Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2021; 9(15): 3758-3764
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3758
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3758
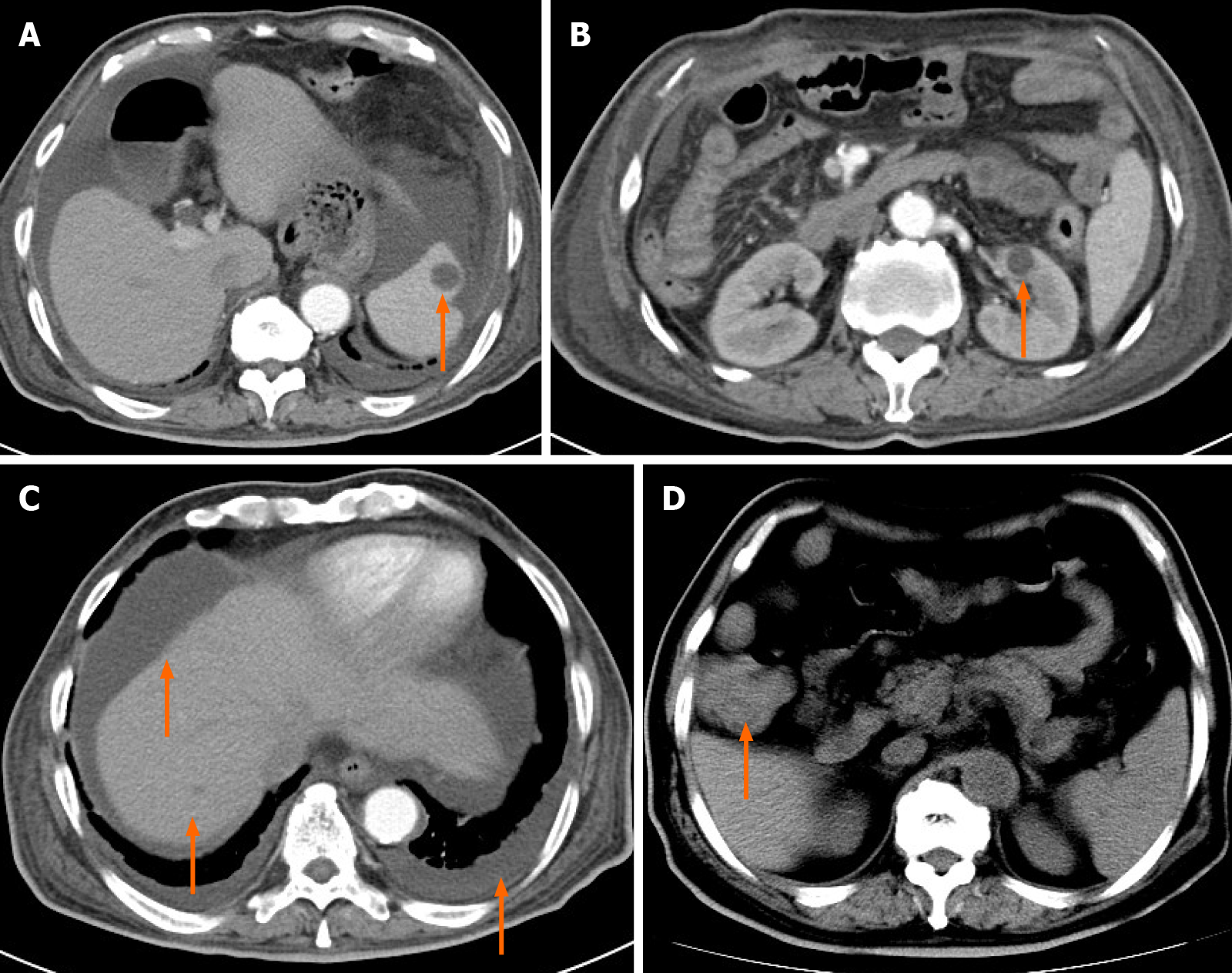
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography.
A: A cystic lesion in the spleen; B: A cystic lesion in the left kidney; C: A cystic lesion in the liver, ascites, and pleural effusion; D: Thickening of the ascending colon wall.
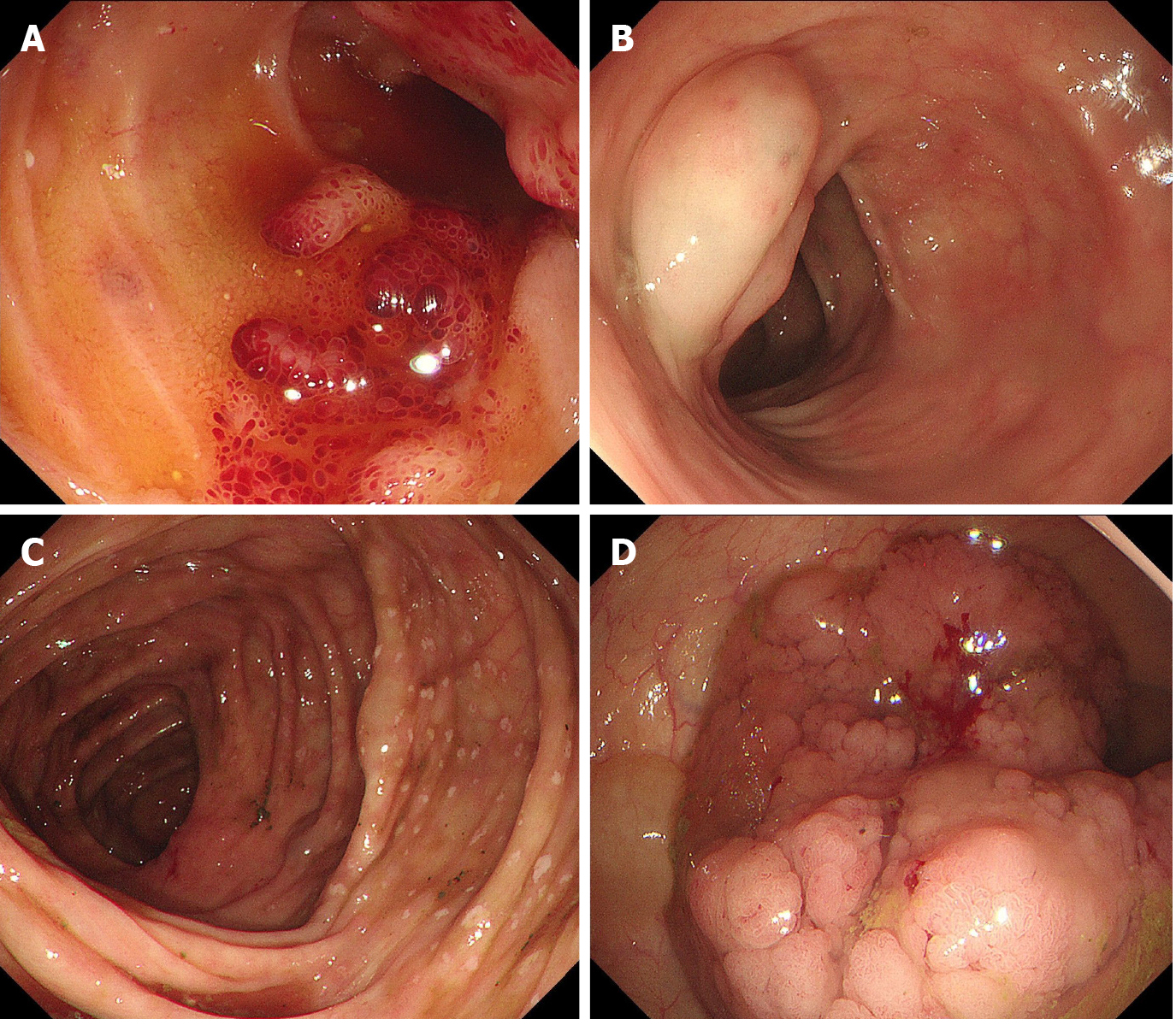
Figure 2 Colonoscopy.
A: Colonoscopy revealed a strawberry mucosa and variable spontaneous bleeding located in the terminal ileum; B and C: Multiple cystic masses with a translucent and smooth surface, and diffuse white spots located in the colon; D: A laterally spreading tumor located in the ascending colon.
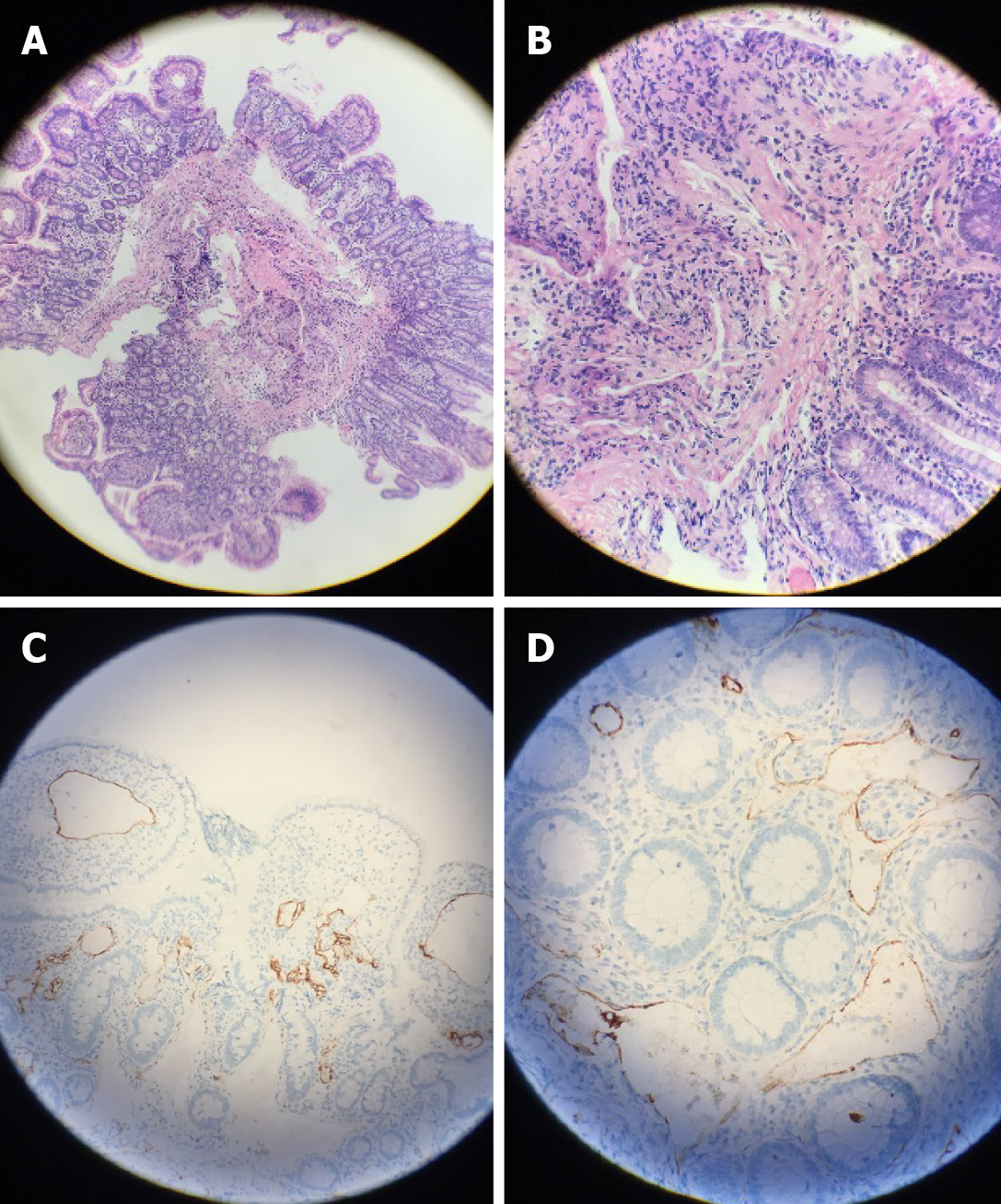
Figure 3 Pathology.
A and B: A large amount of vascular hyperplasia and dilatation was observed in the mucosal muscular layer and submucosa [A: Hematoxylin-eosin stain (HE) × 100; B: HE × 400]; C and D: Immunohistochemically stained tumor sections showed that lymph vessels in the intestine were dilated, and D2-40 was positive (C: × 40; D: × 100).
- Citation: Ding XL, Yin XY, Yu YN, Chen YQ, Fu WW, Liu H. Lymphangiomatosis associated with protein losing enteropathy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(15): 3758-3764
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i15/3758.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3758