Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 16, 2021; 9(2): 476-481
Published online Jan 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.476
Published online Jan 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.476
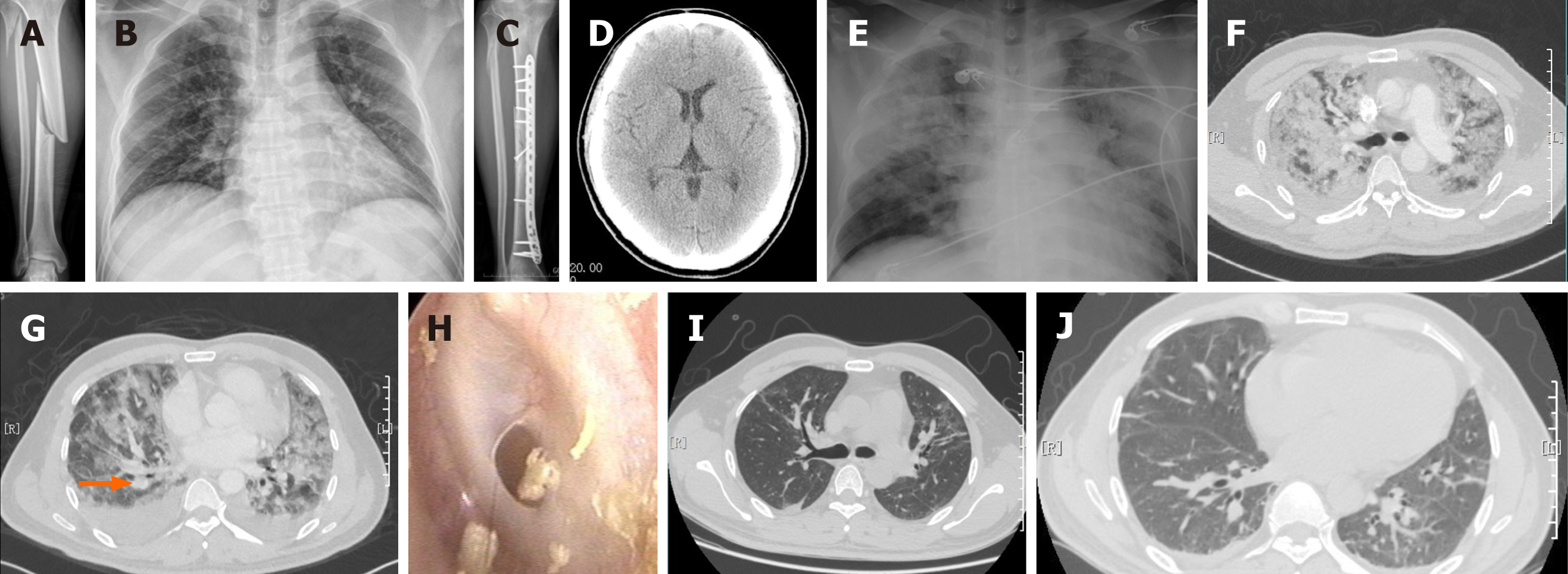
Figure 1 Patient’s imaging data.
A: Anteroposterior radiograph of the fracture of the right tibia and fibula; B: Anteroposterior radiograph of the chest after admission; C: Anteroposterior radiograph of the right tibia and fibula 3 mo after surgery; D: Computed tomography scan of the brain demonstrated no pathological changes; E: Bedside chest radiography with diffuse interstitial opacities 30 h after surgery; F: Computed tomography angiography of the chest demonstrated diffuse superimposed ground-glass abnormalities in both lungs as well as numerous discrete small nodules, which were consistent with fat embolism syndrome; G: Computed tomography angiography of the chest demonstrated a limited mural thrombus at the right distal pulmonary artery (orange arrow); H: Otoscopic examination demonstrated that the left tympanic membrane had a small circular perforation; I and J: Repeat chest computed tomography demonstrated remarkable absorption of the diffuse ground-glass opacities and mural thrombus 10 d after the operation.
- Citation: Shao J, Kong DC, Zheng XH, Chen TN, Yang TY. Postoperative complications of concomitant fat embolism syndrome, pulmonary embolism and tympanic membrane perforation after tibiofibular fracture: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(2): 476-481
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i2/476.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.476