Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2021; 9(1): 252-261
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.252
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.252
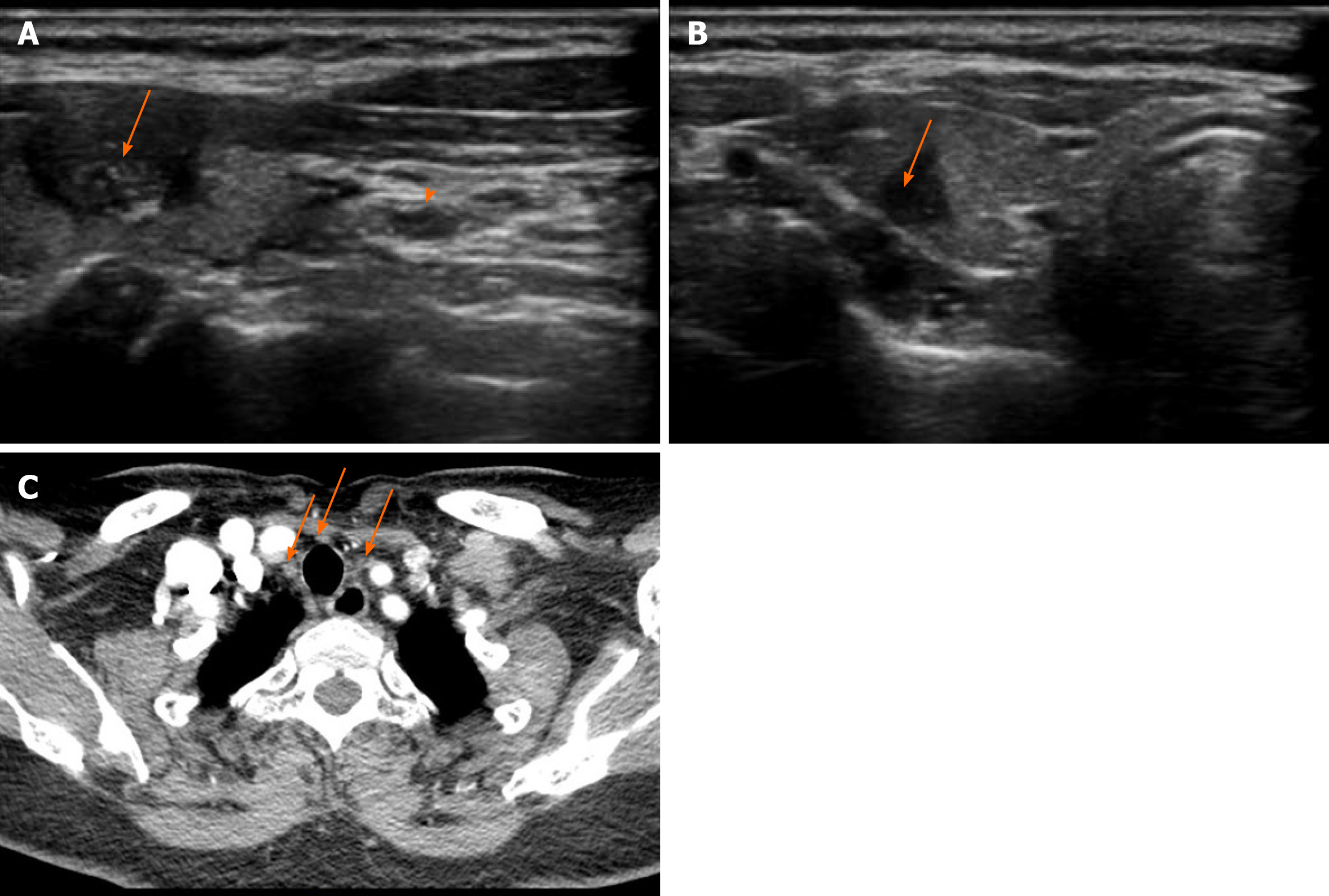
Figure 1 Ultrasound and contrast-enhanced computed tomography images obtained 3 mo after radiofrequency ablation for papillary thyroid carcinoma.
A: The left thyroid nodule (arrow) (6 mm × 8 mm × 12 mm) with hypoechogenicity, unclear margins, and scattered small calcifications on ultrasound was classified as Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System stage 4c. Metastatic central lymph nodes (arrowhead) were also detected; B: The right thyroid nodule (5 mm × 5 mm × 7 mm) with hypoechogenicity and unclear margins on ultrasound was classified as Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System stage 4a; C: Central lymph node metastasis was detected using contrast-enhanced computed tomography.
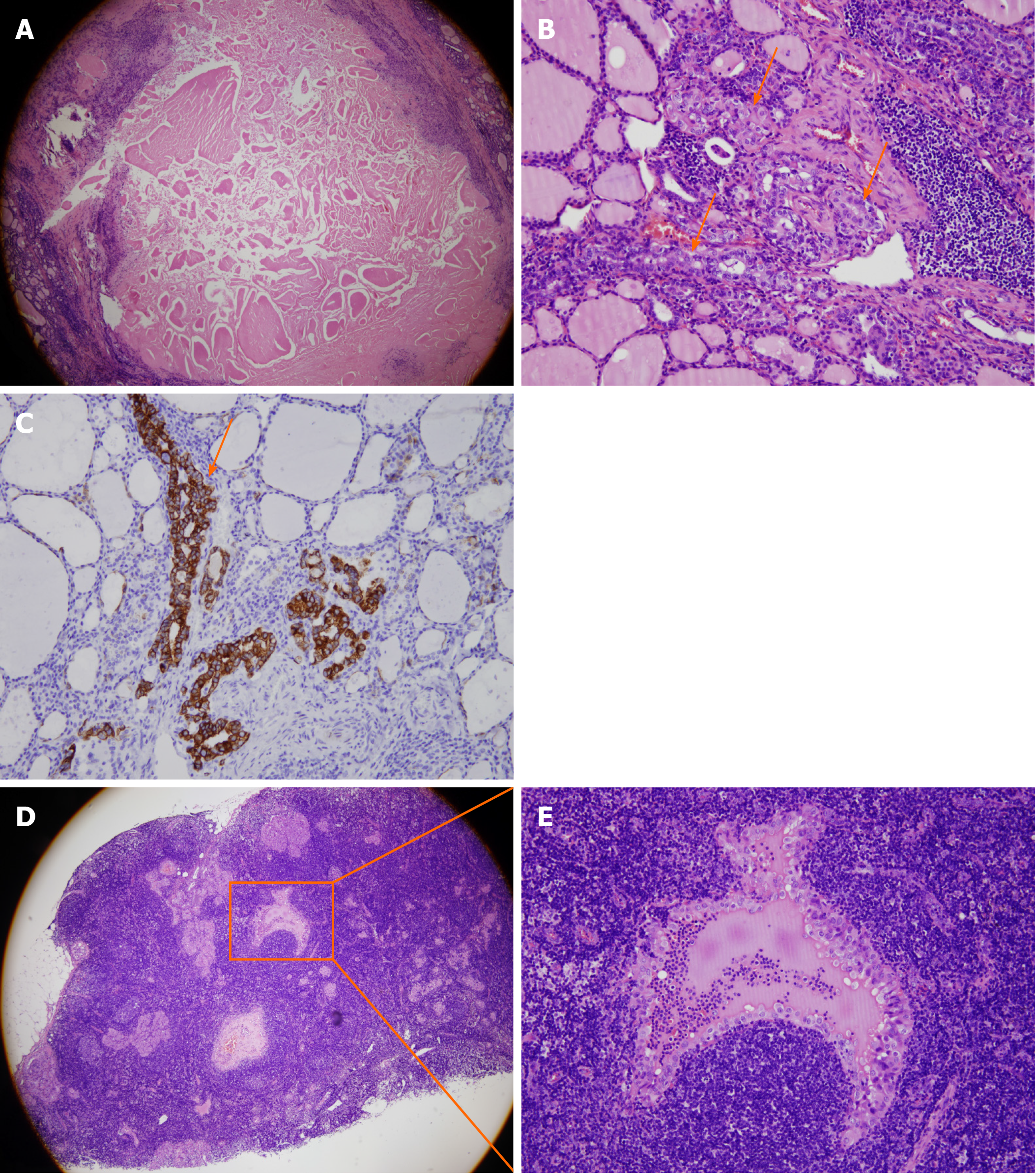
Figure 2 The images of pathological specimens showed residual papillary thyroid carcinoma and central lymph node metastasis.
A: The middle part of the tumor was completely ablated, 50 × magnification; B: Residual tumor cells were detected at the edge of the tumor, 200 × magnification; C: Immunohistochemical staining showed residual tumor cells, 200 × magnification; D: Central lymph node metastasis, 50 × magnification. The boxed region is shown at higher magnification in E; E: Image of the box shown in D at 4 × magnification.
- Citation: Hua Y, Yang JW, He L, Xu H, Huo HZ, Zhu CF. Residual tumor and central lymph node metastasis after thermal ablation of papillary thyroid carcinoma: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(1): 252-261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i1/252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.252