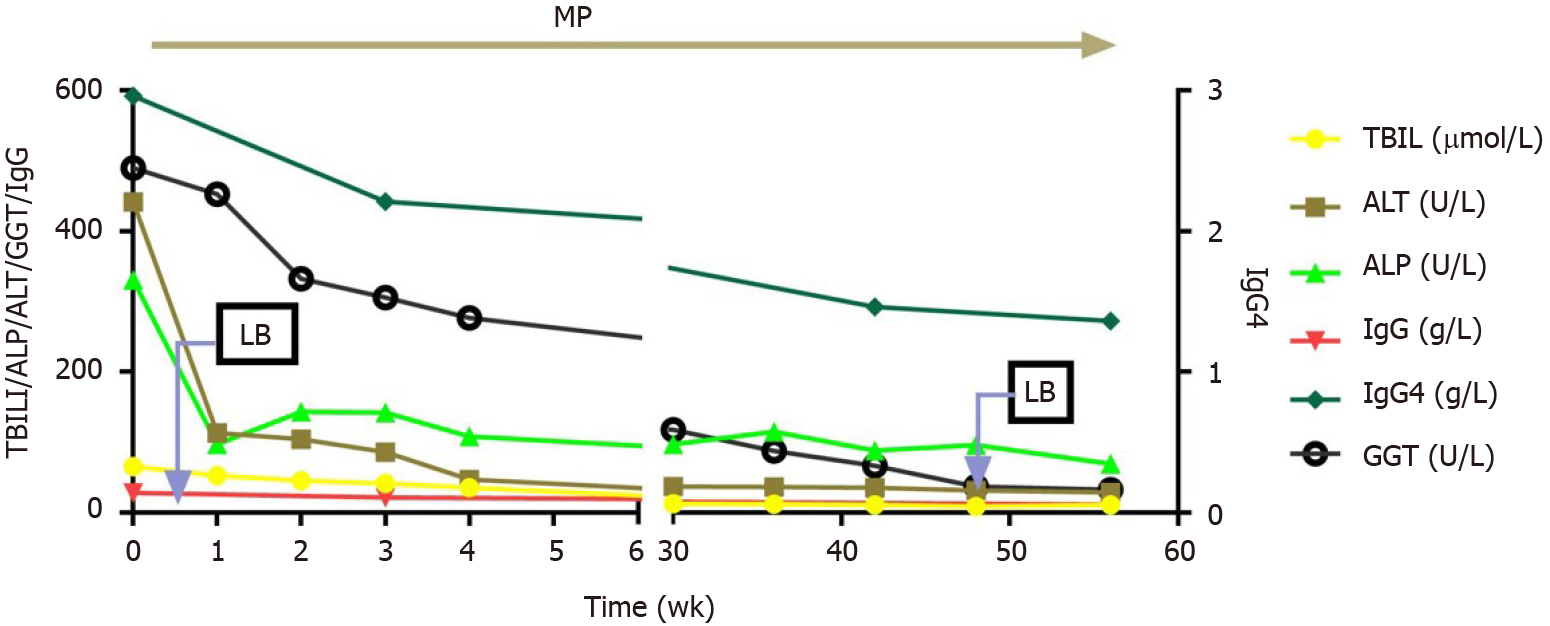
Figure 2 Changes of main liver function and immunological indexes in the patient.
MP: Methylprednisolone; LB: Liver biopsy; TBIL: Total bilirubin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyltransferase.
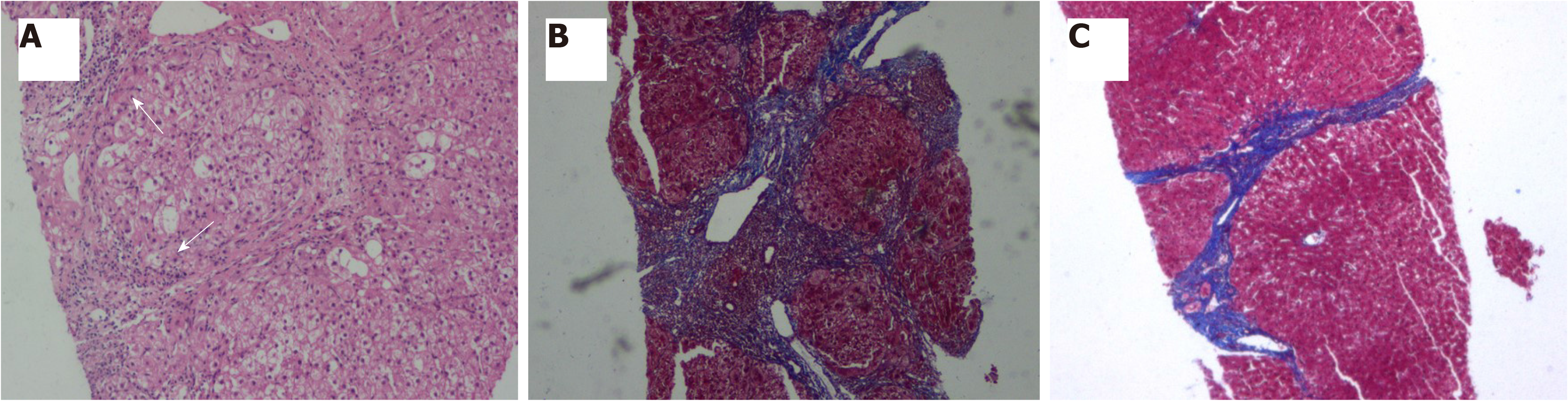
Figure 3 Characteristic pathological changes of liver tissue.
A: The portal area and interface inflammation have improved significantly (arrow) in the second liver biopsy. HE, 200 × magnification; B: The portal area was enlarged and the hepatic lobules were surrounded by fibers in the first liver biopsy. Masson staining, 100 × magnification; C: The fiber spacing is also thinner and improved than before in the second liver biopsy. Masson staining, 100 × magnification.
- Citation: Tan YW, Wang JM, Chen L. Is simultaneous presence of IgG4-positive plasma cells and giant-cell hepatitis a coincidence in autoimmune hepatitis? A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(25): 7527-7534
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i25/7527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i25.7527