Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2020; 8(16): 3534-3541
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i16.3534
Published online Aug 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i16.3534
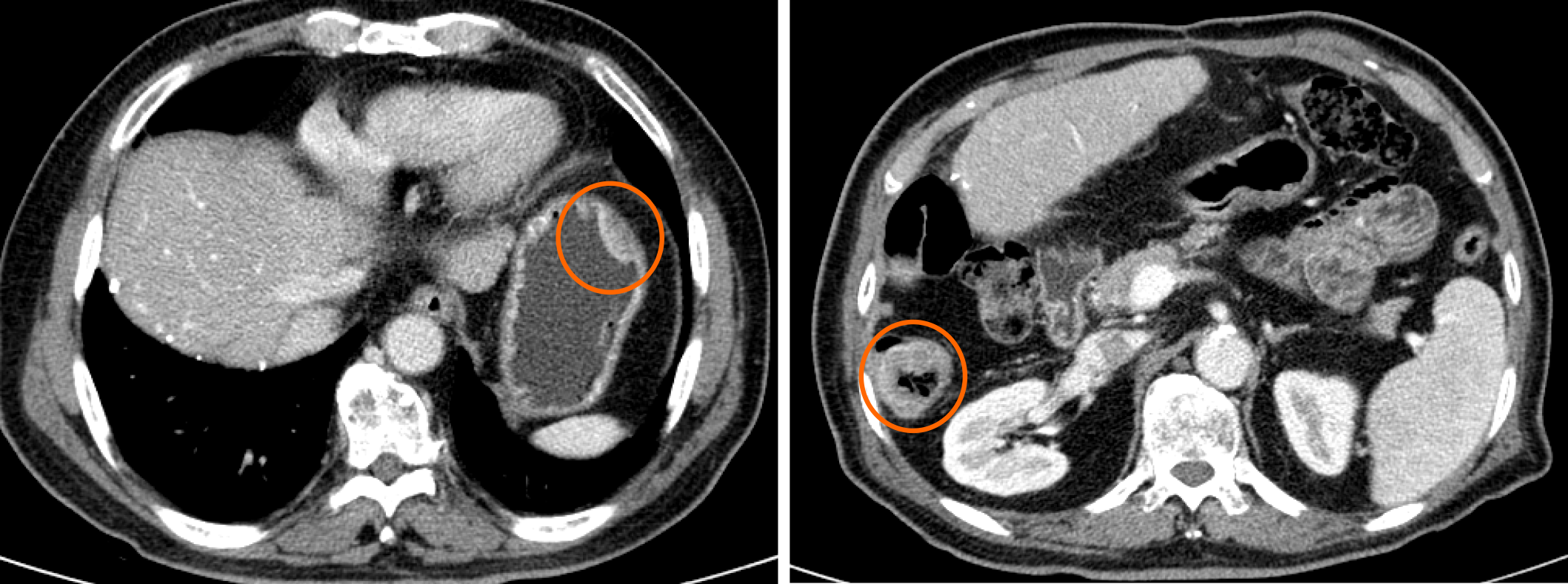
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography.
The computed tomography shows a lesion thickening the lateral wall of the stomach and another lesion partially obstructing the ascending colon (orange circle).
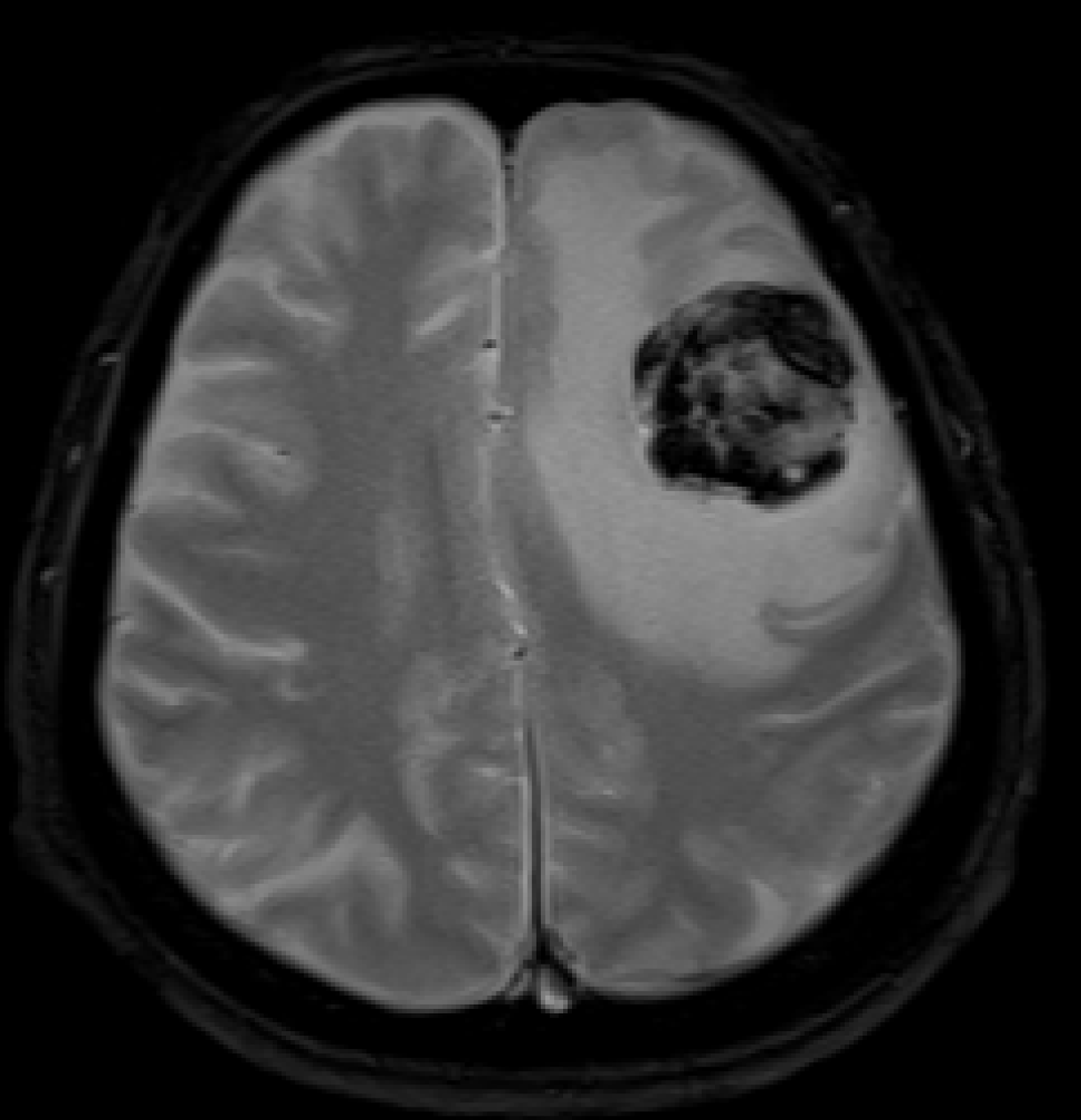
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
The magnetic resonance imaging shows a 3.8 mm enhanced brain metastasis with peritumoral edema in the left frontal lobe.
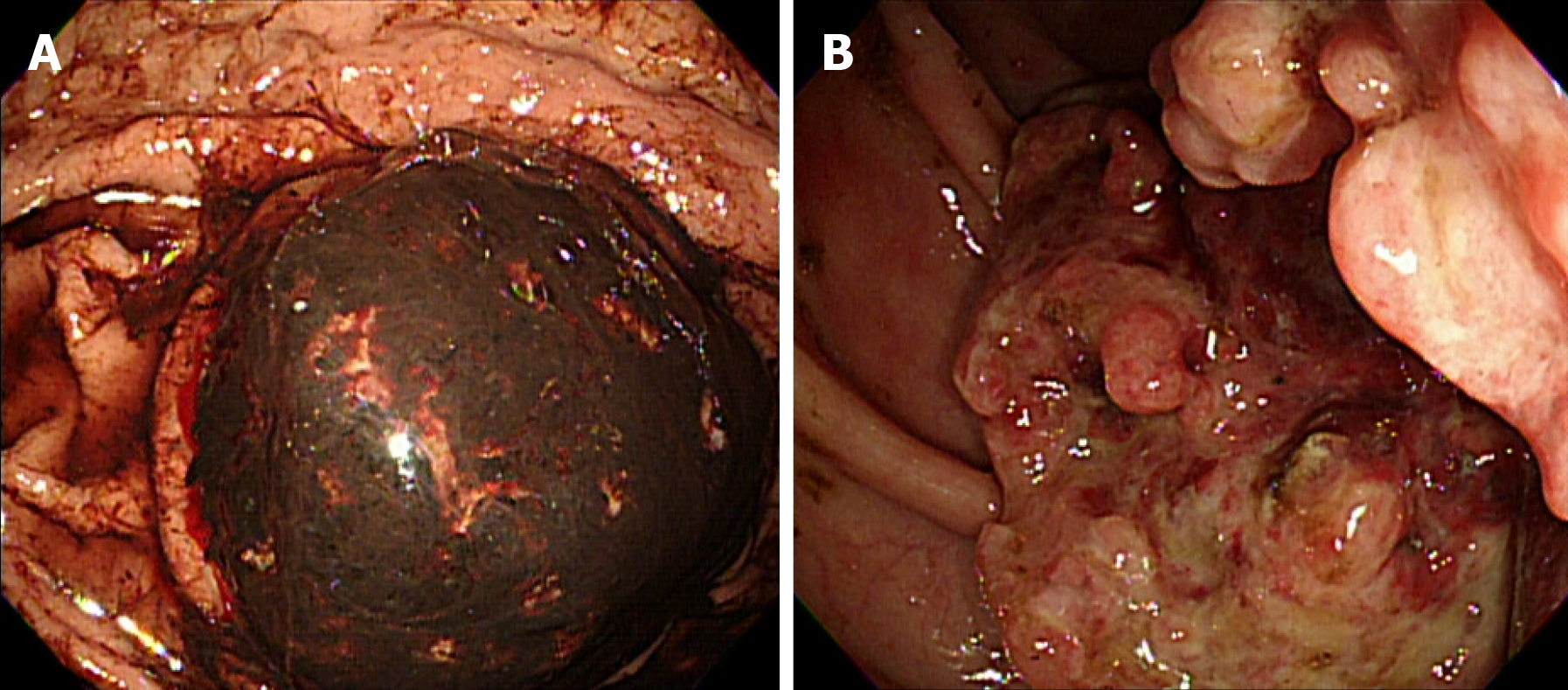
Figure 3 Endoscopic and colonoscopic views of the tumors.
A: Endoscopic view of a bleeding, ulcerofungating mass in the stomach; B: Colonoscopic view of an ulcerofungating mass partially obstructing the ascending colon.
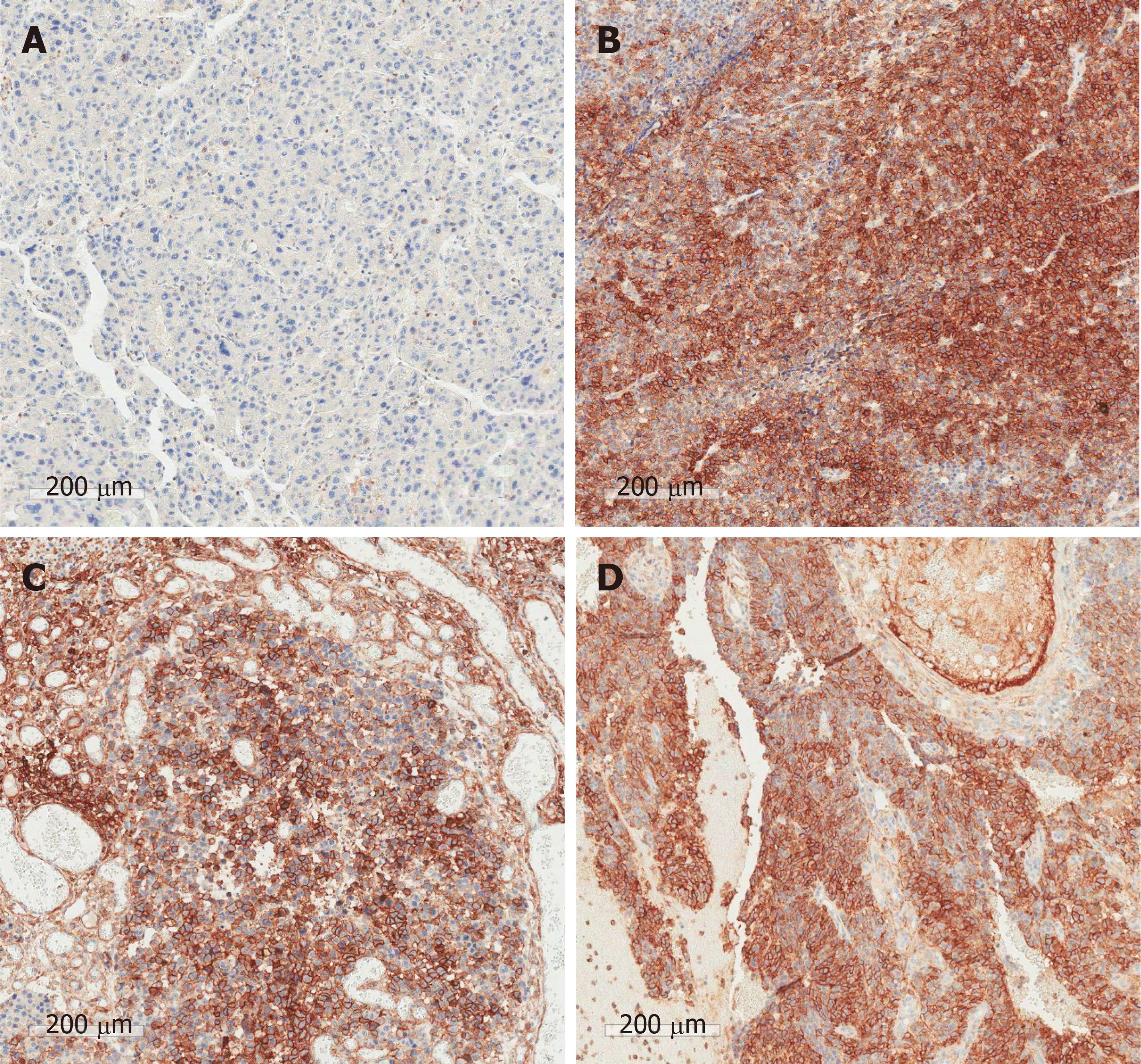
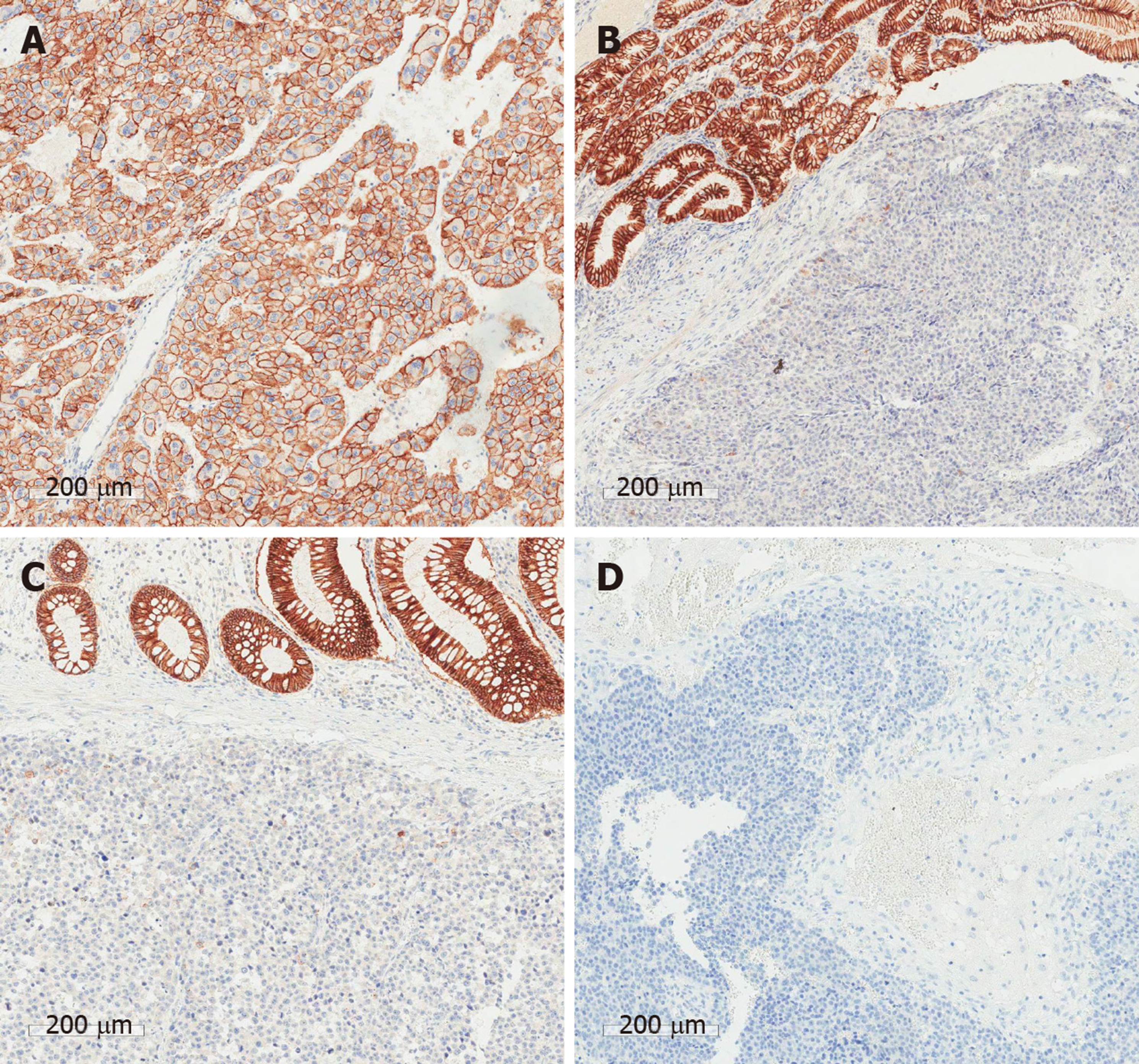
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical results.
A: Liver; B: Stomach; C: Colon; D: Brain. CD44 expression in metastatic lesions is strongly positive compared to the primary tumor.
Figure 5 Immunohistochemical results.
A: Liver; B: Stomach; C: Colon; D: Brain. E-cadherin expression of primary tumor is strongly positive compared to metastatic lesions.
- Citation: Kim R, Song J, Kim SB. Concurrent hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis to stomach, colon, and brain: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(16): 3534-3541
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i16/3534.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i16.3534