Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2020; 8(1): 188-193
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.188
Published online Jan 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.188
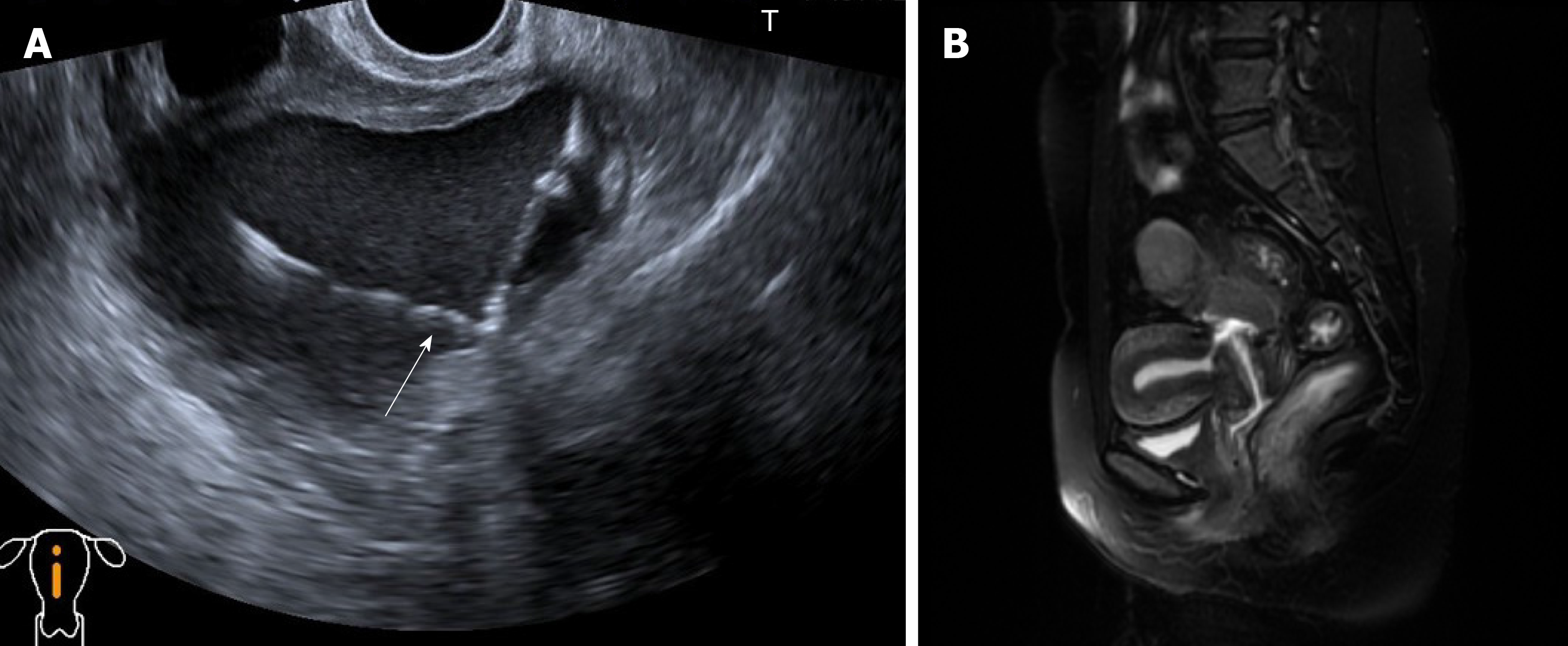
Figure 1 Imaging examinations.
A: B-mode ultrasound showed an anterior and normal uterus size and a cystic echogenic mass that measured 9.5 cm × 7.4 cm × 7.4 cm located at the posterior uterine isthmus. The white arrow indicates an intrauterine device contained within this cystic mass; B: On the T1-weighted image, the uterine isthmus muscle was discontinuous, and the cervical canal lost its normal shape. A communication was observed between the posterior isthmus of the uterus and the endometrial cavity and cervical canal.
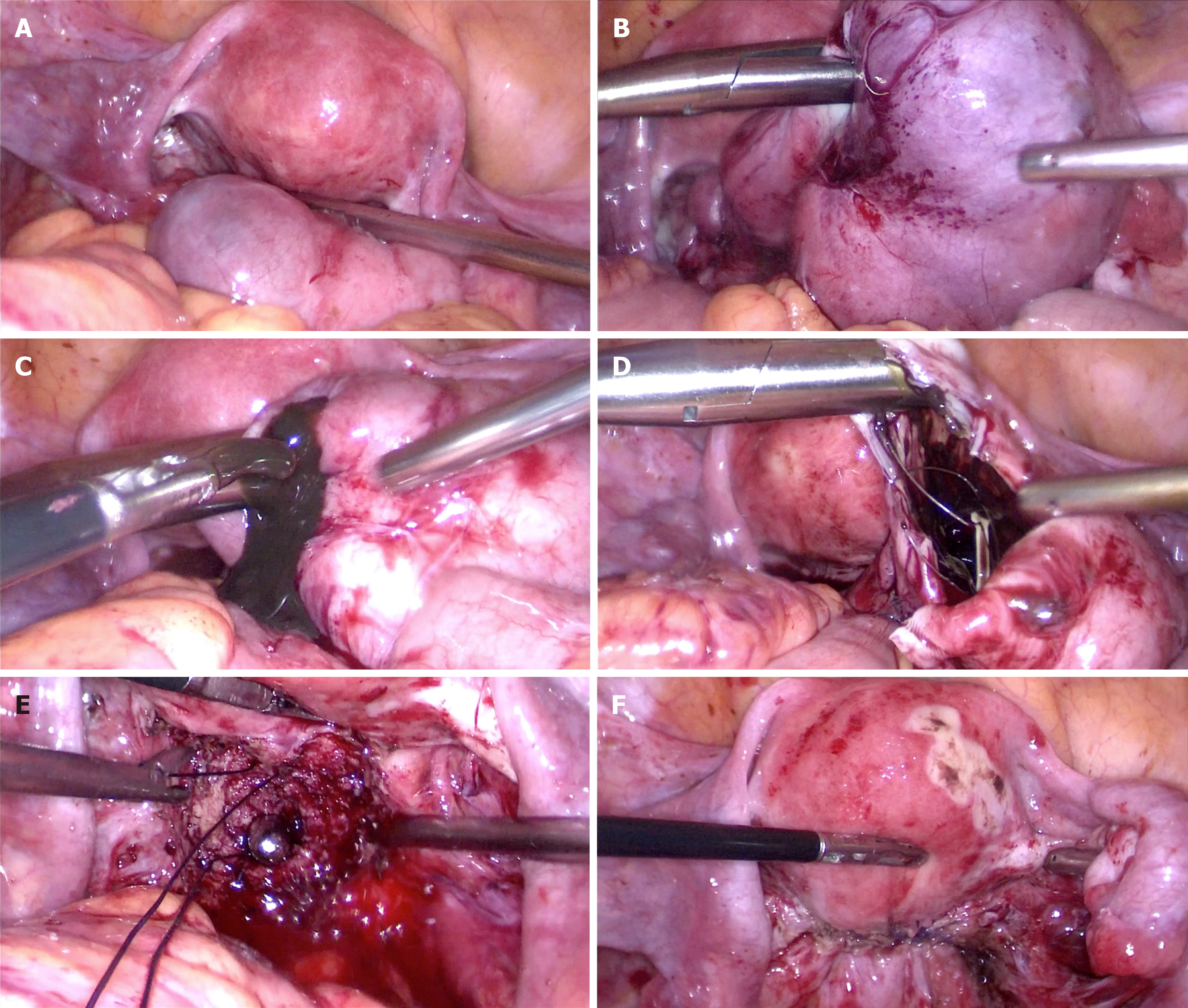
Figure 2 Laparoscopic excision of the mass was performed for the patient.
A and B: Appearance of the cystic adenomyosis at different directions; C: Chocolate-colored liquid content overflowed from the incision; D: The incision was enlarged and a levonorgestrel-containing intrauterine device was exposed after sucking the cystic fluid; E: The cervical canal was enlarged by the expanding-uterus stick to prevent stenosis; F: Continuously suturing the entire uterine wall twice to reconstruct the uterine wall.
- Citation: Zhou Y, Chen ZY, Zhang XM. Giant exophytic cystic adenomyosis with a levonorgestrel containing intrauterine device out of the uterine cavity after uterine myomectomy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(1): 188-193
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i1/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.188