Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2021; 9(15): 3662-3667
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3662
Published online May 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3662
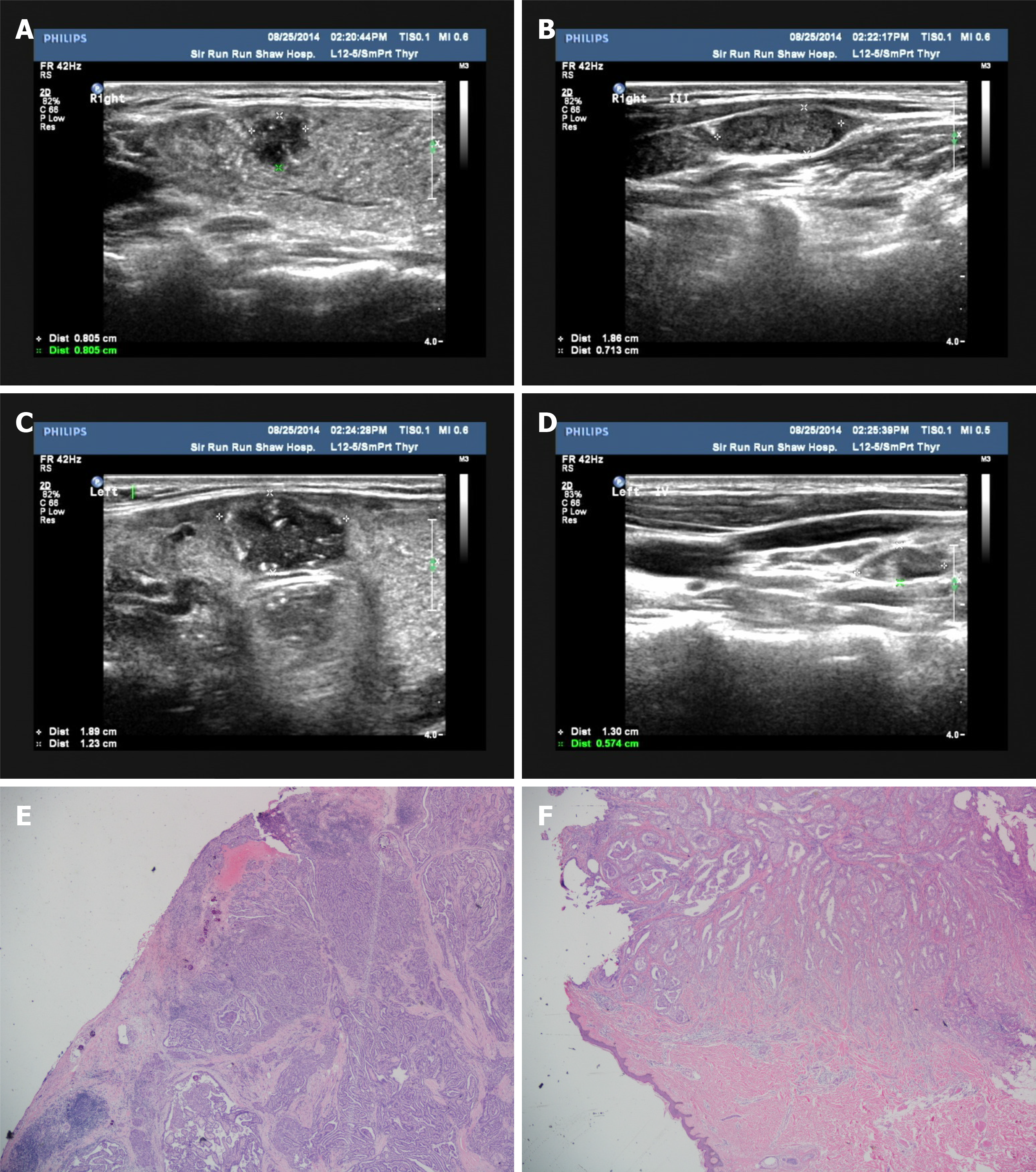
Figure 1 Ultrasonography and histopathology.
A: Ultrasound image of the largest primary papillary carcinoma in the right thyroid lobe; B: Ultrasound image of a suspicious malignant lymph node in the right lateral neck of level III; C: Ultrasound image of the largest primary papillary carcinoma in the left thyroid isthmus; D: Ultrasound image of a suspicious malignant lymph node in the right lateral neck of level IV. E: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of the largest thyroid nodule, 40 × magnification; F: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of the subcutaneously implanted nodule, 40 × magnification.
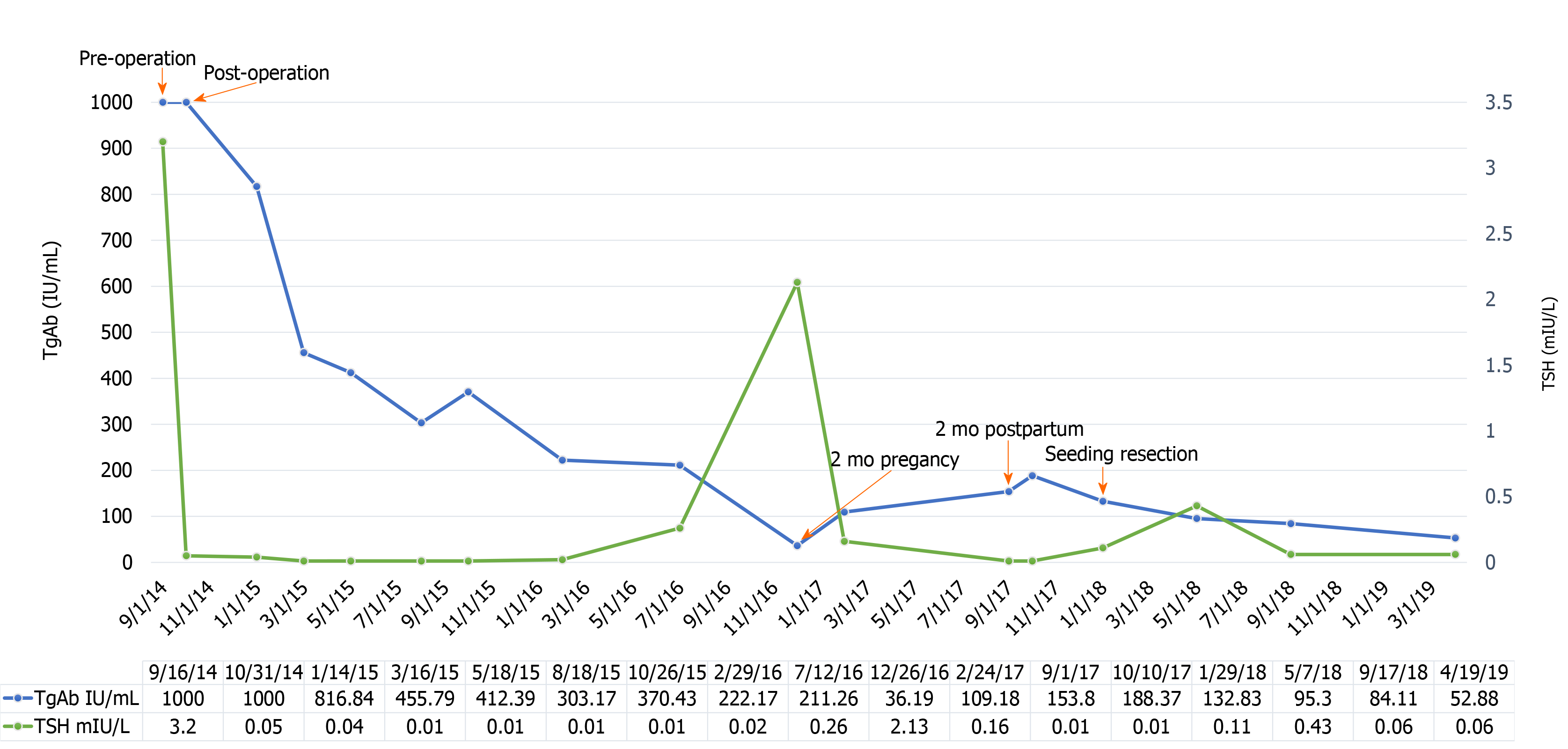
Figure 2 The fluctuations in thyroglobulin antibody and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels.
TgAb: Thyroglobulin antibody; TSH: Thyroid-stimulating hormone.
- Citation: Shi LH, Zhou L, Lei YJ, Xia L, Xie L. Needle tract seeding of papillary thyroid carcinoma after fine-needle capillary biopsy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(15): 3662-3667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i15/3662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i15.3662