Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2020; 8(5): 954-962
Published online Mar 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i5.954
Published online Mar 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i5.954
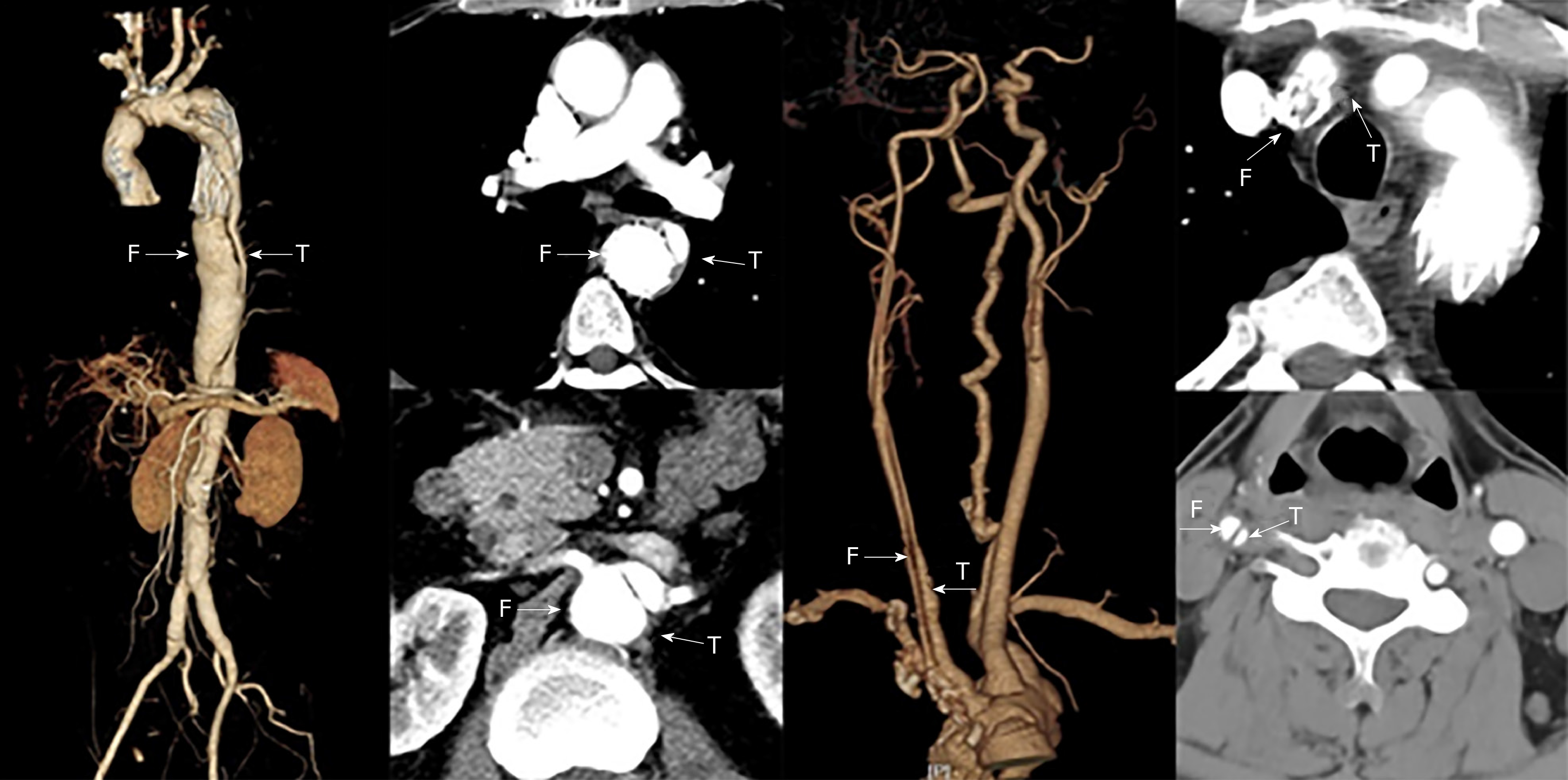
Figure 1 Preoperative computed tomography: The stents of innominate artery and thoracic aorta were located in the false lumen.
There was carotid dissection, and the distal true lumen of the aorta became smaller. T: True lumen; F: False lumen.
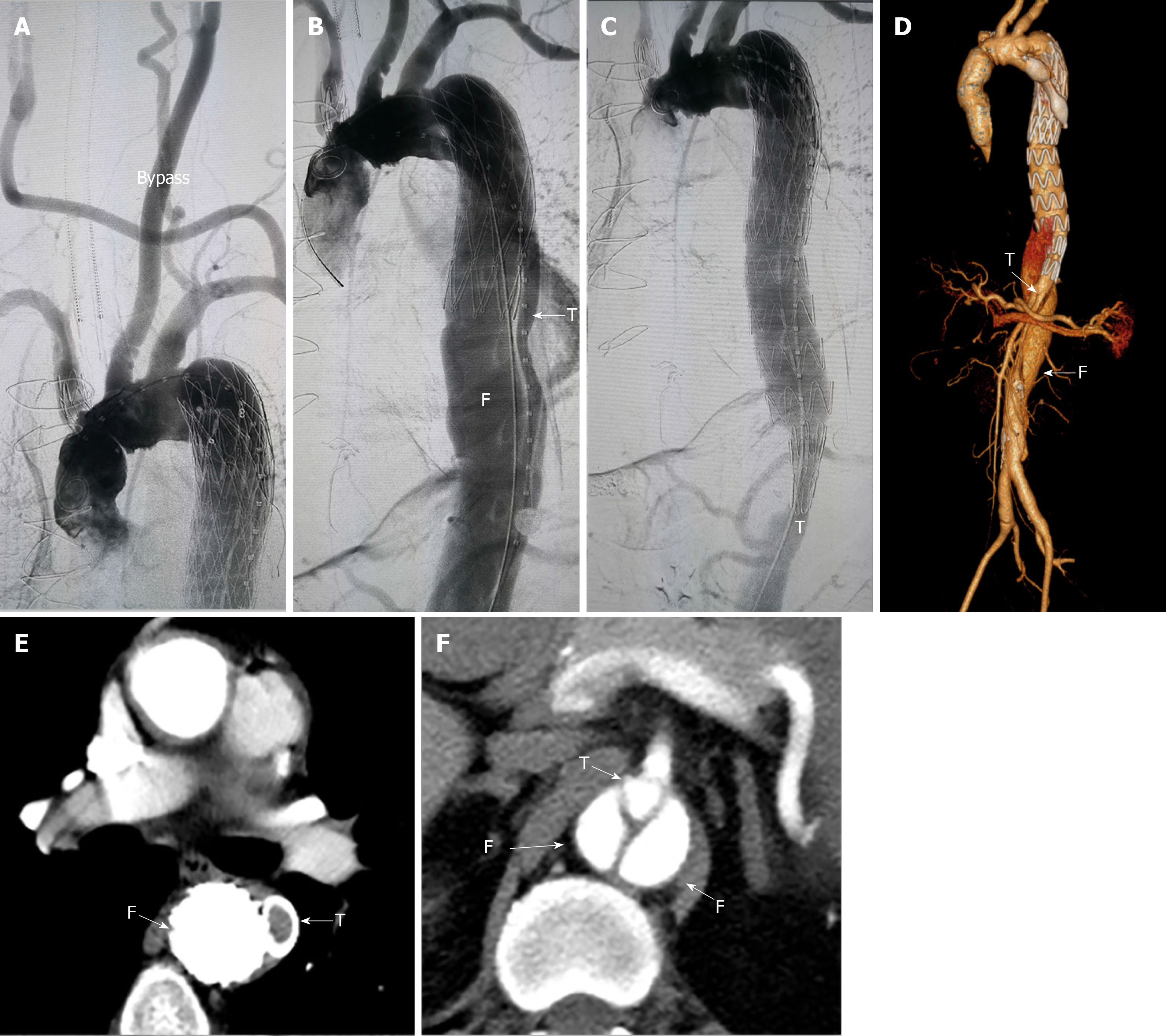
Figure 2 Treatment stage 1 computed tomography.
A: Angiography after the left subclavian artery-right carotid artery bypass; B: Preoperative angiography of the aorta showed that the stent was located in the false lumen and the true lumen was small; C: During the operation, the true lumen of aorta was sealed with an occluder and a conical stent was used to connect the proximal stent with the distal true lumen; D-F: Postoperative computed tomography showed good proximal repair and an enlarged distal false lumen. T: True lumen; F: False lumen.
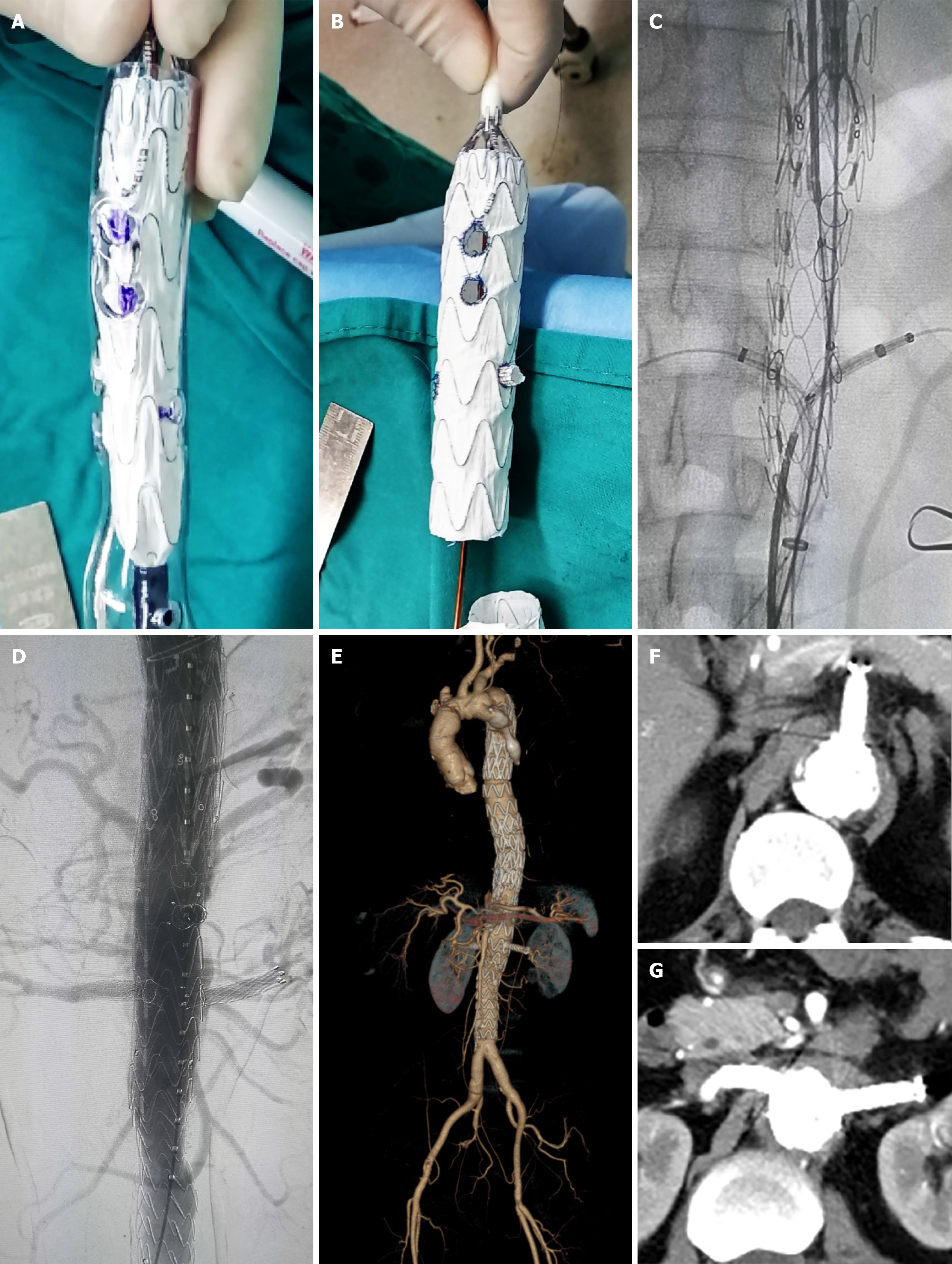
Figure 3 3D printing model, angiography, and computed tomography scan.
A, B: Release the stent in the 3D printing model and modify the stent on the stage; C, D: Intraoperative and postoperative angiography; E-G: Postoperative computed tomography scan that demonstrates successful thoracic and abdominal aortic dissection repair with patency of all target vessels.
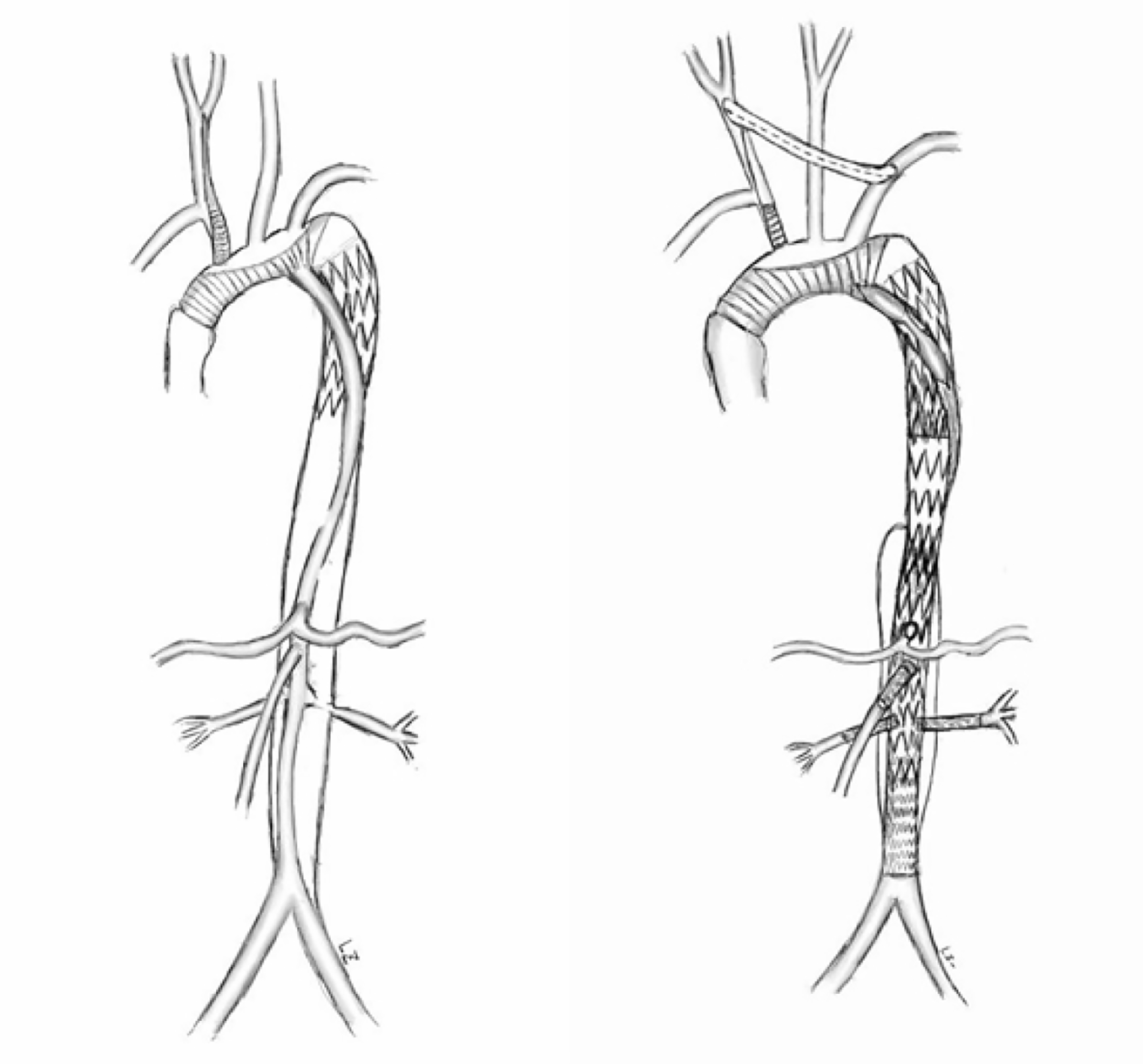
Figure 4 Operation diagram.
- Citation: Li XR, Tong YH, Li XQ, Liu CJ, Liu C, Liu Z. Total endovascular repair of an intraoperative stent-graft deployed in the false lumen of Stanford type A aortic dissection: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(5): 954-962
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i5/954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i5.954