Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2020; 8(4): 831-837
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i4.831
Published online Feb 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i4.831
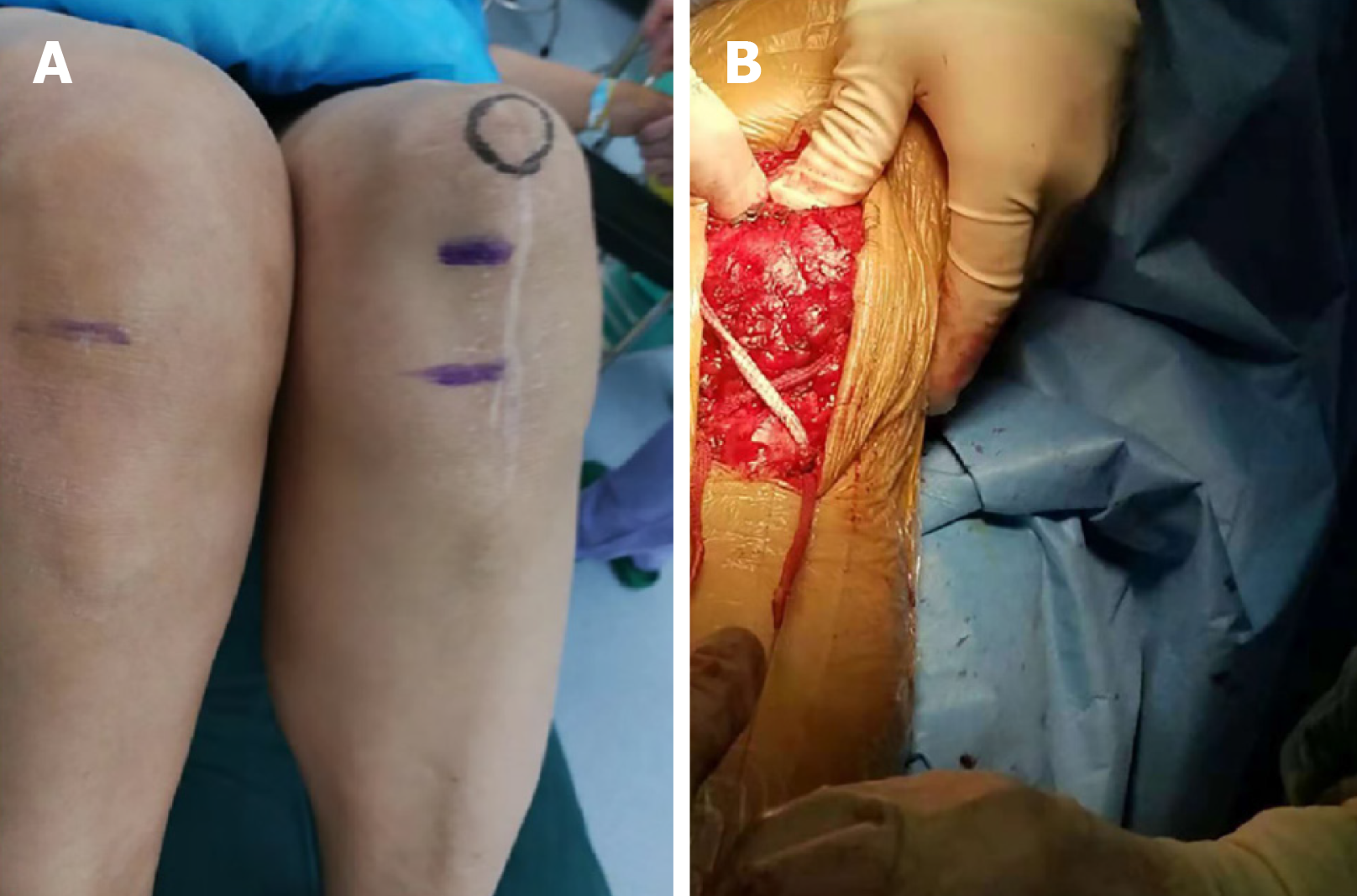
Figure 1 The physical examination and surgical technique.
A: The underlined showing the patella inferior pole of the uninjured knee, the overline showing the patella inferior pole of the injured knee; B: The image demonstrates the way in which the “figure 8” reconstruction was performed.
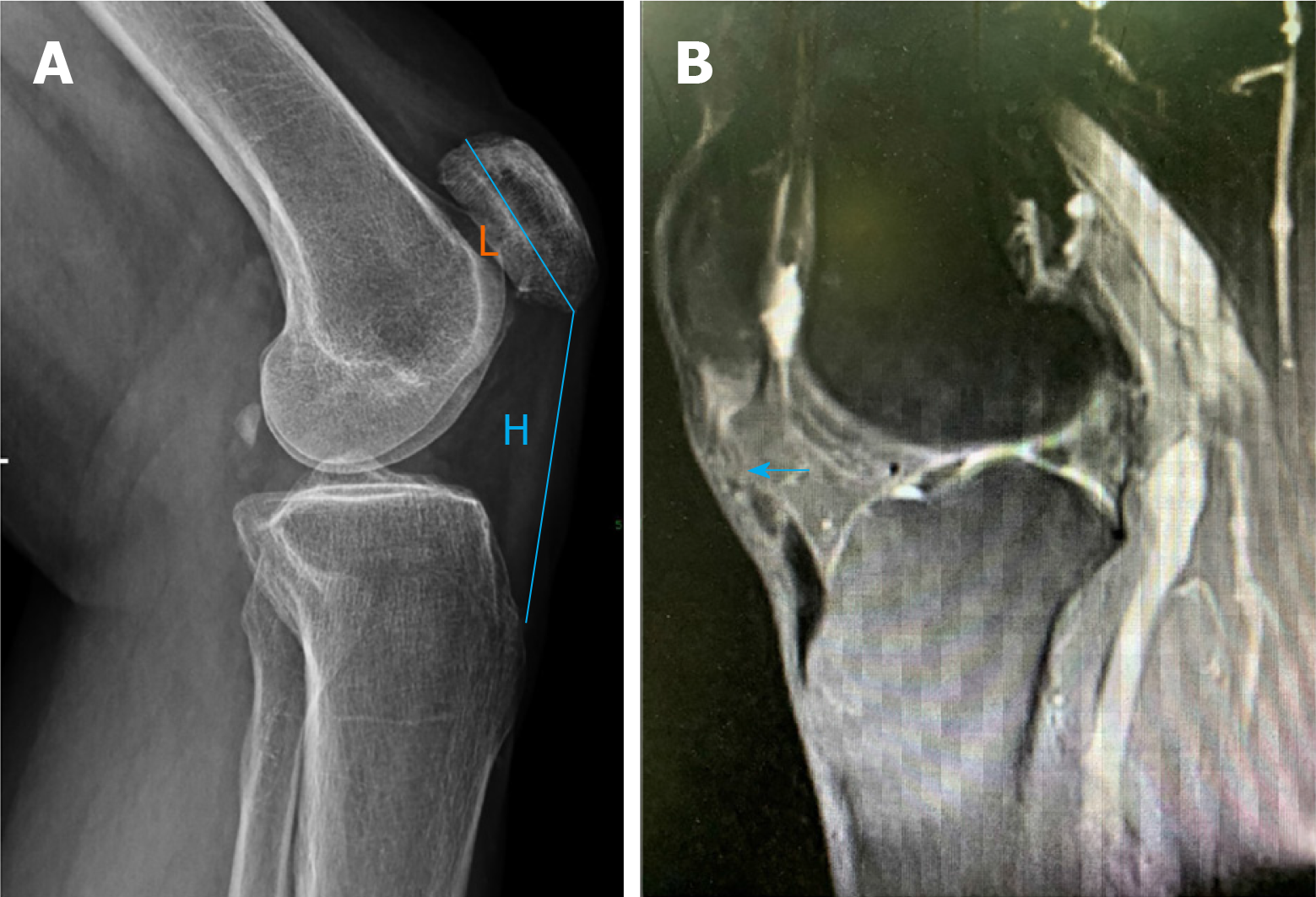
Figure 2 X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging.
A: The X-ray showing a high riding patella; B: Magnetic resonance imaging showing a rupture of the patellar tendon. Patellar tendon height (H) and patellar length (L) were used to calculate the Insall-Salvati ratio.
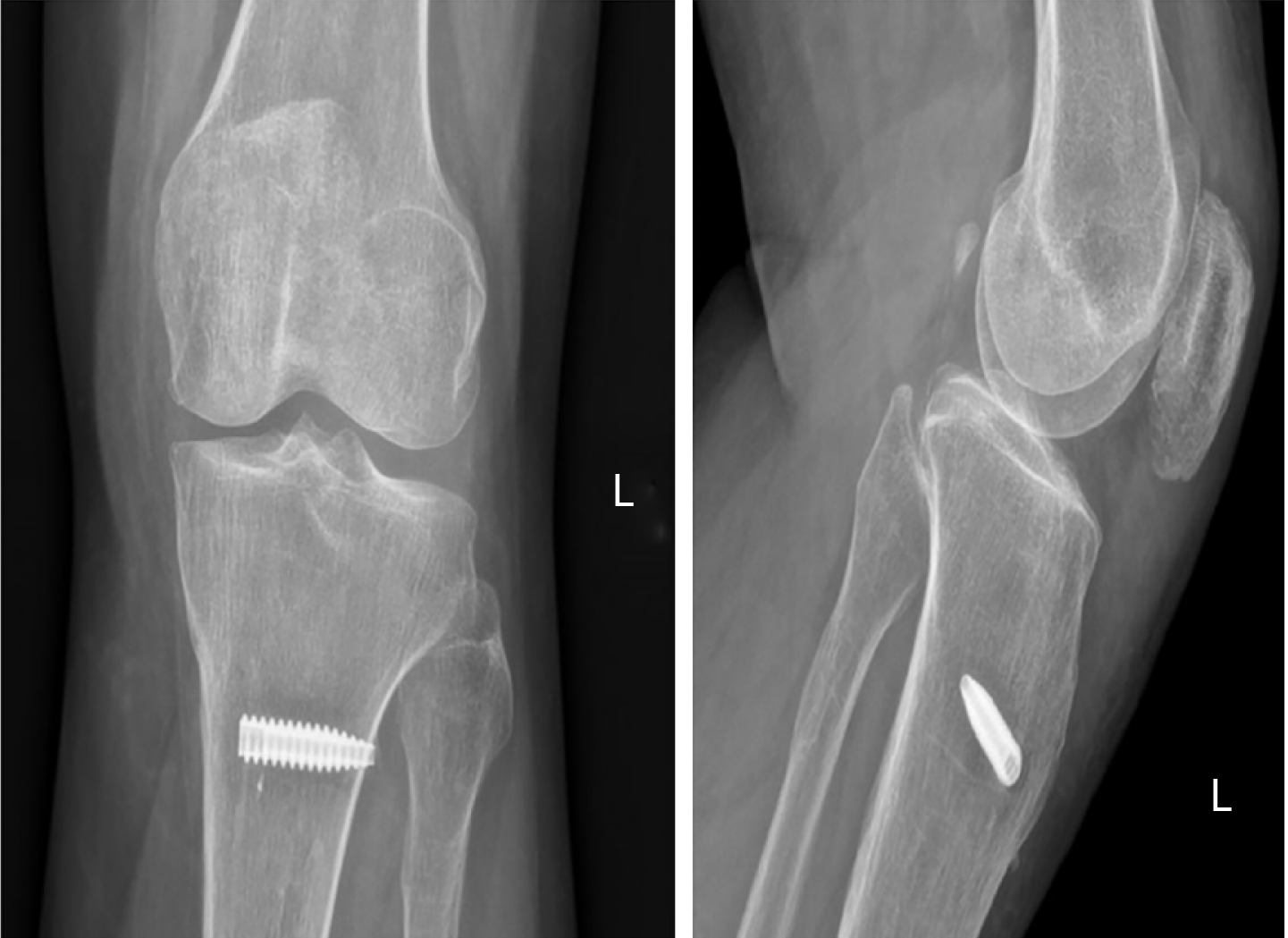
Figure 3 Post-operative X-ray showing that the patella had moved distally.
- Citation: Yang F, Wang GD, Huang R, Ma H, Zhao XW. Ligament augmentation reconstruction system artificial ligaments in patellar tendon reconstruction - a chronic patellar tendon rupture after multiple operations: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(4): 831-837
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i4/831.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i4.831