Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2021; 9(11): 2519-2523
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2519
Published online Apr 16, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2519
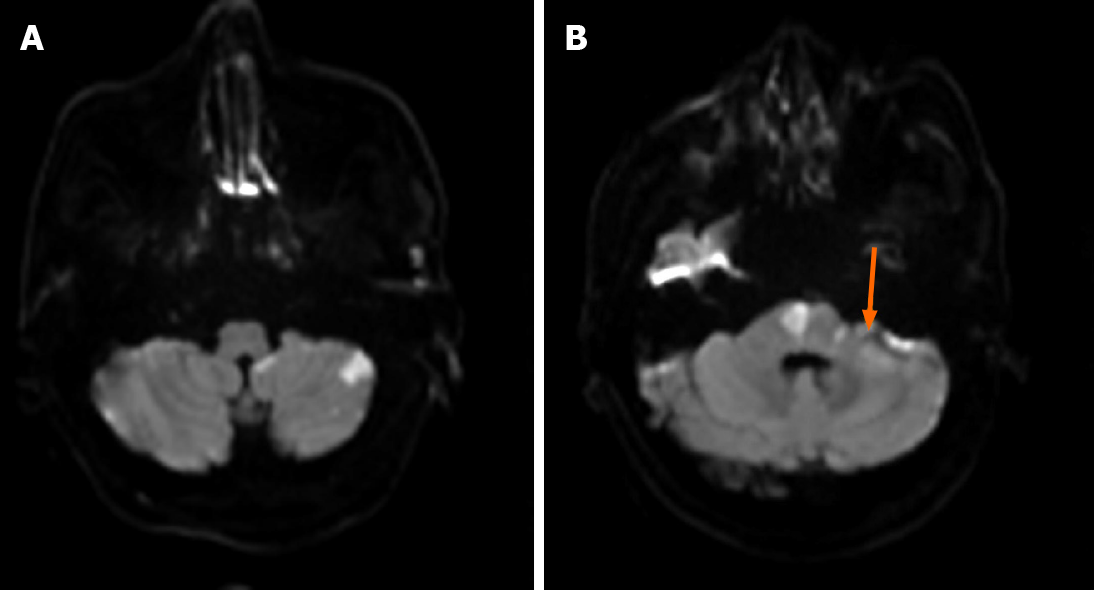
Figure 1 The results of diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with brain magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) revealed high signal intensity in the left posterior inferior cerebellar artery territory of the cerebellar hemisphere; B: DWI revealed high signal intensity in the right pons and bridge cerebellar arm. The yellow arrow indicates that the left auditory nerve was high signal on DWI, suggesting infarction of the auditory nerve.
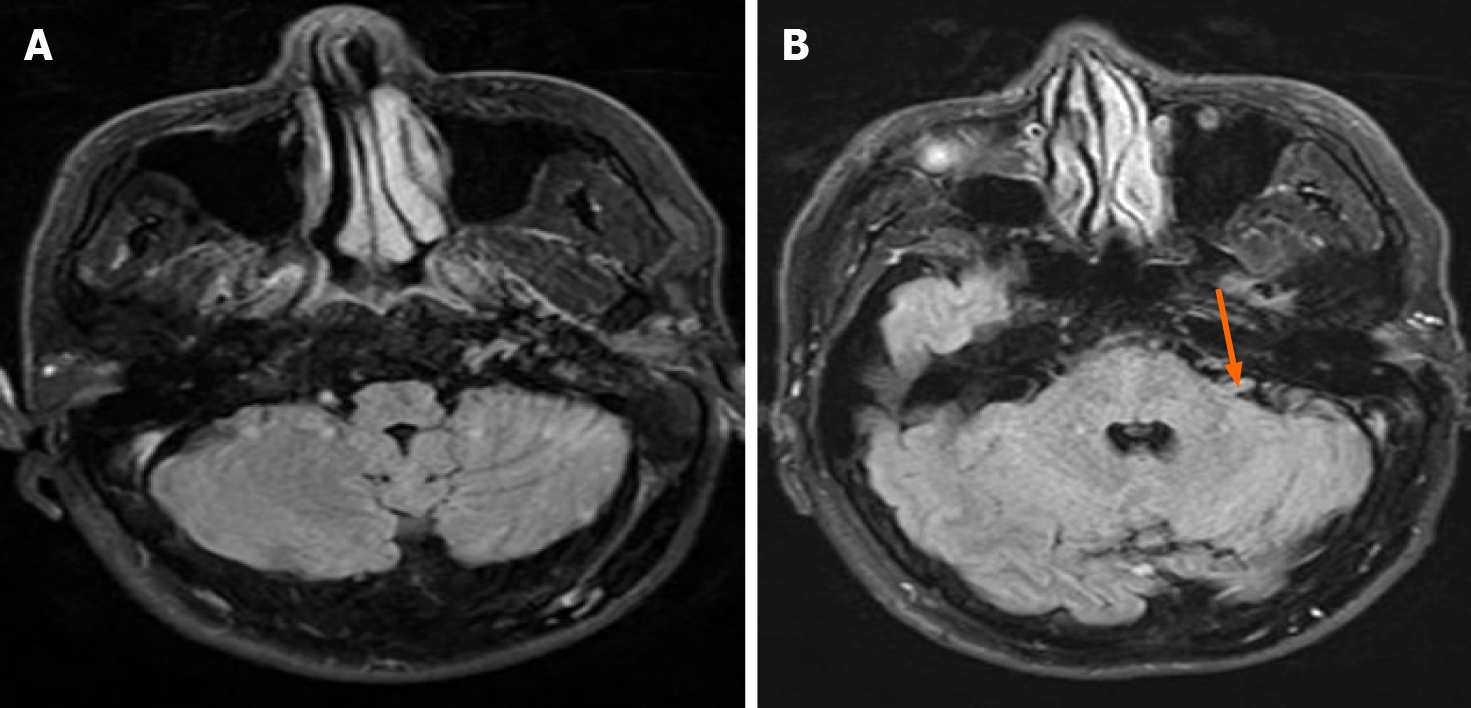
Figure 2 The results of T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery in patients with brain magnetic resonance imaging.
A: T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging revealed normal appearance; B: The yellow arrow indicates that the left auditory nerve was thickened and slightly higher on T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images, suggesting swelling of the auditory nerve.
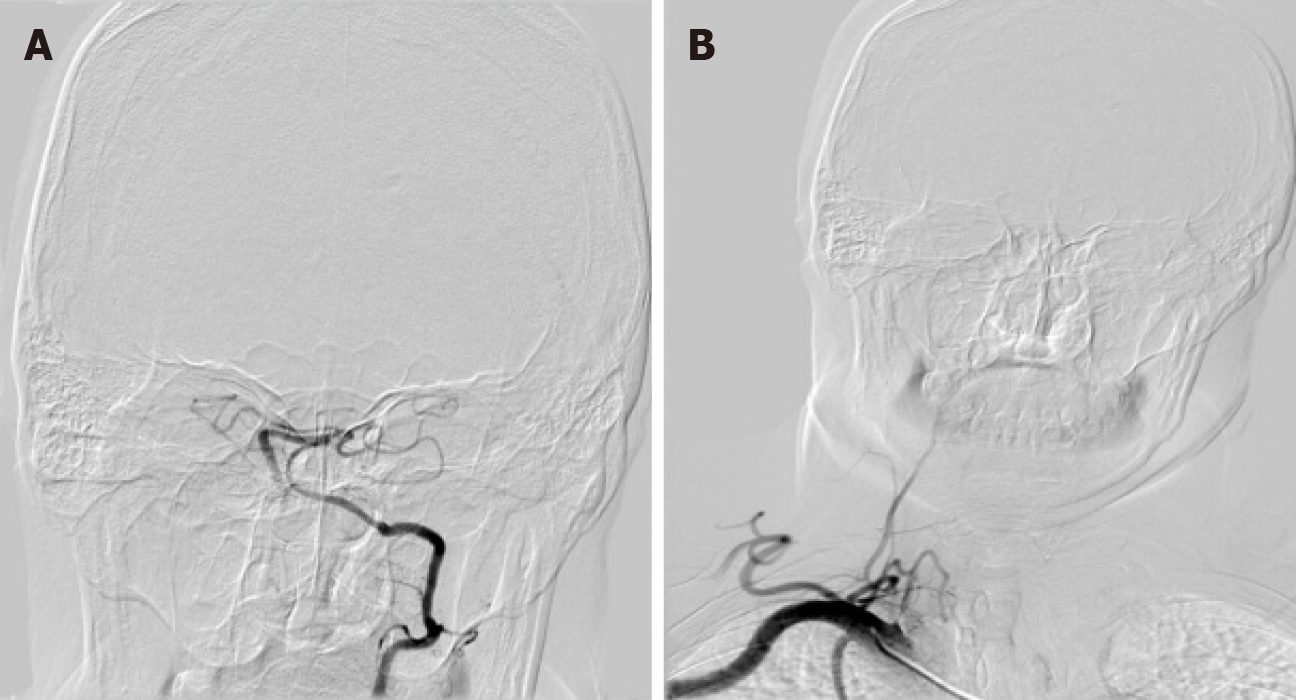
Figure 3 The results of cerebral angiography in the patient.
A: The left vertebral artery supplied blood to the posterior inferior cerebellar artery, but there was no development of the anterior inferior cerebellar artery; B: Linear stenosis of the right vertebral artery and no development of the intracranial artery.
- Citation: Wang XL, Sun M, Wang XP. Cerebellar artery infarction with sudden hearing loss and vertigo as initial symptoms: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(11): 2519-2523
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i11/2519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2519