Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2021; 9(10): 2268-2273
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2268
Published online Apr 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2268
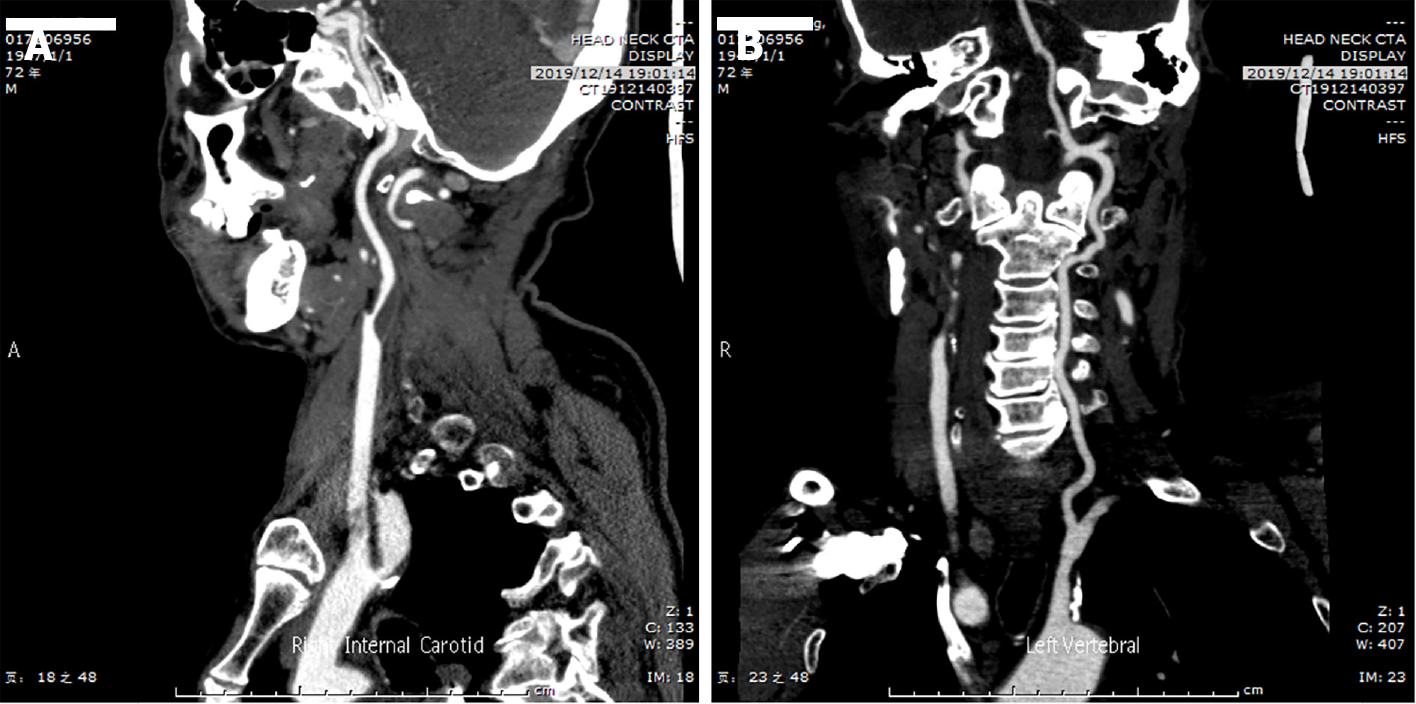
Figure 1 Preoperative computed tomography angiography.
A: Computed tomography angiography (CTA) revealed severe stenosis of the right internal carotid artery; B: CTA revealed the formation of mixed plaques in the left subclavian artery.
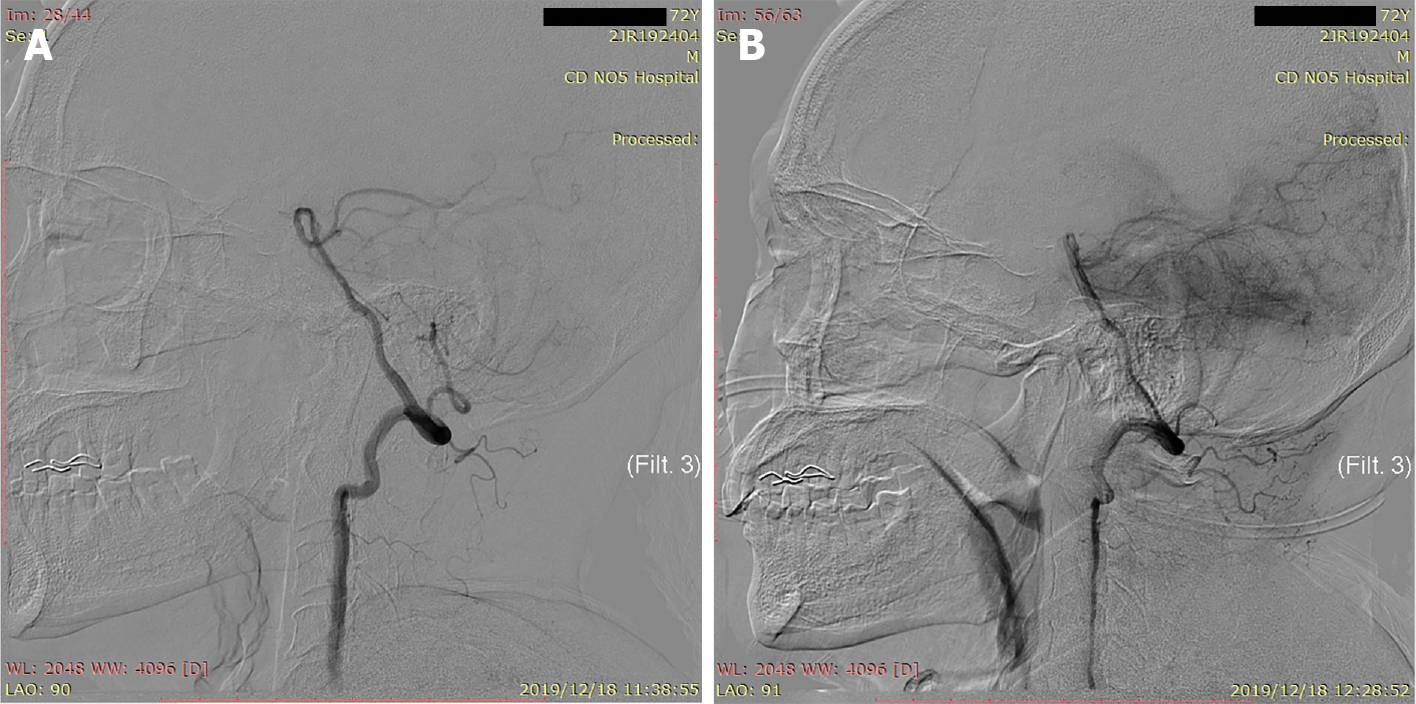
Figure 2 Digital subtraction angiography images.
A: Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) showed that the left vertebral artery and posterior inferior cerebellar artery were unaffected; B: DSA showed that the left posterior inferior cerebellar artery was occluded.
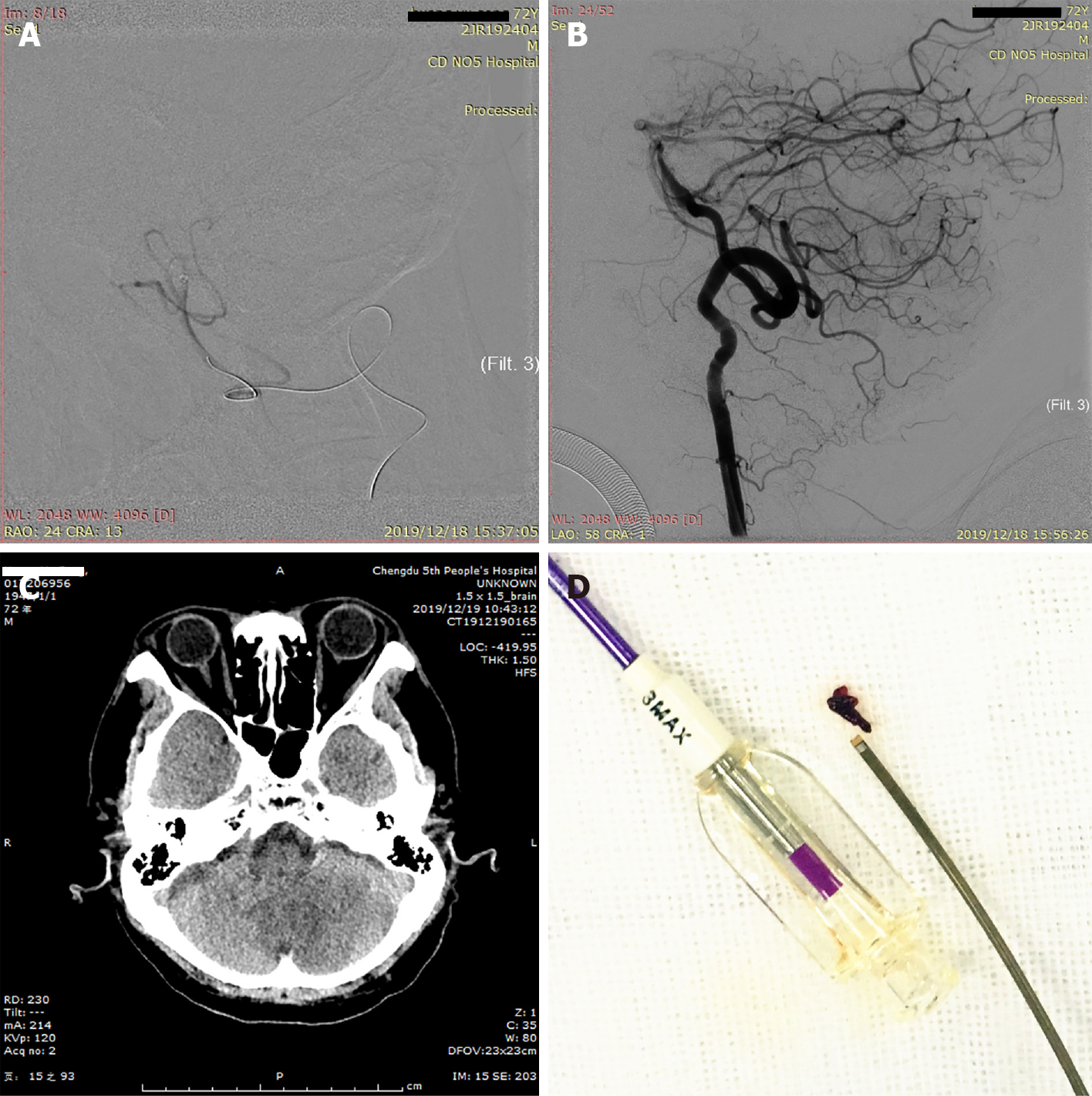
Figure 3 Operating process and outcome.
A: The proximal extent of the embolus was confirmed by 3MAX angiography; B: The posterior inferior cerebellar artery was unobstructed after aspiration (Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction level 3); C: Noncontrast computed tomography on the first day after surgery showed a low-density focus in the left cerebellum; D: Image of the embolus removed by 3MAX.
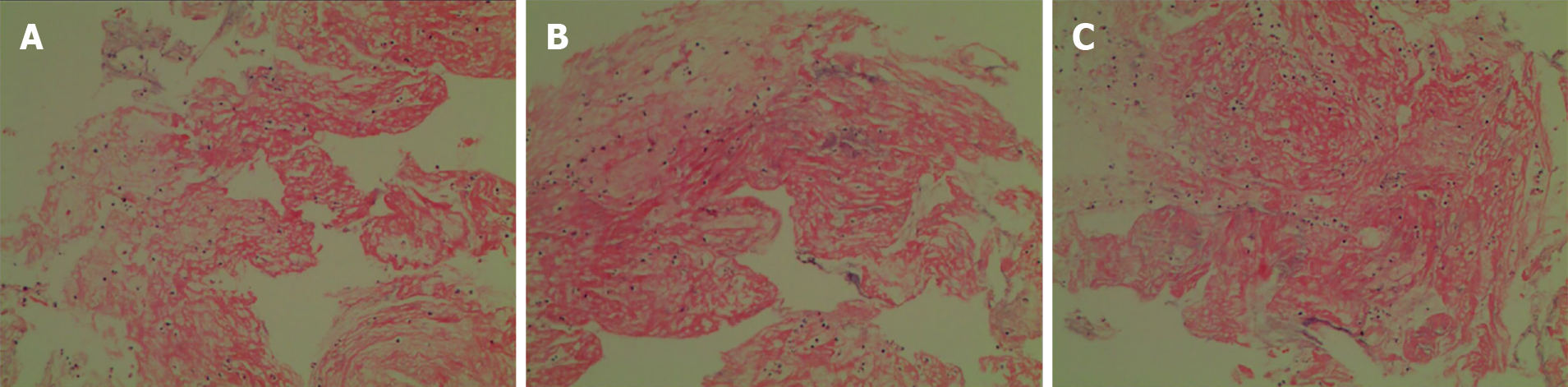
Figure 4 Images of the pathological results of the embolus.
A-C: Fibrinous exudation with inflammatory cell infiltration.
- Citation: Zhang HB, Wang P, Wang Y, Wang JH, Li Z, Li R. Mechanical thrombectomy for acute occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(10): 2268-2273
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i10/2268.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i10.2268