Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2021; 9(1): 163-169
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.163
Published online Jan 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.163
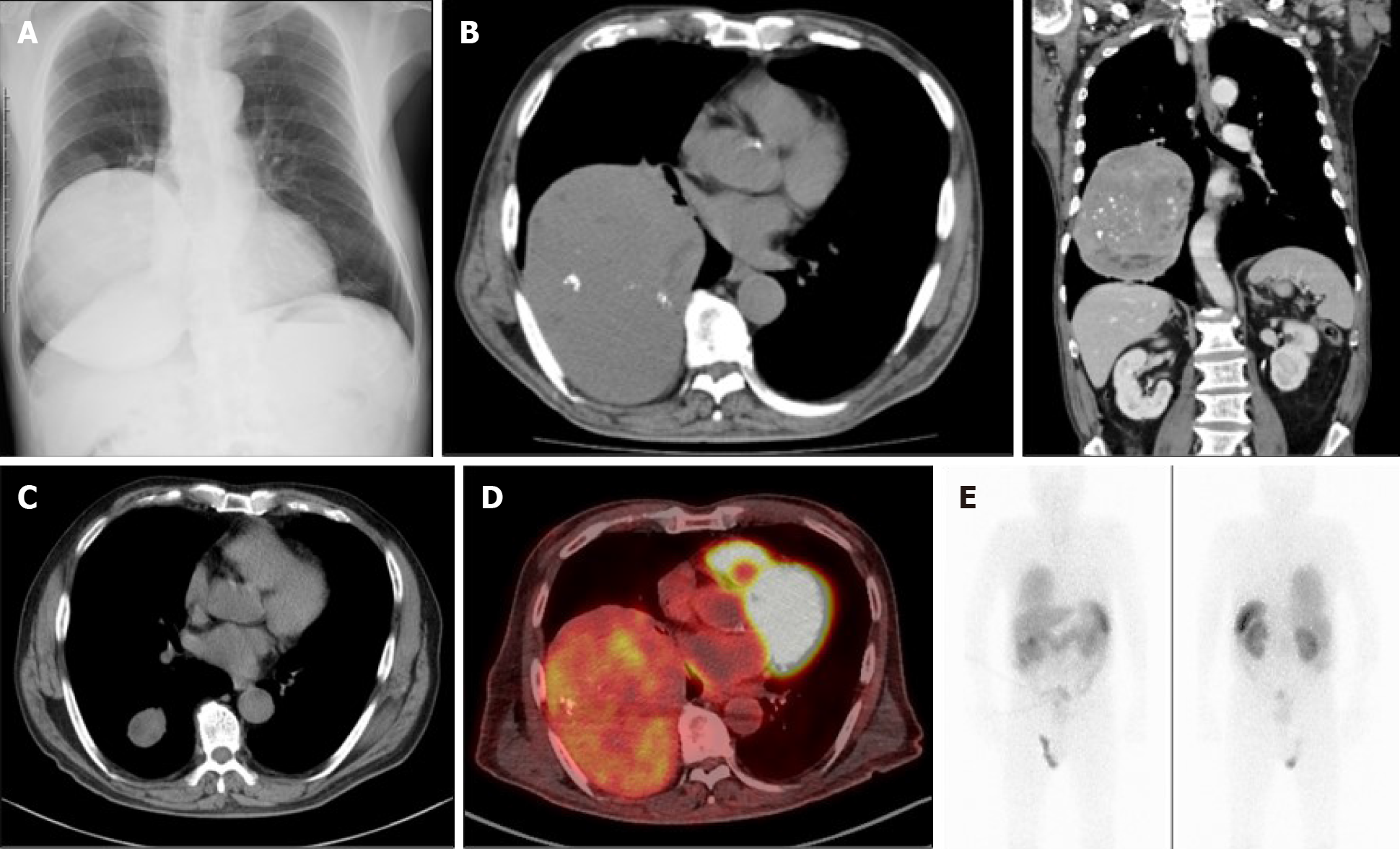
Figure 1 Imaging findings.
A and B: Chest X-ray (A) and computed tomography (B) (left-hand side is transverse plane; right-hand side is coronal plane) showed a heterogenous giant mass measuring 11 cm × 14 cm × 15 cm in size on the right lower chest; C: Computed tomography from ten years ago showed the tumor’s growth in the past decade; D and E: Positron emission tomography (D) and octreotide scintigraphy (E) showed the tumor’s accumulation.
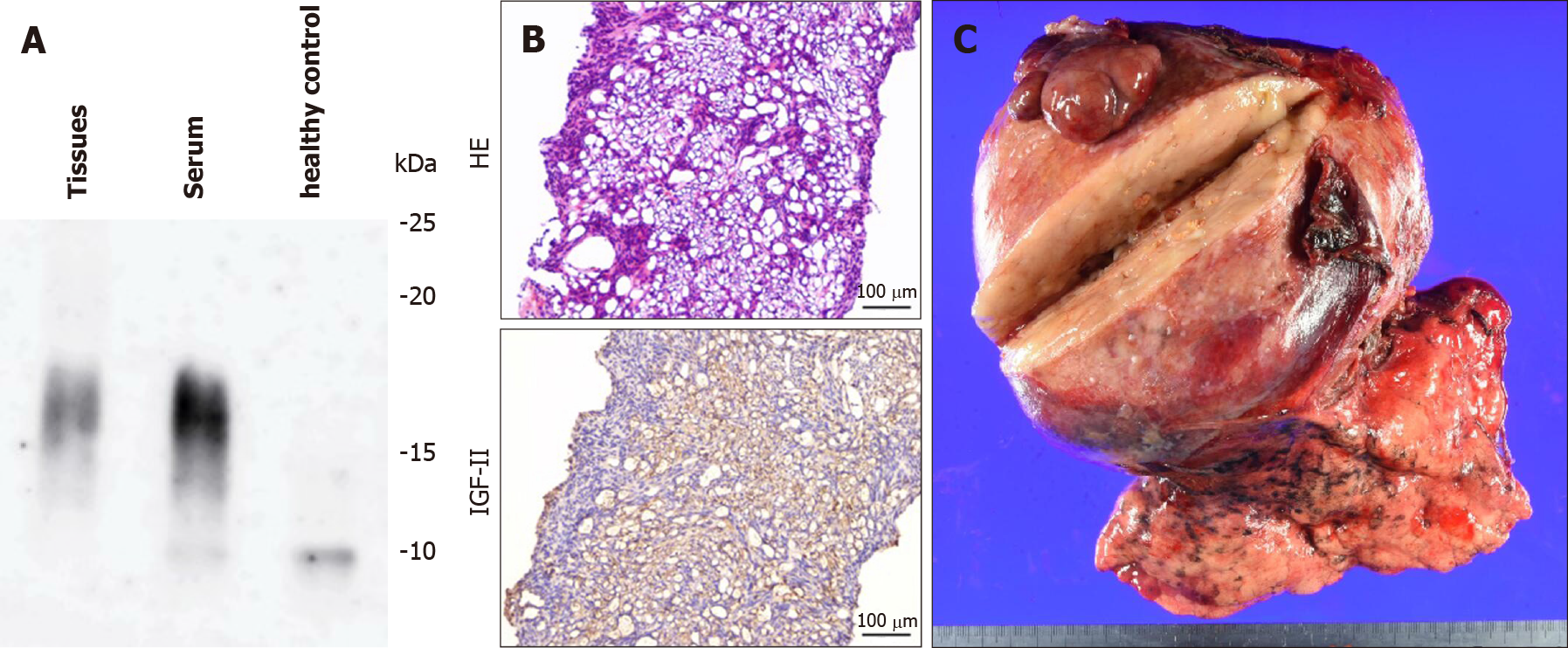
Figure 2 Pathological findings.
A: Western blot analysis of high-molecular-weight insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II). High molecular weight form of IGF-II was detected, both in the tumor tissue and in the serum; B: Histopathological examination of biopsy specimens. The tumor cells were immunopositive for IGF-II. The upper panel shows macroscopic findings of the surgical specimen. HE, hematoxylin and eosin staining; IGF-II, immunohistochemical staining for IGF-II; C: The tumor size was 15.6 cm × 13.7 cm × 10.4 cm. The histological diagnosis was of a solitary fibrous tumor. Histopathological characteristics were as follows: CD34:(-), STAT6(+), c-kit(-), S-100:(-), desmin:(-), αSMA(-), p53(±), and MIB-1: 3.6%. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; IGF-II: Insulin-like growth factor II.
- Citation: Matsumoto S, Yamada E, Nakajima Y, Yamaguchi N, Okamura T, Yajima T, Yoshino S, Horiguchi K, Ishida E, Yoshikawa M, Nagaoka J, Sekiguchi S, Sue M, Okada S, Fukuda I, Shirabe K, Yamada M. Late-onset non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(1): 163-169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i1/163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.163