Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2021; 9(15): 3733-3740
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3733
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3733
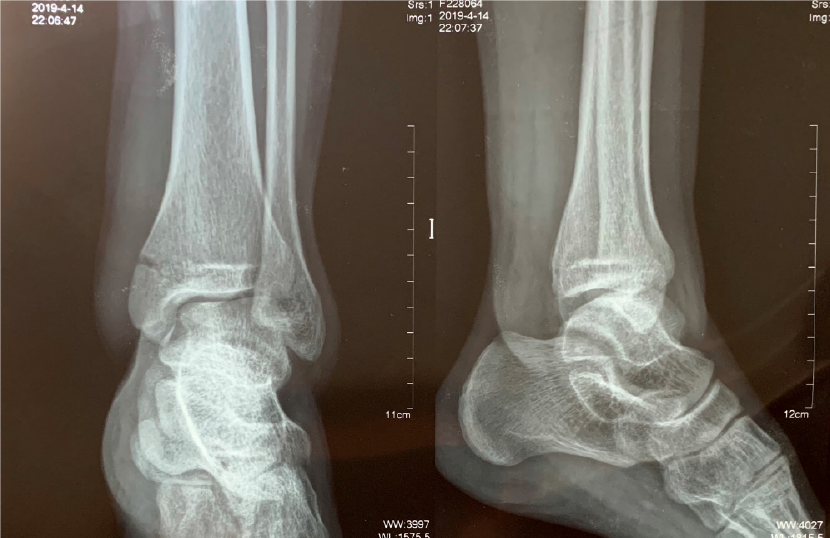
Figure 1 Left ankle radiographs (from another hospital) of anteroposterior and lateral views showing medial malleolar fracture.
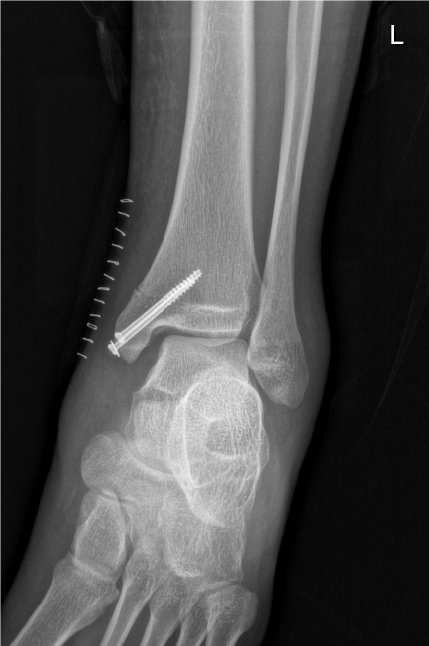
Figure 2 Postoperative radiograph showing the enlarged tibiofibular clear space and medial clear space.
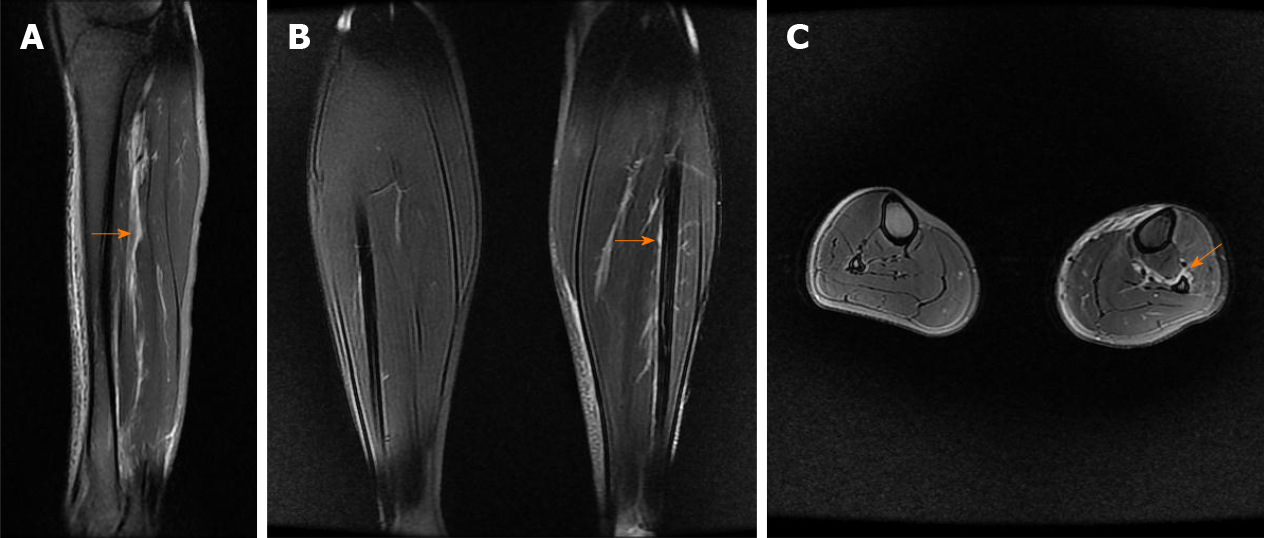
Figure 3 Calf magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Sagittal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showing high-signal intensity (orange arrow) indicating injury of the interosseous membrane (IOM); B: Coronal MRI showing IOM injury (orange arrow) compared with the contralateral uninjured calf; C: Axial MRI showing IOM rupture (orange arrow) compared with the contralateral uninjured calf, torn from the fibular interosseous crest.
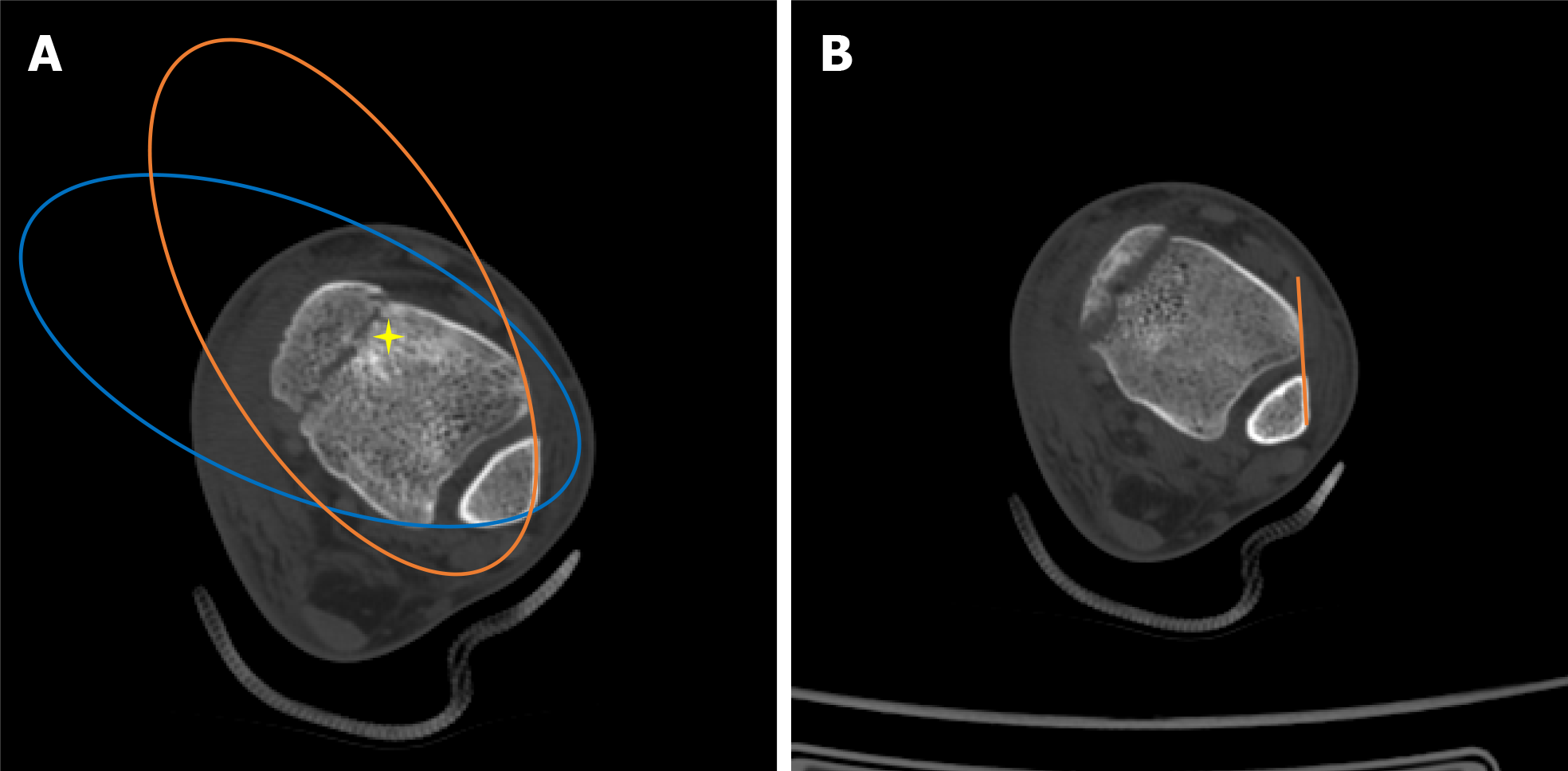
Figure 4 Assessment of inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis in computed tomography scans.
A: Bartoníček et al[6]’s evaluation method: The anterior aspect of the distal fibula and tibia was continuous, similar to the posterior aspect, “star” area of higher density of the subchondral cancellous bone; B: The distance between the Tillaux-Chaput tubercle and Gifford and Lutz[7]’s tibiofibular line did not exceed 2 mm at the level of 10 mm superior to the tibial plafond.
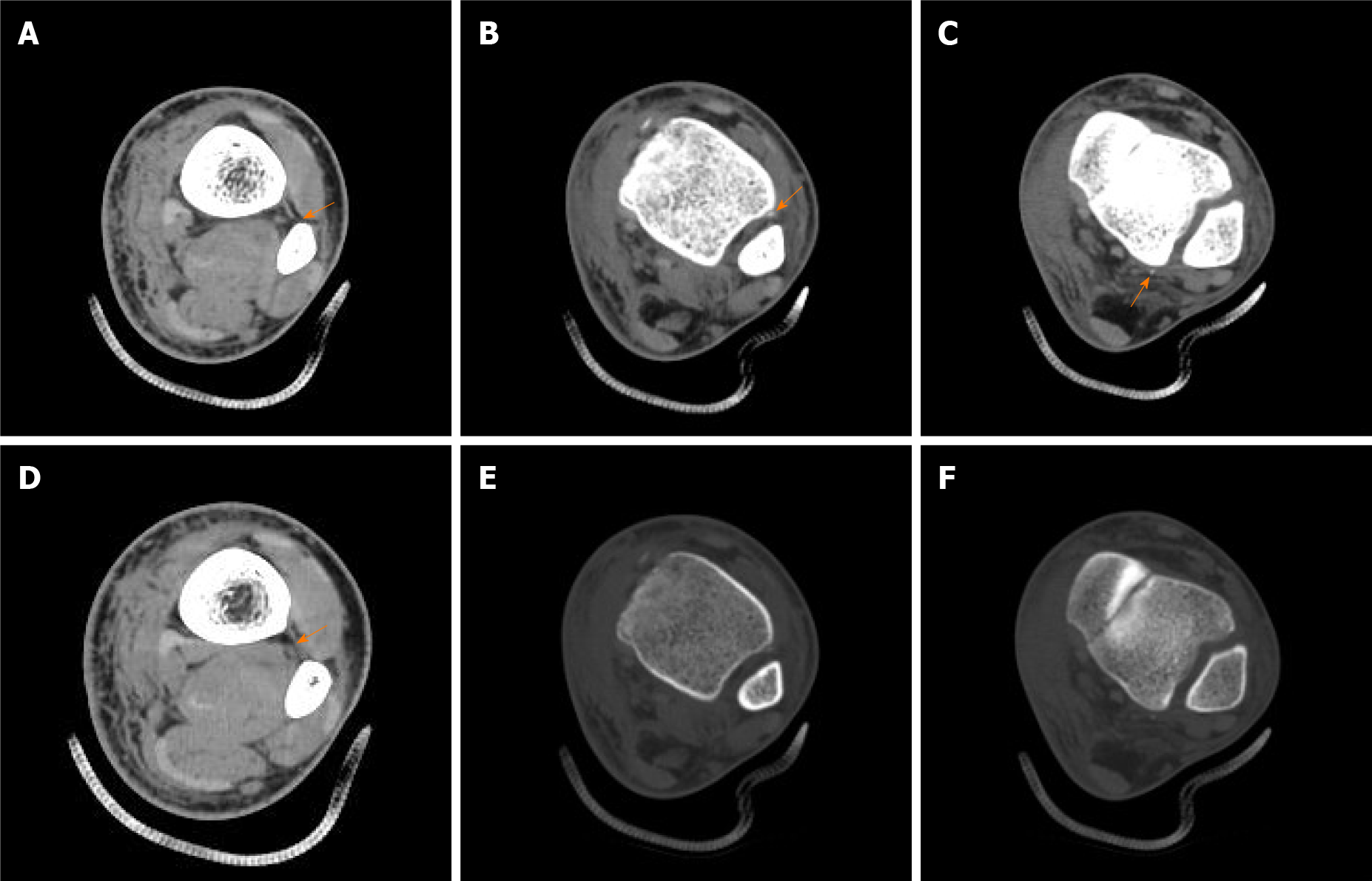
Figure 5 Computed tomography scans indicating complete injury of inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis.
A: Rupture of the interosseous membrane (IOM) torn from fibular interosseous crest; B: Avulsion fracture of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL) in the soft tissue window of computed tomography (CT) scan; C: Avulsion fracture of the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL) in the soft tissue window of CT scan; D: The intact IOM at the proximal part of the calf; E: Avulsion fracture of the AITFL was hardly caught in the bone window of the CT scan (the same B plane); F: Avulsion fracture of the PITFL was hardly caught in the bone window of the CT scan (the same C plane).
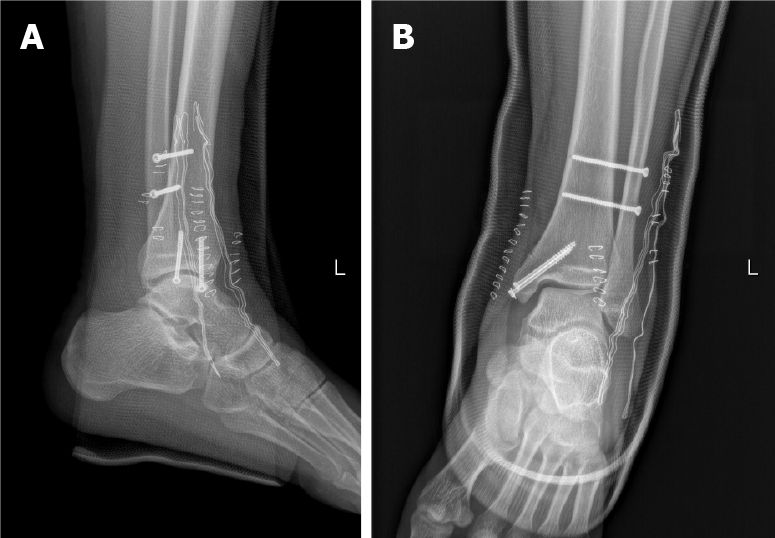
Figure 6 Ankle radiographs of anteroposterior and lateral views after secondary surgery.
A: Anteroposterior; B: Lateral.
- Citation: Liu GP, Li JG, Gong X, Li JM. Maisonneuve injury with no fibula fracture: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(15): 3733-3740
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i15/3733.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3733