Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2020; 8(1): 88-96
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.88
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.88
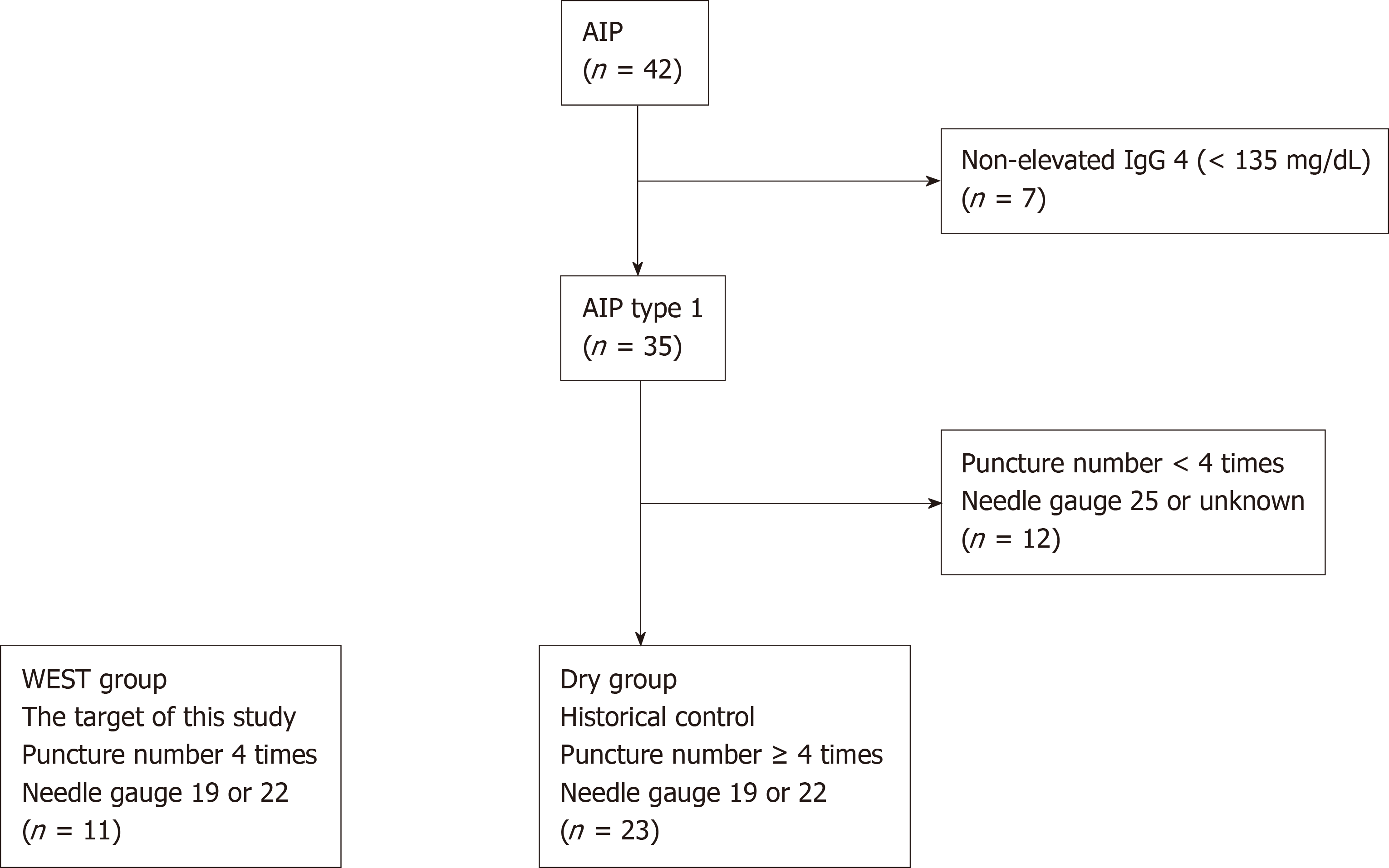
Figure 1 Target patients in this study and historical controls.
The historical controls were 23 autoimmune pancreatitis patients who underwent endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration with no fewer than 4 punctures by 19 or 22 G needles. The target subjects in this study underwent endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration with a wet suction technique. The historical controls were considered the DRY group. AIP: Autoimmune pancreatitis; WEST: Wet suction technique.
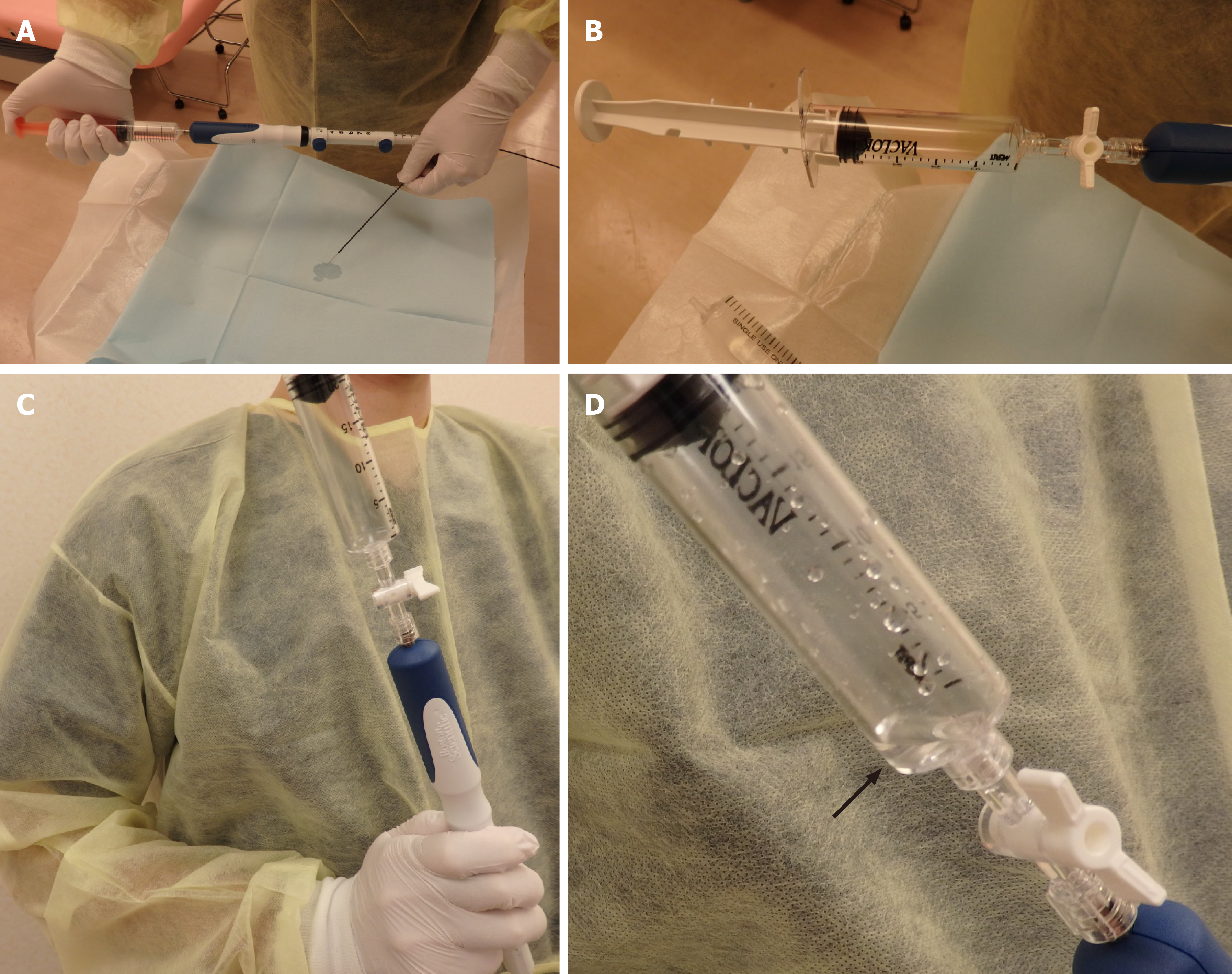
Figure 2 The wet suction technique method of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration.
A: After the stylet of the needle was withdrawn, saline solution was injected into the needle; B: A locked suction syringe with 20 mL of negative pressure was set at the edge of the needle; C: The needle was used to puncture the target lesion; D: then, the lock on the syringe was opened. Saline solution flowed into the suction syringe due to the negative pressure.
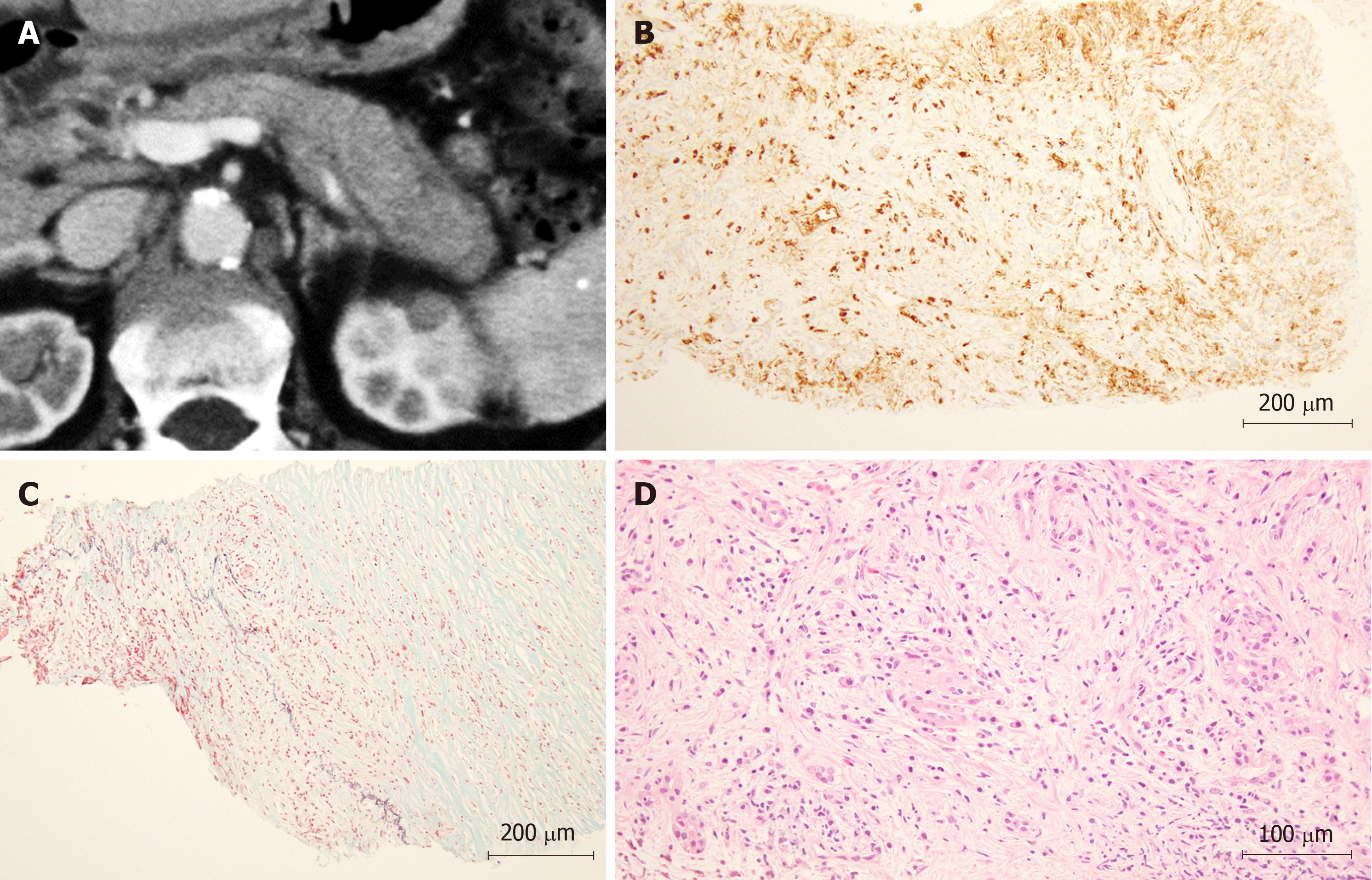
Figure 3 The features of a patient with autoimmune pancreatitis diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration with a wet suction technique.
A: The pancreatic tail is swollen with a capsule-like rim sign as observed on abdominal computed tomography; B: Specimen acquired by wet suction technique (WEST) endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) (HE × 200): IgG4-positive plasma cells were observed; C: Specimen acquired by WEST EUS-FNA (EM × 200): obliterative phlebitis was observed; D: Specimen acquired by WEST EUS-FNA (HE × 400): fibrosis with a storiform pattern of plasma cells was observed.
- Citation: Sugimoto M, Takagi T, Suzuki R, Konno N, Asama H, Sato Y, Irie H, Watanabe K, Nakamura J, Kikuchi H, Takasumi M, Hashimoto M, Kato T, Hikichi T, Notohara K, Ohira H. Can the wet suction technique change the efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing autoimmune pancreatitis type 1? A prospective single-arm study. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(1): 88-96
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i1/88.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.88