Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2020; 8(3): 577-586
Published online Feb 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i3.577
Published online Feb 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i3.577
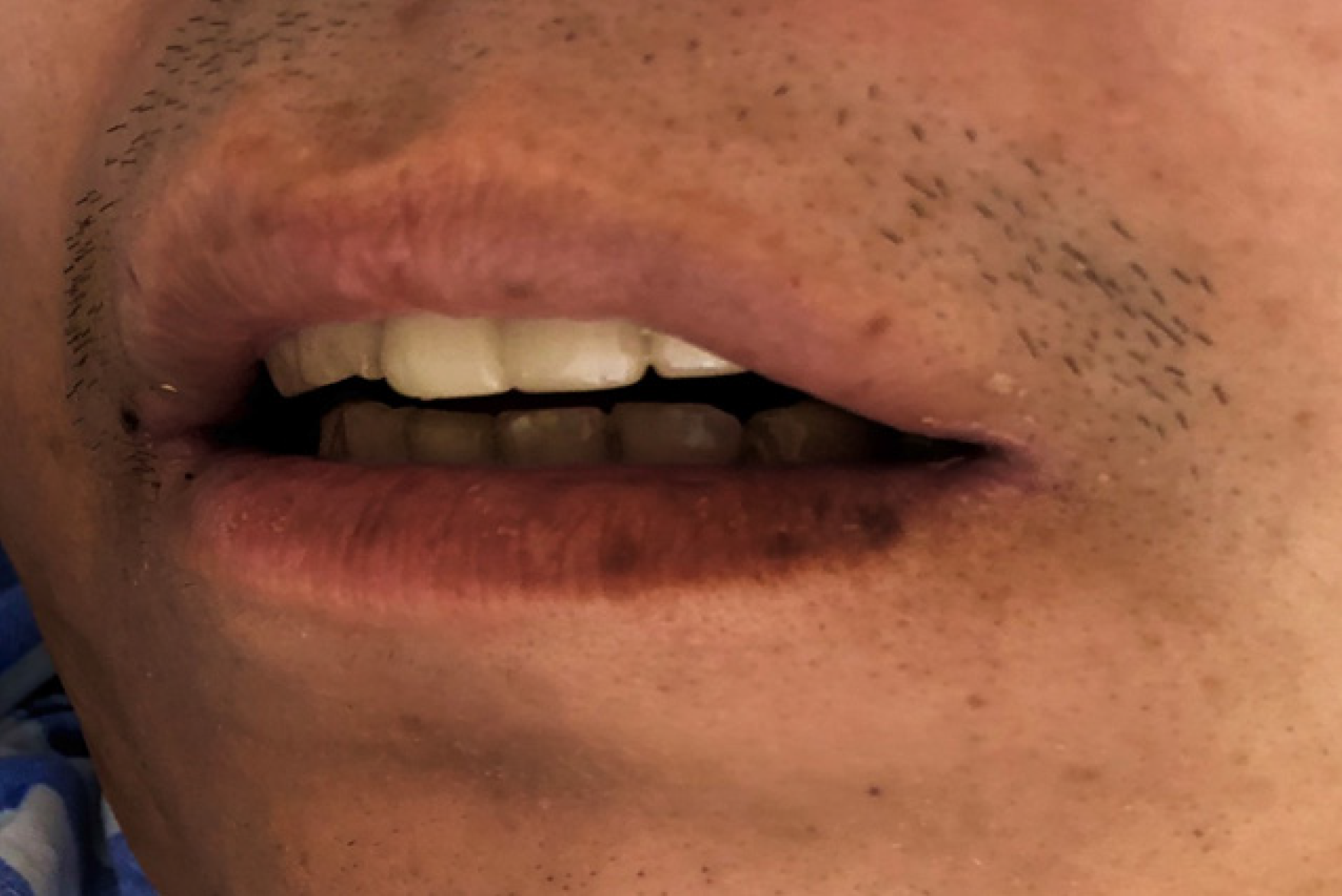
Figure 1 Multiple pigmented spots in the mouth and on the lip of the patient.
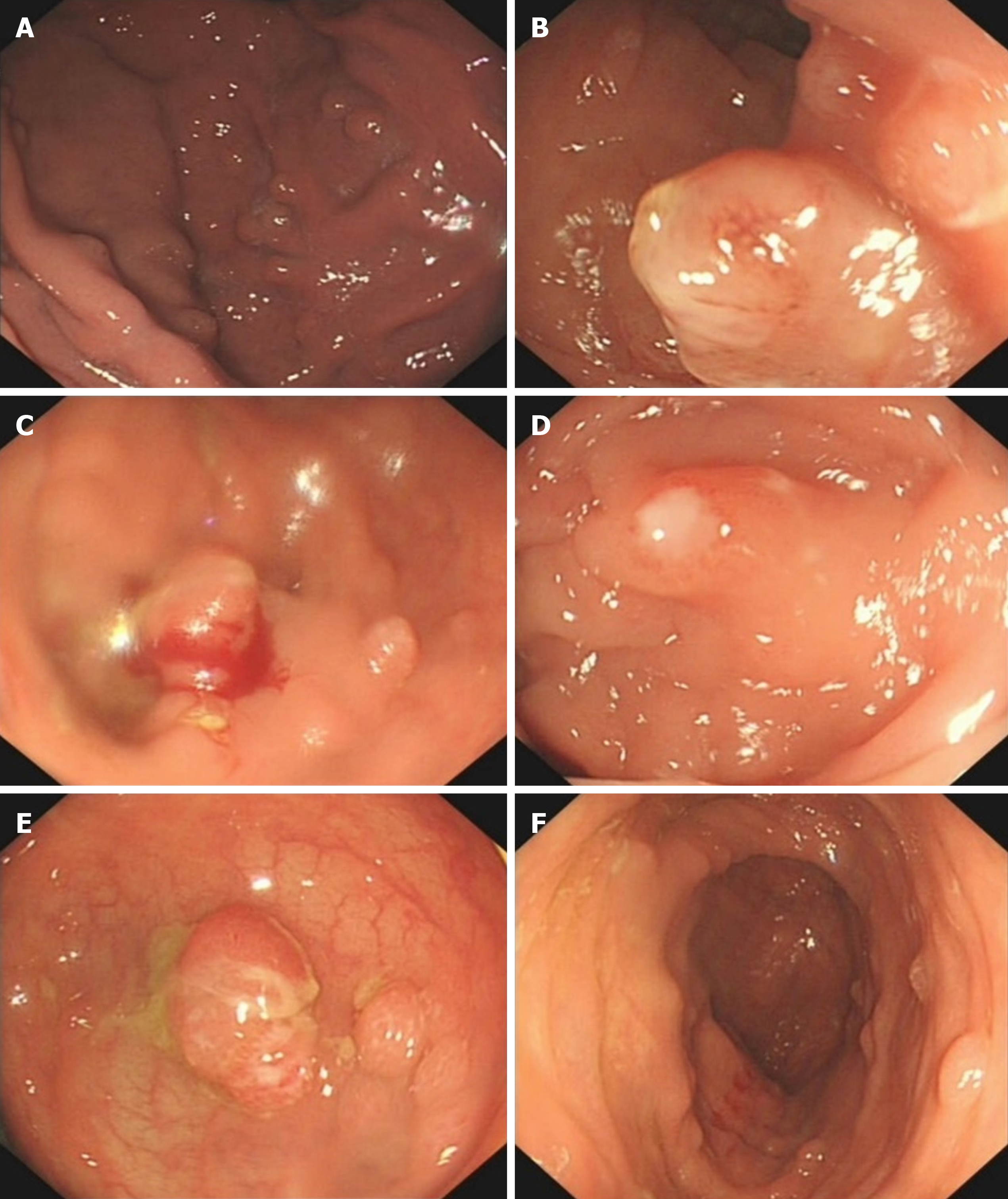
Figure 2 The patient had multiple polyps in the gastrointestinal tract.
A: Multiple soybean-sized polyps in the gastric fundus were regular and smooth; B: Some colon polyps were irregular; C: Partial colonic hemorrhage; D: Colonic polyps with surface ulcer; E: Hyperemia and edema of the surrounding mucosa; F: Multiple polyps throughout the colon.
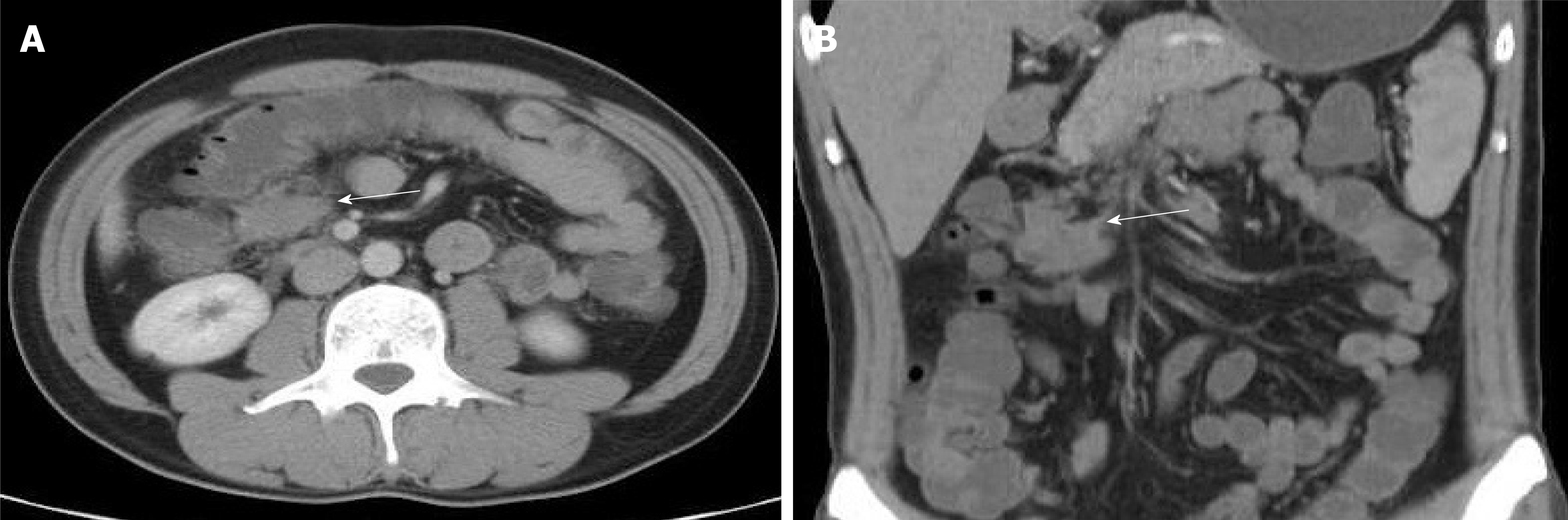
Figure 3 Enhanced computed tomography images revealing mesenteric fibromatosis presented the first time as slightly enhanced masses in the lower right transverse colon and cloudy surrounding fat spaces (white arrows).
A: Coronal plane; B: Sagittal plane.
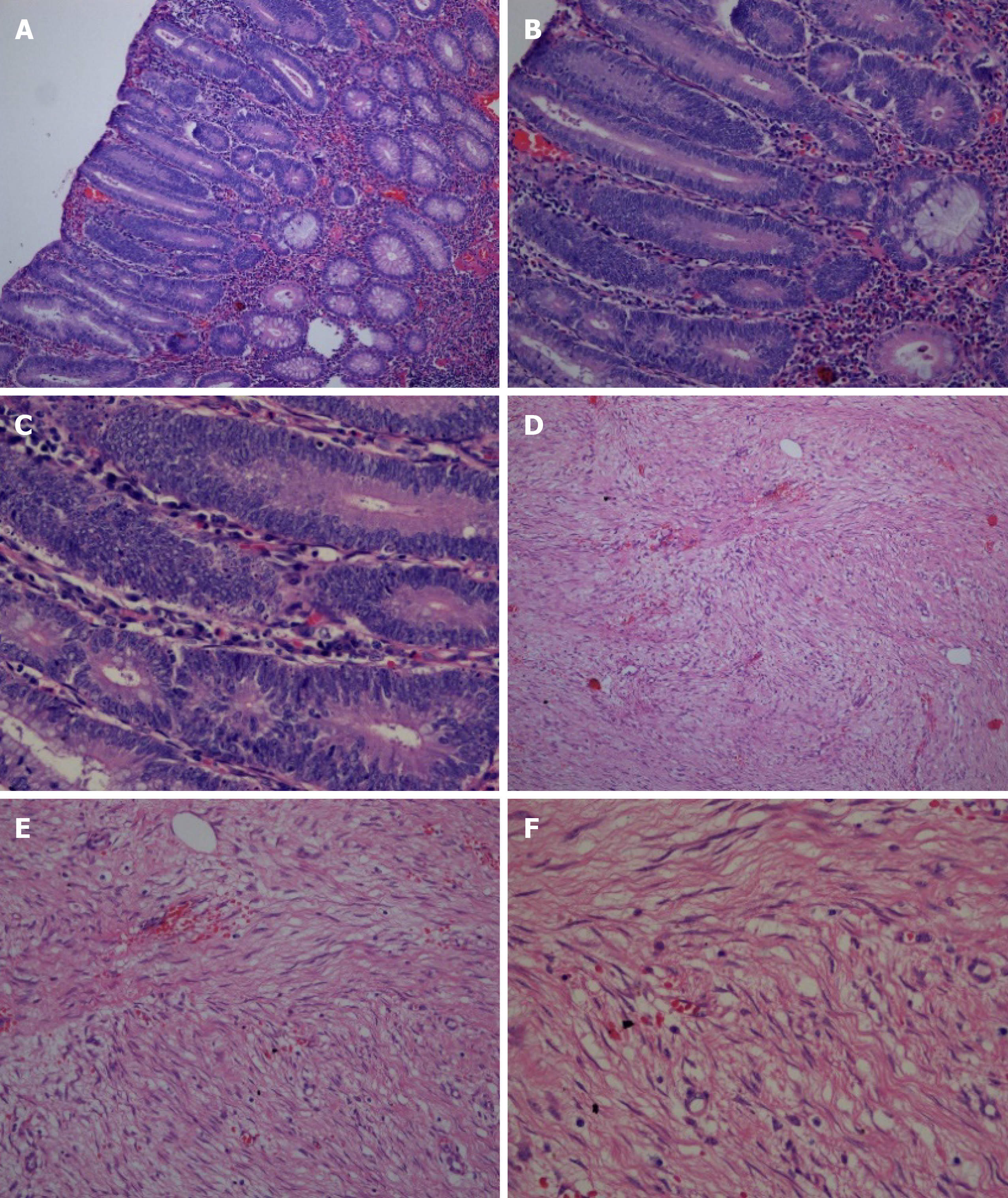
Figure 4 Pathological images of the patient.
A-C: Pathological images showed multiple tubularvillous adenomas with moderate dysplasia [A: hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, 100 ×, B: H&E staining, 200 × and C: H&E staining, 400 ×]; D-F: Fusiform cell tumor-like hyperplasia of the mesentery (D: H&E staining, 100 ×, E: H&E staining, 200 × and F: H&E staining, 400 ×).
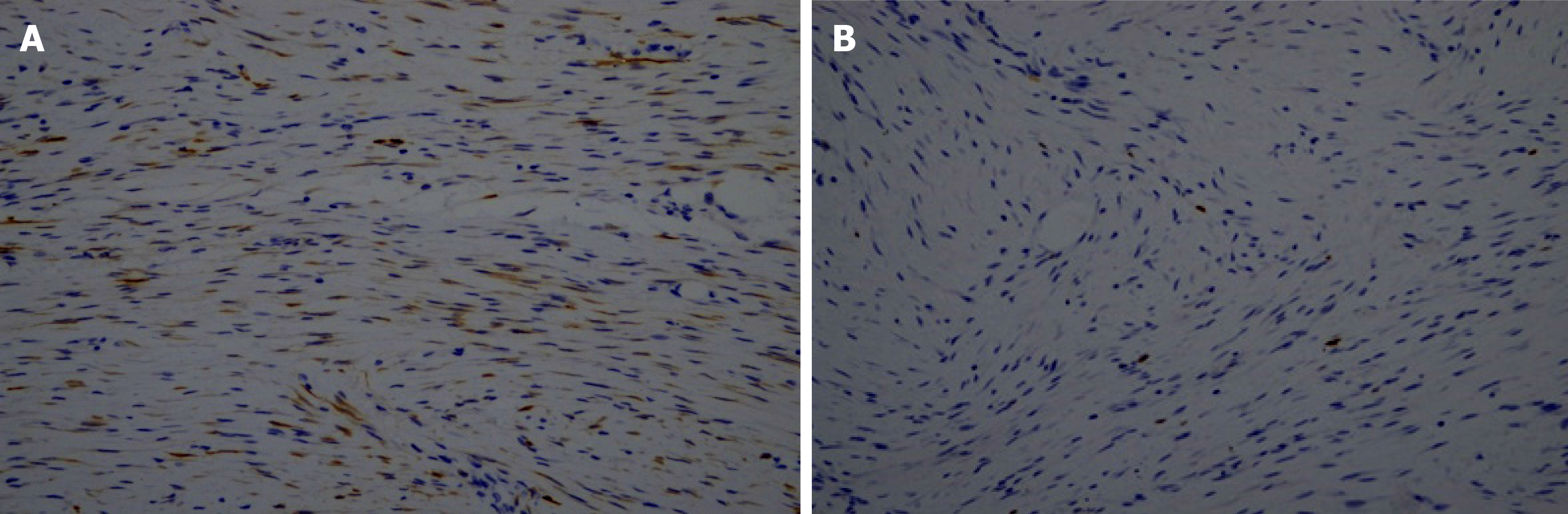
Figure 5 Immunohistochemistry images of the mesenteric fibromatosis.
A: Slight positive Calponin staining of tumor cells [immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining, 200 ×]; B: 2% Ki67 staining of tumor cells (IHC staining, 200 ×).
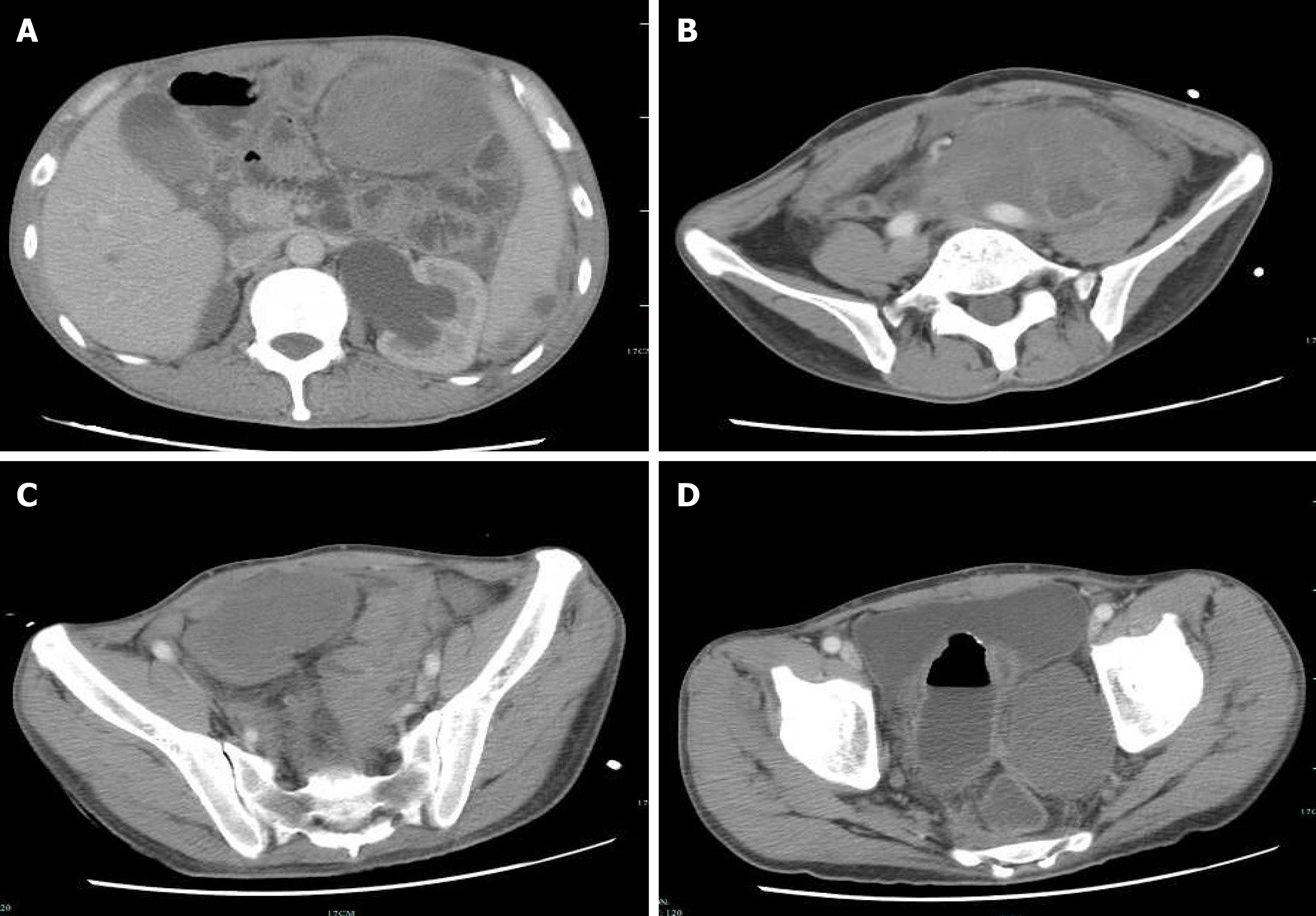
Figure 6 Second reexamination of abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography images.
A-D: The second reexamination of abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography images showed heterogeneous enhancement of multiple masses in the abdomen and pelvic cavity, and an unclear boundary between the masses and adjacent intestine.
- Citation: Cai HJ, Wang H, Cao N, Wang W, Sun XX, Huang B. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome with mesenteric fibromatosis: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(3): 577-586
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i3/577.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i3.577