Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2021; 9(24): 7224-7230
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i24.7224
Published online Aug 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i24.7224
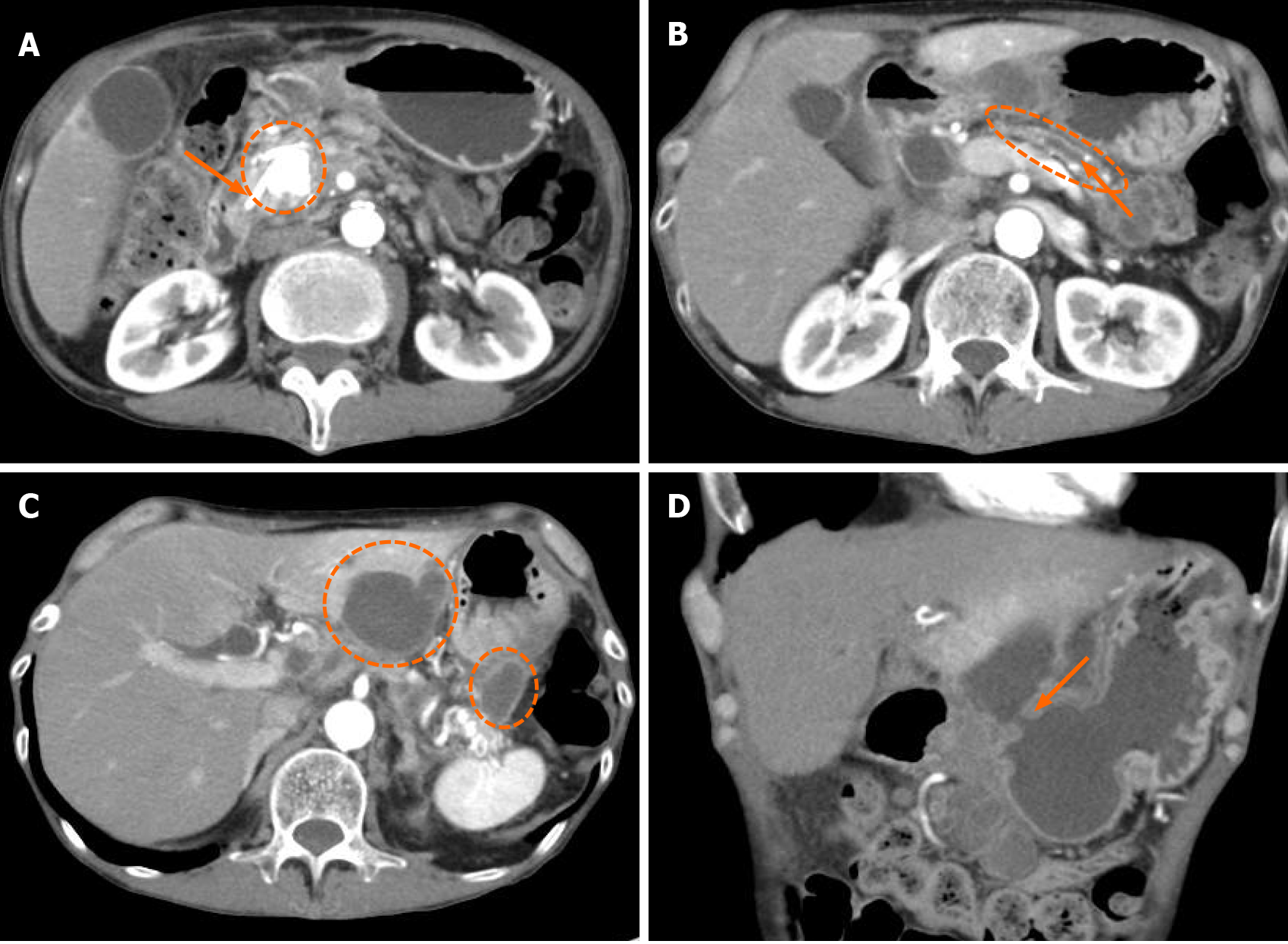
Figure 1 Computed tomography images.
A: Stent in the pancreatic duct (orange arrowhead) and large stone in the pancreas head (dotted line circle); B: Expanded main pancreatic duct (orange arrowhead) and thinning of pancreatic parenchyma (dotted line circle); C: Multiple pancreatic cysts of the hilum of the spleen and the posterior lateral segment of the liver; D: White arrowhead showing a fistula connected to the stomach from the infected pancreatic cysts.
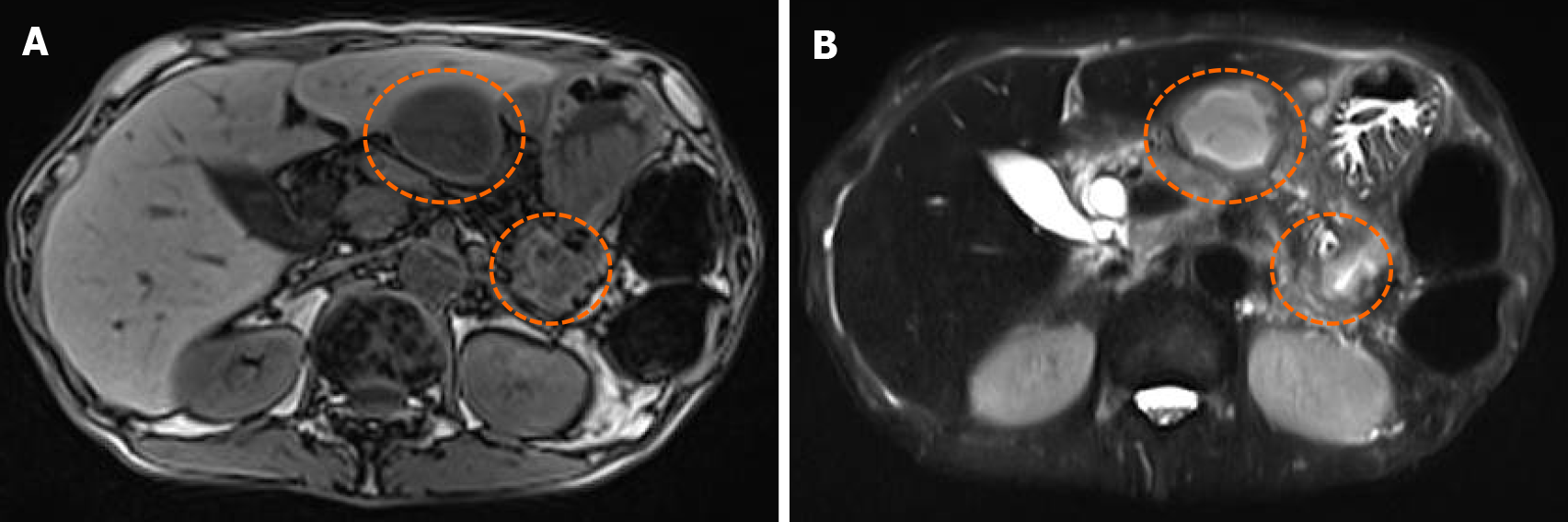
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography images.
A: Cysts showing low intensity in T1-weighted images (dotted line circles); B: Cysts showing high signal in diffusion weighted images (dotted line circles).
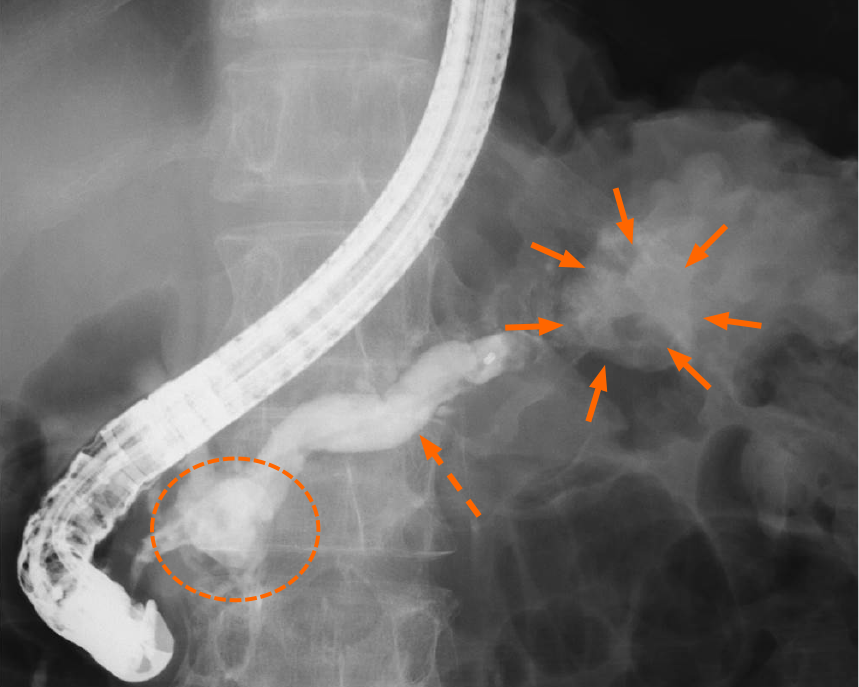
Figure 3 Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography images.
There was a large pancreatic stone in the pancreas head (dotted line circles), expanded main pancreatic duct (dotted orange arrowhead), and a pancreatic cyst in the pancreas tail (orange arrowheads).
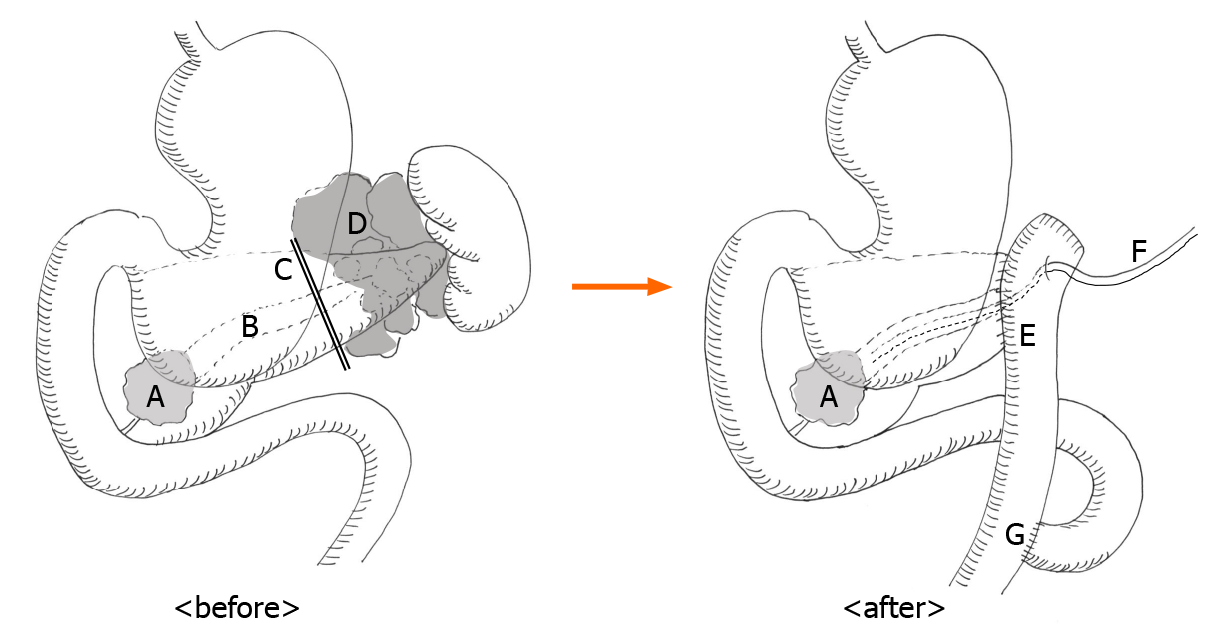
Figure 4 Scheme of surgery.
A: A large stone in the pancreas head; B: Expanded main pancreatic duct; C: Incision line of the pancreatic parenchyma; D: Infected pancreatic cysts; E: Anastomosis of pancreatojejunostomy; F: External pancreatic stent; G: Roux-en-Y anastomosis.
- Citation: Kimura K, Adachi E, Toyohara A, Omori S, Ezaki K, Ihara R, Higashi T, Ohgaki K, Ito S, Maehara SI, Nakamura T, Maehara Y. Successful outcome of retrograde pancreatojejunostomy for chronic pancreatitis and infected pancreatic cysts: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(24): 7224-7230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i24/7224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i24.7224