Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2019; 7(23): 4063-4074
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4063
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4063
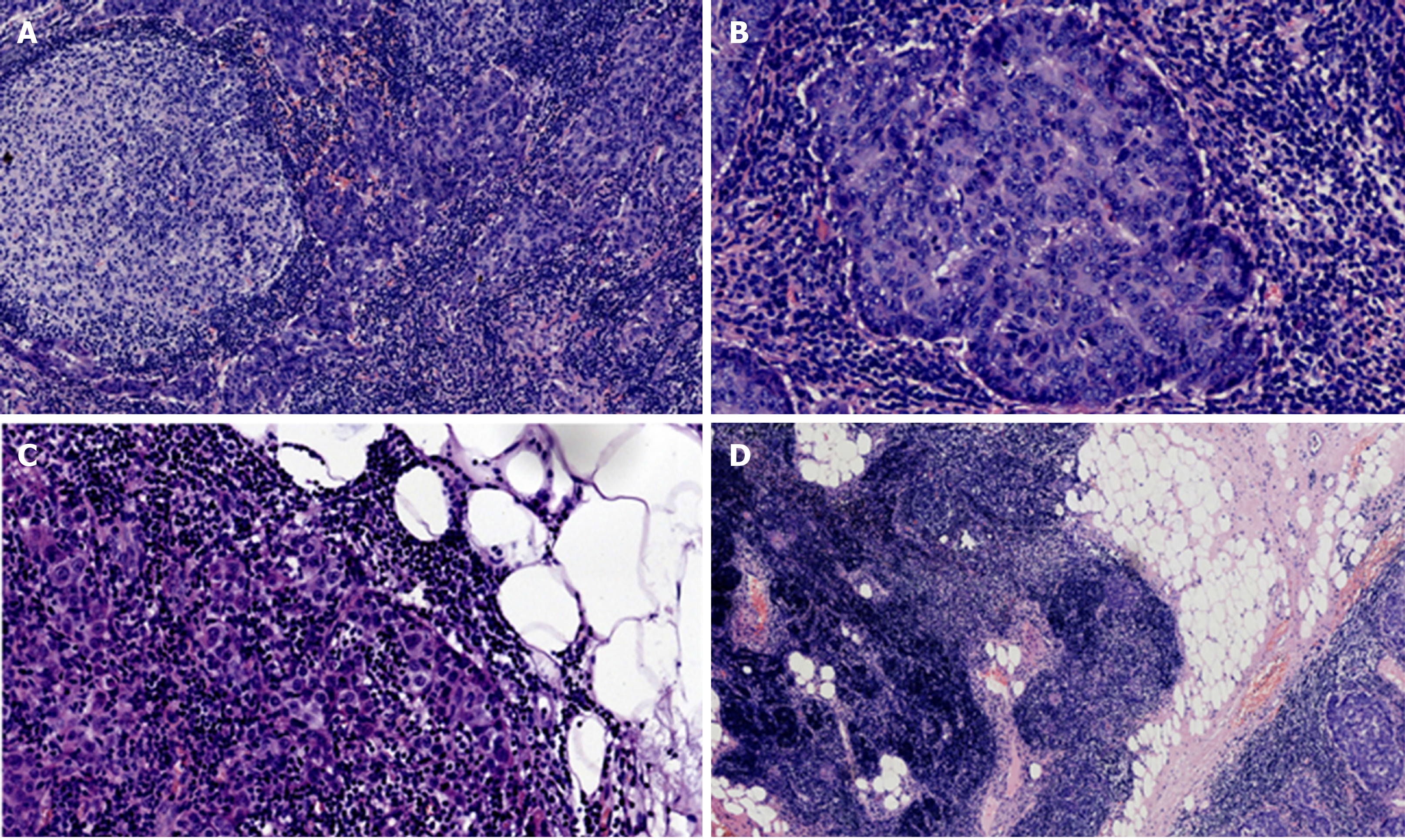
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the tumor tissue.
A: Staining of lymphoid follicle formation sites in the stroma (×10); B: Image of an enlarged interstitial lymphoid follicle formation site at high magnification. The mitotic figures were 1-9/10 high power fields (×20); C: Staining of the fatty portion of the perimeter of the neoplasm. The white tissue is adipose tissue (×10); D: Histogram of the junction between the tumor and normal thymus tissues (×4).
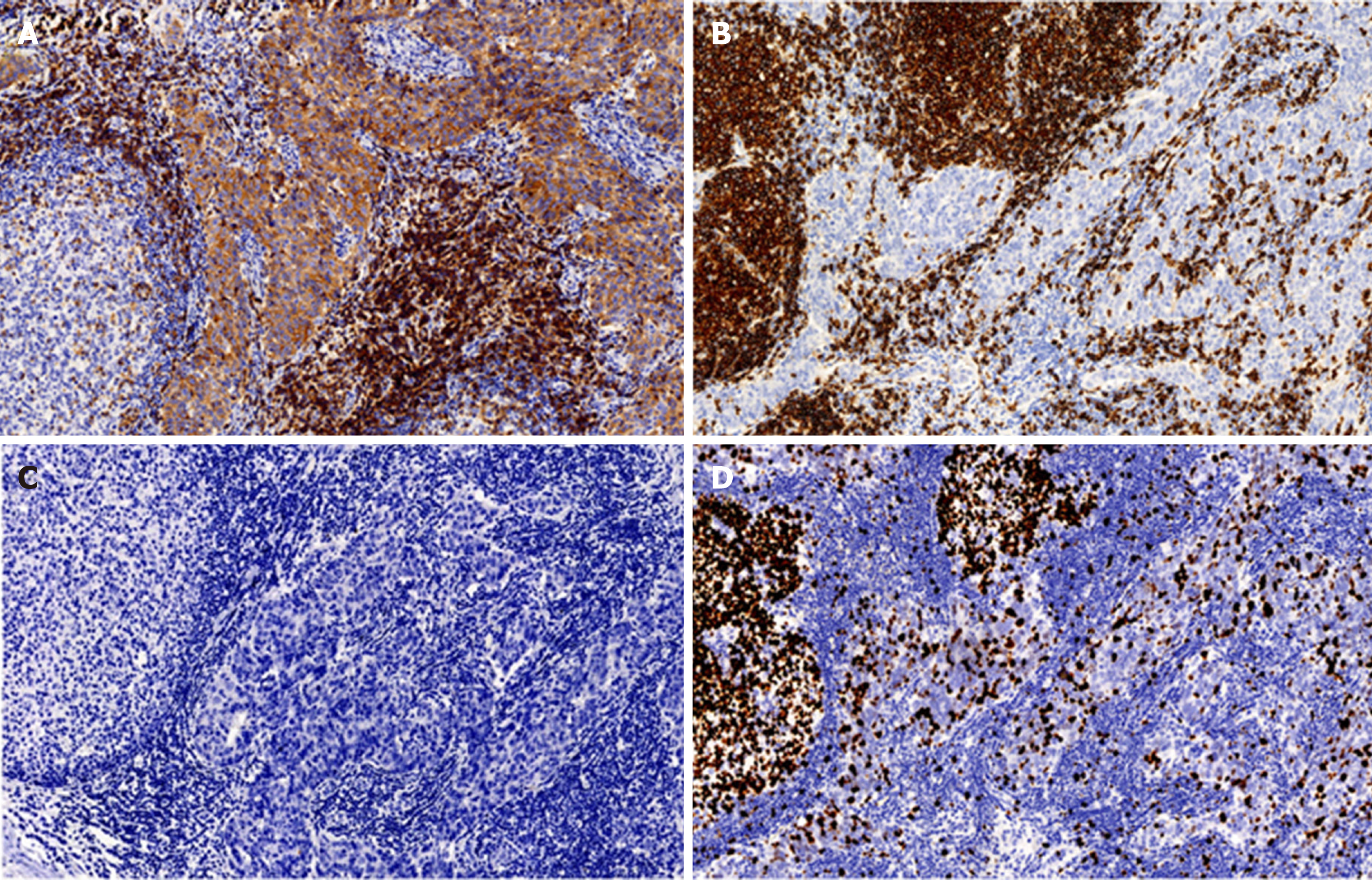
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical photographs of tumor tissue (×20).
A: Immunohistochemical staining for CD5. CD5 was expressed in the tumor epithelium, and the expression of CD5 in epithelial cells was diffuse and bright. The positive expression of CD5 was also observed in peripheral T lymphocytes; B: Immunohistochemical staining for CD20. CD20 was not expressed in the tumor epithelium, but it was positive in B lymphocytes in the stroma. CD20 expression was negative in tumor cells; C: Immunohistochemical staining for TdT. TdT (+) immature T cells were not found in tumor tissue, indicating that there were no immature lymphocytes in the thymoma; D: Immunohistochemical staining for Ki-67. The positive expression rate of Ki-67 reached up to 30% in the tumor cells. The germinal center lymphocytes in the background showed high expression of Ki-67.
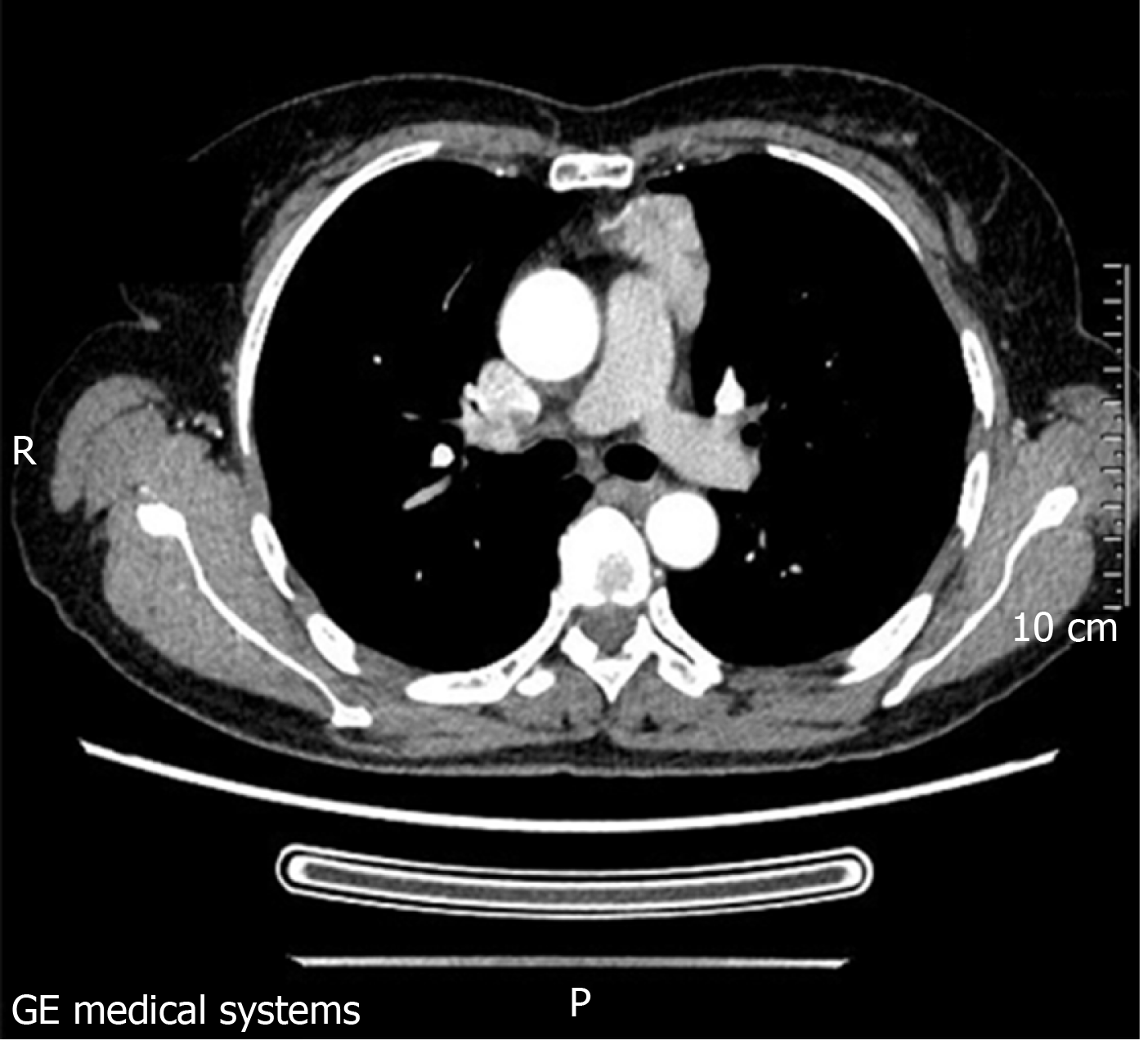
Figure 3 A solid mass with pericardial invasion can be seen in the anterior mediastinum.
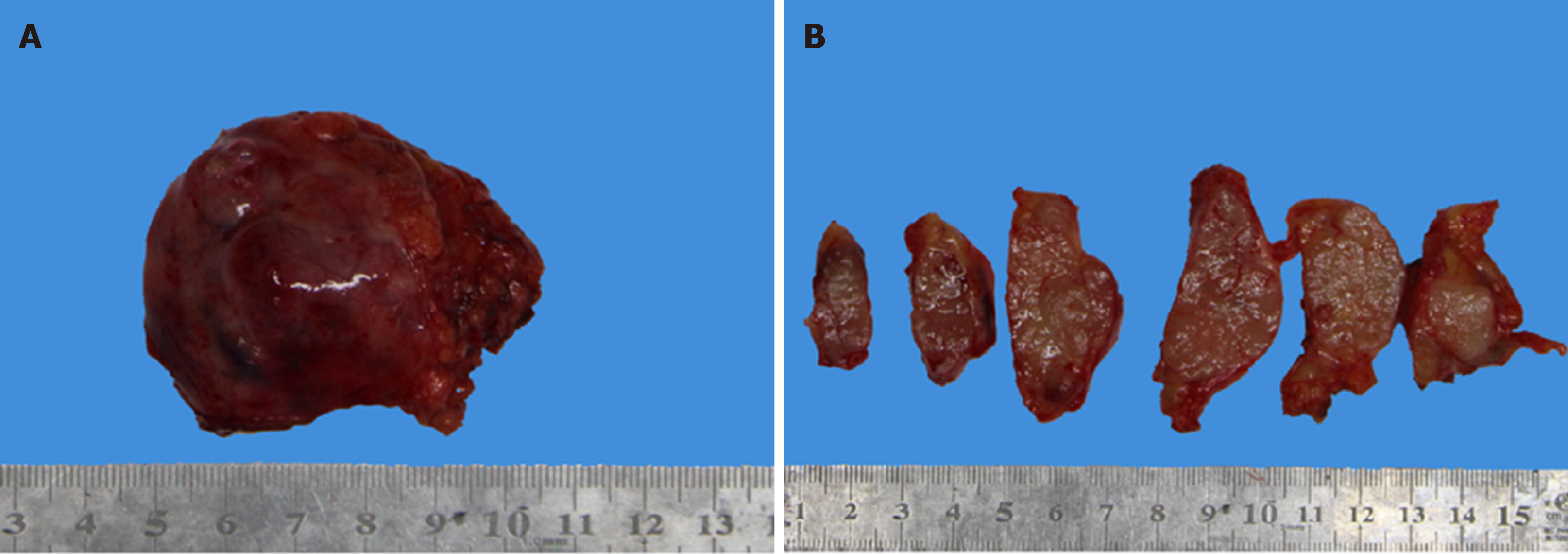
Figure 4 Irregular shape of the tumor tissue, most of which was covered by cysts.
B: Image of tumor tissue that has been transected. Its cross-section was stiff and moderately textured, showing a grayish-white and grayish-brown color. The boundary between the tumor tissue and the surrounding adipose tissue was not chiseled.
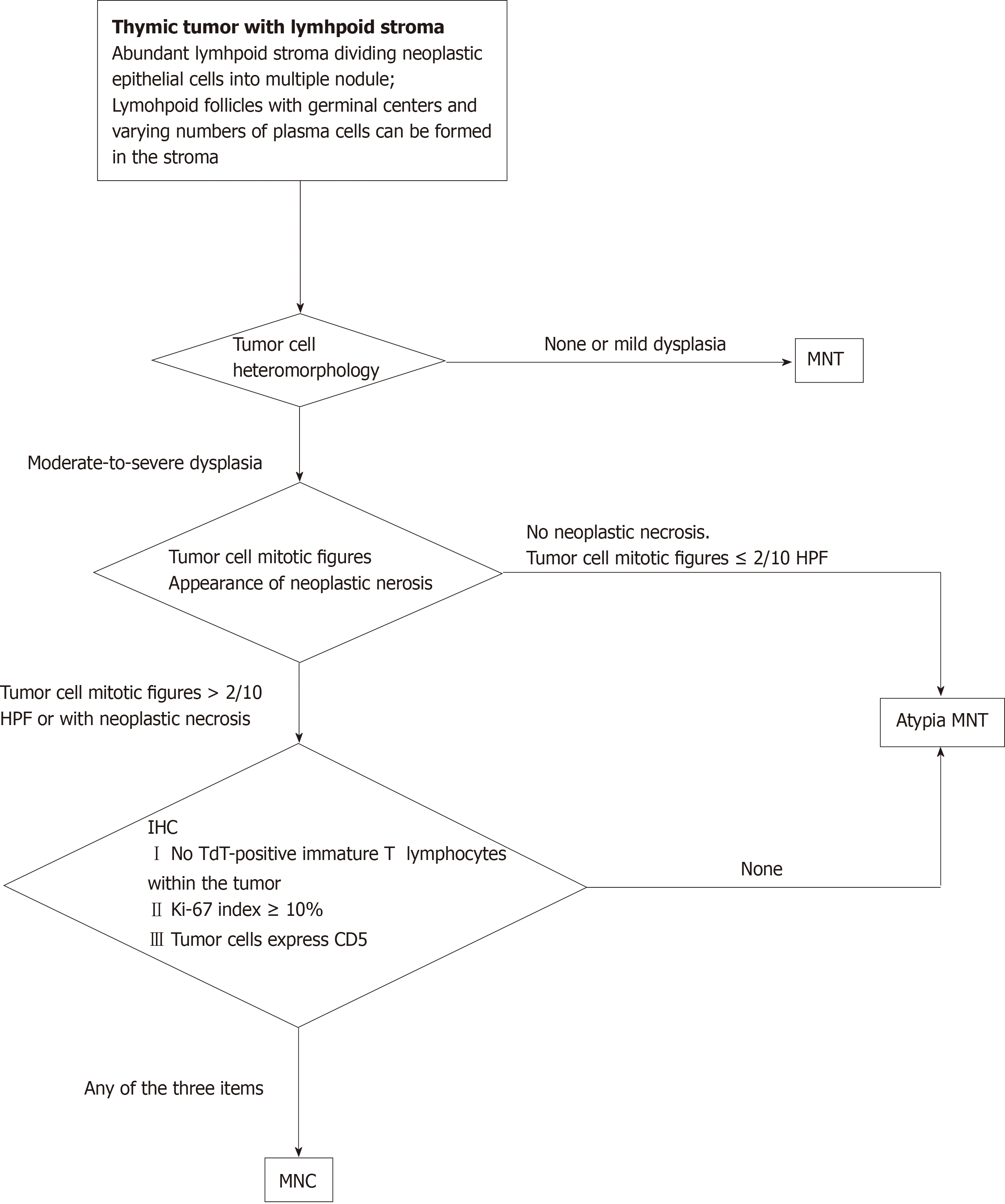
Figure 5 Algorithm to diagnose a small nodular thymic tumor with lymphoid stroma.
- Citation: Wang B, Li K, Song QK, Wang XH, Yang L, Zhang HL, Zhong DR. Micronodular thymic tumor with lymphoid stroma: A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(23): 4063-4074
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i23/4063.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4063