Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 26, 2020; 8(18): 4245-4251
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.4245
Published online Sep 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.4245
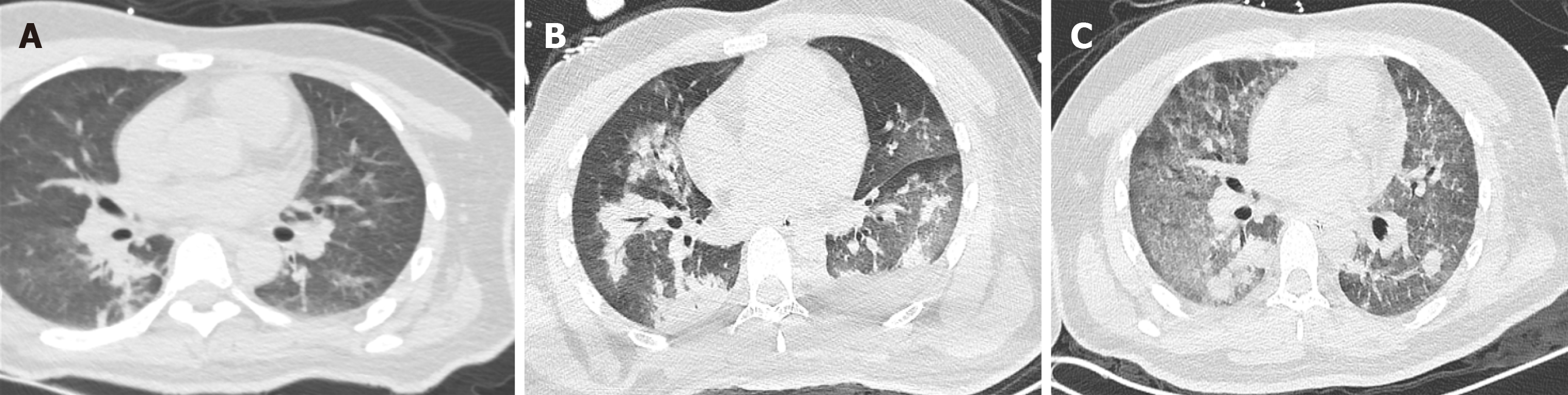
Figure 1 Changes in chest computed tomography.
A: The chest computed tomography (CT) on admission showed mild pulmonary contusion on both sides of the lung; B: The chest CT after intubation and support of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) revealed substantial consolidation in both lungs; C: The chest CT on the second day after the termination of ECMO showed resolution of the lung consolidation.
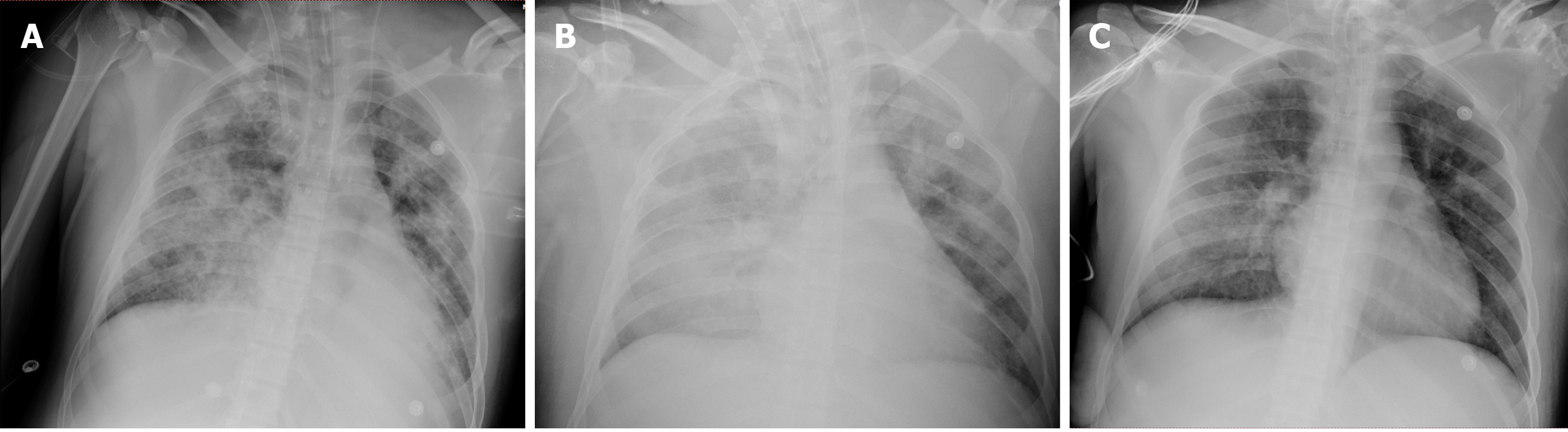
Figure 2 Changes in bedside chest X-ray.
A: The bedside chest X-ray after intubation showed diffuse infiltration in both sides of the lung; B: The bedside chest X-ray on day 3 after admission to the intensive care unit revealed persistent, severe diffuse infiltration of both the lungs; C: The bedside chest X-ray on the day before the termination of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation showed significantly decreased lung infiltration.
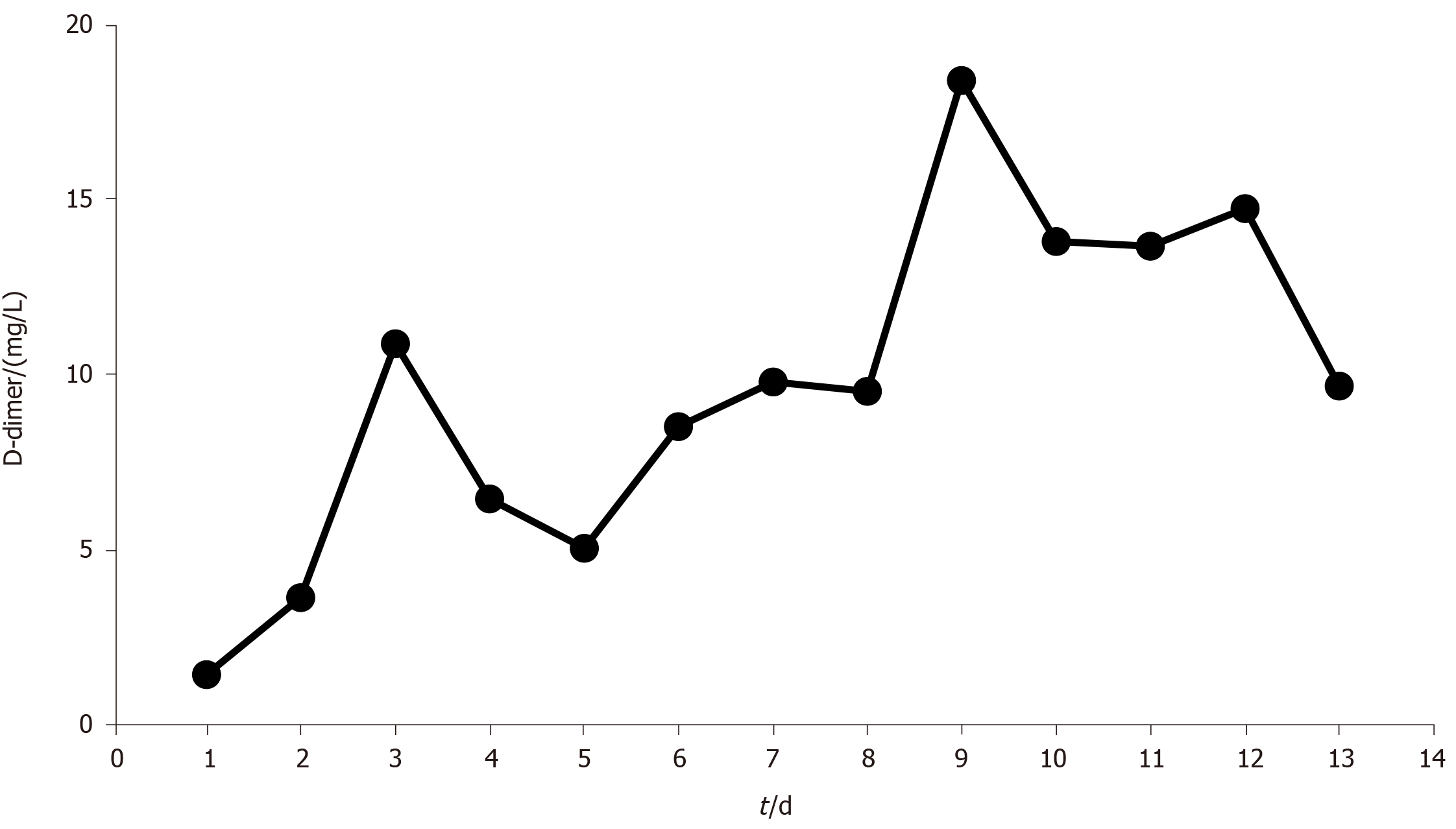
Figure 3 Trend of the D-dimer level during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
The D-dimer level gradually increased until the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was replaced on day 9 and then decreased.
- Citation: Zhang BY, Chen XC, You Y, Chen M, Yu WK. Massive pulmonary haemorrhage due to severe trauma treated with repeated alveolar lavage combined with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(18): 4245-4251
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i18/4245.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.4245