Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2019; 7(3): 366-372
Published online Feb 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i3.366
Published online Feb 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i3.366
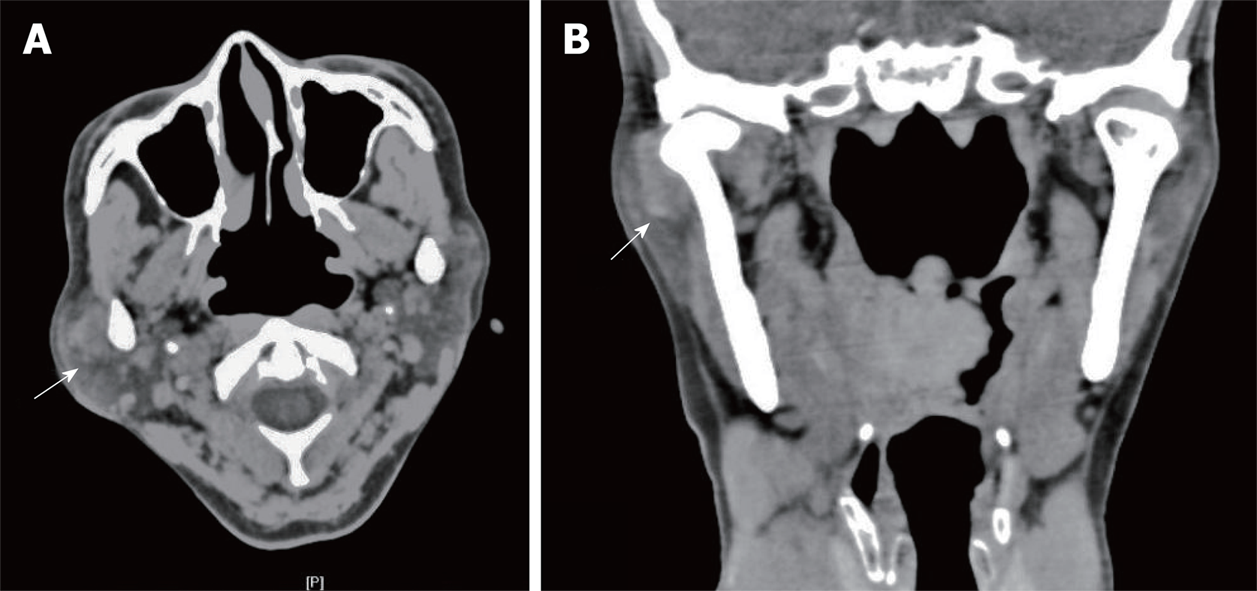
Figure 1 Computed tomography of the right temporomandibular joint.
A: Axial computed tomography (CT) scan; B: Coronal CT scan. Axial and corona CT scans showed a clear semilunar mass (white arrow) surrounding the lateral aspect of the right temporomandibular joint (TMJ). The TMJ was free of bony involvement.
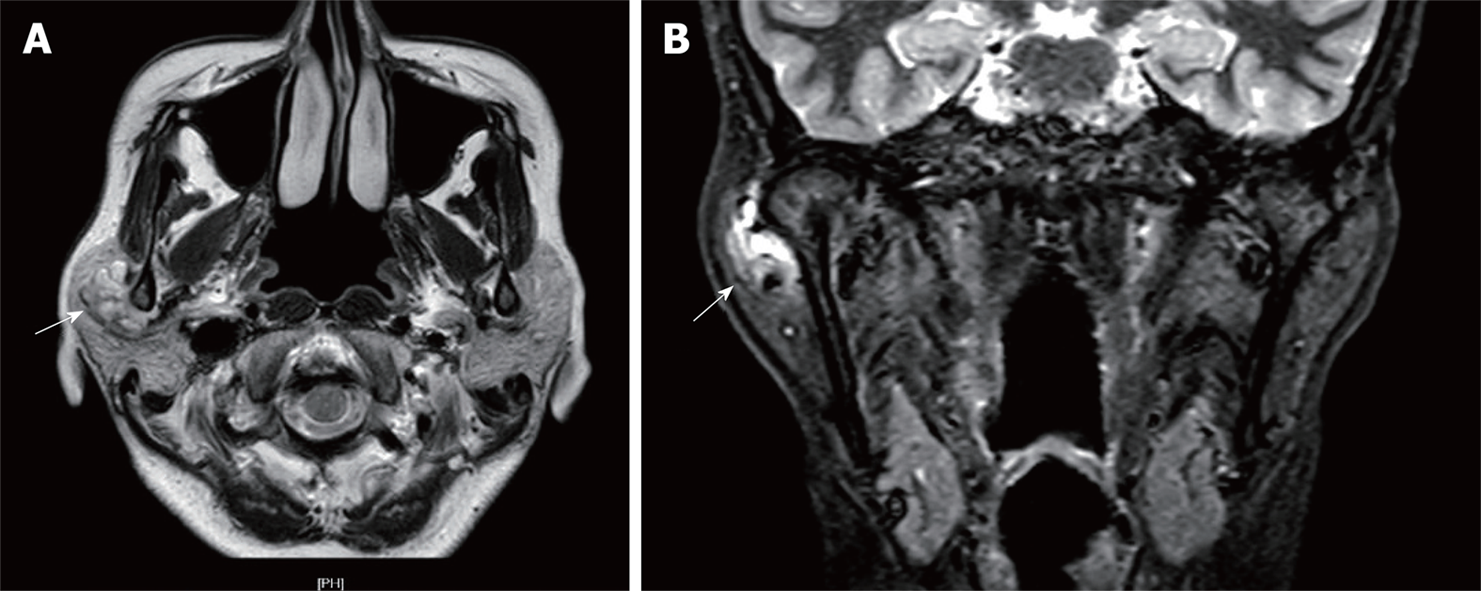
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of the right temporomandibular joint capsule.
A: Axial T2-weighted scan; B: Coronal T2-weighted scan. Axial and coronal T2-weighted scans revealed a hypodense, multicystic, well circumscribed lesion, measuring 2.0 cm × 1.6 cm (white arrow), attached to the lateral side of the right temporomandibular joint capsule.
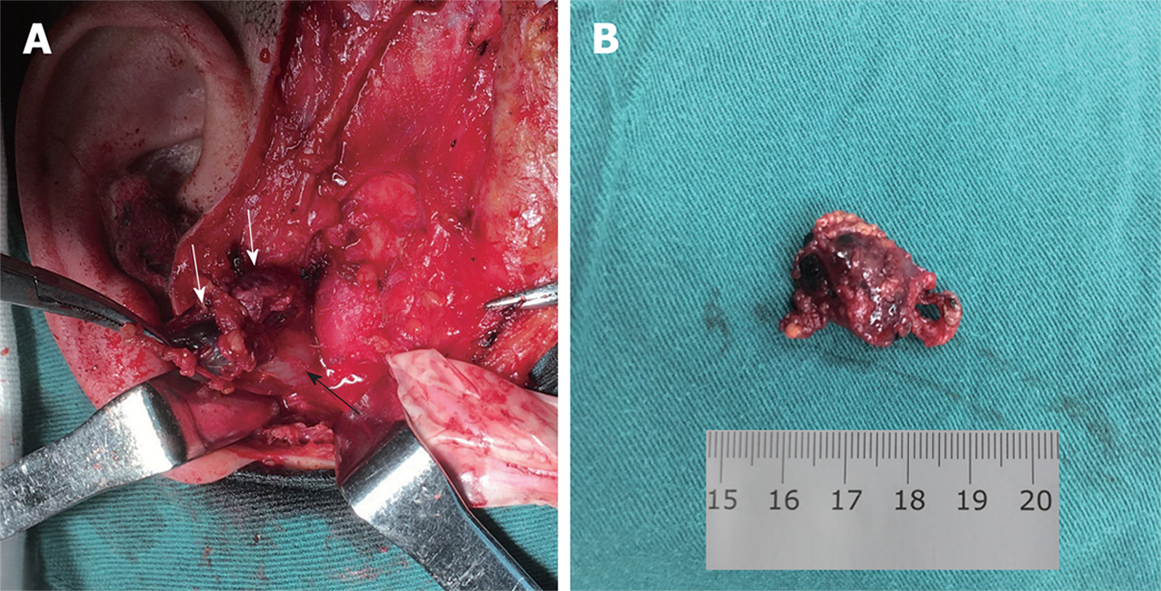
Figure 3 The cystic mass.
A: The 2.0 cm × 1.5 cm mass was located lateral to the temporomandibular joint capsule, deep in the right parotid gland. The mass was soft and dark red in color, similar to a vascular lesion (Mass, white arrow; condyle, black arrow); B: The resected mass.
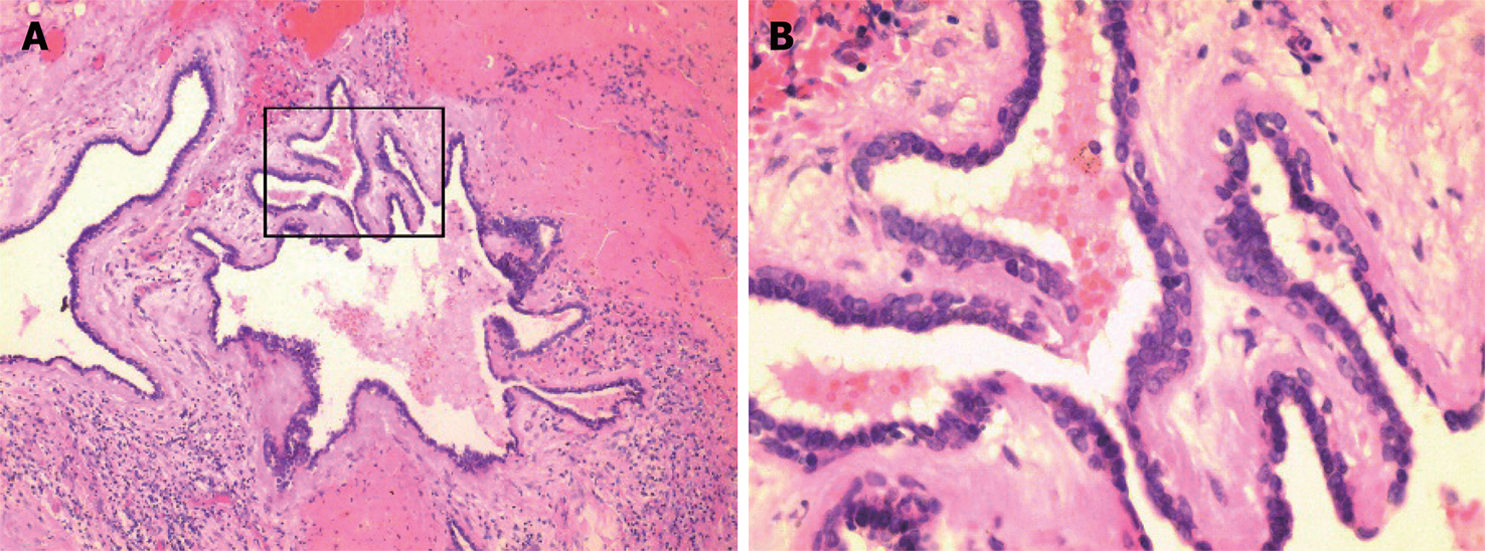
Figure 4 Postoperative histopathology.
A: Cystic spaces with papillary projections supported by fibrous connective tissue and underlying capsular connective tissue; (H and E staining: ×100) B: The cystic papillary projections and the major cyst cavity were lined by one to three layers of oncocytic cuboidal or columnar epithelial cells. (H and E staining: ×400).
- Citation: Wang L, Zhang SK, Ma Y, Ha PK, Wang ZM. Papillary cystadenoma of the parotid gland: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(3): 366-372
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i3/366.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i3.366