Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. May 6, 2020; 8(9): 1666-1673
Published online May 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i9.1666
Published online May 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i9.1666
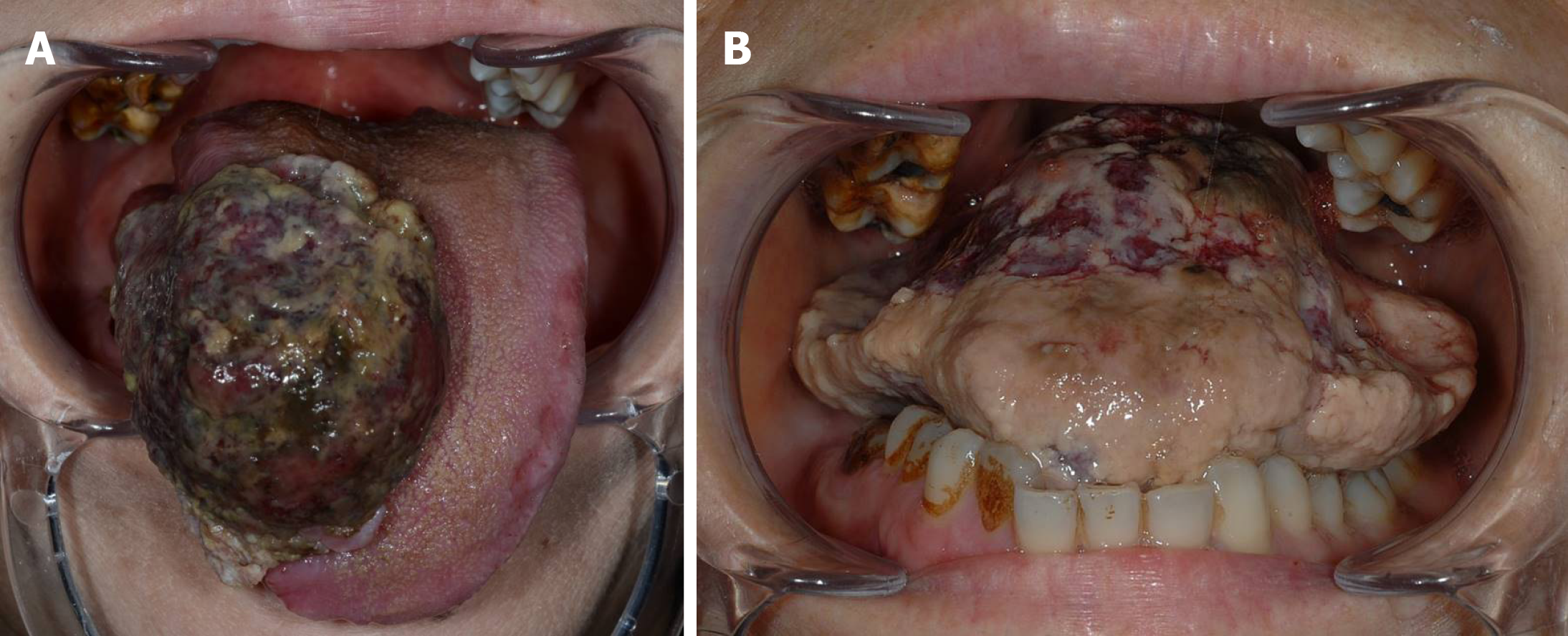
Figure 1 Intraoral view on the first visit (A) and administration (B).
The mass was 30 mm × 40 mm, and the patient was unable to close the mouth due to the tumor, which was growing rapidly.
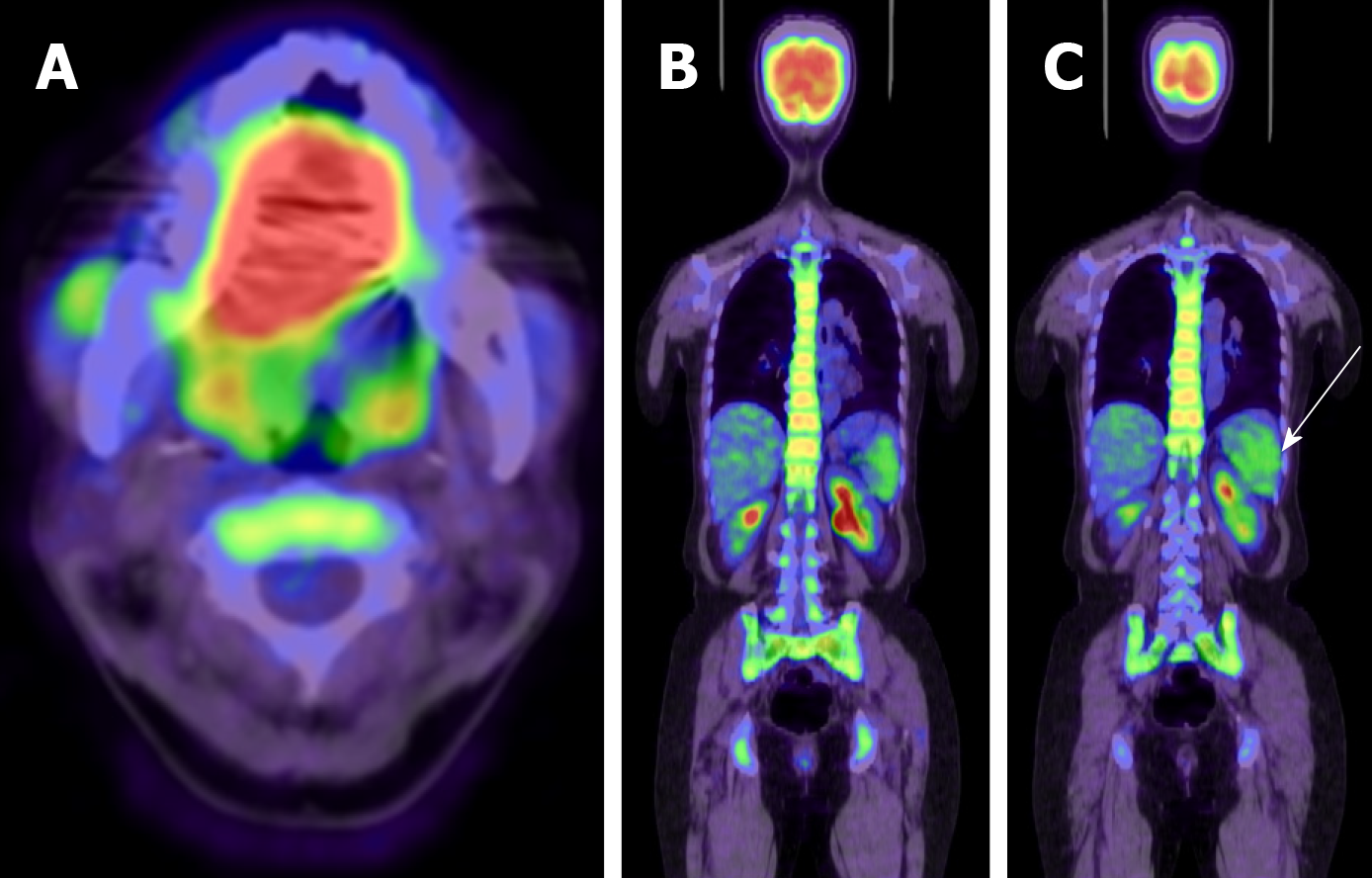
Figure 2 Positron emission tomography-computed tomography scan.
Fluorodeoxyglucose uptake was observed in the primary tumor (A), bone marrow (B), and spleen (C). Fluorodeoxyglucose accumulated in bone marrow throughout whole body in (B). White arrow shows fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation in the spleen.
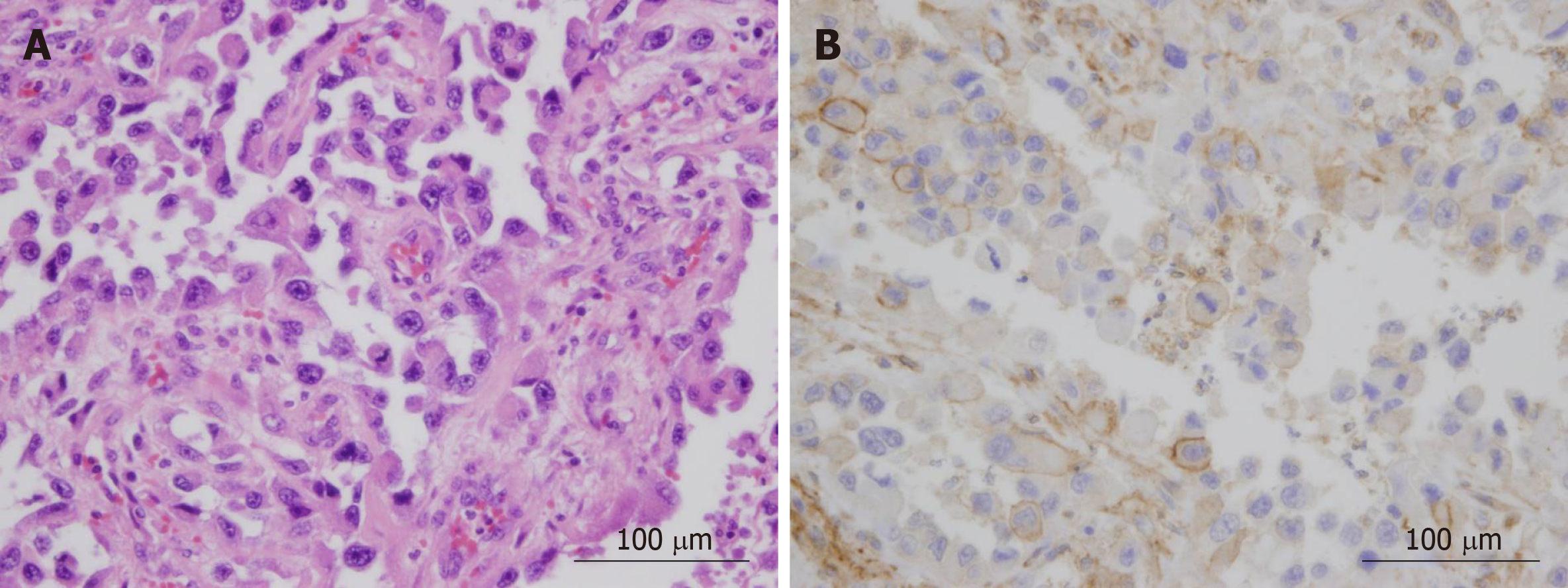
Figure 3 Hematoxylin and eosin (A) and immunohistochemical staining of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (B) of primary tumor.
Cell membrane and cytoplasm of cancer cells was positive for granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.
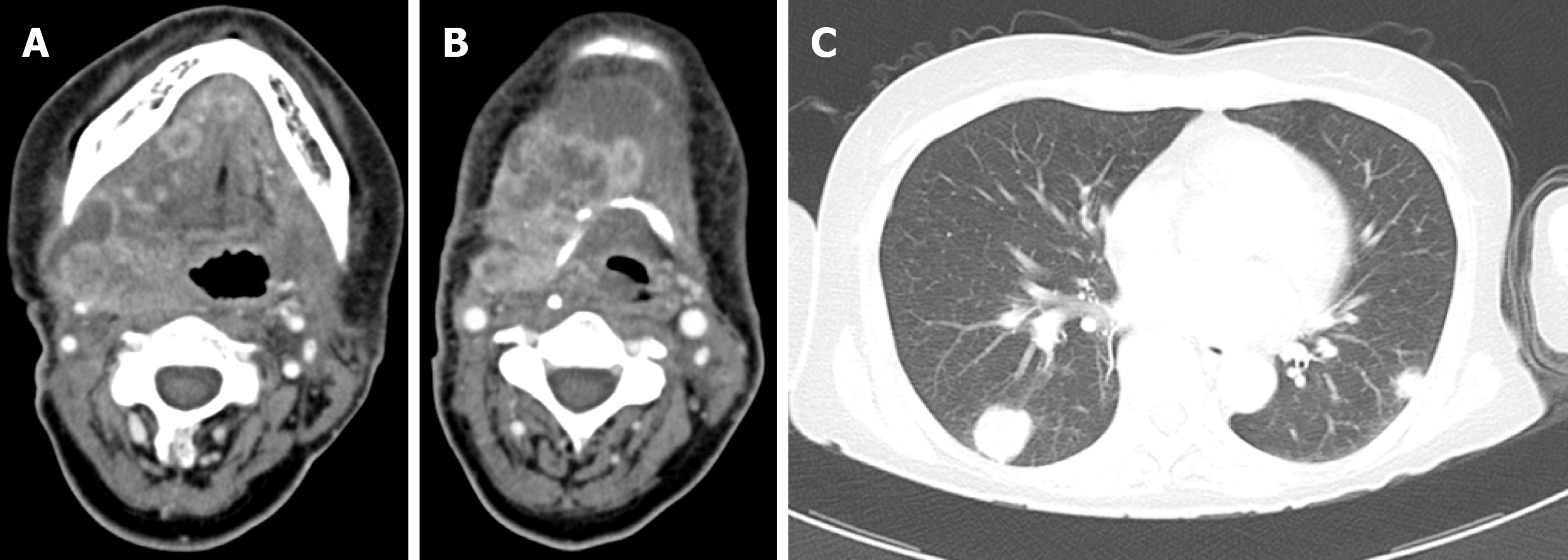
Figure 4 Computed tomography revealed the presence of recurrence in the neck (A, B), accompanied by multiple metastases in the lungs (C) on postoperative day 18.
- Citation: Shimamoto H, Hirota Y, Kashima Y, Kinoshita N, Yokokawa M, Ikeda T, Harada H. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue exhibiting characteristic fluorine-18 deoxyglucose accumulation on positron emission tomography–computed tomography: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(9): 1666-1673
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i9/1666.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i9.1666