Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2020; 8(5): 932-938
Published online Mar 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i5.932
Published online Mar 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i5.932
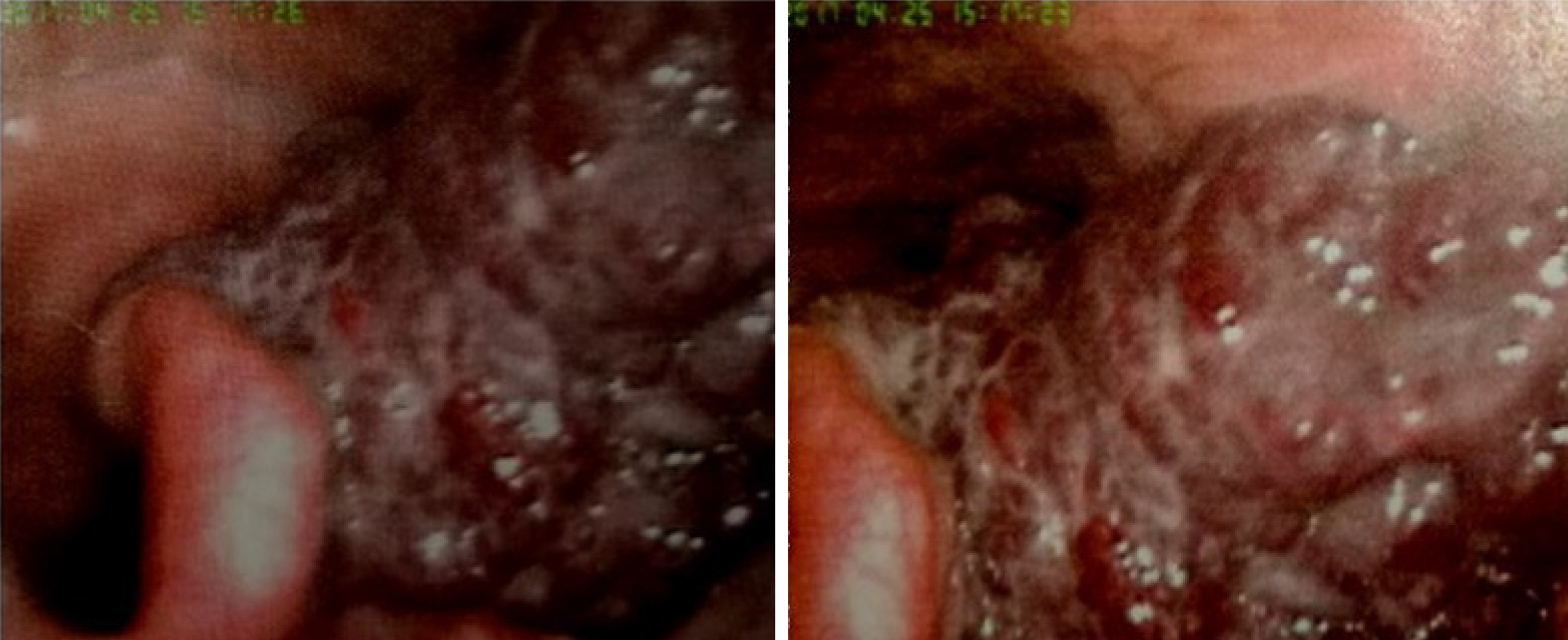
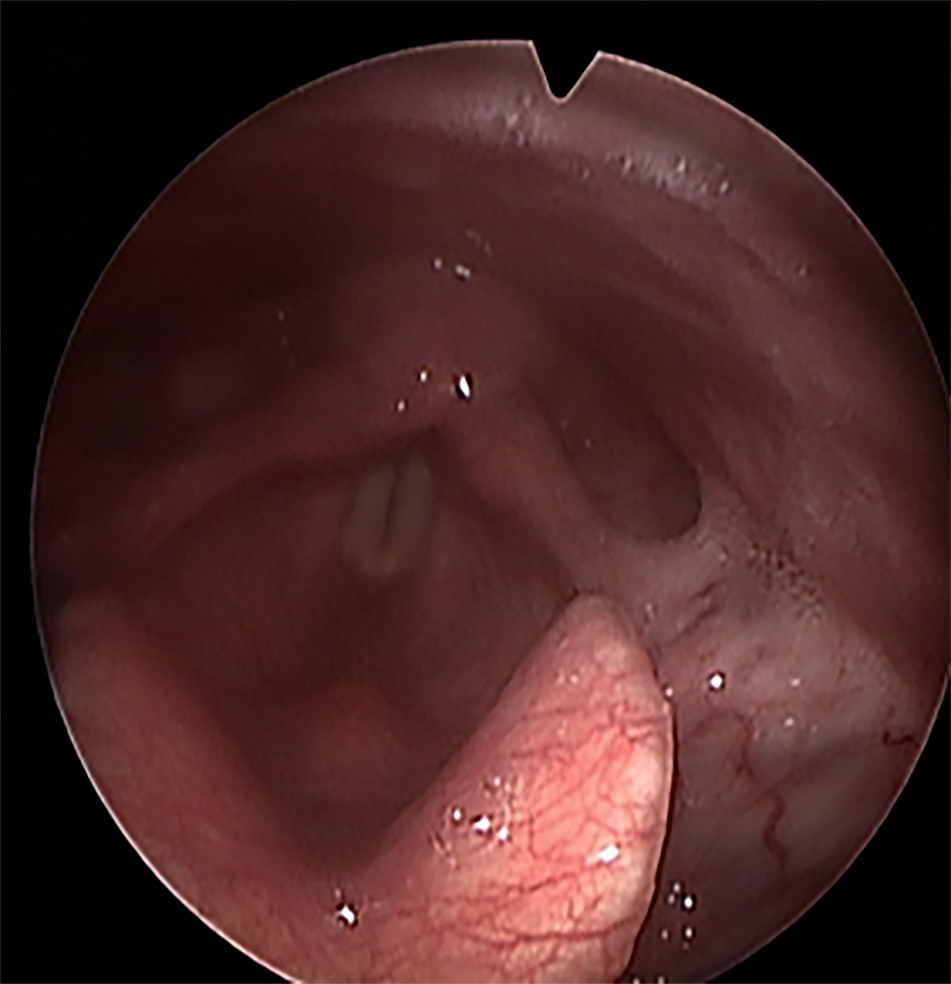
Figure 1 Preoperative laryngoscopic examination showing a hypopharyngeal hemangioma.
A submucosal vascular lesion extending into the epiglottis, left arytenoid cartilage, lateral to the aryepiglottic fold, and pyriform sinus was visualized.
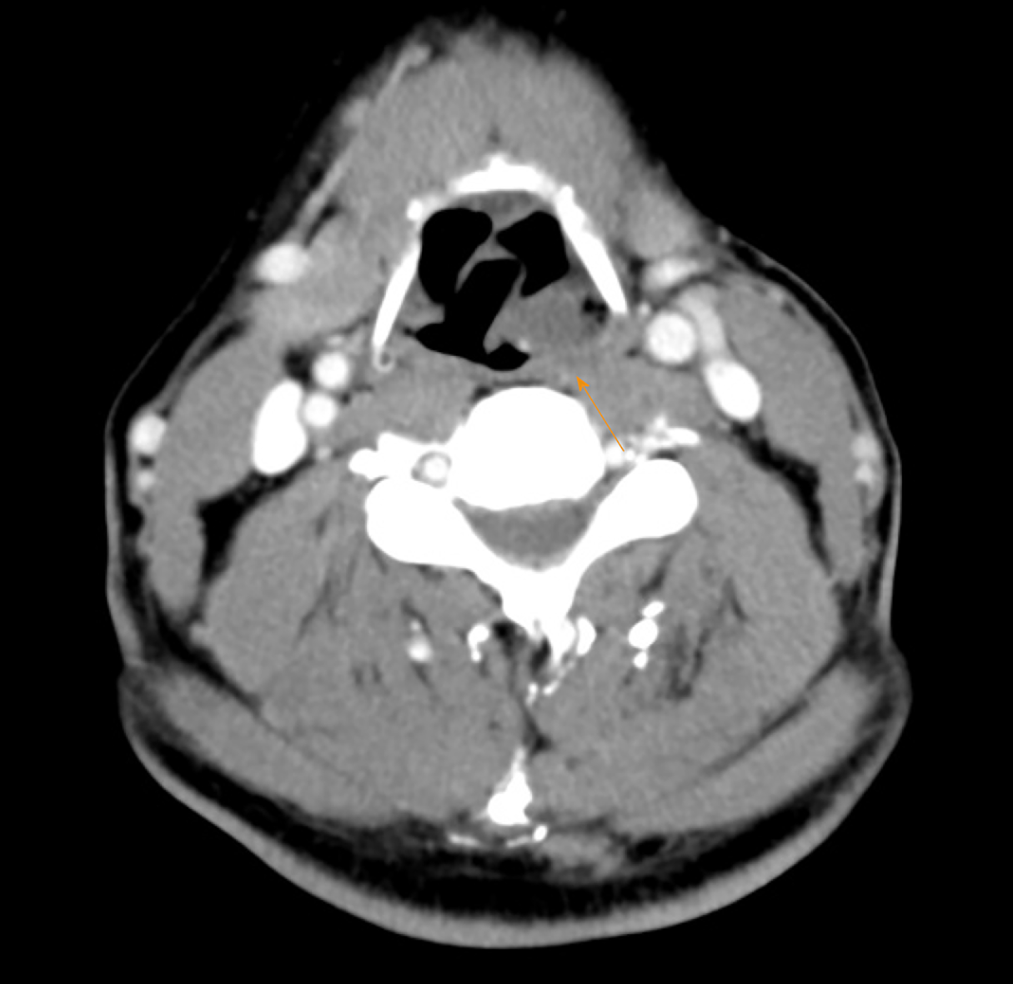
Figure 2 Computed tomography showing a vascular tumor (arrow) in the hypopharynx.
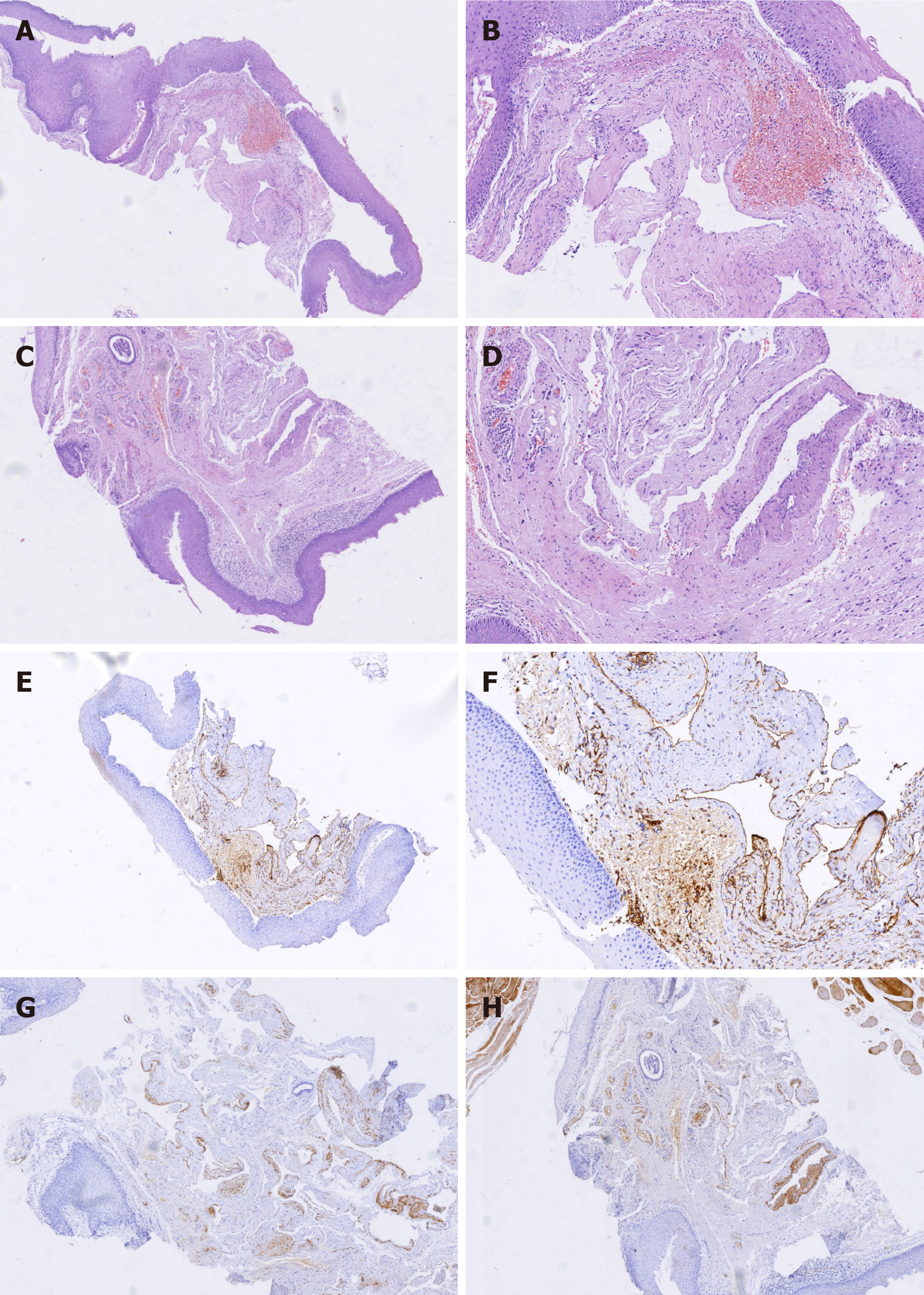
Figure 3 Histopathological examination of the tumor showed a cavernous hemangioma.
Vascular hyperplasia and hemangiectasis were observed beneath the squamous mucosal layer. A and C: Hematoxylin and eosin staining (40 ×); B and D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining (100 ×); E: Immunohistochemical staining for CD31 (40 ×); F: Immunohistochemical staining for CD31 (100 ×); G: Immunohistochemical staining for Desmin (40 ×); H: Immunohistochemical staining for Desmin (100 ×).
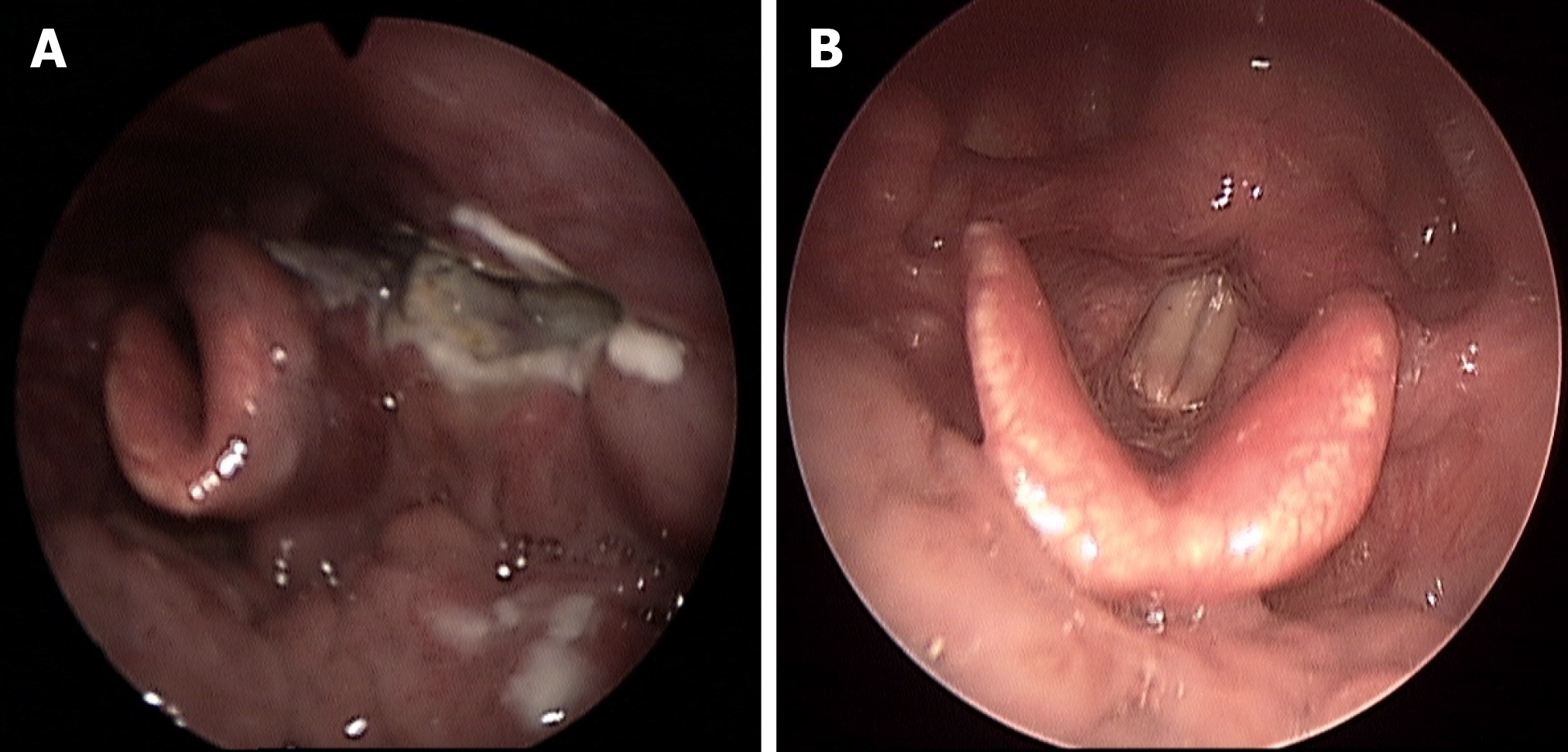
Figure 4 Postoperative laryngoscopy of the patient.
A: Laryngoscopic examination demonstrating reduced mucosal edema and absence of bleeding; B: Laryngoscopic examination showing excellent repair of the arytenoid cartilage mucosal incision.
Figure 5 Laryngoscopy performed on November 14, 2018 showed no recurrence of the hypopharyngeal hemangioma.
- Citation: Jin M, Wang CY, Da YX, Zhu W, Jiang H. Surgical resection of a large hypopharyngeal hemangioma in an adult using neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(5): 932-938
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i5/932.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i5.932