Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2020; 8(10): 1859-1870
Published online May 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1859
Published online May 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1859
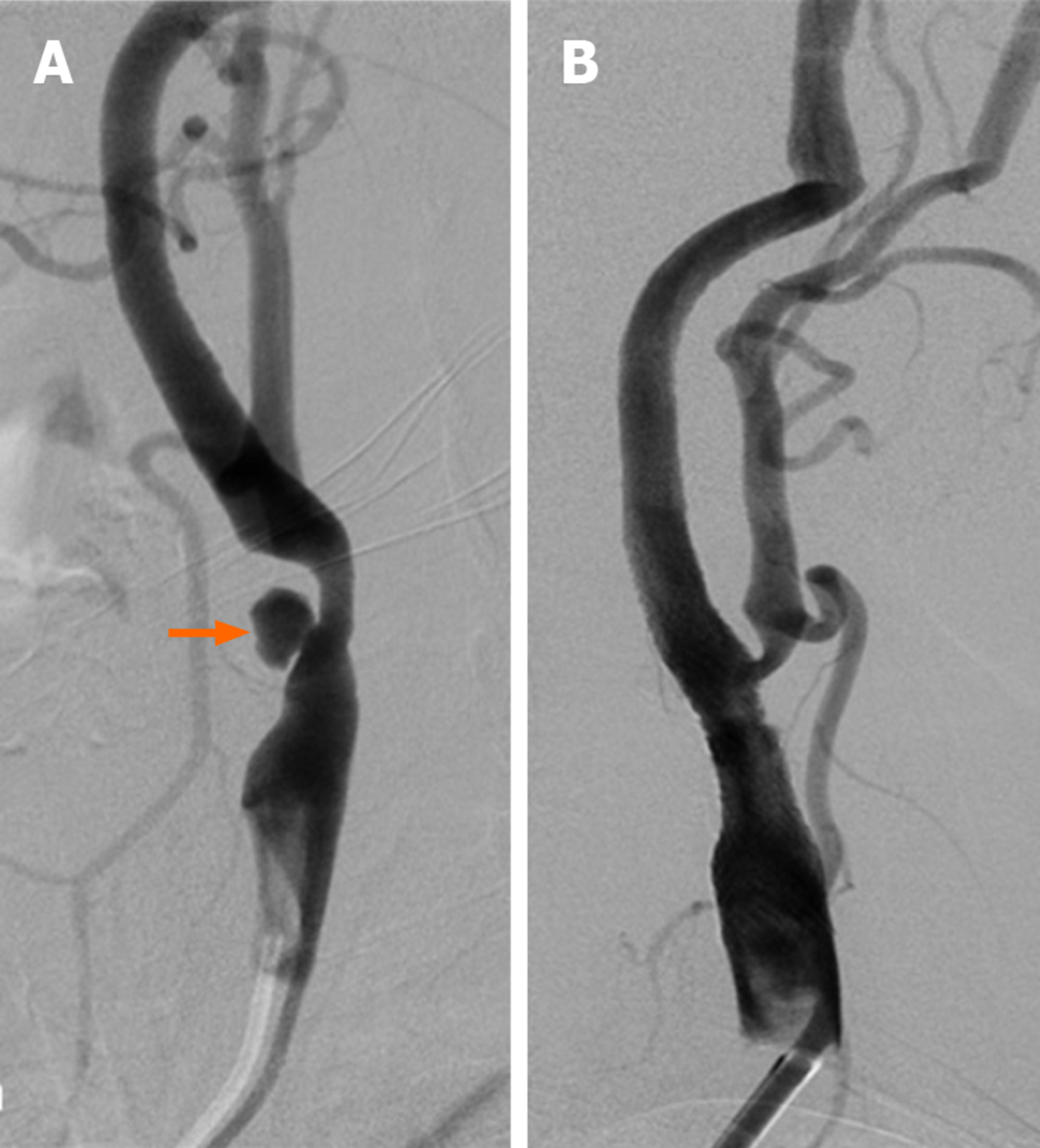
Figure 1 Fifty-five-year-old female patient with long segment ulcerated plaque (Patient no.
25). A: Appearance on digital subtraction angiography of long segment, irregular surfaced, ulcerated plaque (orange arrow) that caused 70% stenosis that originated from left common carotid artery distal region and extended to internal carotid artery bulb; B: Stenosis and ulcerated plaque disappeared on common carotid artery injection after carotid artery stenting.
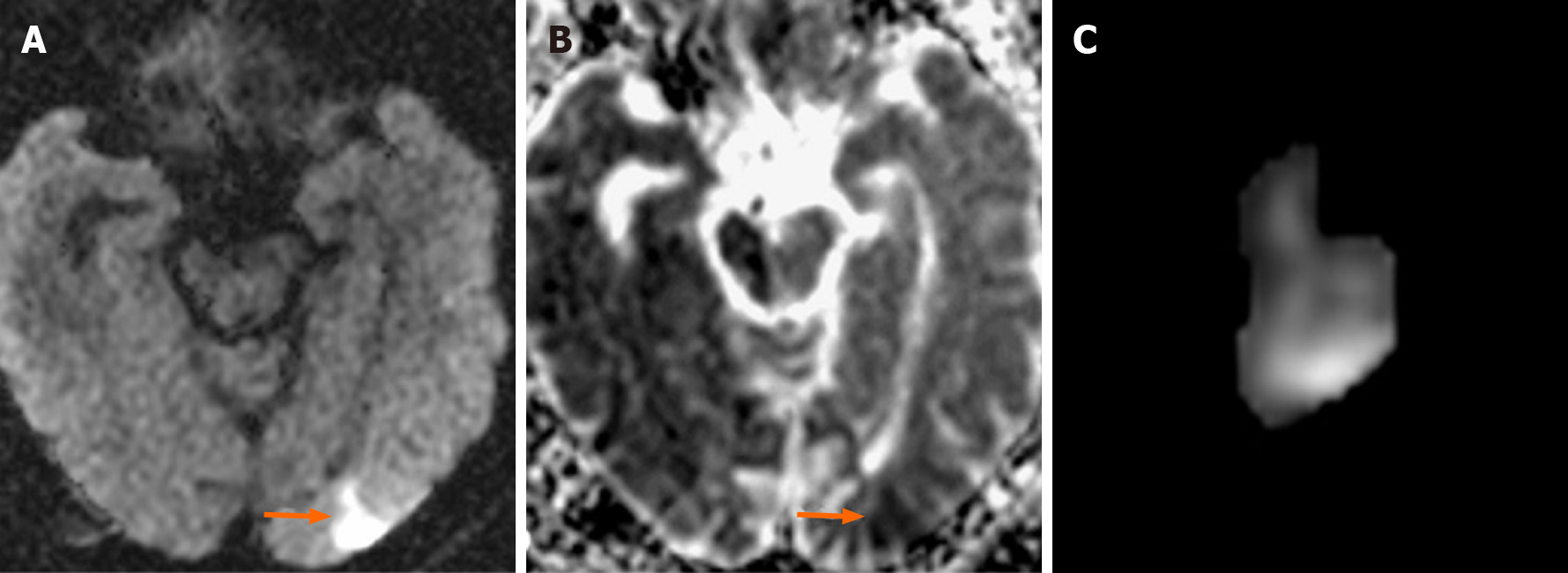
Figure 2 Seventy-six-year-old male patient with new ipsilateral ischemic lesion after left carotid artery stenting (Patient No.
29). A-B: Focal acute ischemic lesion in the occipital lobe cortical-subcortical surface that is hyperintense in diffusion-weighted imaging (arrow) but hypointense in apparent diffusion coefficient mapping (arrow); C: Ischemic lesion volume (2.730 cm³) measured by the first observer is illustrated.
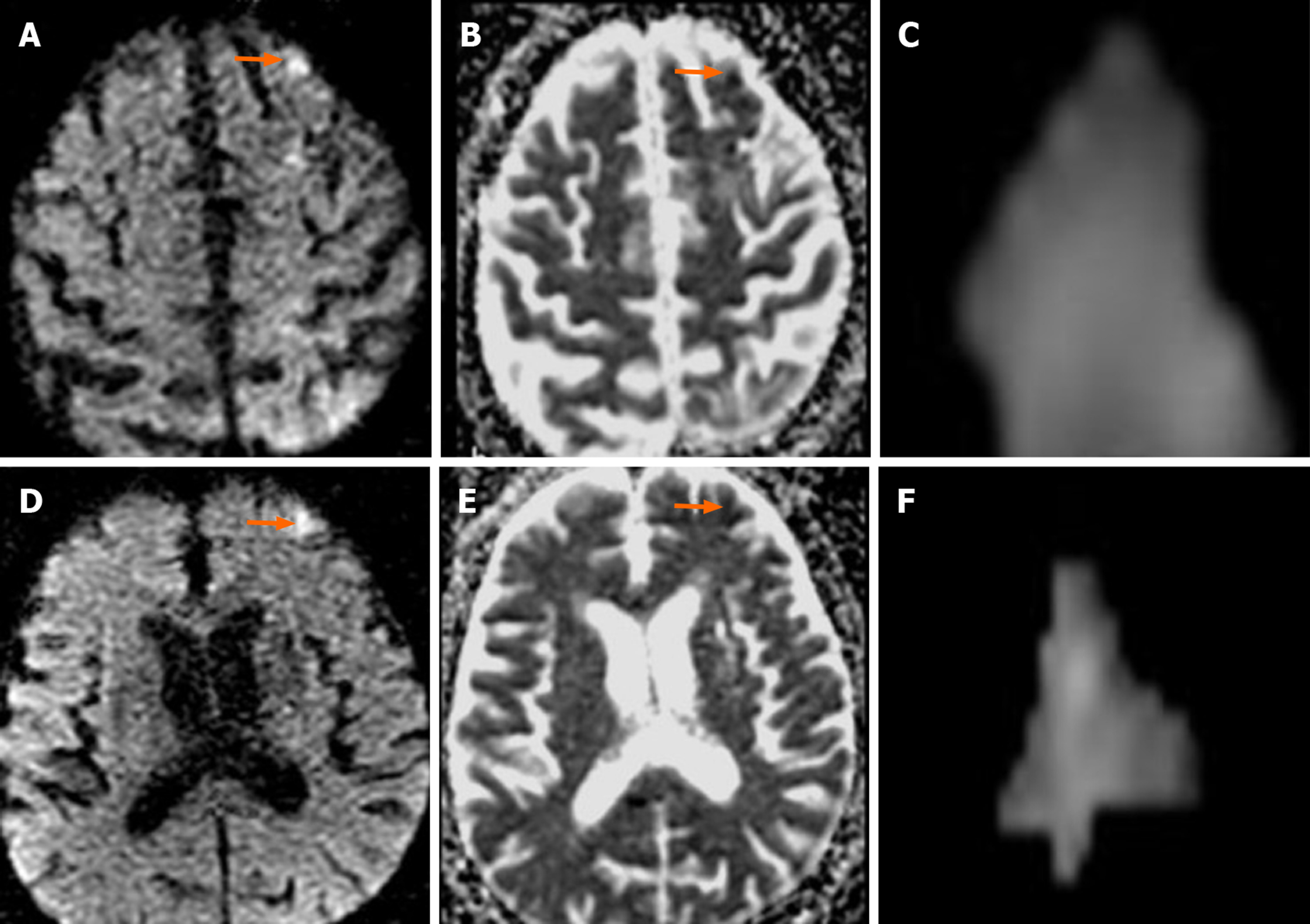
Figure 3 Sixty-eight-year-old male patient with two new ipsilateral ischemic lesions after left carotid artery stenting (Patient No.
19). A-B: Focal acute ischemic lesion in the left middle frontal gyrus cortical surface that is hyperintense in diffusion-weighted imaging (arrow) but hypointense in apparent diffusion coefficient mapping (arrow); C: Ischemic lesion volume (0.263 cm³) measured by the first observer is illustrated; D-E: Focal ischemic lesion during acute phase in the left superior frontal gyrus lateral cortical surface that is hyperintense in diffusion-weighted imaging (arrow) but hypointense in apparent diffusion coefficient mapping (arrow); F: Ischemic lesion volume (0.577 cm³) measured by the second observer is illustrated.
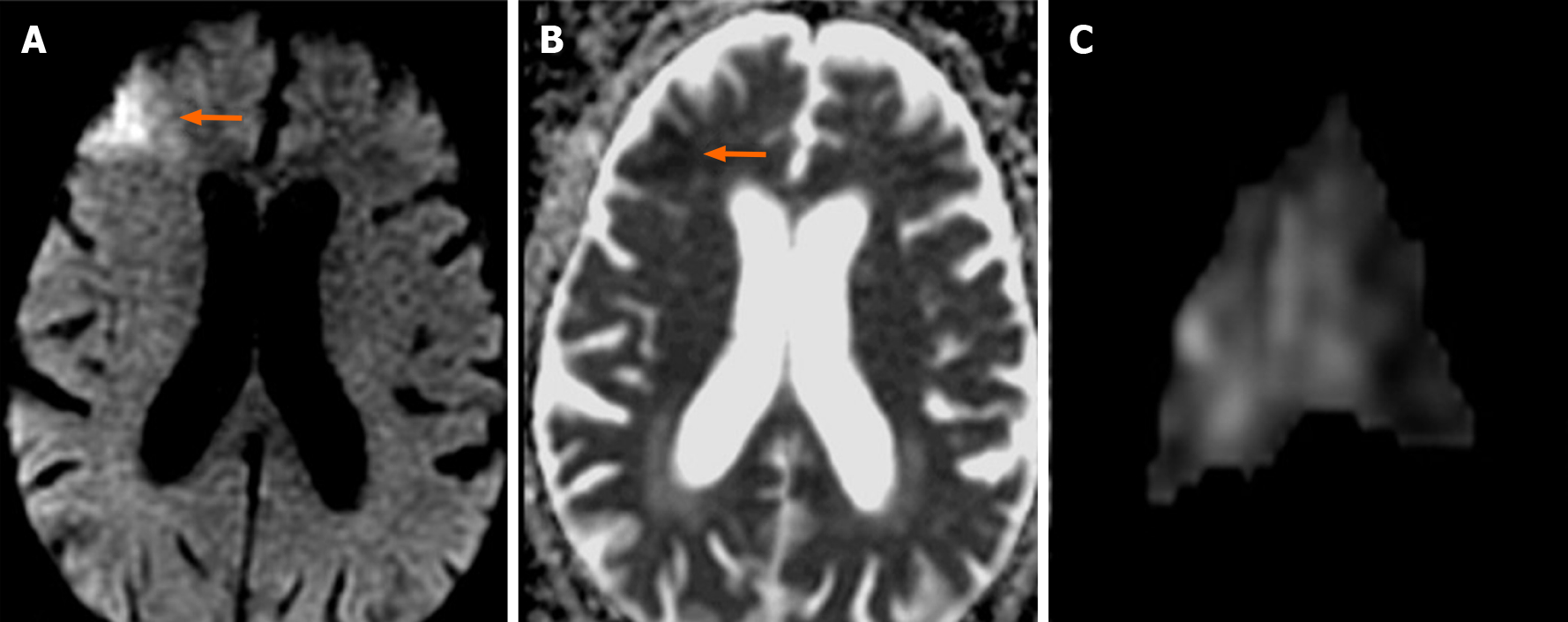
Figure 4 Eighty-four-year-old male patient with new contralateral ischemic lesion after left carotid artery stenting (Patient No.
26). A-B: Focal acute ischemic lesion in the right middle frontal gyrus cortical-subcortical surface that is hyperintense in diffusion-weighted imaging (arrow) but hypointense in apparent diffusion coefficient mapping (arrow); C: Ischemic lesion volume (5.506 cm³) measured by the first observer is illustrated.
- Citation: Beyhan M, Acu B, Gökçe E, Fırat MM. Evaluation of ischemic lesions after carotid artery stenting with diffusion-weighted imaging. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(10): 1859-1870
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i10/1859.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1859