Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2019; 7(23): 4157-4162
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4157
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4157
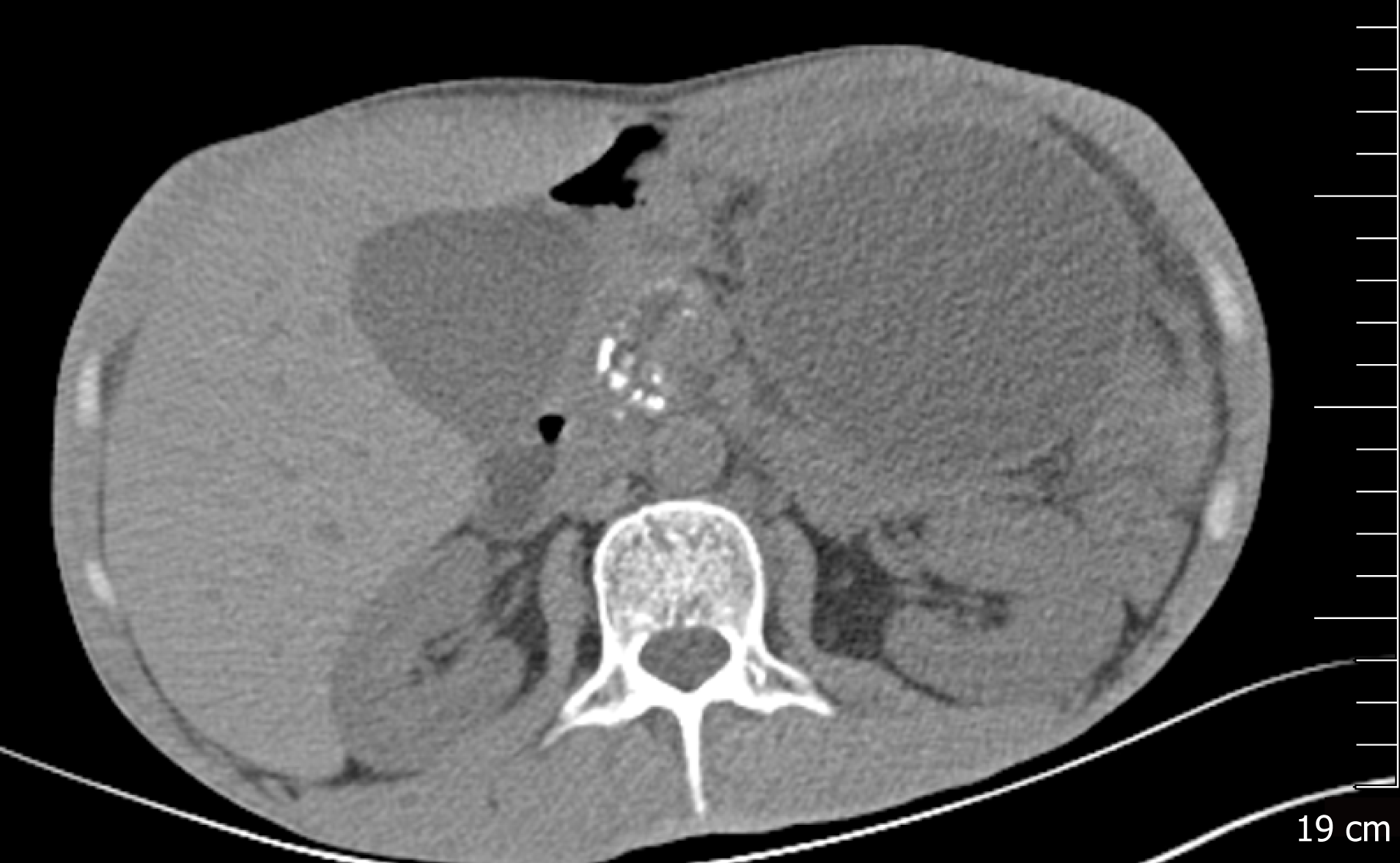
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography image revealing atrophy of the pancreatic parenchyma and dilation of the main pancreatic duct with multiple stones.
A pancreatic pseudocyst was located in the tail of the pancreas, measuring 9.8 cm × 8.0 cm.
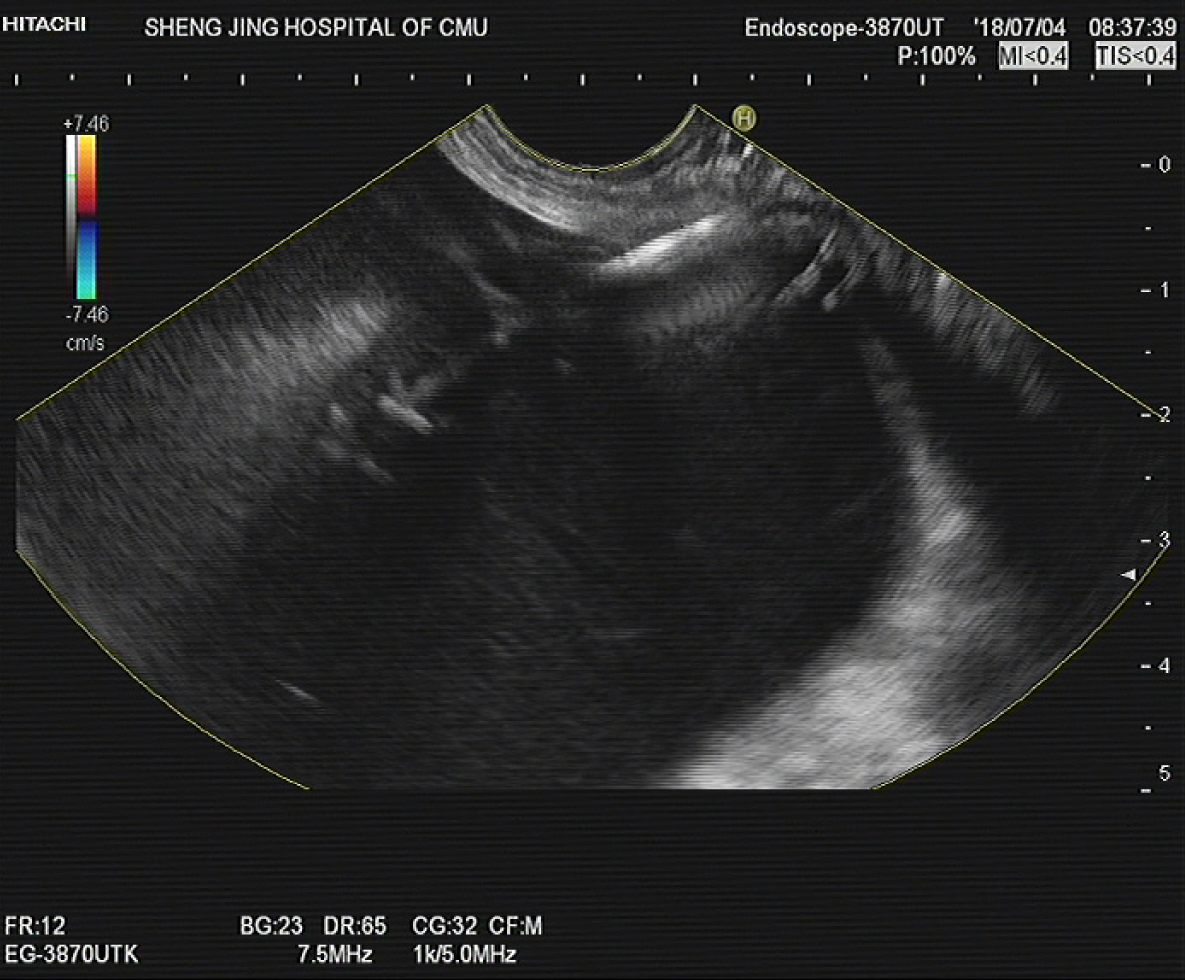
Figure 2 The pancreatic fluid collection was punctured by fine-needle aspiration under endoscopic ultrasound guidance.
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasound images.
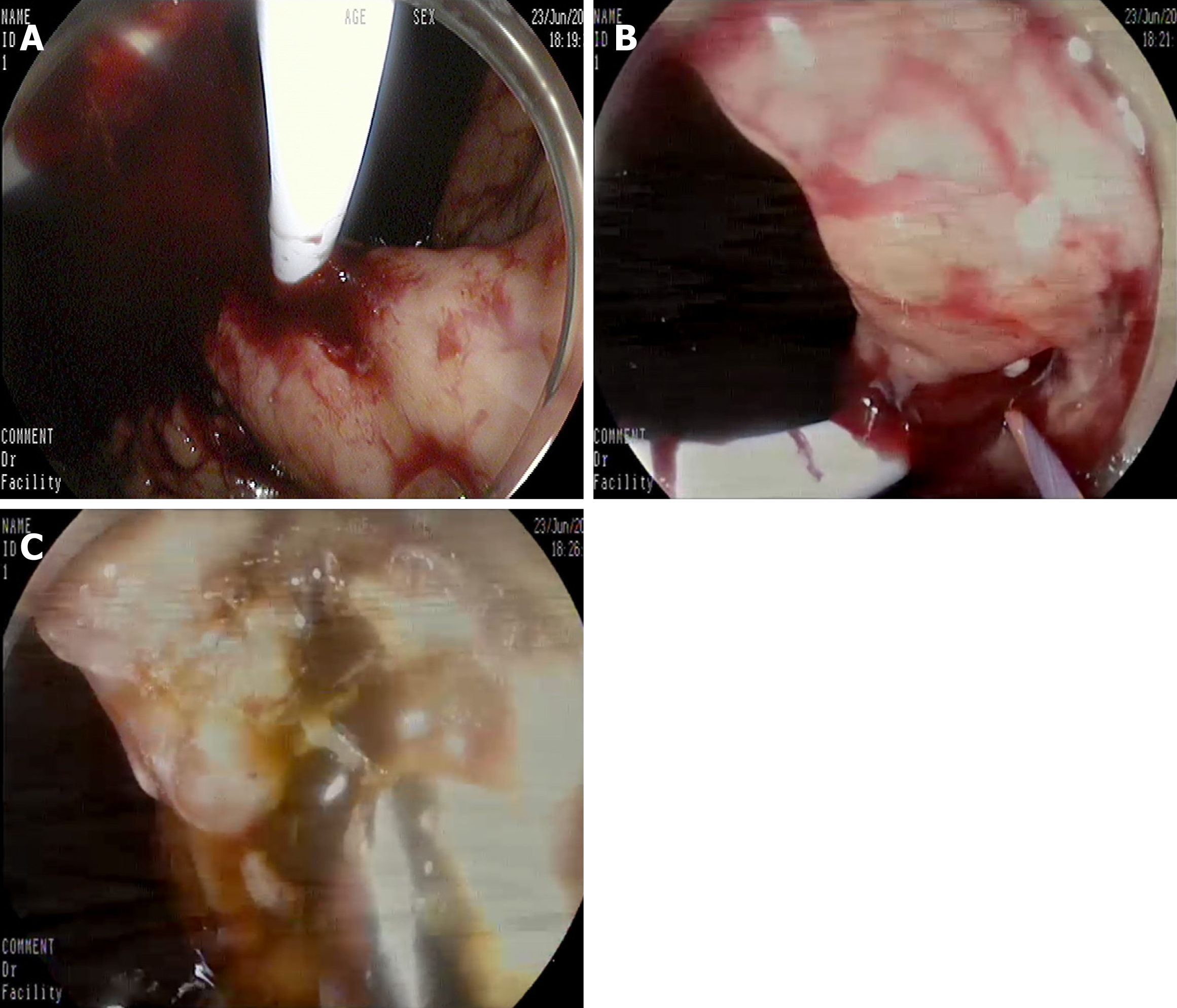
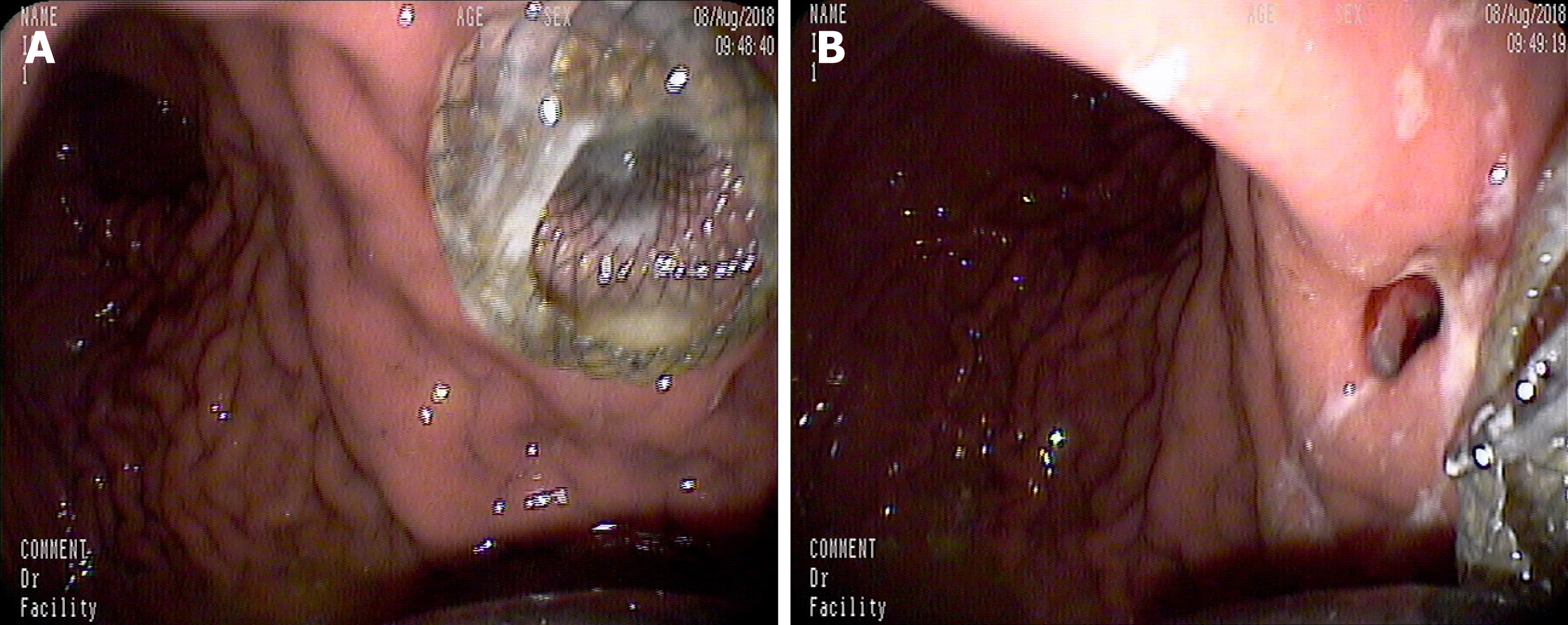
A: After the stent placement, massive bleeding was noted from the fistula; B: The bleeding vessel was viewed within the fistula; C: Hemostasis was successfully achieved.
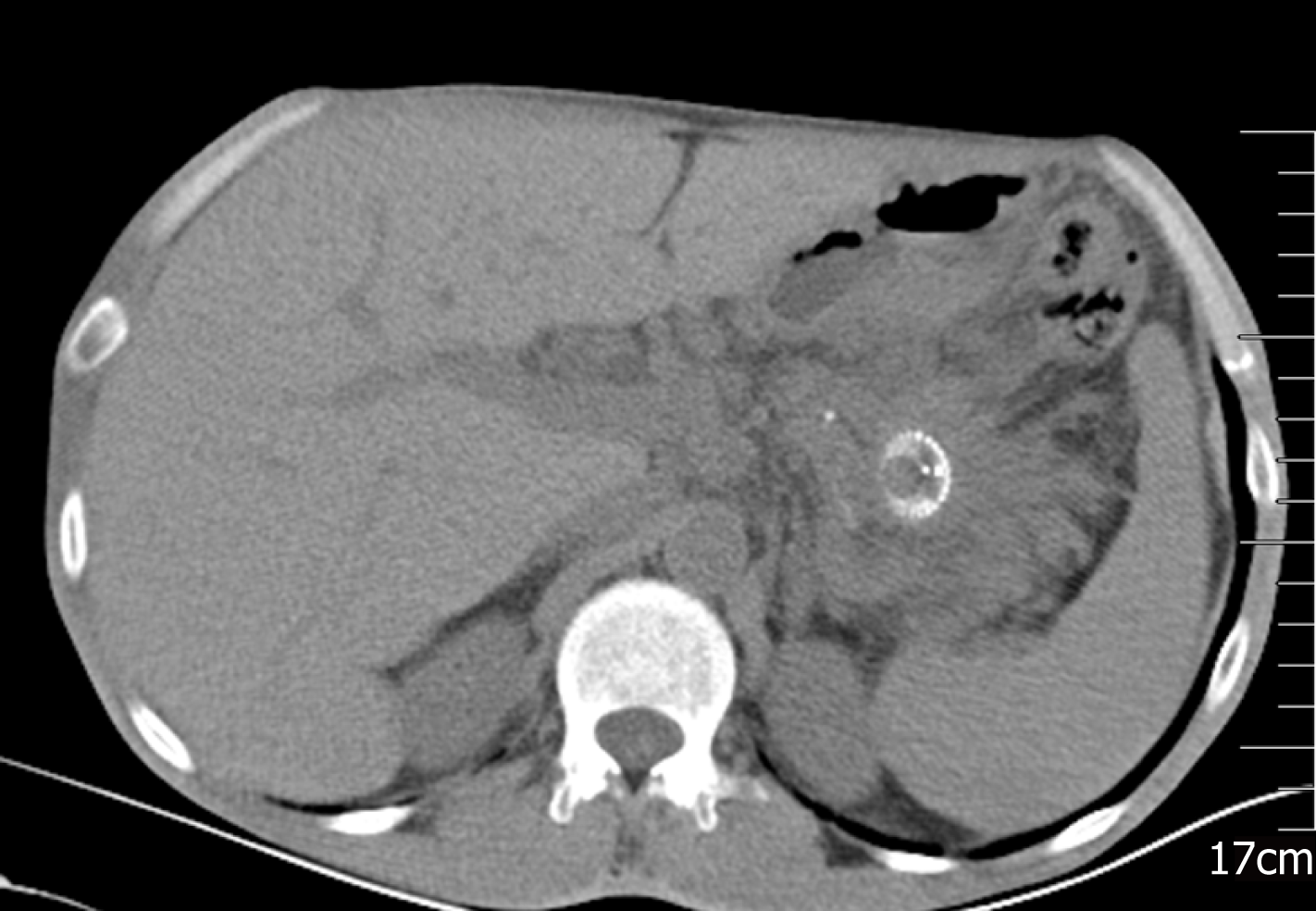
Figure 4 A follow-up abdominal computed tomography scan 1 mo later showed almost complete resolution of the pancreatic fluid collection.
Figure 5 The placed metal stent (A) and the stent was removed (B).
- Citation: Ge N, Sun SY. Management of massive fistula bleeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic pseudocyst drainage using hemostatic forceps: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(23): 4157-4162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i23/4157.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4157